Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
24 Beamer
Caricato da
Mrityunjay Kumar JhaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
24 Beamer
Caricato da
Mrityunjay Kumar JhaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Training Manual Table of Contents
A318/A319/A320/A321 EASA Part 66 Cat. B1B2A
24 Electrical Power Generator Operation Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Generator Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Generator 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
24-00 General Generator Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Main Components and Subsystems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Integrated Drive Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
AC Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Servicing of IDG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
DC Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 AC Main System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Circuit Brakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Generator Control Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Generator Control and Protection Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Normal Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Differential Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Abnormal Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Engine Fire and Open Feeder Cable Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
System Identification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 Other Protections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Circuit Identification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 AC Generation Enhanced Electrical Power Generating System (EEPGS) 21
Enhanced Electrical Power Generating System (EEPGS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 EEPGS IDG Drive Part D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
EPGS to EEPGS Evolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 EEPGS IDG Disconnection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
New Main Generator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 EEPGS IDG Monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
GCU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 EEPGS IDG Cooling System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
GAPCU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 EEPGS IDG Generator Part D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Control and Indicating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 EEPGS GCU D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Distribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Engine Fire and Open Feeder Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
EEPGS Main Control Panel Presentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 Differential Current Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
EEPGS APU Generation General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
24-01 System Report / Test EEPGS APU Generation D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
AC Generation Interfaces (Enhanced Electrical Power Generating System) EEPGS AC Generation Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
13 IDG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
AC Generation MCDU Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
System Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Specific Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 GCU Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Generator Operation Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
24-22 AC Main Generation Generator Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Generator Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Generator Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Generator Temperature Monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Speed Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Control and Protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Control and Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Generator Control Unit Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
Contents - I
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Table of Contents
A318/A319/A320/A321 EASA Part 66 Cat. B1B2A
Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Configuration of Circuit Breakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
CSM/G Control Unit Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Galley Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Generator Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 GALY & CAB and Commercial P/BSW (A318) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Speed Regulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Load Monitoring (A318). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Voltage Regulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Refueling on Batteries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Generation Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Static Inverter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 24-Study Questions
24-30 DC Generation
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Loss of the Transformer Rectifier 1, 2, or Essential . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Transformer Rectifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
DC Essential & Normal Generation Switching - D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
DC Generation Monitoring and Indicating - D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
DC GENERATION - BATTERIES - D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
24-40 External Power
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Normal Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Abnormal Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Bite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
AC/DC Ground Service Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
DC Ground Service Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Enhanced Electrical Power Generating System (EEPGS) External Power. 9
External Power Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
External Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
EXT PWR in use (on) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
GAPCU D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
AC/DC Ground Service Distribution D/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
AC/DC Sheddable Bus Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
24-50 Load Distribution
AC Electrical Power Distribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Circuit Breaker Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
Contents - II
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00
24 Electrical Power
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
24-00 General A Generator Control Unit (GCU) is associated with the emergency generator.
Its functions are:
• To regulate the emergency generator constant speed.
The electrical power system consists of a 3 phase 115/200 V 400 Hz constant fre- • To control the generator voltage.
quency AC system and a 28 V DC system.
• To protect the network by controlling the emergency generator line contactor.
Normally, the system produces AC current which is then transformed into DC cur-
• To control the emergency generator start-up.
rent. Each generator, engine or APU can supply the complete AC and DC system.
Galley supply has secondary priority. In case of loss of normal AC generation the Static lnverter
aircraft can be supplied by an emergency generator (Ram Air Turbine, RAT). In
case of total loss of AC generation, the aircraft can be supplied from the batteries. A static Inverter transforms the DC voltage from battery 1 into single phase 115 V
In this case, DC current can be transformed into AC current. - 400 Hz AC supplied to part of the AC ESS Bus. When the aircraft speed is more
than 50 kts, the static inverter is automatically activated if only batteries are sup-
plying the aircraft, regardless of BAT1 and BAT2 P/B position.
Main Components and Subsystems With aircraft speed below 50 kts, the static inverter is activated
AC Generation when batteries only are supplying the electrical system provided both BAT 1 and
BAT 2 P/B are switched on.
Main Generators
Aircraft electrical power is provided by two three phase DC Generation
AC engine generators driven by an integrated drive (GEN 1, -GEN 2) with an out- Transformer Rectifiers (TR)
put rated at 90 KVA - 115/200 V - 400 Hz. A third equal generator (APU GEN) driv-
Two main Transformer Rectifiers TR1 and TR2 permanently provide the DC pow-
en directly by the APU can replace either or both engine generators at any time.
er.
Power supply control of each generator is performed by a Generator Control Unit
(GCU). A third identical transformer rectifier, the ESS TR is used to supply the DC ESS
BUS from the emergency generator in case of total loss of ENG and APU gener-
The main functions of each GCU are:
ators or if TR1 orTR2 fails.
• To control the generator frequency and the voltage.
Each TR controls its contactor by internal logic.
• To protect the electrical system by controlling the associated Generator Line
Contactor (GLC). Batteries
External Power Two main batteries of normal capacity of 23 Ah each are permanently connected
to the two hot busses.
A ground power connector is installed near the nose wheel to supply the complete
AC and DC system. A Ground Power Control Unit (GPCU) ensures the system Each battery has an associated Battery Charge Limiter (BCL).
protection by controlling the external power contactor. The BCL monitors battery charging and controls its battery contactor.
Emergency Generator (RAT) Note:
• In normal configuration the batteries are disconnected most of the time.
An emergency generator, AC three phase, 5 KVA - 115/200 V - 400 Hz driven by
the blue hydraulic system, automatically provides emergency power in case of fail- • A battery automatic cut off logic prevent batteries from complete discharge
ure of all generators. when on ground (parking).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 1: Electrical Power Distribution
DC BAT BUS
DC TIE BAT ESS DC DC TIE
CONT CONT TIE CONT
HOT BUS 1 HOT BUS 2
BAT 1 STAT BAT 2
INV
CONT
DC BUS 1 DC ESS BUS DC BUS 2
DC ESS SHED
STAT
INV
DC GND / FLT
AC STAT INV
EMER
TR ESS GEN TR
1 TR 2
AC ESS BUS
AC ESS SHED AC GND / FLT
AC ESS FEED
AC BUS 1 AC BUS 2
BUS TIE BUS TIE
PUMPS
CONT CONT
FUEL
GEN
LINE APU EXT
CONT LINE PWR
CONT CONT
GEN APU GEN
GEN EXT
1 PWR 2
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Circuit Brakers
Two types of C/Bs are installed:
• Monitored C / Bs, (green). When pulled more than 1 mm., the “C / B TRIPPED’
ECAM warning is triggered.
• Non monitored C/Bs (black).
Red C/B caps are installed on Wing Tip Brakes C/Bs to prevent any WTB reset.
A320 only:
Moreover, yellow rings are installed on C/Bs which must be pulled when flying on
batteries only (Refer to Emergency/Abnormal checklist).
Operations
GEN 1 and 2, when operating, have priority over the APU generator and over the
external power.
The generators cannot be connected in parallel.
The external power has priority over the APU generator when the EXT PWR P/B
is ON.
One engine generator, the APU generator or the external power may supply the
complete AC and DC system.
On ground, when only ground services are required, AC and DC GND / FLT BUS-
ES can be supplied directly from the external power without supplying the entire
aircraft system.
This configuration is selected through the MAINT BUS switch located in the for-
ward entrance area.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 2: Emergency Generation Control Logic
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 3: Distribution Table
AC AC AC AC AC ESS DC DC DC DC DC HOT HOT
BUS BUS ESS ESS STAT TR1 TR2 TR BUS BUS BAT ESS ESS BUS BUS
1 2 BUS SHED INV 1 2 BUS BUS SHED 1 2
TR1 TR2 TR1 TR1 TR1
NORM CONF GEN1 GEN2 GEN1 GEN1 / GEN1 GEN2 / BAT1 BAT2
GEN1 GEN2 GEN1 GEN1 GEN1
ONE GEN INOP TR1 TR2 TR1 TR1 TR1
-X- for GEN GENX GENX GENX GENX / GENX GENX / BAT1 BAT2
1, 2 or APU GENX GENX GENX GENX GENX
EMER CONF ST ST
INV INV
BEFORE EMER / / / / / / / / / BAT2 / BAT1 BAT2
GEN RUNNING
(about 5 sec) BAT1 BAT1
ESS ESS
EMER GEN TR TR
RUNNING / / EMER EMER / / / EMER / / / BAT1 BAT2
GEN GEN GEN
EMER EMER
GEN GEN
(A320 only) ST ST
AFTER L/G INV INV
EXTENSION / / / / / / / / / BAT2 / BAT1 BAT2
BAT1 BAT1
(A319/321 only) ST ST
AFTER INV INV
TOUCH / / / / / / / / BAT BAT2 / BAT1 BAT2
DOWN (RAT 1-2
stall or speed BAT1 BAT1
<100kt )
AFTER TOUCH ST
DOWN INV
(Speed < 50 kt) / / / / / / / / / BAT BAT2 / BAT1 BAT2
1-2
BAT1
ON GROUND
BATTERIES / / / / ST / / / / / BAT BAT2 / BAT1 BAT2
ONLY INV 1-2
BAT1
ESS ESS
TR2 TR2 TR2 TR TR
TR1 FAULT GEN1 GEN2 GEN1 GEN1 / / GEN2 GEN1 BAT1 BAT2
GEN2 GEN2 GEN2 GEN1 GEN1
ESS ESS
TR1 TR1 TR1 TR TR
TR2 FAULT GEN1 GEN2 GEN1 GEN1 / GEN1 / GEN1 BAT1 BAT2
GEN1 GEN1 GEN1 GEN1 GEN1
ESS ESS
TR1 + 2 TR TR
FAULT GEN1 GEN2 GEN1 GEN1 / / GEN1 / / / BAT1 BAT2
GEN1 GEN1
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Normal Configuration Figure 5: External Power only
Engine Generator 1 and 2
Each engine driven generator supplies its associated AC BUS (1 and 2) via it’s
Generator Line Contactor (GLC 1 and GLC 2). AC ESS BUS is normally supplied
from AC BUS 1 via the AC ESS FEED contactor. TR 1 normally supplies DC BUS
1, DC BAT BUS, and DC ESS BUS. TR 2 normally supplies DC BUS 2. The two
batteries are connected to the DC BAT BUS if charging is needed. When they are
fully charged the Battery Charge Limiter (BCL) disconnects them.
Figure 4: Engine Generator 1 and 2
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-7
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 6: APU Generator and Engine Generator 2 Figure 7: APU Generator only
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-8
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Abnormal Configuration Failure of the AC BUS 1
• The AC ESS and DC ESS BUSES will be supplied by the AC 2 BUS and the
Failure of one Engine Generator ESS TR if the AC ESS FEED P/B is pressed.
The failed generator is automatically replaced by: • The DC 1 and DC BAT buses are automatically supplied by the DC 2 BUS after
• The APU GEN if available or, 5 sec.
• The other engine generator (with automatic partial galley load shedding). Figure 9: Failure of the AC BUS 1
Figure 8: Failure of one Engine Generator
12H24 12H24
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-9
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Failure of one TR Failure of TR1 and TR2
The contactor of each TR is automatically open in case of: If TR1 and TR2 are lost: DC1 BUS, DC2 BUS and DC BAT BUS are also lost. The
• Overheat. DC ESS BUS is supplied by the ESS TR.
• Minimum current. Figure 11: Failure of TR1 and TR2
The faulty TR is automatically replaced be the other one.
The DC ESS BUS is supplied by the ESS TR.
Figure 10: Failure of one TR
12H24
12H24
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-10
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Loss of all Main Generators (EMER GEN Running): Smoke Configuration
In the event of loss of both AC 1 and AC 2 BUS, with speed above 100 kt, the RAT In case of smoke detection from an electrical source, the procedure leads to shed-
is automatically extended. This powers the blue hydraulic system which drives the ding of the main bus bars.
emergency generator via a hydraulic motor. This generator supplies the AC ESS In this configuration the electrical distribution is the same as in emergency config-
BUS and the DC ESS BUS via the ESS TR. uration (loss of main generators) except for the LH and RH fuel pump 1 which are
A320: When the L/G is down: connected upstream of the GEN 1 line contactor.
A319/321: If the RAT stalls or when on ground with speed below 100 kt: About 75 % of electrical equipment is shed. All the units which remain powered
The emergency generator is no longer powered and the emergency generation are supplied from C/B’s which are located on the overhead panel (except those
system is automatically transferred to the batteries and static inverter with auto- which are supplied from HOT BUSES).
matic shedding of the AC SHED ESS and DC SHED ESS BUS bars. The ECAM ELEC PAGE is identical to the EMER GEN running case.
A320 only: During this phase, APU start is inhibited
When on ground: Figure 13: Smoke Configuration
• Below 100 kt the DC BAT BUS is automatically connected to the batteries.
• Below 50 kt the AC ESS BUS is automatically shed leading to the loss of all
CRT.
• During RAT extension (about 8 sec) the emergency generation system is pow-
ered from the batteries.
• APU start is not inhibited if emergency generation system is powered from the
batteries only when on ground (speed is lower than 100 kt).
Figure 12: In Flight
12H24
12H24
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-11
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 14: Electrical Panel (AC System)
AC ESS FEED P/B
A The AC ESS BUS is normally supplied from the AC BUS 1.
It may be supplied by the AC BUS 2 through the AC ESS
FEED Contactor.
IDG 1 (2) P/B (guarded)
NORMAL - The AC ESS BUS is supplied from AC
BUS 1. Normally springloaded out.
ALTN - The AC ESS BUS is supplied from AC When pressed the IDG is disconnected from its drive shaft
BUS 2. and can only be reconnected by maintenance personnel.
FAULT - Illuminates amber accompanied by CAUTION: If the P/B is pressed for longer than about 3 sec.
ECAM activation when the AC ESS BUS damage may occur to the disconnection mecha
is not electrically supplied. nism.
NOTE: In case of total loss of main generators the AC ESS Do not disconnect the IDG when the engine is not running (or
BUS is automatically supplied by the emergency in windmilling) since IDG damage would be incurred at
generator or by the static inverter if the emergency engine start.
generator is not available. FAULT - Illuminates amber accompanied by
ECAM activation in case of:
GALLEY P/B A IDG oil outlet overheat (above 185˚C),
or
AUTO - Main galley and secondary galley are IDG oil pressure low. Inhibited at low
supplied under normal condition. engine speed (N2 below 14 % ).
The main galley is automatically shed Light extinguishes when the IDG is
if only one engine generator is disconnected.
operating.
All galleys are powered when APU
GEN or EXT PWR is supplying.
OFF - The main galley and secondary galley are
not supplied.
FAULT - Comes on amber accompanied by
ECAM activation when the load of any
generator is above 100 % of rated output.
GEN 1 (2) P/B
EXT PWR P/B
On - The generator is energized and the line
contactor closes provided electrical AVAIL - Illuminates green provided external
parameters are normal. power is connected and external power
APU GEN P/B
parameters are normal.
OFF - The generator is de-energized and the
On - The APU generator is energized and the
line contactor opens. Momentarily pressed:
line contactor closes provided
The fault circuit is reset.
parameters are normal and EXT PWR line - If the AVAIL Iight was on:
FAULT - Illuminates amber accompanied by contactor is open. The external power line contactor
BUS TIE P/B
ECAM activation in the event of: The bus tie contactor 1 and (or) 2 closes.
Protection trip initiated by the automatically closes if GEN 1 and (or) AUTO - The AC Bus Tie Contactors (BTC) open or The AVAIL Iight goes off.
associated Generator Control Unit GEN 2 are not operative. close automatically in order to maintain The ON Iight comes on blue.
(GCU). power supply to AC BUS 1 and 2.
OFF - The generator is de-energized and the - If the ON Iight was illuminated:
Opening of the line contactor (except if
line contactor opens. The fault circuit is - One BTC is closed when: The external power line contactor
GEN P/B selected OFF).
reset. One engine generator supplies the opens.
NOTE: If the protection trip is initiated by a differential fault associated AC BUS, and The ON Iight goes off.
FAULT - Illuminates amber accompanied by
the reset action has no effect after two attempts. The APU GEN or EXT PWR supplies the The AVAIL Iight comes on.
ECAM activation in the event of:
other side.
