Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Summary CH 1 & 2 PMBOK
Caricato da
César Vázquez ArzateTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Summary CH 1 & 2 PMBOK
Caricato da
César Vázquez ArzateCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Key Concepts (Chapter 1.
Introduction)
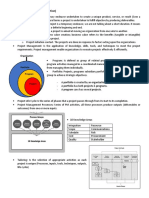
Project: A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result (Even a
combination of them). In general terms a project is undertaken to fulfill objective by producing deliverables.
o When we say that a project is a temporary endeavor, we are not talking about a short duration. It means
that every project has a definite beginning and end.
o Projects drive change, a project is aimed at moving an organization from one sate to another.
o Project enable business value creation; business value refers to the benefits (tangible or intangible)
obtained as result of a project.
o Project initiation context. The projects are done in response to factors acting upon the organizations.
Project Management: Is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet the project
requirements. Project management enable organizations to execute projects effectively & efficiently.
Program: Is defined as group of related projects, subsidiary programs, and
program activities managed in a coordinated manner to obtain benefits not available
from managing them individually.
Portfolio: Projects, programs subsidiary portfolios and operations managed as a
group to achieve strategic objectives.
- A portfolio is created by an organization.
- A portfolio has both projects & programs.
- A program cans has several projects.
Project Life Cycle: Is the series of phases that a project passes through from its start to its completion.
Project Management Processes: Series of PM activities, all these processes produce outputs (deliverables or
outcomes) from one or more inputs.
10 Knowledge Areas
Integration Resource
Scope Communications
Schedule Risk
Cost Procurement
Quality Stakeholder
Tailoring: Is the selection of appropriate activities as each
project is unique (Processes, inputs, tools, techniques, outputs,
life cycles)
Key Concepts (Chapter 2. The Environment in which Projects Operate)
Enterprise Environmental Factors: Refers to conditions not under the control of the project team, that influence
constrain, or direct the project. These conditions can be internal and/or external the organization. These factors
are considered as inputs.
o Factors Internal to the Organization:
Organizational culture, structure, Infrastructure
and governance. Information Technology software
Geographic distribution of facilities Resource availability
and resources. Employee capability
o Factors External to the Organization:
Marketplace conditions Government or industry
Social and cultural influences standards
and issues Financial considerations
Legal restrictions Physical environmental
Commercial databases elements
Academic research
Organizational Process Assets: Are the plans, processes, policies, procedures, and knowledge bases specific to and
used by the performing organization. These assets influence the management of project.
o Processes, policies and procedures: Are not updated as part of the project work, these assets are usually
established by the project management office (PMO) or another function outside the project.
o Organizational Knowledge Bases: Are updated throughout the project with project information.
Organizational systems: The interactions of multiple factors within an individual organization creates a unique
system that impacts the project operating in that system. The resulting organizational system determines the
power, influence, interests, competence, and political capabilities of the people who are able to act within the
system.
o Management Elements
o Governance Frameworks
o Organizational Structure
types.
Project Management Office (PMO): Is an organizational structure that standardizes the project-related
governance processes and facilitates the sharing of resources, methodologies, tools, and techniques. It provides
PM support functions to the direct management of one or more projects. Below it can be found the 3 different
types of PMO’s:
o Supportive – Consultative role, it has a low degree of control.
o Controlling – Supportive role, it has moderate degree of control.
o Directive –Manage role, it has high degree of control.
