Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
EC6801 Notes PDF
Caricato da
Akshay JayantTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EC6801 Notes PDF
Caricato da
Akshay JayantCopyright:
Formati disponibili
www.rejinpaul.
com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
What is Wireless Communication?
Transmitting voice and data using electromagnetic waves in open space
Why Wireless?
Freedom from wires
No cost of installing the wires, No bunches of wires
running around e.g. Bluetooth , Wi-Fi
Global coverage
where wires communication is not feasible or costly
e.g. rural areas, battle field and outer space.
Stay Connected
Any where any time
Flexibility
Connect to multiple devices simultaneously
Wireless History
Ancient Systems: Smoke Signals, Carrier Pigeons…
Using light and flags for wireless communication remained important for the navy until radio
transmission was introduced. Even today a sailor has to know some codes represented by
flags if all other means of wireless communication fail.
James C Maxwell ( 1831- 1879) laying the theoretical foundation for EM fields with his
famous equations
Heinrich Hertz (1857- 1894 ) was the first to demonstrate the wave character of electrical
transmission through space (1886).(Note Today the unit Hz reminds us of this discovery).
Radio invented in the 1880s by Marconi
The first transatlantic transmission followed in 1901.
WARC – World Administration Radio Conference took place ,coordinating world wide use of
radio frequencies
The 1st radio broadcast took place in 1906 when Reginald A Fessenden transmitted voice
and music for Christmas.
The invention of electronic vacuum tube in 1906 by Lee De Forest ( 1873- 1961) &Robert
Von Lieben ( 1878 – 1913 )Helped to reduce the size of sender and receiver .
One of the 1st mobile transmitter was on board at Zeppelin in 1911
In 1915 , the first wireless voice transmission was set up between New York and
San Francisco
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 1 Page 1
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
The 1st commercial radio station started in 1920
–Note Sender & Receiver still needed huge antennas High transmission power.
In 1926, the first telephone in a train was available on the Berlin – Hamburg line
1928 was the year of many field trials for TV broadcasting. John L Baird ( 1888 – 1946 )
transmitted TV across Atlantic and demonstrated color TV
Until 1932 , all wireless communication used AM which offered relatively poor quality due to
interference.
Invention of FM in 1933 by Edwin H Armstrong [ 1890 - 1954 ] .
Both the modulation schemes are still used for todays radio broadcasting with FM having
much better quality.
o 1946, Public Mobile in 25 US cities, high power transmitter on large tower. Covers
distance of 50 Km. Push to talk, uses 120khz of RF bandwidth.1950 channels
doubled and BW 60k, 1960 4times increase, BW 30khz
After 2nd world war (in 1958) ,a network in Germany was build namely the analog A- Netz
using a carrier frequency of 160 Mhz.
Connection setup was only possible from the mobile station and no handover was possible
1982: Groupe Spéciale Mobile was launched to develop standards for pan-European mobile
network
GSM now stands for Global System for Mobile Communications
1992 Official commercial launch of GSM in Europe
1995 GSM specifications ported to PCS 1900
1997 - Wireless LANs
1998 - Specification for next generation CDMA starts Qualcomm starts work on wideband
CDMA spec.
2000 - Bluetooth with 1Mbit/s specification, single cell Later work on 10Mbit/s spec with
multi cell capability
In 2002 Camera phones are first introduced in the U.S. market.
In 2005 mobile phone subscribers exceed fixed phone subscriber.
iTunes Application Store (July) and Android Market (October) open in 2008
In 2010 First 4G handset is introduced at International CTIA WIRELESS show.
In 2010 Apple introduced the iPad, another revolution in portable “tablet” computing.
In 2010 FCC proposes National Broadband Plan, recommending 500MHz of spectrum be
allocated for commercial use by 2020.
In 2012 the number of subscriber reaches 1 million.
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 1 Page 2
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electromagnetic waves:
Travel at speed of light (c = 3x108 m/s and Has a frequency (f) and wavelength (ƛ)
c=fxƛ
Higher frequency means higher energy photons
The higher the energy photon the more penetrating is the radiation
Wavelength of Some Technologies
o GSM Phones:
frequency ~= 900 Mhz
wavelength ~= 33cm
o PCS Phones
frequency ~= 1.8 Ghz
wavelength ~= 17.5 cm
o Bluetooth:
frequency ~= 2.4Gz
wavelength ~= 12.5cm
Federal Communications Commission(FCC)
PTA
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 1 Page 3
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
Frequency Carries/Channels
The information from sender to receiver is carrier over a well defined frequency band.
