Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
KKXX
Caricato da
ThilagaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
KKXX
Caricato da
ThilagaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
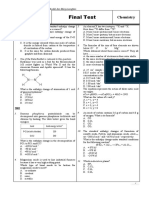
Section A [15 marks]
Answer all the questions in this section.
1. The energy level diagram shown represents the dissolving of anhydrous magnesium
I. The lattice energy of magnesium chloride is - 2526 kJ mol-1.
II. The enthalpy change of hydration of the chloride ion is - 384 kJ mol-1.
III. The enthalpy change of solution of anhydrous magnesium chloride is - 132 kJ mol-1.
IV. Magnesium chloride is insoluble in water.
A. I, II, and III only B. I, II, and IV only
C. I, III, and IV only D. I, II, III, and IV
2. When 0.285 g sample benzoic acid C6H5COOH is burned completely in bomb calorimeter,
the temperature of the water in the calorimeter increase by 2.9oC. The enthalpy of
combustion of benzoic acid is -3227 kJmol-1. Determine the heat capacity of the bomb
calorimeter. [Relative molecular mass of benzoic acid = 122]
A. 5.2 kJ oC-1 B. 2.60 kJ oC-1 C. 3.5 kJ oC-1 D. 1.9 kJ oC-1
3. The standard enthalpy of formation of several compound are given below.
Compound ΔHfo/kJmol-1
CO2 -394
H20 -286
C3H4 +184
Using Hess’s law, the value for the standard enthalpy of combustion of propyne, C3H4 is
A. + 1938 kJmol-1 B. - 1938 kJmol-1
C. + 846 kJmol-1 D. - 846 kJmol-1
4. The standard electrode potentials for three half-cells are given below:
J2+/J Eo = -0.44 V
L2+/L Eo = -0.76 V
T2+/T Eo = +0.34 V
Which of the following can reduce Sn2+ (aq) to Sn (s) at 298 K (The standard electrode
potential for Sn2+(aq)/Sn (s) at 298 k is – 0.14 V.
A. J and L only B. J, L and T C. J2+ and L2+ D. L2+ and T only
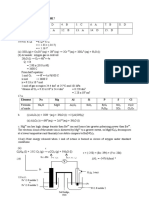
5. The respective electrolyte of three electrolytic cells are aqueous sodium hydroxide,
concentrated aqueous sodium chloride and aqueous silver nitrate. Each cell has carbon
electrodes connected in series. What is the ratio of the number of moles of hydrogen gas in the
first cell, chlorine gas in the second cell and oxygen in the third cell when an electric current
flows through the three cells?
A. 1 : 1 : 0 B. 1 : 1 : 1 C. 1 : 1 : 2 D. 2 : 2 : 1
6. The ionic radii of the ions P3-, S2- and Cl- are 0.212 nm, 0.184 nm and 0.181 nm respectively.
The decrease in atomic radius from P3- to C1- is caused by
A. The increase in nuclear charge and the increase in the number of electrons.
B. The increase in nuclear charge while the number of electrons remain constant.
C. The increase in the number of electrons while the nuclear charge remain constant.
D. The decrease in the number of electrons while the nuclear charge remain constant.
8. Which of the graphs correctly shows the change of melting point across the second period
of the periodic table?
Melting point Melting point Melting point Melting point
Ne Li C
Li
F B Be Ne
N F
Be O
O B Be B N
C C
Be N
B O Li
Li F N C
Ne O F Ne
A B C D
9. Magnesium sulphate is soluble in water while barium sulphate is insoluble. Which
statement explains the different solubilities of the two sulphates?
A. Magnesium sulphate is ionic while barium sulphate is covalent.
B. The lattice energy of barium sulphate is smaller than that of magnesium sulphate.
C. The lattice energy of barium sulphate is larger than the hydration energy of barium ion
and sulphate ion.
D. The lattice energy of magnesium sulphate is larger than the hydration energy of
magnesium ions and sulphate ions.
10. When 4.80 g magnesium nitrate sample was heated strongly, the final mass of the residue
is 1.00 g. What is the percentage purity of the sample?
[ Relative atomic mass: N= 14, O = 16, Mg = 24]
A. 92.1% B. 81.4% C. 86.8 % D. 77.1%
11. Which of the following statements best explains why the Group 2 carbonates becomes
increasingly less stable towards heat when going up the group?