Reflection: These chapters introduce us to the world of PM, now we are going to be able to understand the concepts
related to this area of knowledge.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Summary CH 3 & 4Documento2 pagineSummary CH 3 & 4César Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Concepts (Chapter 3. Introduction)Documento2 pagineKey Concepts (Chapter 3. Introduction)César Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary CH 1 & 2 PMBOKDocumento2 pagineSummary CH 1 & 2 PMBOKCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimizing Total Costs in a Multi-Stage Supply Chain Using a Transshipment ModelDocumento9 pagineMinimizing Total Costs in a Multi-Stage Supply Chain Using a Transshipment ModelCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Behind The Low PricesDocumento2 pagineBehind The Low PricesCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- HW07 - A01370849 - A01371184 - A01372388Documento11 pagineHW07 - A01370849 - A01371184 - A01372388César Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- HW07 - A01370849 - A01371184 - A01372388Documento11 pagineHW07 - A01370849 - A01371184 - A01372388César Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Team 1: Bárbara César Claudia GilDocumento7 pagineTeam 1: Bárbara César Claudia GilCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Change ManagementDocumento3 pagineChange ManagementCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Instituto Tecnológico Y de Estudios Superiores de Monterrey: Lab-Activity #1: Pilot Company Selection & LocalizationDocumento20 pagineInstituto Tecnológico Y de Estudios Superiores de Monterrey: Lab-Activity #1: Pilot Company Selection & LocalizationCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Activity #12Documento3 pagineClass Activity #12César Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- ABC Exercise and Case StudyDocumento5 pagineABC Exercise and Case StudyCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- EOQ HomeworkDocumento4 pagineEOQ HomeworkCésar Vázquez ArzateNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- NMAT Vocab - Previous Year PDFDocumento8 pagineNMAT Vocab - Previous Year PDFSambit ParhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn English Greetings and Express Likes and DislikesDocumento27 pagineLearn English Greetings and Express Likes and DislikesBetzalel Emprendimiento50% (2)
- Extensive vs Intensive Reading TechniquesDocumento31 pagineExtensive vs Intensive Reading TechniquesSelçuk AktüreNessuna valutazione finora
- CampusRecruitmentBook PDFDocumento108 pagineCampusRecruitmentBook PDFAnonymous 1aCZDEbMM40% (5)
- Alaska Sporting Journal FALL 2013Documento7 pagineAlaska Sporting Journal FALL 2013Jessy LakinNessuna valutazione finora
- Orlando Patterson - Slavery and Social Death - A Comparative StudyDocumento265 pagineOrlando Patterson - Slavery and Social Death - A Comparative Studymccss100% (8)
- Literature Review On AttitudeDocumento6 pagineLiterature Review On Attitudenodahydomut2100% (1)
- Imt Lisa Benton Atanu SahaDocumento5 pagineImt Lisa Benton Atanu SahaAtanu Saha100% (1)
- Learn LenormandDocumento3 pagineLearn LenormandDianaCastle100% (2)
- FM3 The Evolution of Premature EjaculationDocumento12 pagineFM3 The Evolution of Premature EjaculationDave_Sadvertfile100% (2)
- End Is Near For Time Is Space Metaphor PaperDocumento14 pagineEnd Is Near For Time Is Space Metaphor PaperJan KowalskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rommel M. San Mateo Alejandro L. Petacio Jr. Rainger M. Mantile Jimbo T. GutierrezDocumento5 pagineRommel M. San Mateo Alejandro L. Petacio Jr. Rainger M. Mantile Jimbo T. GutierrezDenell N. AgnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Emotional Quotient: Emotional Quotient or Emotional Intelligent Set Apart Good LeadersDocumento31 pagineEmotional Quotient: Emotional Quotient or Emotional Intelligent Set Apart Good LeadersAmber Chourasia100% (1)
- GUIDELINES FOR REPORT WRITINGDocumento8 pagineGUIDELINES FOR REPORT WRITINGShumaila MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zone of Proximal Development: (Lev Vygotsky)Documento21 pagineZone of Proximal Development: (Lev Vygotsky)Wing CausarenNessuna valutazione finora
- MGT 212 - Mid 1 - LT 6 - Decision MakingDocumento32 pagineMGT 212 - Mid 1 - LT 6 - Decision MakingNajmus Rahman Sakib 1931937630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Xavier College Agriculture Practicum EvaluationDocumento3 pagineXavier College Agriculture Practicum EvaluationGio BitoyNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - MTB 1 - Q1 - W2Documento5 pagineDLL - MTB 1 - Q1 - W2Cel Rellores SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Support GroupDocumento13 pagineCancer Support GroupIndah PratiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Giver Chapters 1-10 1Documento25 pagineThe Giver Chapters 1-10 1api-315186689100% (1)
- School Management EssentialsDocumento21 pagineSchool Management Essentialsjein_amNessuna valutazione finora
- MGMT-GB 4301 20Documento19 pagineMGMT-GB 4301 20baradatNessuna valutazione finora
- 8623 Assignment No 2Documento63 pagine8623 Assignment No 2Asad ullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Storytelling Is The Conveying of Events in Words, Images, andDocumento9 pagineStorytelling Is The Conveying of Events in Words, Images, andly_meyhNessuna valutazione finora
- Rancangan Pengajaran Kolej VokasionalDocumento22 pagineRancangan Pengajaran Kolej VokasionalAizi ElegantNessuna valutazione finora
- Celebrity Worship SyndromeDocumento21 pagineCelebrity Worship SyndromeVictoria JungNessuna valutazione finora
- UNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Secondary Lesson Plan TemplateDocumento5 pagineUNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Secondary Lesson Plan Templateapi-463538537Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Design Process of ToysDocumento1 paginaThe Design Process of ToysaravinthNessuna valutazione finora
- U6w4 Lesson PlansDocumento6 pagineU6w4 Lesson Plansapi-239626791Nessuna valutazione finora
- Testing Sexual Orientation: A Scientific and Legal Analysis of Plethysmography in Asylum and Refugee Status ProceedingsDocumento30 pagineTesting Sexual Orientation: A Scientific and Legal Analysis of Plethysmography in Asylum and Refugee Status ProceedingsLGBT Asylum NewsNessuna valutazione finora