Protection trip initiated by the NOTE: - The external power has priority over the
associated Generator Control Unit - Both contactors are closed in case of one APU GEN. The engine generators have priority
(GCU). engine, or APU GEN, or EXT PWR supply. over the external power.
Opening of the line contactor (except if - ON Iight remains on even when the engine gener
OFF - Both bus tie contactors open.
GEN P/B selected OFF). APU GEN ators supply the aircraft.
FAULT light is inhibited when APU
speed is too low.
NOTE: APU GEN FAULT is inhibited when APU speed is too
low or in case of APU GEN line contactor opening af
ter EXT PWR or ENG GEN take over.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-12
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 15: Electrical Panel (DC System and Emergency Power)
BAT 1 (2) Indication
A
Battery voltage is indicated in white.
B BAT 1 (2) P/B
Controls the operation of the corresponding battery charge
B limiter.
Auto - The battery charge controller unit
automatically controls the connection/
disconnection of the corresponding
battery to the DC BAT BUS by closing /
opening of the battery contactor .
- The batteries are connected to the
DC BAT BUS in the following cases:
APU starting (MASTER SW ON and
N 1< 95 %).
EMER GEN TEST P/B (guarded)
NOTE: The connection is limited to
When pressed and held: 3 min. when the emergency
generator is running.
- If AC bus 1 and 2 are supplied:
Battery voltage below 26.5 V (battery
The EMER GEN is hydraulically
charge).
powered provided blue electric pump
Charging is completed when battery
is running.
charge current becomes lower than
The AC ESS BUS and the DC ESS BUS
4A, and in flight only, after a time delay
are connected to the emergency
of 30 min.
generator (the DC ESS SHED and AC
Loss of AC BUS 1 and 2 when below
ESS SHED busses are not powered).
100 kt (EMER GEN not supplying).
The ELEC page is automatically
displayed on ECAM (only on ground). MAN ON P/B (guarded) - If AC BUS 1 and 2 are not supplied, and
If BAT only supply the aircraft:
A AUTO - The RAT will automatically extend when
emergency generator is not supplying
during RAT transit or (A320 only: after
the following conditions are met:
- The AC ESS BUS is powered by the static L/G extension, A319/321 only: after RAT
AC BUS 1 not electrically supplied.
inverter. stall at landing or on ground below
AC BUS 2 not electrically supplied.
100kt):
Aircraft speed above 100 kt.
Battery 1 supplies the AC STAT INV
- The CSM/G (Constant Speed BUS and, provided speed is greater
Motor/Generator) is hydraulically than 50 kt, the AC ESS BUS.
powered by the blue system. Battery 2 supplies the DC ESS BUS.
A320 only : Provided the L/G is up.
Automatic battery contactors opening occurs when:
- As soon as the emergency generator - A/C is on ground.
GEN 1 LINE P/B electrical parameters are within - BAT P/B are at auto.
tolerances the emergency generator is - Main power supply (EXT PWR + GEN) is cut off.
OFF - GEN 1 line contactor opens. connected to the aircraft system. - Battery voltage is lower than 23V for more than 16 sec.
The AC BUS 1 channel is supplied from Reset is achieved by switching BAT P/B to OFF then auto.
GEN 2 through bus tie contactors. (Used When depressed:
for smoke drill). OFF - The battery charge control unit is not
- RAT extension is manually selected. operating, the battery contactor is open.
SMOKE: - Comes on amber associated with ECAM ± Emergency generator is activated within OFF light illuminates white provided the
warning when smoke is detected in the 3 sec. DC BAT BUS is supplied. Hot buses
avionics ventilation duct. A320 only: Provided the L/G is up. remain supplied.
RAT & EMER GEN FAULT Light FAULT - Illuminates amber accompanied by
ECAM caution activation when the
Illuminates red if the emergency generator is not supplying charging current for corresponding
the AC and DC ESS BUS when AC BUS 1 and AC BUS 2 are battery increases at an abnormal rate. In
lost (A320 only: Inhibited if L/G is down). this case the battery contactor opens.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-13
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 16: System Display Electrical
DC 1 (DC 2, DC ESS) Bus Indication Battery Indications
Normally green. Becomes amber when the corresponding BAT P/B OFF: Battery Charge / Discharge Indication DC BAT BUS Indication
bus is off.
"SHED" appears in amber when DC ESS SHED BUS is off. BAT 1 Indication white Green Battery contactor closed. Normally green. Becomes amber if DC BAT voltage <
_ 25.
Battery charging current > 1A .
TR 1 (2) Indication OFF APU Indications
Amber Battery contactor closed,
BAT P/B AUTO: Battery discharge current > 1A
TR 1 Indication white. Becomes amber: APU MASTER SW P/B OFF :
± When voltage or current change to amber. BAT 1 Indication white. Becomes amber: Green Battery contactor closed.
Current < 1A . APU GEN Indication white irrespective of APU GEN
28V TR voltage (green). Becomes amber if ± When voltage or current change to amber SW P/B position.
or Battery contactor open.
V > 31V or V < 25V .
± In case of BAT FAULT warning. APU MASTER SW P/B ON;
150A TR current (green). Becomes amber if - APU GEN P/B OFF
current is <
_ 5A. 28V Battery voltage (green). Becomes amber if
V > 31V or V < 25V . APU GEN Amber APU GEN indication.
ESS TR Indication 150A Battery current (green). Becomes amber if OFF White OFF indication.
discharge current is > 5A .
ESS TR Indication white. Becomes amber:
± When voltage or current change to amber. - APU GEN P/B ON
28V TR voltage (green). Becomes amber if APU GEN APU GEN indication white. Becomes amber:
V > 31V or V < 25V . ± When voltage, load or frequency change to
130A TR current (green). Becomes amber if amber.
current is <
_ 5A.
26% GEN load (green). Becomes amber if
SYSTEM DISPLAY
Voltage and current indications are not displayed when the load > 100%.
essential TR contactor is open. 116V GEN voltage (green). Becomes amber if
V > 120V or V < 110V.
EMER GEN Indication
400HZ GEN frequency (green). Becomes amber if
EMER GEN Indication white. Becomes amber: F > 410Hz or if F < 390Hz.
± When voltage or frequency change to
amber.
AC 2 (AC 1, AC ESS) Bus Indication
116V EMER GEN voltage (green). Becomes
Normally green. Becomes amber when the corresponding
amber if V > 120V or V < 110V .
bus is off.
400HZ EMER GEN frequency (green). Becomes "SHED" appears in amber when AC ESS SHED BUS is shed.
amber if F > 410Hz or if F < 390Hz.
Voltage and frequency indications are not displayed when
EXT PWR Indications
the EMER GEN line contactor is open.
External power not available.
GEN 1 (2) Indications Blank.
GEN P/B OFF: -
GEN 1 "GEN" white if generator energized, amber External power available:
OFF if de-energized. EXT PWR Indication white. Becomes amber:
"1" or "2"indication: ± When voltage or frequency change to
± White if associated engine running. amber.
± Amber if stopped. 116V EXT PWR voltage (green). Becomes amber
"OFF" indication white. if V > 120V or V <110V.
GEN P/B ON: 400HZ EXT PWR frequency (green). Becomes
amber if F > 410Hz or if F < 390Hz.
GEN 1 "GEN" indication white. Becomes amber:
± When voltage, load or frequency change to
amber. STAT INV - Appears during static inverter test and in
use.
26% GEN load (green). Becomes amber in case 14H27
of overload (threshold between 100% and 115V Normally green.
110%). 400Hz Amber if . V < 110V or V > 120V
116V GEN voltage (green). Becomes amber if F < 390HZ or F > 410Hz.
V > 120V or V < 110V.
400HZ GEN frequency (green). Becomes amber if
F > 410Hz or if F < 390Hz.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-14
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 17: System Display Electrical
GALLEY SHED Indication
Appears white when:
- GALLEY P/B is OFF or
- Main galleys are shed if only one generator is operating.
Not displayed in normal configuration.
SYSTEM DISPLAY
IDG 1 (2) Indication
IDG Normally white, becomes amber:
± Oil outlet temp. above 185˚C.
± Oil low press.
± IDG disconnected.
1 or 2 - White if associated engine is running.
± Amber if stopped and FADEC powered.
DISC Indication
DISC - Appears amber when IDG is
disconnected.
14H27
IDG Oil Outlet Temperature
Normally green - Pulsing green if temp. between 147˚ C
and 180˚C.
± Amber if temp. > 185˚C.
LO PR Indication
LO PR - Appears amber when IDG oil low
pressure is detected and associated
engine is running
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-15
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 18: Warnings and Cautions
E / WD : FAILURE TITLE SD LOCAL FLT
AURAL MASTER
PAGE WARNING PHASE
WARNING LIGHT
Conditions CALLED LIGHT INHIB
RAT AND
EMER CONFIG CRC MASTER NIL* EMER GEN
Loss of main generators. WARNING FAULT
AC BUS 1 FAULT
AC BUS 2 FAULT
AC ESS BUS SHED
DC BUS 1 FAULT
DC BUS 2 FAULT NIL 4, 8
DC BUS 1 + 2 F AULT
DC ESS BUS FAULT
DC ESS BUS SHED
Busbar(s) is (are) no longer supplied.
AC ESS
AC ESS BUS FAULT FEED
Busbar is no longer supplied. FAULT
DC BAT BUS FAULT
Busbar is no longer supplied. 4, 5, 7, 8
ESS BUSES ON BAT 1, 2, 3, 4,
NIL
DC and AC ESS BUSES are supplied by batteries. 8, 9, 10
SINGLE MASTER
DC EMER CONFIG ELEC
CHIME CAUTION 4, 8
DC BUS 1 and 2 and DC ESS BUS are not supplied.
GEN 1 (2) FAULT
- Protection trip initiated by associated GCU or GEN 1(2) 1, 4, 5,
- Opening of line contactor with GEN P/B ON. FAULT 7, 8, 10
GEN 1 (2) OFF 1, 3, 4, 5,
GEN 1 (2) P/B OFF with no FAULT. NIL 7, 8, 10
APU GEN FAULT
- Protection trip initiated by associated GCU or APU GEN 4, 5, 7, 8
- Opening of line contactor with APU GEN P/B ON. FAULT
GEN 1 (2) or APU GEN O VERLOAD GALLEY
Load of one generator is above 100% of rated output. FAULT 3, 4, 5, 7, 8
IDG1 (2) OIL L O PR
IDG oil pressure low. IDG 1(2) 1, 4, 5, 7, 8,
IDG1 (2) OIL O VHT FAULT 10
IDG outlet oil temperature above 185˚ C.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-16
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 19: Warnings and Cautions
E / WD : FAILURE TITLE SD LOCAL FLT
AURAL MASTER
PAGE WARNING PHASE
WARNING LIGHT
Conditions CALLED LIGHT INHIB
BAT 1(2) FAULT BAT 1(2)
Charging current increases at an abnormal rate. FAULT
ELEC 3, 4, 5, 7, 8
ESS TR FAULT
SINGLE MASTER
C/B TRIPPED ON O VHD PNL CHIME CAUTION
C/B TRIPPED ON L (R) ELEC BAY 3, 4, 5, 7, 8,
C/B TRIPPED ON REAR PNL J-M or N-R or S-V or NIL
9, 10
W- Z
One C/B tripped in the designated zone.
BAT 1(2) OFF 1, 3, 4, 5, 7,
BAT P/B at OFF without fault. NIL 8, 9, 10
ELEC
TRU 1(2) FAULT
BCL 1(2) FAULT NIL NIL 3, 4, 5, 7, 8
STATIC INV FAULT
NIL
EMER GEN 1 LINE OFF 1, 3, 4, 5, 7,
GEN 1 LINE P/B at OFF position. 8, 9, 10
5MIN AFTER
1500 ft
ELEC PWR
800 ft
STARTED
2ND ENG
SHUT DN
LIFT OFF
1ST ENG
1ST ENG
TO PWR
TOUCH
DOWN
80 kt
80 kt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-17
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 20: Generation and Distribution AC/DC
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-18
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 21: External Power Panel
121AL
108VU
121AL
EXT PWR AVAIL
Illuminates amber to indicate that external power is
available and the voltage is correct.
EXT PWR NOT IN USE
connected but does not supply the aircraft electrical
system.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-19
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 22: Ground Service
2PP
DC BUS 2
6PP
DG GND/FLT
TR2
AC GND/FLT
MAINT BUS ON 212XP,214XP,216XP
MAINT BUS SW NO TR2 OVHT AND
A/C NETWORK NOT
SUPPLIED
Allows electrical loads for ground servicing to be energized
without supplying entire aircraft electrical system. 1XP 2XP
AC BUS 1 AC BUS 2
2000VU ON The switch is magnetically latched provided the
external power parameters are normal (AVAIL Iight BUS TIE BUS TIE
CONT CONT
on).
MAINT BUS The AC and DC GRND / FLT buses are supplied GEN APU EXT
ON and the following systems can be energized: LINIE GEN PWR
CONT CONT CONT
- Passenger compartment lighting
- Galley lighting GEN APU GEN
- Entrance area lights 1 GEN 2
- Lavatory lighting and service
- Vacuum cleaner sockets
OFF - Flight compartment service outlets
EXT
- Hydraulic pump (yellow system) PWR
- Flight compartment flood lighting
- Fuel quantity indications
- Refueling
- Cargo compartment lighting, cargo loading system
- Main and nose L/ G compartment lighting
- Belly fairing panel service outlets
- Ground call
- Eqpt. compartment lights and service outlets
- Navigation lights.
The switch trips when the external source is
removed.
OFF The AC and DC GROUND/FLIGHT buses are
connected to AC BUS 2 and DC BUS 2.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-20
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 23: Main Components
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-21
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 24: Panels
120VU 49VU
122VU 35VU
21VU
25VU
121VU
124VU 125VU
123VU
Spare Lamps and Fuses
Spare Fuse
120VU Contactors etc
APU
AC2 EXT AC1 DC
PWR
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-22
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 25: GCU and GPCU
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-23
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 26: Contactors, Relais and Fuses Typical
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-24
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
System Identification Circuit Identification
Table 1: Table 2: X - AC Generation
C Flight Control Systems XA Galley Supply Control
D De-Icing XB Static Inverter (Generation)
E Engine Monitoring XC AC Essential Generation Switching
F Flight Instrumentation XE AC Emergency Generation (CSM/G, GCU)
G Landing Gear Hydraulics XG AC External Power Control (GPCU)
H Air Conditioning XH AC Essential Distribution
J Ignition. XN AC Main Distribution
K Engine Control and Starting XP AC Equipment Ancillary
L Lighting XS AC Auxiliary Generation (APU generator GCU)
M Interior Arrangement XI Integrated Drive Generator (1DG, GCU)
P DC Power Supply Distribution XU AC Main Generation
Q Fuel XV AC Generation Monitoring & Indicating
R Radio (Navigation and Communication) XX AC Ground Service Bus Control
S Radar Navigation
T Special Electronics
Table 3: P - DC Power Supply Distribution
V Fictitious Circuits
PB DC Generation - Batteries
W Fire Protection and Warning System
PC DC Essential and Normal Generation Switching
X AC Generation and Distribution
PE DC Emergency Generation (IR)
PH DC Essential Distribution
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-25
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Table 3: P - DC Power Supply Distribution
PN DC Main Distribution
PP DC Ancillary Equipment
PN Refuelling on Battery
PU DC Main Generation (TR)
PV DC Generation Monitoring and Indicating
PX DC Ground Service Bus Control
Table 4: V - Fictitious Circuits
VB Wire Bundles
VC Electrical Connectors
VD Diode Module
VG Ground Terminal Block
VN Ground Points
VP Pressure Seal Feed Through
VS Splices
VT Terminal Block
VU Panels & Racks
VZ Spare Wires
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-26
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Enhanced Electrical Power Generating System GAPCU
(EEPGS) The GAPCU monitors and controls the APU operation and the external power op-
eration.
EPGS to EEPGS Evolution
Control and Indicating
The Electrical Power Generating System (EPGS) includes two main engine Gen-
erator Control Units (GCU), an APU generator Control Unit (APU GCU) and a The IDGs are controlled by pushbutton switches located on the overhead ELEC
Ground Power Control Unit (GPCU). The control units control and monitor their re- panel.
lated power supply sources. The three GCUs and the GPCU interface with the • Pushbutton GEN: to switch the generator ON or OFF and to reset the corre-
System Data Acquisition Concentrators (SDAC) via two Electrical Generation In- sponding GCU.
terface Unit (EGIU) as follows: GCU 1 and GPCU to EGIU 1, GCU 2 and APU • Pushbutton IDG: to disconnect mechanically the IDG from the gearbox.