A. The radius of the metal cation decreases.
B. The metals become increasingly electropositive.
C. The polarization power of the metal cation towards the carbonate anion increases.
D. The ionic bond in the carbonate compounds become increasingly weaker.
12. A group 14 tetrachlorides, XCl4 has the following properties
Undergoes hydrolysis readily
Decomposes at room temperature to produce chlorine
The tetrachloride is
A. SiCl4 B. PbCl4 C. SnCl4 D. GeCl4
13. Stopper of bottles containing SiCl4 often become sealed due to to SiO2.2H2O being
deposited around the stopper. This is formed by the following reaction:
SiCl4 + 4H2O → SiO2.2H2O + 4HCl
Why does the reaction occur with SiCl4 and not with CCl4?
A. The atomic radius of silicon is greater than that of carbon.
B. The ionization energies of silicon are lower than those of carbon.
C. Silicon atoms have 3d orbitals which are available for bonding.
D. The +4 oxidation state become less stable on descending group 14.
14. Reaction between chlorine and sodium hydroxide solution is
Cl2(g) + 6NaOH(aq) → 5NaCl(aq) + NaClO3(aq) + 3H2O(l)
Which of the following is not true of the above equation?
A Dilute NaCl is used in the reaction.
B The reaction takes place when the mixture is heated.
C Chlorine has gone through dispropotionation.
D Chlorine has highest oxidation state in NaClO3.
15. Teflon or polytetrafluoroethene is a polymer used as a non-stick lining in cooking
utensils and electric irons. Which of the following explains why this polymer is heat
resistant?
A. The polymer is non polar.
B. The C-F covalent bond is non polar.
C. The C-F covalent bond is very strong.
D. The polymer chains are linear and packed closely together.
16. Which of the following statements is true about KF and KI?
A. KF is more volatile than KI.
B. F- has o lower charge density than I-.
C. KF is weaker reducing agent than KI.
D. Kf is colourless but KI is light yellow in colour.
17. The anti-cancer drug cisplatin has the formula Pt(NH3)2Cl2. In the human body, one of
the chloride ions in cisplatin is replaced by one water molecules to form an aqua complex
as shown below.
Pt(NH3)2Cl2 + Cl2 → Pt(NH3)2(H2O)Cl]+ + Cl2
What is the oxidation number of platinum in cisplatin and aquacomplex?
Cisplatin Aquacomplex
A. +2 +1
B. +2 +2
C. +4 +3
D. +4 +4
18. The hexaaquacopper (II) ion, [Cu(H2O)6]2+ is blue because the water ligands
A. split the both p and d orbitals energies and d-d electron transition emit blue light.
B. split the d orbitals energies and d-d electron transitions absorbs all the blue light.
C. split the d orbitals energies and d-d electron transitions emit blue light.
D. split the d orbital energies and d-d electron transition absorb all and then emit blue
light.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Catalytic Reactions: The Organic Chemistry of PalladiumDa EverandCatalytic Reactions: The Organic Chemistry of PalladiumNessuna valutazione finora
- Yr10 Chemistry Paper 2 YE22Documento14 pagineYr10 Chemistry Paper 2 YE22Ern QiNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Pis Final TestDocumento4 paginePis Final TestArda RahmainiNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM 2017 Sem 2Documento7 pagineSTPM 2017 Sem 2Aprillia ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Actual Repeat Paper 2013Documento10 pagineActual Repeat Paper 2013Jasmeet Kaur SandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A (Question) FINALDocumento8 pagineSection A (Question) FINALcalderteoNessuna valutazione finora
- Uppp2 Sem 2 2017Documento5 pagineUppp2 Sem 2 2017Loh Wai YeeNessuna valutazione finora
- LW F6 Chem Mock Exam P1 1718 PDFDocumento23 pagineLW F6 Chem Mock Exam P1 1718 PDFVincent haNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer ALL The Questions in This Section in Space ProvidedDocumento6 pagineAnswer ALL The Questions in This Section in Space ProvidedfaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Joint Universities Preliminary Examinations Board 2015 Examinations Chemistry: Sci-J153 Multiple Choice Questions: Answer All QuestionsDocumento11 pagineJoint Universities Preliminary Examinations Board 2015 Examinations Chemistry: Sci-J153 Multiple Choice Questions: Answer All QuestionsDeborahNessuna valutazione finora
- GROUP 14 ELEMENTS (IVA Group Elements)Documento8 pagineGROUP 14 ELEMENTS (IVA Group Elements)Premangshu GhoshalNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Chew 1Documento7 pagineExam Chew 1ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- North Vista 2015 Prelim Paper 1Documento20 pagineNorth Vista 2015 Prelim Paper 1GM MonsterEtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejc H1 Chem P1Documento11 pagineEjc H1 Chem P1Lim EnningNessuna valutazione finora