This is called a channel
Each channel has a fixed frequency bandwidth (in KHz) and Capacity (bit-rate)
Different frequency bands (channels) can be used to transmit information in parallel and
independently.
Wireless Communication System Examples
Cellular Telephony
Wide Area Wireless Data Systems
High Speed Local and Personal Area Networks
Paging Messaging Systems
Satellite Based Mobile System
Wireless System Definitions
Mobile Switching Center
Switching center which coordinates the routing of calls in a large service area. In a cellular
radio system, the MSC connections the cellular base stations and the mobiles to the PSTN
(telephone network). It is also called Mobile Telephone Switching Office (MTSO)
Subscriber
A user who pays subscription charges for using a mobile communication system
Transceiver
A device capable of simultaneously transmitting and receiving radio signals
Control Channel
Radio channel used for transmission of call setup, call request, call initiation and other
beacon and control purposes.
Forward Channel
Radio channel used for transmission of information from the base station to the mobile
Reverse Channel
Radio channel used for transmission of information from mobile to base station
Simplex System
Communication systems which provide only one-way communication
Examples include Pagers
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 1 Page 4
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
Half Duplex Systems
Communication Systems which allow two-way communication by using the same radio
channel for both transmission and reception. At any given time, the user can either transmit or
receive information.
Push-to-talk and release-to-listen systems
Full Duplex Systems
Communication systems which allow simultaneous two-way communication. Transmission
and reception is typically on two different channels (FDD).
Handoff
The process of transferring a mobile station from one channel or base station to an other.
Roamer
A mobile station which operates in a service area (market) other than that from which
service has been subscribed.
Page
A brief message which is broadcast over the entire service area, usually in simulcast fashion
by many base stations at the same time.
Cellular Telephony
It is Characterized by
High mobility provision
Wide-range
Two-way voice communication
Handoff and roaming support
Integrated with sophisticated public switched telephone network (PSTN)
When mobile is turned on and not engaged in a call monitors the control
channel for strongest BS.
Cellular Telephony Systems
Mobile users and handsets
Very complex circuitry and design
Base stations
Provides gateway functionality between wireless and wire line links
Mobile switching centers
Connect cellular system to the terrestrial telephone network
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 1 Page 5
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
Cellular Networks
o First Generation
Analog Systems
Analog Modulation, mostly FM
AMPS
Voice Traffic
FDMA/FDD multiple access
o Second Generation (2G)
Digital Systems
Digital Modulation
Voice Traffic
TDMA/FDD and CDMA/FDD multiple access
o 2.5G
Digital Systems
Voice + Low-datarate Data
o Third Generation
Digital
Voice + Highdatarate DATA
Multimedia Transmission also
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 1 Page 6
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
CELLULAR SYSTEMS-BASIC CONCEPTS
Cellular system solves the problem of spectral congestion.
Offers high capacity in limited spectrum.
High capacity is achieved by limiting the coverage area of each BS to a small geographical
area called cell.
Replaces high powered transmitter with several low power transmitters.
Each BS is allocated a portion of total channels and nearby cells are allocated completely
different channels.
All available channels are allocated to small no of neighboring BS.
Interference between neighboring BSs is minimized by allocating different channels.
Same frequencies are reused by spatially separated BSs.
Interference between co-channels stations is kept below acceptable level.
Additional radio capacity is achieved.
Frequency Reuse-Fix no of channels serve an arbitrarily large no of subscribers
FREQUENCY REUSE
used by service providers to improve the efficiency of a cellular network and to serve
millions of subscribers using a limited radio spectrum
After covering a certain distance a radio wave gets attenuated and the signal falls below a
point where it can no longer be used or cause any interference
A transmitter transmitting in a specific frequency range will have only a limited coverage
area
Beyond this coverage area, that frequency can be reused by another transmitter.
The entire network coverage area is divided into cells based on the principle of frequency
reuse
A cell = basic geographical unit of a cellular network; is the area around an antenna where a
specific frequency range is used.
when a subscriber moves to another cell, the antenna of the new cell takes over the signal
transmission
a cluster is a group of adjacent cells, usually 7 cells; no frequency reuse is done within a
cluster
the frequency spectrum is divided into sub-bands and each sub-band is used within one cell
of the cluster
in heavy traffic zones cells are smaller, while in isolated zones cells are larger
The design process of selecting and allocating channel groups for all of the cellular base
stations within a system is called frequency reuse or frequency planning.