GCU to EGIU 2.
With the Enhanced Electrical Power Generating System (EEPGS), the two EGIUs Distribution
are removed and a new control unit replaces the GPCU and the APU GCU. Both There are two distribution networks.
Integrated Drive Generator (IDGs) are also replaced by two new ones. The
• Network 1 consist of AC BUS 1, AC ESS BUS and AC ESS SHED BUS.
EEPGS includes two main engine Generator Control Units (GCU) and a Ground
and Auxiliary Power Control Unit (GAPCU). • Network 2 consist of AC BUS 2.
The GAPCU combines the functions of the GPCU and the APU GCU in the old Network 2 is also a backup supply for AC ESS BUSe.
EPGS.
The two GCUs and the GAPCU interface directly with the SDACs.
New Main Generator
The IDG consists of a Constant Speed Drive (CSD) and a generator, in a commom
housing.
GCU
The 2 identical GCUs fulfill several functions for the 2 IDGs. The main functions of
the GCU are:
• Voltage and frequency regulation,
• Generator Line Contactor (GLC) control,
• Generator control and protection,
• IDG speed regulation (servo valve controlled),
• Built-in Test Equipment (BITE) function,
Interface with the SDACs
The BITE signals are sent by the GAPCU to the Centralized Fault Display Inter-
face Unit (CFDIU).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-27
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 27: EEPGS Introduction
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-28
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 28: EEPGS Introduction
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-29
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
EEPGS Main Control Panel Presentation damage. Open the safety guard and push the momentary action IDG P/BSW ( not
longer than 3 seconds). This action disconnects the IDG clutch and the white OFF
BAT 1(2) P/BSW light comes on when the disconnection is completed.
The BATtery 1 and 2 P/BSW control the battery contactors. In normal opera-
tion,the BAT P/BSWs are pushed in AUTO position. The batteries are automati-
GEN 1(2) P/BSW
cally connected to, or disconnect from the DC electrical network, according to the The GENerator (GEN) P/BSW allows the associated generator to be connected
DC electrical configuration and the battery charge condition. The FAULT light leg- or disconnected from the electrical network and to reset the related GCU. The
end on the P/BSW comes on amber in case of thermal runaway or short circuit. FAULT light comes on amber in case of generator failure, Generator Line Contac-
When the BAT P/BSW is released out, the selected battery is disconnected and tor (GLC) failure or engine not running. When the GEN P/BSW is released out, the
the OFF light comes on white. OFF light comes on white, the generator is diconnected and the GCU is reset.
Voltmeter APU GEN P/BW
The voltmeters permanently display the battery 1 and 2 voltage. The APU GEN P/BSW allows the APU generator to be connected to, or discon-
nected from the electrical network and to reset the Ground ans Auxiliary Power
AC ESS FEED P/BSW Control Unit (GAPCU). The FAULT light comes on amber in case off generator or
In normal configuration, the AC ESSential BUS is supplied by the AC BUS 1. If GLC failure. When the APU GEN P/BSW is releaded out, the OFF light comes on
there is no power on AC BUS 1, the AC ESS BUS is not supplied and the amber white, the GEN is disconnected and the GAPCU is reset. The FAULT light is in-
FAULT light comes on, on the AC ESS FEED P/BSW. Pushing the AC ESS FEED hibited when APU is not running or in underspeed.
P/BSW allows to recover the AC ESS BUS power supply. Thus, the white ALTer-
Nate (ALTN) light comes on, on the AC ESS BUS P/BSW and AC BUS 2 supplies
BUS TIE P/BSW
the ACESS BUS. The BUS TIE P/BSW controls the two Bus Tie Contactors (BTCs). In automatic
mode, the two BTCs automatically control the supply transfer of the AC network
Galley and Cabin P/BSW according priority logic. When released out, the OFF light comes on white and the
In automatic mode, switch pressed in, the galley and some SUB-Buses are auto- two BTCs are permanently open.
matically supplied or shed according to the electrical configuration. If a generator
overload is detected but there is no automatic load shedding, the amber FAULT
EXT PWR P/BSW
light comes on, on the GALleY and CABin P/BSW. Push to release the GALY & The EXTernal PoWeR P/BSW allows an EXT PWR source to be connected to, or
CAB P/BSW. The white OFF light comes on and all the galleys and Sheddable disconnected from the electrical network. If the external power is correctly plugged
busbar are shed. Note that automatic shedding can occur in flight, when only one in and all parameters are normal, the green AVAILable (AVAIL) light comes on.
generator supplies the AC network. Push the momentary action EXT PWR P/BSW to connect the external power to
the electrical network. The External Power Contactor (EPC) closes, the AVAIL
Commercial P/BSW light goes off and the blue ON light comes on. Push the EXT PWR P/BSW again
The COMMERCIAL P/BSW allows loads to be shed (galleys, cabin and commer- and the external power is disconnected from the electrical network. The EPC
cial related loads) when it is released out. The OFF legend comes on white. opens, the ON light goes off and the AVAIL light comes on.
IDG 1(2) P/BSW MAINT BUS Switch
The safety guarded IDG P/BSW allows the associated IDG to be disconnected The MAINTenance BUS switch is located in the forward cabin ceiling, on the panel
from the accessory gearbox. The IDG FAULT light comes on amber in case of IDG 2000VU. This switch enables the AC and DC ground service network to be ener-
low pressure or oil overheat, Immediately disconnect the IDG, to avoid internal gized, when the aircraft is on the ground and supplied from the external power.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-30
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 29: EEPGS Control Panel Presentation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-31
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-00 General
Figure 30: EEPGS New Design
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-00-32
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
24-01 System Report / Test
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 1: AC Generation System Report/Test
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 2: AC Generation Test
AC GEN
LAST LEG REPORT
TEST
CLASS 3 FAULTS
RETURN
AC GEN
TEST
Displayed if system TEST WAIT
needs more than 3 sec.
to send the result
AC GEN AC GEN
TEST TEST
24-41-34 TEST OK
GPCU
RESET GEN1
RESET GEN2
RETURN PRINT * RETURN PRINT *
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 3: MCDU Messages from GPCU
E / WD : FAILURE TITLE SD LOCAL FLT
AURAL MASTER
PAGE WARNING PHASE
WARNING LIGHT
Conditions CALLED LIGHT INHIB
BAT 1(2) FAULT BAT 1(2)
Charging current increases at an abnormal rate. FAULT
ELEC 3, 4, 5, 7, 8
ESS TR FAULT
SINGLE MASTER
C/B TRIPPED ON O VHD PNL CHIME CAUTION
C/B TRIPPED ON L (R) ELEC BA Y 3, 4, 5, 7, 8,
C/B TRIPPED ON REAR PNL J-M or N-R or S-V or NIL
9, 10
W- Z
One C/B tripped in the designated zone.
BAT 1(2) OFF 1, 3, 4, 5, 7,
BAT P/B at OFF without fault. NIL 8, 9, 10
ELEC
TRU 1(2) FAULT
BCL 1(2) FAULT NIL NIL 3, 4, 5, 7, 8
STATIC INV FAULT
NIL
EMER GEN 1 LINE OFF 1, 3, 4, 5, 7,
GEN 1 LINE P/B at OFF position. 8, 9, 10
5MIN AFTER
1500 ft
ELEC PWR
800 ft
STARTED
2ND ENG
SHUT DN
LIFT OFF
1ST ENG
1ST ENG
TO PWR
TOUCH
DOWN
80 kt
80 kt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 4: MCDU Messages from GPCU
GPCU
TEST MODE
LRU POWER MCDU IN MCDU - MESSAGES
UP TEST OPERATION
TEST TEST
IDGs (4000XU) X X X CHECK GCU 1(2) PIN B11D, B13D
CHECK IDG 1(2) FEEDER PIN; T1, T2, T3 SHORT TO GROUND
X X X CHECK IDG 1(2) PHASE SEQ
X X X CHECK IDG 1(2) DISCONNECT CKT
IDG 1(2) BULB TOLERANCE
X X X IDG 1(2) DISCONNECTED
IDG 1(2) HIGH DELTA TEMP
X X X IDG 1(2) LOW OIL PRESSURE
IDG 1(2) (GEN DIODE)
IDG 1(2) (OVERTEMP)
CHECK GLC 1(2) PIN D, E, F, GCU 1(2) PIN B1A, B2B, B3A
CHECK CT 42XU1 42XU3 GCU1; PIN B11A TO B11D WIRING
CHECK CT 42XU2 42XU4 GCU2; PIN B11A TO B11D WIRING
CHECK GCU 1(2) PIN A15D; IDG 1(2) PIN CA, CB WIRING
CHECK GCU 1(2) PIN A8A, A9B; IDG 1(2) PIN B7, B8 WIRING
CHECK GCU 1(2) PIN A9A, A9B; IDG 1(2) PIN B9, B8 WIRING
CHECK GCU 1(2) PIN B14A, B14B; IDG 1(2) PIN B1, B2 WIRING
CHECK GCU 1(2) PIN C1, C5; IDG 1(2) PIN A9, A10 WIRING
CHECK GCU 1(2) PIN C2 TO C4; IDG 1(2) PIN B12 TO B14
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 5: MCDU Messages from GPCU
GPCU
TEST MODE
LRU POWER MCDU IN MCDU - MESSAGES
UP TEST OPERATION
TEST TEST
TDC AC SENSORS (50XU1, IDC AC SENSORS 50XU1(2)
50XU2)
CHECK IDG 1(2) 1999 (1998)VT WIRING
GCU3 (1XS) CHECK GCU APU PIN B11D, B13D
CHECK GEN APU FEEDER PIN; T1, T2, T3 SHORT TO GROUND
X X X GCU APU
X X X NO DATA FROM GCU APU
X X X CHECK GCU APU PIN A3A; APU CTL RLY 6KD CKT
X X X CHECK GCU APU PIN A6A; APU CTL RLY 6KD CKT
GLC APU
CHECK GLC APU GCU APU PIN B2D WIRING
CHECK GLC APU PIN D, E, F; GCU APU PIN B1A, B2B, B3A
CHECK GLC APU AND/OR CONTROL CKT
CHECK SERIAL LINK GPCU TO GCU APU
CHECK CT 42XS GCU APU; PIN B11A TO B11D WIRING
CHECK GCU APU PIN C1, C5; GEN APU PIN A9, A10
CHECK GCU APU PIN C2 TO C4; GEN APU PIN A12 TO A14
X X X CHECK GEN APU PHASE SEQ
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 6: CSM / GCU Test
GCU EMER
TEST
RETURN
GCU EMER GCU EMER
24-22-34 TEST OK
GCU X
RETURN PRINT * RETURN PRINT *
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-7
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 7: Reset Procedure for TR
SYSTEM REPORT/TEST SYSTEM REPORT/TEST
AIR COND F/CTL AC GEN TR 1
SELECT
AFS FUEL GCU EMER TR 2
ELEC
COM ICE&RAIN BCL 1 TR 3
ELEC INST BCL 2
FIRE PROT L/G
RETURN NAV RETURN
SELECT SYSTEM
REPORT/TEST
CFDS MENU SELECT TR1
LAST LEG REPORT
LAST LEG ECAM REPORT
PREVIOUS LEGS REPORT TR 1
AVIONICS STATUS
RESET
SYSTEM REPORT/TEST
* POST FLIGHT REPORT
SELECT CFDS
MCDU MENU RETURN
FMS
SELECT RESET
DATA LINK
CFDS RESET RESET
AIDS IMPOSSIBLE EFFECTIVE
SELECT DESIRED SYSTEM
PRESS KEY TR 1 TR 1
MCDU TR 1 NO FAULT
MENU
RETURN PRINT * RETURN PRINT *
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-8
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 8: Maintenance Test Procedure for BCL
SYSTEM REPORT/TEST SYSTEM REPORT/TEST
ELEC
AIR COND F/CTL AC GEN TR 1
AFS FUEL GCU EMER TR 2
SELECT
COM ICE&RAIN ELEC BCL 1 TR 3
ELEC INST BCL 2
FIRE PROT L/G
RETURN NAV RETURN
SELECT
SYSTEM
REPORT/TEST
SELECT BCL 1
CFDS MENU
LAST LEG REPORT
LAST LEG ECAM REPORT
BCL 1
PREVIOUS LEGS REPORT
AVIONICS STATUS LAST LEG REPORT
SYSTEM REPORT/TEST TEST
* POST FLIGHT REPORT CLASS 3 FAULTS
SELECT TEST SELECT LAST
RETURN "TEST WAIT" LEG REPORT
SELECT CFDS
IS DISPLAYED
BCL BCL
MCDU MENU TEST LAST LEG REPORT
245100 243800
FMS
RELAY 19XN1.BCL1 CIRCUIT CHECK DC BUS 3PP......BCL1
DATA LINK
CFDS
AIDS
RETURN PRINT * RETURN PRINT *
SELECT DESIRED SYSTEM
NEGATIVE TEST IF TEST IS NEGATIVE TEST (IF NO FAILURE
PRESS KEY POSITIVE "TEST OK" IS DISPLAYED "NO RESPONSE" IS DISPLAYED)
MCDU
MENU
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-9
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 9: MCDU Messages from BCL
BCL
TEST MODE
LRU POWER MCDU IN MCDU - MESSAGES
UP TEST OPERATION
TEST TEST
BAT 1 PUSHBUTTON FAULT (7PB1) X X X PUSH BUT 7PB1/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
BAT 1 CNTOR LINE (6PB1) X X X CHECK CONTACTOR 6PB1/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
BCL 1
PUSH BUT 7PB1/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
BAT 1 (2PB1) X BATTERY 1
STAT INV (3XB) X STATIC INVERTER 3XB
ESS TR CNTOR (3PE) X CHECK CONTACTOR 3PE/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
FUSE (4PB1) X FUSE 4 PB1
BCL 1 (1PB1) X X X BCL 1
SHUNT (3PB1) X X X SHUNT 3PB1/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
DC BAT BUS (3PP) X CHECK DC BAT BUS 3PP/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
HOT BUSSES X CHECK HOT BUS 701PP/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
X CHECK HOT BUS POWER CONSUMPTION
LGCIU/ADIRU DISAGREE X BCL 1; LGCIU/ADIRU1 SIGNAL DISAGREE
LGCIU/BCL INTFC X X X CHECK LGCIU/BCL 1 CIRCUIT
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-10
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 10: Interface GCU’s - GPCU - CFDIU
TO EGIU1
GEN 1 GCU1
PARAMETERS
GEN 2 GCU2 GPCU CFDIU
PARAMETERS
TO EGIU2
GCU3
APU GEN
PARAMETERS MCDU
EXT PWR
PARAMETERS
RS 422
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-11
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Figure 11: Interface CFDIU - ECAM
GEN 1 GEN APU GEN 2
EXT PWR PARAMETERS PARAMETERS PARAMETERS PARAMETERS
TYPE 2 AC SYSTEM
SYS DATA
GPCU GCU 1 GCU APU GCU 2
CHANNEL 2 CHANNEL 1 CHANNEL 2 CHANNEL 1
EGIU 1 EGIU 2
TEST
DISCRETE
SDAC 1
(SYSTEM
ECAM)
SDAC 2
(SYSTEM
ECAM)
TYPE 2 SYS
STAT BCL
INV 1&2
FAULT
BITE
CFDIU
TYPE 3 SYS NOTE:
TR RS 422
1, 2 & 3;
EMER GCU
ARINC 429
ANALOG AND
DC SYTEM DISCRETE SIGNALS
DATA
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-12
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
AC Generation Interfaces (Enhanced Electrical Power information through MIL-STD 1553 data links from the GCUs and transmits a fail-
ure list to the CFDIU (ARINC 429).
Generating System)
GAPCU/CFDIU
Communication The GAPCU transmits the fault message in clear english language to the CFDIU
The Ground and Auxiliary Power Control Unit (GAPCU) is the interface between by ARINC 429 input/output busses. (Type 1). The maintenance test can be per-
the Generator Control Unit (GCU) 1 and 2 and the Centralized Fault Display Inter- formed only on ground with engine shut down. It is initiated either:
face Unit (CFDIU). • Automatically at each GAPCU power-up.