- JC2 Chemistry H2 2018 VictoriaDocumento68 pagineJC2 Chemistry H2 2018 VictoriamagnusremixicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer All Questions in This Section: Electrode System EDocumento9 pagineAnswer All Questions in This Section: Electrode System EChang DiNessuna valutazione finora
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam Term 2 2019 (Chemistry)Documento7 pagineSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam Term 2 2019 (Chemistry)AlyciaLeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem P2 Trial - 2013 - Marking SchemeDocumento17 pagineChem P2 Trial - 2013 - Marking SchemeMelody OngNessuna valutazione finora
- PRACTICE TO PERFECT A CHEM SK015 (SET 1) SoalanDocumento4 paginePRACTICE TO PERFECT A CHEM SK015 (SET 1) SoalanaNessuna valutazione finora
- DiagnosticsDocumento8 pagineDiagnosticsNORBERTUS KRISNU PRABOWONessuna valutazione finora
- Top Univ - Soal Latihan Kimia 01 PDFDocumento7 pagineTop Univ - Soal Latihan Kimia 01 PDFDarma YogaNessuna valutazione finora
- CB - 1Documento2 pagineCB - 1AaRaV KuShWaHaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Class Xii Sample Paper 01 AnswersDocumento8 pagineChemistry Class Xii Sample Paper 01 Answerssouparnikar1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Documento16 pagine2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Chow Kim WanNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer All Question in This SectionDocumento8 pagineAnswer All Question in This SectionMuhd FaiZNessuna valutazione finora
- Catholic Junior College: Chemistry Higher 1Documento9 pagineCatholic Junior College: Chemistry Higher 1chuasioklengNessuna valutazione finora
- p1 ChemistryDocumento15 paginep1 ChemistryHumza SohailNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal KimdasDocumento13 pagineSoal KimdasNur SyahrainiNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM 2019 Sem 2uDocumento7 pagineSTPM 2019 Sem 2uAprillia ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 SAJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Documento19 pagine2010 SAJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Giovanni AndersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 12Documento8 pagineChemistry 12dhritibarak548Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample PaperDocumento3 pagineSample Paperaparna patwalNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEMISTRYDocumento41 pagineCHEMISTRYLindsayyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem 2 Uppp 1 2017Documento7 pagineSem 2 Uppp 1 2017Wong Lee FongNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 UNIT 1 Paper 1Documento5 pagine2009 UNIT 1 Paper 1cilacax404Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 1 & 2 Ws-MsDocumento31 paginePaper 1 & 2 Ws-MsPirate HunterNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemDocumento10 pagineChemYnnoNessuna valutazione finora
- SCH3U - Practice ExamDocumento9 pagineSCH3U - Practice ExamWaqas AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Day1 CompiledDocumento39 pagineDay1 CompiledWinsletJoyDauagNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry Boards Practice ExamDocumento10 pagineGeneral Chemistry Boards Practice ExamKriel MuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento14 pagineChemistryAdil ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Practice Test 2 Class 12 - Chemistry: Volume Occupied by Fow Spheres Inthe Unit Cell Total Volume of Unit CellDocumento6 pagineSolution Practice Test 2 Class 12 - Chemistry: Volume Occupied by Fow Spheres Inthe Unit Cell Total Volume of Unit Cell39 Yogendra KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocarbons Chemistry NotesDocumento29 pagineHydrocarbons Chemistry NotesBhavesh KNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper +2 Chemistry 18.01.23Documento3 pagineSample Paper +2 Chemistry 18.01.23Raj Online ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry PHD - Set 1 - Questions PDFDocumento5 pagineChemistry PHD - Set 1 - Questions PDFvksumanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions-Chemical BondingDocumento5 paginePractice Questions-Chemical BondingAtif NaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- DLRC Chemistry 16 Comprehensive Samplex For Long Exam 2Documento11 pagineDLRC Chemistry 16 Comprehensive Samplex For Long Exam 2kate_acamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Chemistry Question PapersDocumento4 pagine2011 Chemistry Question Papersalex scottNessuna valutazione finora
- Pretest in General Chemistry 2 MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read and Analyze The Statements and Questions Carefully. Identify The Best OptionDocumento2 paginePretest in General Chemistry 2 MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read and Analyze The Statements and Questions Carefully. Identify The Best OptionSalinas SalinasNessuna valutazione finora