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 2 Page 1
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
Cell labeled with same letter use the same set of frequencies.
Cell Shapes: Circle, Square, Triangle and Hexagon.
Hexagonal cell shape is conceptual , in reality it is irregular in shape
In hexagonal cell model, BS transmitter can be in centre of cell or on its 3 vertices.
Centered excited cells use omni directional whereas edge excited cells use directional
antennas.
A cellular system having ‘S’ duplex channels, each cell is allocated ‘k’ channels(k<S).
If S channels are allocated to N cells into unique and disjoint channels, the total no of
available channel is S=kN.
The Frequency Reuse factor is given as 1/N, each cell is assigned 1/N of total channels.
Lines joining a cell and each of its neighbor are separated by multiple of 600,certain cluster
sizes and cell layout possible
Geometery of hexagon is such that no of cells per cluster i.e N, can only have values which
satisfy the equation
N=i2+ij+j2
N, the cluster size is typically 4, 7 or 12.
In GSM normally N =7 is used.
i and j are integers, for i=3 and j=2 N=19.
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 2 Page 2
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
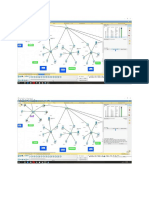
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 1
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 2
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 3
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 4
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 5
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 6
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 7
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 8
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 9
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 10
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 11
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 12
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 13
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
www.rejinpaul.com
Sri Vidya College of engineering & Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Lecture Notes)
EC2401 Wireless Communication Unit 3 Page 14
Get useful study materials from www.rejinpaul.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- SQL (Notes)Documento59 pagineSQL (Notes)Akshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- BT Wholesale Ethernet: What You Need To KnowDocumento4 pagineBT Wholesale Ethernet: What You Need To KnowAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- SOC Internship LetterDocumento1 paginaSOC Internship LetterAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 University of Sydney Engineering and Computer Science Postgraduate GuideDocumento42 pagine2020 University of Sydney Engineering and Computer Science Postgraduate GuideRomarioSebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- Ipu Official Website NoticeDocumento1 paginaIpu Official Website NoticeAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Vivo Ipl 2021 - Match Schedule UaeDocumento1 paginaVivo Ipl 2021 - Match Schedule UaeGaurav ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Vivo Ipl 2021 Terms and Conditions For Use of Licensed ImagesDocumento4 pagineVivo Ipl 2021 Terms and Conditions For Use of Licensed ImagesAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- 5final Syllabus-ECE - (1st To 8th Semester)Documento130 pagine5final Syllabus-ECE - (1st To 8th Semester)Tanmay GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet SimulationDocumento2 paginePacket SimulationAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- B K Birla Institute of Engineering & Technology: No Objection CertificateDocumento1 paginaB K Birla Institute of Engineering & Technology: No Objection CertificateAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Or Dinan C 11020815Documento13 pagineOr Dinan C 11020815tejashraj93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rajesh Cat 2019 Score CardDocumento1 paginaRajesh Cat 2019 Score CardAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Request Backlog CertificateDocumento1 paginaRequest Backlog CertificateAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide For AustraliaDocumento17 pagineStudy Guide For AustraliaAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Course ECEDocumento3 pagineCourse ECEAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- SydneyDocumento40 pagineSydneyNugraha BintangNessuna valutazione finora
- Call For 2020 CCUDocumento8 pagineCall For 2020 CCUAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- 1ielts Support Tools 2018Documento28 pagine1ielts Support Tools 2018Bacem FarhatNessuna valutazione finora