• Or manually from the MCDU.
GCU/GAPCU
The GAPCU receives the fault information from GCU 1 and 2, and compiles them
with its own failures and transmits them to the CFDIU. The GAPCU receives fault
Figure 12: GAPCU - CFDIU Interface
MIL-STD 1553
GEN 1
GCU 1 GAPCU ARINC 429 CFDIU
Parameters
ARINC 429
EXT PWR + APU GEN
Parameters
GEN 2
GCU 2
Parameters
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-13
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
AC Generation MCDU Pages
EPGS Menu Differences
The AC GEN system in the standard Electrical Power Generation System (EPGS)
is a type 2 system. The AC GEN system in the Enhanced EPGS is a type 1 sys-
tem, so the EPGS menu has additional sub menus related to type 1 systems.
Figure 13: EPGS Menu Differences
EPGS SYSTEM REPORT/TEST
EEPGS
<AIR COND F/CTL>
<AFS FUEL>
SYSTEM REPORT/TEST SYSTEM REPORT/TEST
ELEC <COM ICE&RAIN> ELEC
<AC GEN TR 1> <AC GEN TR 1>
<ELEC INST>
<GCU EMER TR 2> <GCU EMER TR 2>
<FIRE PROT L/G>
<BCL 1 TR 3> <BCL 1 TR 3>
<RETURN NAV>
<BCL 2 <BCL 2
<RETURN <RETURN
SYSTEM REPORT/TEST EPGS
ELEC LAST LEG CLASS 3
<LAST LEG REPORT <REPORT FAULTS>
PREVIOUS LEGS SYSTEM
<TEST <REPORT TESTS>
<CLASS 3 FAULTS <LRU IDENT
TROUBLE SHOOT GROUND
<DATA REPORT>
SPECIFIC
<RETURN <RETURN DATA>
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-14
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
System Test the example the GAPCU has passed, GCU 1 test did not run and GCU 2 has
failed. A test will not run is the related engine or APU is running. More information
The SYSTEM TEST pages show the result of EPGS tests. The system test is done
about the failed test (GCU 2) is available by selecting the line keys. Slecting the
on the ground, with the GAPCU in the interactive mode. Only internal GAPCU and CLASS 1 line key gives snapshot troubleshooting data.
GCU tests are done. The first test page asks for confirmation that engines and
APU are not running. The test displays the GAPCU and each GCU test results. In
Figure 14: System Test
EPGS
LAST LEG CLASS 3
<REPORT FAULTS>
PREVIOUS LEGS SYSTEM
<REPORT TESTS>
<LRU IDENT
TROUBLE SHOOT GROUND EPGS
<DATA REPORT> SYSTEM TEST
SPECIFIC
<RETURN DATA> CONFIRM APU AND ENGINES
ARE NOT RUNNING
<START TEST
<RETURN PRINT*
EPGS GCU 2
SYSTEM TEST SYSTEM TEST
GAPCU TEST PASSED ATA CLASS
GCU 1 TEST NOT RUN 24 2234 1>
GCU 2 (1xU2)
GCU 2 FAILED
<START TEST
<RETURN PRINT* <RETURN PRINT*
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-15
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-01 System Report / Test
Specific Data computer and the display shows the Last Flight Leg Data in hexadecimal code.
There is one report per page and each NEXT PAGE selection goes to a PREVI-
The SPECIFIC DATA REPORT presents encoded data, recorded by each EPGS
OUS LEG REPORT. The encoded data includes IDG oil temperature, AC load,
computer channel, every flight leg. The data relates to system performance and is engine speed and IDG ''staight through'' operating time.
not directly related to faults. It is for use at engineering level. Select the required
Figure 15: Specific Data
EPGS
LAST LEG CLASS 3
<REPORT FAULTS>
PREVIOUS LEGS SYSTEM
<REPORT TESTS>
<LRU IDENT
TROUBLE SHOOT GROUND EPGS
<DATA REPORT> SPECIFIC DATA REPORT
<GCU 1 GAPCU>
SPECIFIC
<RETURN DATA>
<GCU 2
<RETURN PRINT*
GCU 1 1/23 GCU 1 1/23
SPECIFIC DATA REPORT SPECIFIC DATA REPORT
LEG DATE UTC LEG DATE UTC
AF-1411 AF-1411
NEXT
00 AUG31 1410 PAGE
00 AUG31 0302
F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF
F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF
F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF
F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF F0F0 A5A5 0F0F 5A5A FFFF
F0F0 A5A5 F0F0 A5A5
<RETURN PRINT* <RETURN PRINT*
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-01-16
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
24-22 AC Main Generation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
General Generator Control Unit Supply
Each engine drives its associated Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) through the The Permanent Magnet Generator supplies the exciter field through the Generator
accessory gearbox. The drive speed varies according to the engine rating. Control Relay and the Generator Control Unit through a Rectifier Unit.
The IDG is split in two parts: the drive and the generator. The Generator Control Unit (GCU) supply from the aircraft network is duplicated
The IDG is cooled and lubricated by the IDG oil system. (Back up supply).
The excitation control and regulation module keeps the voltage at the nominal val-
Generator Drive ue at the Point Of Regulation (POR).
Using the variable speed input, the generator drive produces a constant speed on
the output shaft via a variable ratio differential. Generator Operation Control
The output constant speed is regulated at 12000 RPM. The generator is controlled by the corresponding generator push button. When
pressed in, if the generator speed is high enough, the generator is energized.
Speed Control If the delivered parameters are correct (Power Ready relay closed) the Generator
Line Contactor (GLC) closes to supply its network.
A mechanical governor, acting on a hydraulic trim unit, controls the differential
gear in order to maintain the constant output speed.
Generator Monitoring
The differential gear also controls the oil system pumps in order to lubricate and
cool the IDG components. The FAULT light comes on when any generator parameter is not correct or when
the Generator Line Contactor is open.
Control and Monitoring During the AVIONICS SMOKE procedure, the FAULT light does not come on
when the GEN1 LINE push button is set to off.
AC generation is monitored by the Generator Control Unit (GCU). GEN 1 OR 2
push button Controls generator excitation via its Generator Control Unit. The generator failure signal is sent to SDAC 1 and 2 through the Electrical Gen-
eration Interface Unit (EGIU). When the engine is shut down, the corresponding
For safety reasons and IDG protection, an IDG1 (or IDG2) guarded push button
GEN FAULT light is on.
allows manual disconnection of the IDG.
Reset of the system can only be performed on ground, with engines stopped, by Generator 1
pulling the reset handle mounted on IDG casing.
To avoid complete loss of fuel pumps during the smoke procedure the GEN 1
Generator LINE push button is released out to open the line contactor.
The generator 1 is still excited and supplies fuel pumps 1 LH and 1 RH.
The generator is a conventional 3 co-axial component brushless generator which
consists of:
Generator Reset
• a Permanent Magnet Generator,
• a rotating diode pilot exciter, When the GEN push button is released out after a fault detection, the Generator
Control Unit is reset.
• the generator itself.
The generator is driven at a constant speed of 12000 RPM and cooled by oil
spraying.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
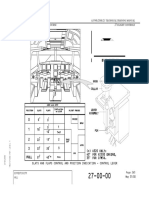
Figure 1: IDG Location
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Integrated Drive Generator DO NOT PUSH THE IDG DISCONNECT PUSHBUTTON SWITCH FOR MORE
THAN 3 SECONDS.
The IDG disconnection signal is inhibited when the corresponding engine is not
running. THERE MUST BE AT LEAST 60 SECONDS BETWEEN TWO OPERATIONS OF
THE SWITCH.
Figure 2: IDG Description
115V
400Hz
Variable IDG
Input Disconnect Generator
Speed Mechanism Constant
Input Output Speed
Stepup Differential Permanent 3 Phase
Gear Gear 12000 RPM Magnet 400 Hz
4500-
9120 RPM Generator Generator
Engine
Accessory
Variable Fixed P
Gear Box F
Unit Unit M
G I
Reset E
Handle Hydraulic Trim Unit L
S
U D
P
Mechanical P E
Governor L X
Y C
I
T T
O A
Oil System T
Charge Pump I
Drive Deaerator G
C O
Scavenge N
U
Pumps
IDG 1 Oil
GEN 1 Generator
ELEC Panel Control
FAULT FAULT
Unit
OFF
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 3: IDG System Control Schematic
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 4: IDG Oil Cooling and Warning
IDG 1
GCU 1
Drive C
G
Fuel/Oil F
P
Oil in Heat D
Oil Inlet Temp C
Temp Exchanger I
Oil U
Sensor U
System T° Rise
Indication
E S
G D E/W
I A Display
Oil Outlet U C
Oil out 1
Temp Temp
Master
Sensor Caut
Overheat
Temp S SC
>185°C D
Charge Charge IDG
A System
Pressure Generator Pump De-Activator
Low C Display
Switch 2
Pressure
U Differential
Low S Gear
Input Speed Sensor Oil in
Speed E Charge Temp
IDG 1 R Hydraulic Pressure Sensor
Disconnect Solenoid S Trim Unit Switch
FAULT Cooler
Governor Bypass
Generator Valve
Relief Valve
Oil out
Scavenge Pump Temp
Sensor Fuel/Oil
Oil Filter Heat Exchanger
Oil Sump
Pressure
Fill Port Clogging
Indicator
Fuel System
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 5: IDG Oil Level and Differential Pressure Indication DO NOT OPERATE THE IDG:
IF IT CONTAINS TOO MUCH OIL
IF IT DOES NOT CONTAIN ENOUGH OIL
IF YOU DO, YOU CAN CAUSE DAMAGE TO THE IDG.
THE OIL OVERFLOW DRAINAGE PROCEDURE CAN TAKE UP TO 20 MIN-
UTES TO COMPLETE. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THE OVERFLOW TIME RE-
QUIREMENTS CAN CAUSE HIGH IDG OIL LEVEL CONDITION RESULTING IN
ELEVATED OPERATING TEMPERATURES AND DAMAGE TO THE IDG.
Figure 6: IDG Front View
A
A
Normal
(Reset)
B
A320 ΔP Indicator Button
Red OVER 1 (Silver End, Red
FULL
Cylindrical Side)
Yellow
2
Green
ADD ADD 3
Red OIL OIL
CFM-66 Extended
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-7
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Servicing of IDG 2. If the oil level is within the green band (IDG cold) or within green or yellow
bands (IDG hot), oil servicing is not required.
1. If the oil level is above the line between the green and the yellow band (IDG
cold) or above the yellow band (IDG hot), oil servicing is required. 3. If the oil level is below the green band, oil servicing is required.
The yellow band corresponds to the oil thermal expansion margin.
Figure 7: Servicing of IDG
Red Band OVER 1
FULL
Yellow Band 2
Filter Clogging
ADD 3
Vent Valve Indicator Green Band
ADD
(Vacuum) Oil Filter OIL OIL
Electrical Red Band
Connectors
ΔP INDICATOR
Disconnect BUTTON
Reset Handle
Oil Level
Indicator
NORMAL
EXTENDED
(RESET)
DPI RESETS
REFER TO APPROPRIATE
Oil Out DOCUMENTATION FOR DETAILS OF
Port Oil IN THE ALTERNATE DPI PROCEDURE
Port REMOVE
1 2 3 4 IDG
Overflow Pressure Case Drain
Drain Port Fill Port Plug DPI RESET LABEL
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-8
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 8: Servicing of IDG
Step One
Attach overflow drain and pressure
fill hoses.
Some oil may come out of the overflow
drain hose when it is connected.
Pump filtered oil into the IDG until
at least 1 more quart of oil comes out Overflow
the overflow drain hose. Drain Hose
Pressure
Fill Hose
Step Two
Remove pressure fill hose only.
Install dust cap.
Dust
Overflow CAP
Allow to drain the overflow- Drain Hose
drain about 20 minutes!
Step Three
Remove overflow drain hose when
drainage slows to drops.
Install dust cap.
Dust
Overflow CAP
Drain Hose
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-9
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 9: IDG Oil Filter / IDG Installation
4
3
2 Phase Lead Installation
1
Alternate
Configuration
Terminal
Square Block Stud
Washer
Terminal Generator
Block Terminal Lead
Assembly
QAD
Ring
Bracket
Lockwire
O-Rings Bracket
Tension
Bolt
Tension
Bolt
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-10
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
AC Main System • AC BUS 1,
The two engine generators provide the AC main generation. The AC main gener- • AC ESSENTIAL BUS,
ation supplies the whole aircraft in normal flight configuration. The transfer circuit • AC SHEDABLE ESSENTIAL BUS.
supplies either one or the two distribution networks from any generation source: Generator 2 supplies network 2, corresponding to AC BUS 2.
• main, Networks 1 and 2 are supplied in priority order:
• auxiliary, • by their generator,
• or ground. • by the electrical ground power unit,
System Description • by the auxiliary generator,
• or by the other generator.
When the two engines run in normal conditions, generator 1 and generator 2 sup-
ply their own network. Generator 1 supplies network 1, including: GEN1 and GEN2 push button switches, on the panel 35VU on the overhead pan-
el, control the generators 1 and 2 respectively via the GCU.
Figure 10: Main AC Distribution System
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-11
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Generator Control Unit • the Servo Valve Relay (SRV) which controls the generator speed by means of
the servo valve.
The 3 GCUs are identical and interchangeable. The GCU functions (GCU1, GCU
2 and GCU3) are selected by Pin Programming. The GCU has four different func- GCU Control of the various indications (warnings and annunciators)
tions:
The GCU controls the warnings and annunciators related to the IDG channel.
• voltage regulation,
• Generator FAULT comes on when the protections come into operation (PR
• frequency regulation,
opening)
• control and protection of the network and the generator,
• Generator FAULT also comes on when the GLC is open
• control of the various indications,
• Galley FAULT when an overload is detected
• system test and self-monitoring.
• IDG FAULT for a low pressure or high temperature of the cooling and lubrica-
All these functions are performed in the digital form. tion oil system.
The GCUs are supplied:
Communication between the GCU and the SDAC
• directly from the PMG, for generator excitation and 28VDC internal and exter-
nal supply, The other functions on the GCU is to provide main electrical parameters to the
• from the aircraft normal network (28 VDC) for the internal and external supply. SDACS via ARINC 429 data links. The information provided to the SDACs is as
follows:
This dual supply constitutes a back up supply. • POR voltage (phase A),
Voltage Regulation • Load (phase A),
• Line Frequency (phase A),
The voltage regulation is achieved by controlling the current through the exciter
field. The voltage is kept at nominal value (115 VAC) at the Point of Regulation • Oil Inlet/Outlet Temperature,
(POR). The POR is located in the electrical power centre (120VU) at the end of • Overload,
the generator feeder, upstream of the line contactor. The principle of operation of • Generator Fault,
the voltage regulator is by constant frequency variable pulse width modulation of • IDG Disconnect Status,
the voltage through the exciter field. • IDG Low Oil Pressure
Regulation of the Generator Speed
The regulation of the generator speed is accomplished by means of a servo valve
located in the IDG. The GCU controls the servo valve position.