- Scholastica: Mock 1Documento14 pagineScholastica: Mock 1Fatema KhatunNessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganic Chem 11Documento68 pagineInorganic Chem 11hisrom286Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prelim P1 (Print Version)Documento15 paginePrelim P1 (Print Version)Pham Nguyen QuangNessuna valutazione finora
- IChO Phase1 Test2 2014 PDFDocumento11 pagineIChO Phase1 Test2 2014 PDFNdjskaNessuna valutazione finora
- QP Chemistry Pb2 Xii Set2Documento13 pagineQP Chemistry Pb2 Xii Set2Yug GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank Chemistry XI Term - 2Documento4 pagineQuestion Bank Chemistry XI Term - 2GHOSTX GAMERNessuna valutazione finora
- Sy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Documento7 pagineSy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Kia AsherNessuna valutazione finora
- TEST Chemical Bonding & Chemical EnergeticsDocumento17 pagineTEST Chemical Bonding & Chemical Energeticszafarchem_iqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Test1 More Intermolecular Force PracticeDocumento10 pagineTest1 More Intermolecular Force PracticeKyla BaysaNessuna valutazione finora
- Karnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Chemistry Class 12 Question Paper 2016Documento18 pagineKarnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Chemistry Class 12 Question Paper 2016sparkysanthosh69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Group TEDocumento6 pagineNotes Group TEThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Candidate'S Performance ReportDocumento7 pagineCandidate'S Performance ReportThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sinopsis SekolahDocumento2 pagineSinopsis SekolahThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Guru Kelas: PN Thilagavathy Sethuramah Kelas: 6 Atas SC Epsilon Dan DeltaDocumento2 pagineGuru Kelas: PN Thilagavathy Sethuramah Kelas: 6 Atas SC Epsilon Dan DeltaThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- K WentworthDocumento195 pagineK WentworthThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemDocumento10 pagineChemThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- K WentworthDocumento195 pagineK WentworthThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- RevisionDocumento2 pagineRevisionThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Excel 1 2017 Term 2Documento2 pagineAnswer Excel 1 2017 Term 2ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 1 ThermochemDocumento1 paginaExercise 1 ThermochemThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- QUIZ 6 ThermochemistryDocumento1 paginaQUIZ 6 ThermochemistryThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 BH Didik 3 Apr PDFDocumento17 pagine12 BH Didik 3 Apr PDFFAZARINessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Chew 1Documento7 pagineExam Chew 1ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- T4Documento18 pagineT4ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Both The Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces ProvidedDocumento5 pagineAnswer Both The Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces ProvidedThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Okeke, ODocumento132 pagineOkeke, OThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Attendance List For Extra Class: U 6 SC ZetaDocumento1 paginaAttendance List For Extra Class: U 6 SC ZetaThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple MachinesDocumento14 pagineSimple MachinesThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- NameDocumento1 paginaNameThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemDocumento10 pagineChemThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Confidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)Documento9 pagineConfidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 6186105941197324304 PDFDocumento56 pagine5 6186105941197324304 PDFThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Chew 1Documento7 pagineExam Chew 1ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemDocumento1 paginaChemThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 Exercise 1Documento2 pagine4.1 Exercise 1ridithaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawDocumento2 pagine2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawHorro8480100% (1)
- Organic ChemistryDocumento193 pagineOrganic ChemistryThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Confidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)Documento9 pagineConfidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- INORGANIC Periodic Table 1Documento26 pagineINORGANIC Periodic Table 1ThilagaNessuna valutazione finora
- FAQ Lecture 1Documento5 pagineFAQ Lecture 1Richard De Medeiros Castro100% (1)