- TipsForListening V2 PDFDocumento6 pagineTipsForListening V2 PDFNancy OnuigboNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ListDocumento1 paginaProject ListAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Notification Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited Non Executive Posts Advt No. 90 2019 Cd40cca3 PDFDocumento14 pagineNotification Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited Non Executive Posts Advt No. 90 2019 Cd40cca3 PDFHareeshNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE Research PAPER On Cell Phone JammerDocumento2 pagineIEEE Research PAPER On Cell Phone JammerAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ES PDFDocumento176 pagineFinal ES PDFFarida ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ES PDFDocumento176 pagineFinal ES PDFFarida ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Beyond SVGFDocumento66 pagineBeyond SVGFLiliana QueiroloNessuna valutazione finora
- X 09 CDX 09 High Security LocksDocumento8 pagineX 09 CDX 09 High Security LocksBenoit CarrenandNessuna valutazione finora
- Esolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroDocumento31 pagineEsolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroAll About MusicNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid-Term Engr 6201 2020Documento3 pagineMid-Term Engr 6201 2020Naseri ShaunNessuna valutazione finora
- Vendor Information Vishay BLH Handbook TC0013 Solutions For Process Weighing and Force Measurement Electronic Weigh SystemsDocumento59 pagineVendor Information Vishay BLH Handbook TC0013 Solutions For Process Weighing and Force Measurement Electronic Weigh SystemsAndrew JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Echotrac Mkiii: Operator'S ManualDocumento48 pagineEchotrac Mkiii: Operator'S ManualKhắc PhongNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methods in PsychologyDocumento2 pagineResearch Methods in PsychologyHillaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths EnglishDocumento26 pagineMaths EnglishmeenasarathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of Engineering and Computing Sciences: Annexure-IDocumento2 pagineFaculty of Engineering and Computing Sciences: Annexure-IAkshay MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- HP LaserJet 5P - 6P Service Manual (Proper)Documento116 pagineHP LaserJet 5P - 6P Service Manual (Proper)maroudasp100% (1)
- Transient Step Response Specification of Z-Source DC-DC ConverterDocumento5 pagineTransient Step Response Specification of Z-Source DC-DC ConverterijsretNessuna valutazione finora
- IO SystemDocumento32 pagineIO Systemnanekaraditya06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Various Types of Steering System, Steering GeometryDocumento32 pagineVarious Types of Steering System, Steering GeometrySumit Choudhary100% (1)
- Manual X-C EFC Diversey Namthip - ENDocumento37 pagineManual X-C EFC Diversey Namthip - ENthouche007Nessuna valutazione finora
- FragAnal RC QDocumento26 pagineFragAnal RC QhjmaranhaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Timetable Saturday 31 Dec 2022Documento1 paginaTimetable Saturday 31 Dec 2022Khan AadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Text 01Documento110 pagineFull Text 01GumbuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Swat Luu: User ManualDocumento13 pagineSwat Luu: User ManualgjferreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dell EMC Avamar NDMP Accelerator For NASDocumento58 pagineDell EMC Avamar NDMP Accelerator For NASmanish.puri.gcpNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Guide R-410A ZJ/ZR/ZF Series 15 - 25 TON 60 Hertz: DescriptionDocumento103 pagineTechnical Guide R-410A ZJ/ZR/ZF Series 15 - 25 TON 60 Hertz: DescriptionmanthoexNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nature of Philosophy and Its ObjectsDocumento9 pagineThe Nature of Philosophy and Its Objectsaugustine abellanaNessuna valutazione finora
- External DC fuse board for Sunny Island battery invertersDocumento2 pagineExternal DC fuse board for Sunny Island battery invertersrhadammantysNessuna valutazione finora
- A B C D Supply I1 1 2 3 4 Deman D I1Documento7 pagineA B C D Supply I1 1 2 3 4 Deman D I1Shaurya DewanNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To Cosc 3101/ Internet Programming: Five Cookies and Session Management in PHPDocumento18 pagineWelcome To Cosc 3101/ Internet Programming: Five Cookies and Session Management in PHPSerkalem NegusseNessuna valutazione finora
- DNV Os C104 2014Documento40 pagineDNV Os C104 2014Moe LattNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 10 - Dry Etching PDFDocumento7 pagineLecture 10 - Dry Etching PDFSiddhant ModiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1-5 Atomic and Molecular Physics by Nek M ShaikhDocumento25 pagineLecture 1-5 Atomic and Molecular Physics by Nek M Shaikh125-The Legend StarNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual F700GS 2013Documento164 pagineManual F700GS 2013j gfatggNessuna valutazione finora
- GD-1884 Manual PDFDocumento10 pagineGD-1884 Manual PDFAnonymous srwHCpANessuna valutazione finora
- GPT 7000L User: Manual'Documento26 pagineGPT 7000L User: Manual'Adel Abo AdamNessuna valutazione finora