Control and Protective Functions
The GCU controls the connection and disconnection of the power provided by the
generator to and from the aircraft electrical system. This control is provided by
means of 3 relays:
• the Generator Control Relay (GCR) which controls the generator excitation,
• the Power Ready Relay (PRR) which controls the generator line contactor and
the FAULT warning light in the cockpit,
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-12
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 11: Generator / GCU
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-13
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Generator Control and Protection Functions "absent" - Pin Programming Error detected on GCU power-up. The generator
shall be "reset" when the protective faults (identified above) are still not present
The following control or fault signals cause generator shutdown or de-energiza-
and one of the following occurs: - Cold Start (which is defined as POWER-UP RE-
tion: - No controlled Shutdown recognized upon power-up of the control unit - Ov- SET or the application of 28 volts to the control unit) occurs, - Generator Control
ervoltage Fault - Undervoltage Fault - Overfrequency Fault - Underfrequency Switch (GCS) is toggled (OFF to ON). The following functions shall be limited to a
Fault - - Underspeed - Shorted Rotating Diode (PMG to chassis short) Fault -
total of 2 resets after which a cold start will be required for reset: - Overvoltage
Open Cable Fault - Differential Protection Fault - Overcurrent Fault - Delta Over- Fault - Overfrequency 2 Fault - Differential Protection Fault - Overcurrent 2 Fault
current Fault - Phase Sequence Fault with the Power Ready Relay "absent" - - Servo Valve Deterioration Fault - Welded GLC Fault - GLC Control Circuit Fault
Servo Valve Deterioration Fault - Disconnect Trip Fault - Welded GLC Fault -
GLC Control Circuit Fault - Shorted/Open PMG Fault with the Power Ready Relay
Figure 12: Location of Current Transformer (CT)
GALLEY GALLEY
AC BUS 1 MAIN SEC ASS BUS GND/FLT BUS MAIN SEC AC BUS 2
A B B A
4MC 13MC 6MC 5MC
AC MAIN BUS 1 1XP 3XC 12XN 12XN AC MAIN BUS 2 2XP
14PU 14XX
BTC1 DPCT ECAM DPCT BTC2
CFDS
DPCT DPCT
GLC
GLC1 EPC GLC2
APU
DPCT
EGIU EGIU
GCU GCU GCU
GPCU
1 3 2
IDG APU APU IDG
NO.1 UP GEN EXT NO.2
POWER
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-14
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Differential Protection Figure 13: Differential Protection Schematic
Zone 1
The zone 1 protected area comprises the generator coils and feeders between the
IDG Current Transformer (CT) and the GLC. ZONE 1 ZONE 2
The zone 2 protected area comprises the wiring between the GLC and the Current GEN.
Transformer (CT). GLC BTC
FEEDERS FROM
In the event of a short circuit between phases or to the ground, a noticeable differ- CT GEN CT AC BUS
ence between transformer currents activates the protection system. When activat- NO 2
TDG
ed the protection system opens GLC and BTC (GEN FAULT light comes on) and CT TO SUB-BUS
the generator is still excited. If the fault persists, the Generator Control Relay is BARS
tripped thus the generator is de-excited. The Bus Tie Contactor closes automati- AC BUS
cally, therefore allowing the network to be supplied by another generation source. NO 1
In that configuration, the short circuit is located in zone 1.
ΔI ABOVE
When the generator is cut off, the protection system of zone 2 remains operation- 45 AMP
al. The IDG senses a null current. If there is no short circuit in zone 2, the sum of PR
currents sensed by the line CTs is null (opposite current direction). TD SET LATCH DE-
35 ms ENERGIZED
If a short circuit occurs in zone 2, an unbalanced current is detected by the GCU
which activates the protection system. TD GCR
85 ms TRIPPED
LATCH
RESET
GCU
GEN 1
FAULT
OFF
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-15
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Zone 2 Figure 14: Differential Protection Schematic
If a short circuit occurs, the protection system opens the GLC and confirms the
BTC opening. The generator is still excited. The GEN1 FAULT light comes on.
If the fault does not persist, the short circuit has been isolated and the GCR is ZONE 1 ZONE 2
tripped thus the generator is de-exited.
In this case, the BTC remains open and is locked out, and the AC BUS 1 supply GEN. GLC BTC
cannot be recovered. The AC ESSential Bus supply is recovered through the AC FEEDERS FROM
ESS FEED control. CT GEN CT AC BUS
NO 2
The system is recovered by resetting the protection system from the associated IDG
GEN pushbutton. Two reset actions maximum can be performed. CT TO SUB-BUS
DP RESET BARS
The Generator Control Relais (GCR) closes enabling generator excitation. The AC BUS
Power Ready relay is re-energized to control the Generator Line Contactor clos- NO 1
ing.
The Bus Tie Contactor lock out function is removed. The DP Counter is reset ei- ΔI ABOVE
ther by pressing the DP Reset push button on the front face of the GCU or at each 45 AMP
PR
power-up. DP RESET
LATCH DE-
PUSHBUTTON ENERGIZED
RESET
TD GCR
POWER 85 ms TRIPPED
UP
LATCH
RESET
COUNTER GCU
GEN 1
FAULT
OFF
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-16
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Engine Fire and Open Feeder Cable Protection released out, the GCU trips the GCR and the GLC and turns off the voltage regu-
lator. The Ground Power Control Unit (GPCU) determines whether a fire trip or an
The feeder cable is duplicated from the engine pylon to the forward cargo com-
open cable trip has occurred.
partment. Each cable is monitored by a Current Transformer and a sensor. If an
open parallel condition exits (Delta I > 80A), or if the Engine Fire push button is
Figure 15: Open Cable / Feeder Protection
Generator ENGINE
Side PYLON
ENGINE FWD CARGO
WING GLC BTC
FROM
CT GEN CT CT AC BUS
NO 2
IDG
CT TO SUB-BUS
GPCU BARS
Load 6-Hole AC BUS
Side Current NO 1
Transformer Assembly
LEVEL
DETECT
TIMER
ELEC/GCU/1 TDC AC SENSOR
50XU1-103VU
PR
DE-ENERGIZED
301PP
GEN1
FAULT GCR
TRIPPED
OFF ENG FIRE
PUSH
GCU1
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-17
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Other Protections Note that the overload protection is only processed to give warning on the ECAM.
In underspeed conditions the Under-Frequency and the Under-Voltage protec-
The GCR and PR relays are deenergized by the Protection module which proc-
tions are inhibited. If the GLC remains closed (welded contact) after tripping of the
esses various electrical parameters necessary for the protection functions. PR relay, the BTC lock-out function is activated.
Figure 16: Generator Protections
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-18
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 17: Main Generation Schematic 1
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-19
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 18: Main Generation Schematic 2
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-20
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
AC Generation Enhanced Electrical Power Generating GEN Line P/BSW
System (EEPGS) In SMOKE configuration (red smoke light on) an activation of this P/BSW opens
GLC but the generator stays energized to supply directly (S01) the fuel pumps 1
Integrated Drive Generator D/O LH and 1 RH side (the OFF legend indicates, the P/BSW position.
Two identical Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs) are used to supply the main AC Notice that during the AVIONICS SMOKE procedure (GEN 1 LINE P/BSW ON),
network. Each IDG is a two pole high speed (24 000 rpm) brushless spray oil the corresponding generator FAULT light remains off.
cooled unit. It comprises, in a common housing:
• the drive part with the monitoring and control items,
GLC/BTC Control and Monitoring
• the generator part which consist of a Permanent Magnet Generator (PMG), The GLC and the BTC are under control of the related GCU and the Bus Tie Logic.
If all parameters are correct, the GLC connects the generator to its own busbar.
• the exciter generator with the rotating diodes and the main generator.
The BTC connects the generator to the transfer line or another power source to
Each IDG is controlled and monitored by its own Generator Control Unit (GCU). the busbar (generator is off) depending on the priority logic.
Generator Control Unit Operation
Each GCU is supplied by the PMG from its related IDG and, as a back-up, by the If all parameters (checked by the Protection Circuit) are correct and the GEN P/
battery bus 301PP. The corresponding engine underspeed information is provided BSW is ON, the GEN 1 AUX relay is energized (cuts the supply to BTC 1). The
by the Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC). The main functions of the GLC is energized via the closed AUX RELAY.
GCU are:
Notice that once the GLC is closed, it is independent of the BTC position (self-
• control of the field excitation via the Generator Control Relay (GCR), holding function).
• voltage regulation via Excitation Control and Regulation module,
• speed regulation through the Servo Valve Relay (SVR),
• control of the Generator Line Contactor (GLC) via the Power Ready Relay
(PRR), the Bus Tie Contactor (BTC) and the AUX RELAY 1
• control and protection of the IDG and the network,
• interface to the ECAM (via the System Data Acquisition Concentrator (SDACs)
and to the Centralized Fault Display System (CFDS) via the Ground and Aux-
iliary Power Control Unit (GAPCU). The status or fault information is sent to the
ECAM and to the CFDS.
Generator P/BSW
The Generator P/BSW is used to connect or disconnect the generator and to reset
the GCU. The FAULT legend comes on when the P/BSW is pressed in and the
related engine is shutdown or during operation if any parameter is not correct. The
fault information is sent via the SDACs to the ECAM. The OFF legend comes on
when the P/BSW is released out. After a fault detection (tripping of the generator)
the GCU must be reset by cycling the GEN 1 (2) switch OFF/ON.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-21
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS IDG Drive Part D/O The servovalve works by porting oil to an hydraulic control cylinder which deter-
mines the position of a variable displacement hydraulic unit. Depending on the er-
General ror signal, the servovalve ports more or less oil to the cylinder to maintain the
The Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) consists of a Constant Speed Drive (CSD) desired generator frequency (IDG output speed). As IDGs speed (thus PMG fre-
and an AC generator mounted side by side in a single housing. The CSD compo- quency) decreases below the reference frequency setpoint, the servovalve supply
nent converts a variable input speed to a constant output speed. The CSD portion current increases, resulting in an IDG output speed increase.
of the IDG is a hydromechanical device that adds to or subtracts from the variable During normal operation, the SVR is closed to allow current flow in the servovalve
input speed of the engine gearbox. The CSD performs this operation by controlled control loop. Under certain channel failure conditions, the SVR is opened to make
differential action to maintain the constant output speed required to drive the AC sure that servovalve drive current from GCU is completely removed.
generator.
The IDG is cooled and lubricated by the oil circulation system. The oil is cooled by
Engine Speed Sensing
an external mounted IDG oil cooler. The FADEC provides the GCU with the corresponding engine speed information,
which is used for the underspeed protections.
IDG Drive Control
The Constant Speed Drive converts the variable input speed (4 900 to 9120 rpm)
Oil Temperature Sensing
provided by the engine gearbox to the constant output speed (24 000 rpm) through There are two oil temperature sensors in the IDG:
the CSD hydromechanical components. • One on the IDG oil inlet port,
• One on the IDG outlet port.
IDG Speed Control
Both sensors are thermistors.
The GCU performs the output speed control for the IDG via the servovalve control
loop whenever several conditions are met: The GCU uses the sensor signals to determine oil inlet, oil outlet and rise temper-
ature for IDG protection. The temperature information is also sent to the ECAM. If
The GCU is powered-up, oil outlet temperature is above 185°C, the FAULT legend comes on amber on the
Engine input speed to the IDG is sufficient for speed control to begin, IDG pushbutton.
No failure is present in the channel to trip the servovalve control circuit.
Delta Pressure Indicator (DPI)
Servovalve Control Loop The scavenge filter is fitted with an oil filter Differential Pressure Indication (DPI).
The servovalve control loop is composed of a hydraulic servovalve in the IDG and The indicator shows when the filter element requires replacement. If the delta
control circuitry in the GCU which includes the Servo Valve Relay (SVR). The out- pressure across the scavenge filter is 50+/-8 psi, the DPI (pop out) shows the
put speed control is performed as follows: clogged position. In that case, the IDG should be serviced.
the GCU control circuit monitors the Permanent Magnetic Generator (PMG) fre- Oil Pressure Switch
quency to determine the generator frequency.
A Low Oil Pressure (LOP) switch located in the IDG charge oil circuit provides a
Note that the PMG is mounted on the IDG differencial output gear. signals to the GCU when IDG charge oil pressure is less than 140 psi. In low oil
The PMG frequency signal is compared with a GCU internal frequency refer- pressure condition, not caused by underspeed, the IDG pushbutton FAULT leg-
ence.The difference, between the actual PMG frequency reference, create an er- end comes on amber and an ECAM warning is triggered.
ror signal in the servovalve loop circuity. The frequency error signal is then used
to control the servovalve current flow via the SVR.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-22
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 19: EEPGS AC Operation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-23
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS IDG Disconnection
The IDG P/B FAULT legend comes on if the IDG oilpressure is less than 140 psi
or if the IDG oil outlet temperature is above 185°C. In both conditions, the IDG
must immediately be disconnected. IDG disconnection is achieved by a solenoid
activated clutch.
It must be performed via the IDG switch if the IDG pushbutton FAULT legend is on.
If the temperature reaches 200°C, a solder fuse melt and automatically releases
the disconnect mechanism to open the IDG disconnect clutch.
When the IDG pushbutton is depressed and no underspeed is detected, a 28V DC
signal is sent to the disconnection solenoid which will open the clutch.
In case of low oil pressure due to underspeed, the FAULT legend remains off. In
underspeed condition, when the engine has just been shutdown, it is not possible
to disconnect the IDG.
After a thermal disconnection, the IDG must be replaced.
IDG reset must be performed on the ground with the engine shutdown, by pulling
the reset handle mounted on the IDG casing.
Fire Switch
In case of engine fire, if the related fire switch is released out, a 28V DC signal is
sent to the corresponding GCU which shuts down its IDG. In such a case, the re-
set is not require.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-24
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 20: EEPGS IDG Interior
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-25
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS IDG Monitoring message ''THERMAL DISC. FAILED'' is sent to the CFDS and a warning message
is sent to the ECAM system.
Oil Temperature Monitoring Note: After a thermal disconnection, the IDG should be replaced.
Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) oil temperature sensors monitor the input and
the output oil temperature. If a high difference between the input and output tem-
perature is detected, a status message is sent to the ECAM. This difference is
called a temperature rise.
The normal IDG oil inlet temperature is between 40°C to 105°C. When the oil out-
let temperature reaches 142°C, an advisory mode is available on the lower ECAM.
If the oil outlet temperature exceeds 199°C the IDG is automatically disconnected.
Oil Pressure Monitoring
A pressure switch operates in case of oil low pressure (lower than 140 psi) not
caused by underspeed.
Temperature and Pressure Indication
The oil outlet temperature is displayed on the ECAM system display. In case of
high oil outlet temperature or oil low pressure, the following warnings are trig-
gered:
• MASTER CAUTION light,
• Single chime
• The message ''ELEC IDG 1 (2) OIL OVHT or ELEC IDG OIL LO PR''is dis-
played on the EWD.
• The FAULT legend on the corresponding IDG P/BSW illuminates amber,
The IDG must be disconnected immediately by:
• Opening the safety guard,
• Pushing the IDG P/BSW for a maximum of 3 seconds.
Note: Disconnection is only possible if the corresponding engine is running.
Do not push the disconnect switch if engine speed is less than idle, The engine
must be stopped for IDG reconnection.
Automatic IDG Disconnection
If the IDG disconnection is not performed at 185°C, the temperature will increase
and at 199°C an automatic thermal disconnection should occur to protect the IDG.
A warning message is sent to the ECAM system and a BITE MESSAGE (THER-
MAL DISCONNECT) is sent to the CFDS. If this thermal disconnection fails, the
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-26
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 21: EEPGS IDG Monitoring
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-27
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS IDG Cooling System
General
The Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) oil cooling system consist of an IDG Oil
Cooler, which is part of the engine fuel/oil heat management system. The IDG Oil
Cooler is connected to the IDG by two oil connections (in and out).
Operation Principle
A scavenge pump in the IDG pumps the oil through the scavenge filter and the
IDG Oil Cooler.
The engine heat management system regulates the fuel flow through the IDG Oil
Cooler to cool the IDG oil.
A charge pump provides regulated cooled oil supply pressure to the generator and
others users.
The purpose of the IDG oil cooler bypass valve is to protect the IDG oil from over-
cooling. Note that the cooler bypass valve is not part of the engine fuel/oil heat
management system.
Cold Condition
In cold conditions (oil temp <40°C) the oil pressure increases due to high oil vis-
cosity, then the cooler bypas valve opens to bypass the IDG Oil Cooler.
When IDG oil temperature is between 40°C and 70°C, the valve is in regulating
position. This position mixes uncooled oil from the IDG and cooled oil from the IDG
Oil Cooler and returns it to the IDG.
Filter Clogged
A clogged filter indication is provided by a local visual Delta Pressure pop-out In-
dicator (DPI). In case of clogging filter condition, the visual indicator pops out. The
DPI reset can be done in some conditions and associated with maintenance pro-
cedures. When the filter is clogged, the relief valve opens.
Temperature and Pressure Monitoring
The IDG contains two oil temperature sensors to sense the inlet and outlet oil tem-
perature in the IDG.
The outlet oil temperature is sensed to determine an oil temperature ADVISORY
and OIL OVERHEAT detection.