- Motor SizesDocumento10 pagineMotor SizesBruno KosNessuna valutazione finora
- Monel K500 PDFDocumento6 pagineMonel K500 PDFOZAIRTRADELINKNessuna valutazione finora
- An-1009 Application Note On ASTM E313 WhitenessDocumento3 pagineAn-1009 Application Note On ASTM E313 WhitenesskcadavidNessuna valutazione finora
- SF6 Circuit BreakerDocumento2 pagineSF6 Circuit Breakerarundas16Nessuna valutazione finora
- AQA GCSE NOV2020 Combined Science Trilogy Chemistry Paper 1H QPDocumento24 pagineAQA GCSE NOV2020 Combined Science Trilogy Chemistry Paper 1H QPmakintolu7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stireno 1Documento2 pagineStireno 1jhonNessuna valutazione finora
- EC203-C Image Marked Image MarkedDocumento2 pagineEC203-C Image Marked Image MarkedManjunath BadigerNessuna valutazione finora
- FAQ Performance PipeDocumento7 pagineFAQ Performance PipeSalman AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Information About Your 140 & 210 Climate Control PanelsDocumento4 pagineImportant Information About Your 140 & 210 Climate Control PanelsLesia DeFeliceNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Specifications For Road Works SERIES 4000-Bituminous Layers and SealsDocumento51 pagineStandard Specifications For Road Works SERIES 4000-Bituminous Layers and SealsKisali SarakikyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Water Treatment Operations Plan TemplateDocumento8 pagineSurface Water Treatment Operations Plan TemplateSkid RowNessuna valutazione finora
- Schultz 1987Documento18 pagineSchultz 1987Ruiz ManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- BHEL Standards IS EN PDFDocumento103 pagineBHEL Standards IS EN PDFBodhan Prasad50% (2)
- Indonesian Mineral Deposits - IntroductoryDocumento11 pagineIndonesian Mineral Deposits - IntroductoryridofambudiNessuna valutazione finora
- F1055 15708Documento15 pagineF1055 15708Alejandro ValdesNessuna valutazione finora
- Generalized Guidelines For Structural Steel Welding InspectionDocumento19 pagineGeneralized Guidelines For Structural Steel Welding InspectionHariPrasath100% (1)
- Report Radiation Exchange Between SurfacesDocumento52 pagineReport Radiation Exchange Between SurfacesStephen TabiarNessuna valutazione finora
- Halal and Haram IngredientsDocumento26 pagineHalal and Haram IngredientsMuhammad A RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- BenzilDocumento5 pagineBenzildeviycNessuna valutazione finora
- Failure Rate Data Analysis For High Technology ComponentsDocumento9 pagineFailure Rate Data Analysis For High Technology ComponentsganeshdhageNessuna valutazione finora
- Elce221 Lab 1Documento6 pagineElce221 Lab 1Little VoiceNessuna valutazione finora
- CHENG 211 Assignment 1 s2 17 18Documento5 pagineCHENG 211 Assignment 1 s2 17 18Hayat YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Explain A Simple Vapour Compression Cycle Giving Clearly Its Flow Diagram?Documento5 pagineExplain A Simple Vapour Compression Cycle Giving Clearly Its Flow Diagram?Ashok DaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bongsuwan D 2008Documento7 pagineBongsuwan D 2008Liona MargaritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Separating Mixtures Particulate NatureDocumento5 pagineSeparating Mixtures Particulate NatureStruggl1ngNessuna valutazione finora
- Bitumat TopsealDocumento5 pagineBitumat TopsealsathiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drilling and Blasting As A Tunnel Excavation MethodDocumento26 pagineDrilling and Blasting As A Tunnel Excavation MethodMIGUEL FERNANDO AGUIRRE QUISPE100% (1)
- Transparent WoodDocumento7 pagineTransparent WoodArnab BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromDocumento9 pagineAntimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromTrần Thuý QuỳnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDa EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDa EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)
- Introduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisDa EverandIntroduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDa EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireDa EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (129)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Da EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilDa EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookDa EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDa EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDa EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsDa EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookDa EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNessuna valutazione finora
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookDa EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNessuna valutazione finora