A charge pressure switch operates in the event of a low charge oil pressure.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-28
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 22: EEPGS IDG Oil Temperature & Pressure Monitoring
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-29
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS IDG Generator Part D/O Current Transformer
The AC generator portion of the Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) is a three- Current transformer (CTs) monitor the three-phase feeder cables, from the gener-
phase, brushless, spay oil cooled unit. The generator rotor consist of an exciter ator to the GLC. The GCUs use the CT outputs for protection functions (differential
rotor, a diode rectifier assembly, and a two-pole main field rotor. The exciter rotor current, overcurrent, overload). One CT is located inside the IDG and the other is
and main field rotor are mounted on a common shaft supported by a roller bearing just before the GLC. They are called the 3 Hole Current Transformers. From the
seat at the drive and a ball bearing set at the opposite end. The Permanent Mag- engine pylon to the forward cargo compartment, each feeder cable is split into two,
net Generator (PMG) rotor is mounted on the output ring gear of the differential so that there are now two cables per phase (total 6). Another CT, located in the
assembly. The main generator stator, exciter stator, PMG stator and generator forward cargo compartment monitors the 6 feeder cables. It is called the 6 Hole
current transformer (CT) are mounted in the IDG housing. Current Transformer and the GCU monitors its current output for open cable pro-
tection.
Permanent Magnet Generator (PMG)
The PMG consist of a 16-pole permanent magnet rotor and three winding stator.
Generator P/BSW
As the engine is running, the PMG rotor induces an AC voltage in the winding od The GEN P/BSW on the overhead ELEC panel is use to connect or disconnect the
the PMG stator. At normal operation speed, the output from the PMG is: generator and to reset the GCU. (Cold Reset)When the GEN P/BSW is pressed
• 3 phases in (on position) and the generator is not connected, the GEN COMMAND circuit is
supplied, enabling the closure of the GCR to excite the generator. If all generator
• 1573 Hz
parameters are correct, the Power Ready Relay (PRR) closes and connects pow-
• 100V AC. er to the Generator Line Contactor (GLC) via the GLC AUX RELAY. The GLC
The output of the PMG is supplied to the Generator Control Unit (GCU) which uses opens or closes to connect 115V AC to the network according to priority rules and
it for the following functions: the network supply status. The FAULT legend comes on amber (in on position on-
• The GCU transforms and rectifies the voltage via a Transformer Rectifier (TR) ly) in the following cases:
to 28V DC for the internal power supply. The GCU sends the PMG voltage via • The related engine is shutdown or the generator is not connected,
the Generator Control Relay (GCR) to the voltage and frequency regulation cir- • During operation with any incorrect parameter,
cuit where it is rectified and applied to the exciter field for voltage regulation. • If the GLC has failed open (STUCK OPEN).
• The PMG frequency is also used to monitor the generator frequency (for the
When the GEN P/BSW is released out (off position), the OFF/R legend appears
IDG drive control).
in white. The GCR opens to de-energize the generator field and the GLC opens.
Generator Exciter Stage In addition, the computer reset circuit is supplied to reset the GCU.
The exciter stage of the generator consist of a three-phase winding rotor which is IDG P/BSW
located on the main generator rotor. The stator windings and a full wave bridge
The IDG P/BSW is used for manual disconnection of the IDG from the engine
rectifier (rotating diode rectifier) are also located on the rotor. As it rotates withing
gearbox. If the internal FAULT legend comes on, the IDG must immediately be
the stator, the exciter stage converts a DC field voltage supplied by the GCU to
disconnected. With the engine stopped, the IDG cannot be manually disconnect-
the exciter stator, to an AC voltage in the windings of the rotor. The induced AC
ed. An underspeed condition, generated by the GCU, inhibits the disconnection.
voltage is rectified by the rotating diode rectfier and supplied to the windings of the
Notice that for a static test of the IDG disconnect mechanism, the circuit breaker
main generator rotor.
2XU1 must be pulled to simulate a running engine 1 and no underspeed.
Main Generator
The main generator consist of a two-pole rotor and a three-phase winding stator.
As the rotor rotates, the DC field induces an AC voltage in the stator windings.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-30
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Point of Regulation
The Point Of Regulation (POR) is located between the 3 hole CT and the GLC. It
takes in account the generator feeder impedance (voltage drop of 1 to 2V AC).
The GCU monitors the three generator phase voltages at the POR for:
• Voltage regulation control
• Over and undervoltage protection
• Incorrect Phase Sequence (IPS) protection.
Voltage Regulation
The GCU monitors the POR in order to keep the voltage at the nominal value
(115V AC) at this point. The principle of operation of the voltage regulator is by
modulation of the voltage through the exciter field. The output from the PMG is
connected via the GCR to the excitation and regulation control module, where it is
converted into DC voltage and applied to the exciter field. The voltage frequency
regulation module senses the average of the three phases at the POR and com-
pares it against a reference voltage. If a difference exists, the voltage regulator ad-
justs the exciter field current as needed to keep a constant voltage at the POR.
Underspeed
Each GCU receives engine speed data from the Full Authority Digital Engine Con-
trol (FADEC) via an ARINC 429 bus. These data are used for the underspeed set-
point, various other controls and protections and BITE functions. In case of these
data are not available, the GCU uses the PMG frequency to determine the input
speed of the generator. With the engine speed below the underspeed setpoint, the
relay 7XT is energized and inhibits an IDG disconnection.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-31
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 23: EEPGS IDG Generator Part
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-32
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS GCU D/O • The Power Ready Relay (PRR) controls the GLC
The Generator Control Unit (GCU) 1 and 2 are identical and interchangeable. Pin • The SVR controls the IDG speed.
programming provide the GCU with the following information: If a protection function is triggered, the GCR, the PRR and, in some case the SVR,
• The aircraft type are deenergized.
• The GCU position
Underspeed
• The current limit for voltage regulation
Engine speed information provided by FADEC is used to sense the IDG input
• The load limit.
speed. When engine speed falls below the underspeed threshold the PRR trips
The main functions of the GCU are: and the excitation is biased off due to underfrequency.
• Regulation of the generator voltage Note: in case of detected underspeed (e.g. engine shut down) no reset action via
• Regulation of the generator frequency the GEN P/BSW is required.
• Regulation of the generator speed (servovalve control)
• Control and protection of the network and the generator Overvoltage
• Interface with System Data Acquisition Concentrator(SDAC) for the ECAM The GCU performs an overvoltage protection function. If the highest individual
• Interface with Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) for engine speed phase at POR reaches 130 +/- 1.5 volts, the PRR and the GCR are tripped. Higher
is the voltage, faster the relay will be tripped.
• Interface with Centralized Fault Display System (CFDS) via the Ground and
Auxiliary Power Control Unit (GAPCU). Overfrequency
Voltage Regulation The GCU performs an overfrequency protection function. If the PMG frequency is
above 435 +/- 1 Hz, for at least 4 seconds, the GCU trips the PRR and the GCR.
The voltage regulation is achieved by regulating the current through the exciter If the PMG frequency is above 452 Hz, for at least 160 miliseconds, the GCU trips
field. The voltage is kept at a nominal value (115V AC) at the Point Of Regulation the PRR, the GCR and also the SVR.
(POR). The POR is located at the end of the generator feeder upstream of the
Generator Line Contactor (GLC). The output from the Permanent Magnetic Gen- Overload/Overcurrent
erator (PMG) is connected via Generator Control Relay (GCR) to the excitation
and regulation control module, where it is converted to DC voltage. The IDG Current Transformers (CTs) provide current sensing information to the
GCU. This information is used to determine generator load for overload, overcur-
Frequency Regulation rent, phase imbalance (delta) and also Differential Current Protection (DCP). In
case of overload, the GCU sends signals to the SDAC for an ECAM message and
The Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) frequency is regulated by a servovalve in to the FAULT light on the GALY & CAB P/BSW. If an IDG fails, the Bus Tie Con-
the IDG and the servovalve control circuit in the GCU (via the ServoValve Relay tactors (BTCs) close and some galleys load are automatically shed. GCUs monitor
(SVR). The PMG frequency is compared with a GCU internal reference frequency. BTC status and determine if overcurrent protection (BTC lockout) should be inhib-
The difference generates a control current to drive the servovalve to produce the ited. If the galleys are not automatically shed, to allow the GALY & CAB P/BSW to
right output frequency. be selected OFF.
Control and Protection Protection Function Summary
The GCU control and protection functions are mainly performed by 3 internal re- The Generator Control P/BSW has ON and OFF/RESET functions. Switch all
lays: power off and then on again to reset the fault logic; this is called a cold reset. Most
• The GCR controls the generator excitation fault protections allow two reset attempts and then the reset function is inhibited.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-33
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
BITE
The GCU is a type 1 computer. Its BITE detects and isolates active and passive
failures. The BITE consist of two sections:
• Operarional BITE
• Maintenance BITE
After generator tripping, the operational BITE identifies the protection, analyses
the conditions and determines the fault origin.
The maintenance BITE completes the operational BITE and performs a self-test
of the GCU to provide an indication of system integrity. Fault are kept in the Non
Volatile Mempry (NVM). The GCU BITE communicates with the CFDS via the
GAPCU (type 1 system).
Interface
Each GCU is interfaced to both SDACs to transmit system failure or caution data
to the ECAM. The Landing Gear Control and Interface Unir (LGCIU) 1 provides
GROUND/FLIGHT information to the GCU (BITE).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-34
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 24: EEPGS Control & Protection
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-35
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Engine Fire and Open Feeder Cable
The feeder cables are duplicated from the engine pylon to the forward cargo com-
partment. A 6 hole CT monitors each cable. If an open cable is detected, or if the
ENG FIRE P/BSW is released out, the GCU trips the GCR and the PRR. The GLC
opens after the PRR trips.
Differential Current Protection
The Differential Protection (DP) is based on the comparison of each phase of the
Line 3 hole CT and the 3 hole CT in the IDG. If a differential current flow is above
50 +/- 10A for at least 60 miliseconds, the PRR and GCR are tripped. Note: the
DP circuit reset is done via the GEN P/BSW, but it is limited to two attempts. After
correcting the fault, a cold reset must be performed.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-36
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 25: EEPGS Open Feeder & Differential Current Protection
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-37
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS APU Generation General Description
The APU generator is not interchangeable with the Integrated Drive Generators
(IDGs). It is driven at a constant speed by the APU and can be connected to the
electrical network in case of any generator failure. It can supply the entire electrical
network if no other power sources are available.
APU Generator Control
The APU generator control module is part of the Ground and Auxiliary Power Con-
trol Unit (GAPCU). The main functions of the module are:
• Voltage and frequency regulation
• Auxiliary Generator Line Contactor (AGLC) control in accordance with the bus
tie logic
• Control and protection
• Interface with System Data Acquisition Concentrators (SDACs)
• Built-In Test Equipment (BITE) function. The Bite messages are sent to the CF-
DIU.
Control, Indication and Distribution
The APU generator is controlled by a P/BSW located on the overhead ELEC panel
and has two lights. White OFF and amber FAULT. The APU GEN is connected to
the network via the AGLC and the Bus Tie Contactors (BTCs).
APU GEN OIL Temperature Sensor
A temperature sensor is located on the APU generator oil outlet. A high oil tem-
perature leads to an immediate automatic shut down of the APU via the Electronic
Control Box (ECB).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-38
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 26: EEPGS APU Control
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-39
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS APU Generation D/O The APU Generator Line Contactor (AGLC) is under control of the GAPCU and
the Bus Tie Logic (BTL). If all generator parameters are correct, the GLC connects
The APU generator can supply all or parts of the normal network, depending on the generator to the transfer line. The connection to the busbars (BTCs and GLCs)
the priority logic provided by the Bus Tie Logic (BTL). The APU generator is a two depends on the priority logic and the network supply status.
pole high speed (24 000 rpm) brushless spray oil cooled generator. Speed regu-
lation is made by the APU engine without a Constant Speed Drive; therefore, it op- Transfer Circuit
erates in the same way but it is not interchangeable with the Integrated Drive The transfer circuit consists of the tranfer line and the two BTCs. This circuit ena-
Generators (IDGs). The APU generator is cooled and lubricated by the APU oil. bles the power sources (GEN 1,2 APU, External Power) to supply all or half of the
An oil temperature bulb is installed on the APU generator oil outlet part. The bulb network according to the priority and BTL.The BTL provides information about the
is directly connected to the APU Electronic Control Box (ECB). In case of oil tem- network supply status. This information is used for:
perature above 185°C, the ECB command an immediate shutdown of the APU. • Non parallel operation,
APU GEN Control Module (GAPCU) • Supply priority,
• Transfer circuit control.
The APU Generator Control Module is part of the Ground and Auxiliary Power
Control Unit (GAPCU). The GAPCU controls both the APU generator and the EXT APU GEN Feeder Cables
PWR. The power supply for the GAPCU is provides by:
• the APU Permanent Magnet Generator (PMG) The feeder cables are routed through the cabin ceiling to the rear c/b panel in the
cockpit where they are sent through a 3 hole current transformer before connec-
• the EXT PWR tion to the AGLC. The Current Transformer (CT) provides differential current pro-
• the BATtery BUS supply as a back-up supply. tection.
The control module main functions are:
• control of the field excitation through the Generator Control Relay (GCR)
Operation with APU Running only
• voltage regulation With the APU MASTER and APU generator switches set to ON and APU running
above 95%, the GCR is closed and the generator is exited. If all parameters are
• control of the APU Generator Line Contactor (AGLC) through the Power Ready
correct, the PRR is closed.
Relay (PRR) in conjunction with the Bus Tie Logic (BTL)
• control and protection of the APU generator and the network. APU and GEN 1 Running
The GAPCU has an interface with the SDAC and to the CFDIU. If the APU GEN is supplying the entire electrical network and the engine 1 is start-
APU ECB ensures the speed regulation. At 95% rpm, the ECB provides an APU ed, the BTL (Bus Transfer Logic) changes as follow:
ready signal to the GAPCU. • GEN 1 has priority on AC BUS 1, so BTC 1 opens to allow GLC 1 to close. This
prevents parallel operation between GEN 1 and APU GEN.
APU GEN Control and Monitoring • The AGLC stays energized via the relaxed contacts of BTC 1 and GLC 2. The
The APU generator switch is used to connect or disconnect the APU generator APU will continue supplying AC BUS 2.
and to reset the GAPCU.
• The FAULT legend only comes on if the switch is pressed in, the APU is run-
ning (>95%), and one parameter is not correct.
• The OFF legend comes on when the switch is released out.
After a FAULT detection (tripping of the generator), the GAPCU must be reset by
setting the switch to OFF and back to ON.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-40
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 27: EEPGS GAPCU (APU Module) Operation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-41
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
EEPGS AC Generation Components • That the external power is correctly plugged in,
• That the voltage and frequency from the GPU is good.
GAPCU If the GPU output is correct, the problem is in the GAPCU.
The Ground and Auxiliary Power Control Unit (GAPCU) is located in the avionics If the AVAIL light is not illuminated on the aircraft and the PTC TRIP light is on,
compartment. this indicates an aircraft problem between the GAPCU and the busbar 1000XG.
Maintenance Tip: When the external power is plugged into the aircraft and the Note: Always confirm the faulty by using the approved Airbus troubleshooting doc-
Ground Power Unit (GPU) is operating. umentation.
If the AVAIL light is not illuminated on the aircraft and the PTC TRIP light is off on
the front face off the GAPCU, this indicates a GPU or GAPCU fault.
GCU
The two Generator Control Units (GCUs) are located in the avionics compartment.
First, check:
Figure 28: EEPGS GAPCU & GCU Location
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-42
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
IDG A Quik Attach Detach (QAD) adapter is used to connect/disconnect the iDG from
the engine.
The Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs) are connected to the engine gear boxes.
The IDG oil level can be checked during servicing through the sight glass. In case Maintenance Tip: The correct servicing of the IDG is important. Too much or too
of IDG disconnection, the IDG is reset on the ground when the engine is off by pull- little oil inside the IDG can seriously damage its operation. Refer to the mainte-
ing the reset handle. In case of thermal disconnection the IDG must be replaced. nance manual for IDG servicing.
Note: This IDG contains two line replaceable oil filters.
Figure 29: EEPGS IDG Components
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-43
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-22 AC Main Generation
Figure 30:
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-22-44
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-23-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
Generator Generator Temperature Monitoring
The APU generator operation principle and the output characteristics are identical A temperature sensor is incorporated in the auxiliary generator to monitor the oil
to those of the IDG generator. The APU directly drives the APU generator at a outlet temperature. The temperature sensor is connected to the Electronic Control
nominal 24000 RPM constant speed. Box (ECB) to shut down the APU in case of excessive temperature.
The cooling circuit is common to the APU and to the generator.
Control and Protection
The generator is a brushless oil-cooled generator with a nominal 115/200 volt, 90
KVA, 3 phase 400 Hz output. (23kg) The generator includes three stages which The Generator Control Unit has four different functions:
are: - the pilot exciter, - the main exciter, - the main alternator. • Voltage Regulation
The operation principle is the same as that of the IDG generator • Generator control and protection of the network and generator
• Control of the various indications and warnings
NOTE: The PMG frequency for the APU generator is 1600 Hz.
• System self-monitoring and Test
A temperature bulb is included in the auxiliary generator. It senses the generator-
oil outlet temperature. This sensor is connected to the Electronic Control Box The GCU is supplied by The Permanent Magnetic Generator (PMG). The GCU is
(ECB) of the APU. Any high oil temperature > 185°) causes the automatic shut- also supplied by the aircraft network (Back-Up supply). The voltage regulation
down of the APU (by the ECB). This in turn causes the APU speed to decrease to function is identical to that of the IDG. The generator control and protection func-
zero. tions are mainly provided by means of the Generator Control Relay and the Power
Ready relay. The GCR controls the generator excitation. The PR controls the Line
GCU Supply Contactor and activates the corresponding warning.
The Generator Control Unit supply operation principle is identical to that of the AC Differential Protection
Main generation.
The differential protection prevents the electrical wiring between the two detection
Current Transformers from being damaged.
Generator Operation Control
The protected area comprises the generator coil and feeders between the APU
The generator is controlled by the APU generation pushbutton. When pressed in, Current Transformer (CT) and the GLC. The differential protection function is iden-
if the APU speed is high enough, the generator is energized. When the APU is tical to that of the IDG zone 1.
available, the APU Ready signal allows the Power Relay to be energized via the
protection module (Delivered Parameters correct). The APU Generator Line Con- Other Protection
tactor (GLC 3) is energized through a priority logic (GLC, BTC, EPC logic).
The Generator Control Relay and Power Ready relay are de-energized by the pro-
tection module which processes various electrical parameters necessary for pro-
Generator Monitoring tection functions. In case of APU generator overload, the GCR and PR relays
The generator monitoring operation is Identical to that of the IDG generator. The remain energized. The under-voltage and under-frequency protections are inhib-
monitoring system (FAULT fight and ECAM system) is inhibited as long as the ited as long as the APU is not available.
APU is not available.
GLC: Generator Line Contactor BTC: Bus Tie Contactor
Generator Reset POR: Point Of Regulation GCR: Generator Control Relay
When the APU generator pushbutton is released out after a fault detection, the PR: Power Ready relay EGIU: Electrical Generation Interface Unit
Generator Control Unit is reset. EPC: External Power Contactor
The Generator Control Relay (GCR) and the Power Ready relay (PR) are reset.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-23-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
Figure 1: APU Electrical Equipment Component Location
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-23-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
Figure 2: APU and Generator Component Location
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-23-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
Figure 3: Auxiliary Generation Schematic
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-23-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation
Figure 4: Protections
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-23-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
24-24 AC Emergency Generation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
General CSM/G Control Unit Supply
The AC emergency generation enables part of the distribution network to be re- The Permanent Magnet Generator supplies the Constant Speed Motor/Generator
covered in case of:- loss of the two main generation sources and,- unavailability control unit and the exciter field through a voltage regulation module. The voltage
of the auxiliary generation. regulation module maintains the Point Of Regulation (POR) at a nominal voltage
value.
Ram Air Turbine
A Ram Air Turbine, which extends automatically in the event of both engine and Generator Control
APU generator failure, allows the blue hydraulic system to be pressurized. RAT The automatic control logic being set, the solenoid control valve is supplied by bat-
delivered pressure is 2500 psi (172 bar). Automatic deployment is inhibited on tery 2 through the Control Unit. The solenoid control valve can also be controlled,
ground. Manual operation from the cockpit is always possible. RAT stowage is in manual mode, by the EMER ELEC MAN ON pushbutton. As soon as the Per-
possible on ground only. manent Magnet Generator is available, it takes over the solenoid control valve
power supply. The Time Delay Opening (TDO) relay is de-energized to allow the
Generator Solenoid Control valve power supply change over from Battery 2 to the PMG.
The emergency generation system is mainly composed of: -a Constant Speed
Motor/Generator (CSM/G) including a hydraulic motor and an AC generator, -a Speed Regulation
Generator Control Unit (GCU). A hydraulic motor drives the emergency genera- The servovalve which regulates the hydraulic motor speed is electrically controlled
tor. A servo valve speed regulator controls the speed: it transforms the oil flow of by the Speed Regulation module of the Control Unit.
the Blue hydraulic system into constant speed for the generator. When emergency
conditions are met, this Blue system is supplied by a Ram Air Turbine (RAT). Voltage Regulation
NOTE: The Blue hydraulic system is supplied by an electric pump in normal con- The Permanent Magnet Generator supplies the exciter field through a Voltage
figuration. Regulation module. The Voltage Regulation module maintains the Point Of Reg-
ulation (POR) at the nominal voltage value.
Constant Speed Motor/Generator
Hydraulic motor: Generation Monitoring
Powered by the Blue hydraulic circuit (RAT in emergency configuration; electrical The Control Unit protection module protects the network and the generator by con-
hydraulic pump in test), -speed regulation by servovalve, -integrated solenoid con- trolling the associated Generator Line Contactor, the generator field current and
trol valve. the solenoid control valve. The control Unit protections are the following:
AC generator: - Three phase 115V/200 V - 400 Hz (12000 rpm), - output power: • Over / Under voltage. Over / Under frequency. Shorted PMG. Fast overspeed
5 KVA continuously, - oil cooled. shutdown. As the generator is lost, the ESS TA is no longer supplied, thus the
RAT and EMER GEN FAULT light comes on.
Static Inverter
When the nose landing gear is selected DOWN the Control Unit protection module
A Static Inverter transforms the direct current voltage from battery 1 into a single deenergizes the solenoid control valve.
phase alternating current voltage. The Static Inverter characteristics are:
After a landing gear extension/retraction sequence, the EMER ELEC PWR MAN
• 1 KVA nominal power. 11 5V, 400Hz. The Static Inverter is used in the follow- ON pushbutton must be pressed in to reset the protection module and to recover
ing cases: APU start (supply of fuel pump) Ram Air Turbine deployment. En- the Solenoid Control valve power supply.
gine start on battery (ignition) Emergency configuration.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 1: CSM/G Parts Location
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 2: RAT and CSM/G Logic Figure 3: Emergency or Smoke Configuration (CSM/G Running)
EMER ELEC PWR GREEN BLUE DC BAT BUS
EMER GEN TEST MAN ON
RAT
& RAT MAN ON
GEN 1 LINE EMER GEN
DC TIE BAT ESS DC DC TIE
H ENG 1 PUMP
ELEC PUMP
CONT CONT TIE CONT
SMOKE FAULT A
U Y FAULT FAULT A
OFF T
O D OFF OFF
U
T
O HOT BUS 1 HOT BUS 2
ADIRS 1 > 100 KT BAT 1 STAT BAT 2
RAT AUTO ON RAT MAN ON INV
AC BUS 1 OFF AND CONT
DC ESS BUS DC BUS 2
OR
AC BUS 2 OFF DC BUS 1
EMER ELEC PWR
MAN ON
SOLENOID 2
SOLENOID 1
DC ESS SHED
STAT
INV
OR
DC GND / FLT
BLUE HYD
AC STAT INV
A320 only: NOSE L / G UP EMER
TR ESS GEN TR
ELEC 1 TR 2
RAT RAT
AND
PUMP
AC ESS BUS
PRIORITY
VALVE AC ESS SHED AC GND / FLT
OPEN
CSM / G AC ESS FEED
TEST
OR CONTROL
UNIT SPEED
AC BUS 1 AC BUS 2
AC ESS BUS EMER HYD BUS TIE BUS TIE
PUMPS
GEN MOT CONT CONT
FUEL
ESS
TR CONSTANT GEN
SPEED LINE APU EXT
CSM / G MOTOR / CONT LINE PWR
DC ESS BUS GENERATOR CONT CONT
GEN APU GEN
GEN EXT
1 2
PWR
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 4: Emergency Generator not Running in Flight Figure 5: Emergency Generator not Running on Ground
DC BAT BUS DC BAT BUS
DC TIE BAT ESS DC DC TIE DC TIE BAT ESS DC DC TIE
CONT CONT TIE CONT CONT CONT TIE CONT
HOT BUS 1 HOT BUS 2 HOT BUS 1 HOT BUS 2
BAT 1 STAT BAT 2 BAT 1 STAT BAT 2
INV INV
CONT CONT
DC BUS 1 DC ESS BUS DC BUS 2 DC BUS 1 DC ESS BUS DC BUS 2
DC ESS SHED DC ESS SHED
STAT STAT
INV INV
DC GND / FLT DC GND / FLT
AC STAT INV AC STAT INV
EMER EMER
TR ESS GEN TR TR ESS GEN TR
1 TR 2 1 TR 2
AC ESS BUS AC ESS BUS
AC ESS SHED AC GND / FLT AC ESS SHED AC GND / FLT
AC ESS FEED AC ESS FEED
AC BUS 1 AC BUS 2 AC BUS 1 AC BUS 2
BUS TIE BUS TIE BUS TIE BUS TIE
PUMPS
PUMPS
CONT CONT CONT CONT
FUEL
GEN FUEL GEN
LINE APU EXT LINE APU EXT
CONT LINE PWR CONT LINE PWR
CONT CONT CONT CONT
GEN APU GEN GEN APU GEN
GEN EXT GEN EXT
1 2 1 2
PWR PWR
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 6: RAT Extension Logic and CSM/G Control
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 7: CSM/G Emergency Generation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-7
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 8: CSM/G AC Essential Supply
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-8
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Static Inverter Test
On the ground, the static inverter can be checked applying the following procedure
General (aircraft supplied by EXT POWER or APU GEN):
The 1000 VA nominal-power static inverter transforms the direct current voltage • EMER GEN TEST: ON
from battery 1 into a single-phase 115 VAC/400 Hz alternating current. • BUS TIE: OFF
System Description • On the ECAM ELEC page, check voltage and frequency of static inverter.
The static inverter is used in these cases: Figure 9: Static Inverter Location
• APU start (supply of fuel pump),
• engine start on batteries (ignition),
• Ram Air Turbine (RAT) deployment (< 10s) (supply of ECAM display units),
• on ground, on batteries only (pushbutton switch supply),
• in emergency configuration after landing, when the CSM/G is switched off
(supply of the 115 VAC ESS BUS 4XP instead of the CSM/G).
Operation/Control and Indicating
The static inverter starts automatically if:
• the AC BUS 1 and 2 are lost,
• the CSM/G is not available, and
• speed is more than 50 Kts.
When the static inverter is faulty, it generates a permanent ground signal to the
BCL1.
The presence of the ground signal means:
• overheat,
• output overvoltage,
• input undervoltage,
• input overvoltage.
The static inverter defect is sent to the battery charge limiter 1 which stores it in a
memory as a class I failure.
When the network is supplied, STATIC INV FAULT message appears on the up-
per ECAM display unit.
The fault indication will be available during BCL BITE reading from the Centralized
Fault Display System (CFDS).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-9
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 10: Static Inverter Control
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-10
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 11: A320/A321 Emergency Configuration
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-11
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
Figure 12: Emergency Generator Test
EMER GEN TEST P/B (guarded)
BAT 1 BAT 2
When pressed and held:
OFF XX OFF
- If AC bus 1 and 2 are supplied:
DC 1 CD 2 The EMER GEN is hydraulically
DC ESS
TR 1 TR 2
powered provided blue electric pump
SHED
28 V 0V is running.
ESS TR EMER GEN
150 A XX The AC ESS BUS and the DC ESS BUS
are connected to the emergency
AC 1
AC ESS
AC 2 generator (the DC ESS SHED and AC
SHED ESS SHED busses are not powered).
GEN 1 GEN 2
XX % APU STAT INV XX % The ELEC page is automatically
XX V XX % 115 V XX V displayed on ECAM (only on ground).
XX HZ XX V 400 HZ XX HZ
XX HZ If BAT only supply the aircraft:
- The AC ESS BUS is powered by the static
inverter.
ELEC BAT 1 BAT 2
28 V DC BAT 28 V
0A 0A
DC 1 CD 2
DC ESS
TR 1 SHED TR 2
28 V ESS TR EMER GEN 28 V
150 A 28 V 116 V 150 A
130 A 400 HZ
AC 1 AC ESS AC 2
SHED
GEN 1 GEN 2
0% APU GEN EXT PWR 0%
0V 116 V 0V
400 HZ 400 HZ 400 HZ
IDG 1 ˚C 45 45˚ C IDG 2
TAT 19˚C G. W. 60300 KG
SAT 15˚C C. G. 28 1%
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-24-12
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
24-30 DC Generation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
General Indication
Three Identical Transformer Rectifiers (TR) are fitted on the aircraft. They operate DC generation indications are displayed on the ECAM and on two voltmeters lo-
as soon as they are supplied. The Transformer Rectifiers (TA) are supplied with cated on the main control panel. The ECAM displays battery voltage and current.
three phase 115 V/ 400 Hz. Each TR controls its contactor via an Internal logic. In The voltmeters give battery voltage indication even in a cold aircraft configuration.
normal configuration, direct current is provided by both normal transformers recti-
fiers (TR1 and TR2) and possibly by batteries. TR1 supplies, through TR1 contac- Monitoring
tor (5PU1) normal bus 1 (DC BUS1), battery bus (DC BAT BUS), essential bus The Battery Charge Limiters monitor the battery charge. In the event of battery
(DC ESS BUS) and sheddable essential bus (DC SHED ESS BUS). The BAT BUS thermal runaway or internal short circuit, the battery is isolated the amber FAULT
is supplied from BUS 1, through DC NORM BUS 1 SWITCHING contactor (1PC1), light comes on and the ECAM system is activated. System fault is sent to the Cen-
and provides power to ESS BUS and SHED ESS BUS through respectively DC tralized Fault Display System. The functions of the BCL are:
ESS BUS SUPPLY contactor (4PC) and DC SHED ESS BUS contactor (8PH) in • battery charge and charge / discharge monitoring. -APU start. -DC BAT BUS
succession. Both batteries and their respective HOT BUS are connected or not to supply on ground. -DC BAT BUS supply during landing (speed < 100 kts) in
BAT BUS, in parallel, through both BATTERY LINE contactors (6PB1 & 6PB2). emergency configuration
TR2 supplies, through TR2 contactor (5PU2), normal bus 2 (DC BUS 2).
Battery Charge Control and Monitoring
DC Emergency Generation The Battery Charge Limiter controls the battery charge cycle. The battery charge
The DC emergency generation consists in the essential Transformer Rectifier cycle begins when the battery voltage is lower than 26.5V and stops when the bat-
(TR) and its associated contactor. It is supplied with 115 VAC/400 Hz either by the tery charge current is lower than 4 Amps. The Battery Charge Limiter Isolates the
emergency generator or by the AC normal busbars, in failure conditions. The es- DC BAT BUS from the battery in case of thermal runaway detection or an internal
sential TR directly controls its contactor (3PE). The essential TR is ventilated by short circuit. The fault detection signal allows the activation of the BAT1 amber
natural convection. Characteristics of the Essential TR. The essential TR is fully FAULT light, the ECAM system and the CFDS.
interchangeable with both normal TRs and has the same electrical characteristics.
Battery Protection
TR Protection In order to keep the integrity of the HOT BUS, in the event of short circuit in the
Each Transformer Rectifier control logic consists of an overheat protection and no DC network, the Battery Charge Limiter Isolates the battery from its distribution
current flow detection to isolate the distribution circuit from the Transformer Rec- network. On ground the batteries are automatically isolated when battery voltage
tifier. decreases to 22V for 1 second.
Batteries Emergency Configuration
The DC generation is provided by two batteries which are mainly used [o start the The batteries are connected to the BATTERY BUS after landing in emergency
APU and to supply the AC and DC essential network in emergency configuration. configuration.The battery contactors are closed by the BCL when the aircraft
speed is lower than 100 Kts.
Battery Control
Each battery is associated with a Battery Charge Limiter which is controlled by the APU Start
corresponding battery pushbutton. When the BAT pushbutton is pressed in (AU- When the APU start sequence is initiated, the DC network is connected to the bat-
TO position), the BLC controls the battery coupling / uncoupling. When released teries in order to withstand the high APU starter motor demand. In flight, in elec-
out the battery is uncoupled from the network and the white OFF light comes on. trical emergency configuration, the APU start sequence is inhibited until the CSM/
In flight, in normal configuration the batteries are uncoupled from the network. G is coupled to the network or after 45 seconds. The APU start sequence is also
inhibited in emergency configuration when the landing gear is extended.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
Test initiated from the MCDU, the BAT amber FAULT light and the RAT & EMER GEN
red FAULT light come on for 6 seconds.
On ground the BITE allows to perform a test of the Battery Charge Limiter at each
power up, and a test from the Centralized Fault Display System. During the test
Figure 1: DC Power Distribution
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
Loss of the Transformer Rectifier 1, 2, or Essential Loss of the TR1 and TR2
In the event of TR1 loss, DC BUS 1 and DC BAT BUS are automatically restored In the event of TR1 and TR2 loss (loss of DC BUS 1 & 2), DC ESS and SHED ESS
from TR2 through DC NORM BUS 2 SWITCHING contactor (1PC2) and DC BUSSES are automatically restored from ESS TR through ESS TR contactor
NORM BUS 1 SWITCHING contactor (1PC1). DC ESS and SHED ESS BUSSES (3PE), from AC normal generation.
are automatically transferred to ESS TR through ESS TR contactor (3PE). ESS
TR supply is provided from AC BUS 1 through AC ESS BUS SWITCHING contac- Essential TR
tor (3XC) and AC ESS BUS contactor (15XE) in succession. The 28VDC SHED The essential TR starts to operate as soon as it is supplied. It is supplied in the
BUSSES 210PP and 212PP are automatically shedded. following cases: - loss of TR1, - loss of TR2, - loss of both TRs, - loss of DC
NORM BUS 1 switching contactor (1PC1) or DC ESS BUS supply contactor
Loss of the Transformer Rectifier 2 (TR2) (4PC), - availability of emergency generator in operation. The essential TR is
TR2 loss leads to symmetrical recovery of DC BUS 2 from TR1; DC ESS and linked to the ECAM system in the same manner as the main TRs.
SHED ESS BUSSES are transferred to ESS TR through ESS TR contactor. The
Figure 2: Loss of TR ‘s
28VDC SHED BUSSES 210PP and 212PP are automatically shedded.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
Transformer Rectifier Description of the reset procedure
The reset procedure must be performed by selecting the SYSTEM REPORT/
Operation TEST item on the CFDS menu, then by selecting the involved TR on ELEC menu.
Each TR controls its contactor via an internal TR logic. This logic, which is intend- • If the reset is effective, NO FAULT appears on the MCDU.
ed to protect the Direct Current (DC) network and the TR, controls contactor open- • If the reset is impossible:
ing in case of:
TR 1(2) is displayed on the MCDU,
• no current flow to the DC BUS (minimum current detection),
TR 1(2) FAULT stays on the upper ECAM display unit.
• TR overheat (171/Deg.C).
NOTE: After the reset procedure is performed, on the panel 35VU, the AC ESS
To ensure these protections, each TR sends a fault signal to the Centralized Fault FEED pushbutton switch must be released, and then pushed. The ESS TR no
Display System (CFDS) for maintenance purpose. Main TR's are ventilated by air longer supplies the DC ESS BUS (4PP). On the lower ECAM display unit, the nor-
extracted from the aircraft ventilation network. mal configuration comes into view.
TR Characteristics Figure 3: Manual TR Reset
Supply: 115 VAC/400 Hz, three phase. DC output current: 200 A in continuous op-
eration 300 A for 5 minutes 500 A for 30 seconds 1000 A for 1 second
DC output voltage: 30.2 V with no load 27.5 V at 200A
Normal Operation
The transformers rectifiers start to operate as soon as they are supplied:
• TR1 is supplied by 1XP busbar,
• TR2 is normally supplied by 2XP busbar.
Note: TR2 can also supply part of the DC network from the ground power unit and
in ground service configuration The parameters such as voltage and current are
available and displayed via the SDAC on the ELEC page on the lower ECAM DU.
Failure of the TR1(2)
In case of failure of the TR1(2), the TR FAULT warning appears on the upper
ECAM display unit and at the same time, the ELEC page is displayed on the
ECAM lower display unit.
Reset of the Protection of the Transformer Rectifier (TR)
Before you reset a TR, make sure that the related electrical network supplies its
primary winding, in any RESET mode.
From the CFDS or on the panel 103VU. Reset of the TR protection is possible
from the CFDIU (CFDS interface). If the CFDIU is not available, it is possible to
start the transformers manually. To do this, push the TR RST pushbutton switch
15PU located on panel 103VU.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
Figure 4: Transformer Rectifier TR
DC
BUS1
5PU1
1PU1
AC BUS 1
2PUT1 CT
4PU1
42XU3
CURRENT
SENSOR
204PP
OVERHEAT 3PU1
DETECTION SET
28VDC
CURRENT
MEASURE MINIMUN
CURRENT
DETECTION
TO 1PC1 AND 1PC2
CONTROL
P/B SW 15PU
SDAC1 SDAC2 CFDIU
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
DC Essential & Normal Generation Switching - D/O is supplied when a TR is lost or in case of DC NORM BUS 1 SWITCHING contac-
tor (1PC1) failure.
These circuits control the supply of DC normal busbars and DC essential busbars.
They enable: - their normal supply in normal flight configuration, - automatic NOTE: There is an electric interlock between contactors 1PC2 and 4PC to inhibit
transfer in some failure conditions. coupling between busbar 2PP and essential busbar 4PP. DC ESS BUS SPLY
Contactor Control (4PC). Contactor 4PC supplies DC ESS BUS 4PP via BAT
Operation/Control and Indicating BUS 3PP if normal DC busbars 1PP and 2PP are not coupled (electrical interlock
DC NORM BUS SWITCHING Contactor Control (1PC1 and 1PC2). Contactor between contactors 1PC2 and 4PC). DC ESS BUS SPLY contactor (4PC) opens
1PC1 is supplied in normal configuration and when a TR is lost. Contactor 1PC2 when a normal TR is lost (coupling of busbars 1PP and 2PP), in emergency con-
ditions or when the DC NORM BUS 1 SWITCHING contactor (1PC1) is lost.
Figure 5: DC Distribution
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-7
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
DC Generation Monitoring and Indicating - D/O . 702PP is connected to Bat 2.
Monitoring and indicating of aircraft DC generation and distribution are performed • the centralized warning system (ECAM) on which the following parameters are
by means of: available:
• two voltmeters located on the overhead ELEC panel (35VU) in the cockpit. • TRs voltage and current,
• batteries voltage and current.
They indicate to the flight crew the voltage of the HOT busses 701PP and 702PP.
Furthermore the ECAM system gives a synoptic of the electrical generation ena-
NOTE: The HOT busses are directly connected to the batteries as follows:
bling the flight crew to know the current electrical configuration (DC essential and
. 701PP is connected to Bat 1, normal switching).
Figure 6: DC Generation Monitoring and Indication
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-8
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
DC GENERATION - BATTERIES - D/O The battery charge limiter is operating and controls the coupling and uncoupling
of the battery. No light comes on on the pushbutton switch in normal operation.
The DC generation is provided by two batteries.
However white BAT1 and BAT2 and green indication of voltage and current are
Each of them has a nominal capacity of 23 Ah. displayed on the ELEC page of the lower ECAM DU, as well as the green symbol
They are mainly used to: when battery is charging and the amber symbol when battery is discharging.
FAULT amber legend comes on on the pushbutton switch if a thermal runaway or
• start the APU in flight and on ground,
internal short-circuit is detected. Simultaneously, the ELEC page is displayed on
• supply AC/DC essential network in emergency configuration during RAT de- the lower ECAM DU with corresponding warnings (MASTER CAUT light + single
ployment and when the emergency generator is not available (CSM/G chime + amber message on the upper ECAM display unit). A BAT OVHT fault
switched off after landing). causes automatic lock out of the battery line contactor.
Each battery is associated with a Battery Charge Limiter (BCL). NOTE: An OFF/ON (Released/Pressed) action on the pushbutton switch allows to
It should be noted that, in normal configuration, the batteries are most of the time reset the BCL.
uncoupled from the network during the flight.
General Operating Principle of the Battery Charge Limiter
Component Description The battery charge limiter has a main function which is to control the battery con-
Batteries: Each battery of the nickel-cadmium type is composed of twenty ele- tactor and three auxiliary functions which are:
ments housed in a stainless steel case. • RAT & EMER GEN FAULT warning control,
Characteristics: • in emergency configuration, inhibition of APU start sequence during RAT de-
• nominal voltage: 24 V, ployment,
• nominal capacity: 23 Ah, • BAT FAULT warning control.
• high instantaneous power, Furthermore, the BCL delivers battery-related parameters and warnings to the
• electrolyte reserve: 60 cubic centimeters, ECAM display units, through busses.
• two ventilation ducts. The functions of battery charge limiter are as follows:
Control of the battery contactor:
Operation/Control and Indicating
• to ensure battery charge,
Control and Indicating Circuits.
• to start or assist starting of the APU,
The operation of each battery charge limiter is controlled from the ELEC panel • to protect the battery against thermal runaway or short circuit,
35VU in the cockpit by means of BAT1(2) pushbutton switches. These pushbutton
• to control equipment DC supply on ground, when no normal power is available,
switches have two stable positions:
• to prevent complete discharge of the battery, when the aircraft is parked,
The pushbutton switch is released
• to supply equipment with DC during transient fault configurations,
The battery charge limiter is not operating and the battery is uncoupled from the • to ensure integrity of the HOT bus.
network. The status of this control is indicated by illumination of the white OFF leg-
end on the pushbutton switch. The same indication is displayed on the ELEC page Battery charge:
of the lower ECAM Display Unit and generates a warning if one or both engines When battery voltage is lower than 26.5 V, beginning of the charging cycle.
are running. When battery charge current is lower than 4 A, end of the charging cycle.
The pushbutton switch is pressed
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-9
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
NOTE: In flight or following APU start, when the battery charge current is lower section of the overhead panel 21VU comes on until the emergency generator is
than 4 A, a 30 mn time delay in the BCL controls the end of the charging cycle. available (operational). The FAULT legend is inhibited when the landing gear is
Thermal runaway and internal short circuit. compressed.
Battery isolation occurs in case of: Inhibition of the APU start sequence
• charge current increasing with a slope greater than 0.375 A/mn. In flight, when the electrical emergency configuration is initiated, the APU start se-
• charge current greater than a threshold (150 A) during 1 minute and 30 sec- quence is inhibited during 45 seconds.
onds. NOTE: If the CSM/G comes on line before 45 seconds, the APU start sequence is
Starting of the APU. available as soon as the CSM/G is coupled to the network.
When the APU start sequence is initiated, the two batteries are connected to 28 BAT - Fault warning control
VDC BAT BUS (3PP) to supply the APU starter motor. When a thermal runaway occurs the FAULT legend of the BAT1(2) pushbutton
Supply on ground switch comes on on the overhead ELEC panel 35VU.
When IDG's, APU generator or external power are not available on ground, the The battery contactors are opened but no action is required from the crew.
batteries supply:
• the 28 VDC BAT BUS (3PP) through the contactors 6PB1 and 6PB2,
• the 28 VDC ESS BUS (4PP) through the contactor 2XB,
• the 115 VAC STAT INV BUS (901XP) through the static inverter 3XB. (the
BAT1(2) pushbutton switches are pushed).
Protection against complete discharge
On ground, the batteries are automatically disconnected from the DC network
when battery voltage is lower than 23 V during 15 seconds.
NOTE: But the disconnected battery always supplies its related HOT bus.
Transient fault conditions
Battery contactors are closed during 7 seconds when DC network is lost.
Integrity of the HOT bus
Battery isolation in case of failure on DC network through monitoring of the battery
discharge current (either I discharge > 400 A for 5 ms or I discharge > 100 A for
300 ms).
Electrical emergency event
Battery isolation in case of AC normal busbars failure (loss of AC main generation)
except when APU start sequence is initiated.
RAT & EMER GEN control
In case of AC normal busbars failure (loss of AC main generation) the red FAULT
legend of the RAT & EMER GEN pushbutton switch on the ELEC EMER PWR
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-10
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
Figure 7: Battery Charge Limiter Schematic
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-11
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-30 DC Generation
Figure 8: Battery and Battery Charge Limiter
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-30-12
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
24-40 External Power
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
General • and Ground Cart switched ON (voltage at pin F below 42 volts and AC voltage
at pins A, B and C within the limits).
The aircraft network can be supplied by a Ground Power Unit connected to an ex-
ternal receptacle located forward of the Nose Landing Gear well enables power If the delivered parameters are correct, the Ground Power Control Unit allows the
supply of the aircraft network up to 90 KVA. (Single three-phase, 400 Hz, 115/200 External Power Contactor to be controlled. Two conditions must be fulfilled to en-
VAC) ergize the PR (Power Ready relay):
This receptacle enables to supply: • valid EP (External Power) Interlock.
• either the whole network via the transfer circuit • and delivered parameters within the limits.
• or only part of it, the ground service network which comprises:
Monitoring
– the AC ground service bus control
– the DC ground service bus control The Ground Power Control Unit monitors the AC and DC parameters.
The power supply control of the whole aircraft network from a ground power unit AC protections are: over/under voltage. over/under frequency. Incorrect Phase
is performed from the cockpit overhead panel This control is associated with a Sequence (IPS).
Ground Power Control Unit (GPCU) which permanently monitors the parameters DC protection is provided by External Power Receptacle pin voltage monitoring.
for the quality of the electrical power supplied. Moreover, the GPCU permanently The protection system also includes a GPCU Internal Fault detection device.
transmits to the Centralized Fault Display Interface Unit (CFDIU) all its fault mes-
sages. Bite
Normal Parameters The Ground Power Control Unit contains an internal BITE system to help in sys-
tem trouble-shooting. The BITE system detects and isolates active and passive
If the External Power parameters are correct, the indicator lights on the external failures. The BITE system consists of two sections:
power receptacle and the EXTERNAL POWER AVAILABLE light on the cockpit
• operational BITE.
overhead panel come on.The Ground Power parameters are monitored by the
Ground Power Control Unit (GPCU) which activates the indicator lights. With such • maintenance BITE.
indications the Ground Cart can supply the aircraft network. As soon as the Exter- The operational BITE identifies the protection, analyses the conditions and deter-
nal Power pushbutton is pressed in, the Ground Power Control Unit closes the Ex- mines the fault origin. The maintenance BITE completes the operational BITE and
ternal Power Contactor to supply the aircraft electrical network. The Bus Tie performs a self test to provide an indication of system integrity in ground mode on-
Contactors (BTC 1 and BTC 2) close only if no generators are on line. ly. A Class 2 failure signal is sent to the Electrical Generation Interface Unit in or-
der to display Ground Power Control Unit message on the ECAM status page. The
Abnormal Parameters CFDS class 2 message is labelled as:
If any external power parameter is not correct, the indicator lights stay off. The ex- IDG 1 (2) HIGH DELTA TEMP
ternal power cannot be connected to the aircraft network. The detection of a To enable the 3 Generator Control Units to dialogue with the Centralized Fault Dis-
GPCU fault causes the EPC to open. play interface Unit (CFDIU) through the Ground Power Control Unit (GPCU), the
GPCU receives a back-up supply from the DC BAT BUS (301PP).
Supply
The Ground Power Control Unit is supplied by the Ground Cart through the Exter-
nal Power receptacle and analyses the voltage inputs. The PMR (Pin Monitoring
Relay) is energized under the following conditions:
• Ground Cart plugged in and running (voltage at pin E between 5 and 42 volts).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 1: Ground Power Control Unit (GPCU)
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 2: External Power/Receptacle/Contactor
BTC.1 BTC.2
AC BUS 1 AC BUS 2
EXT PWR
EPC
AVAIL
ON
TO AC/DC
GROUND GPCU
SERVICE BUS
EXT PWR
EXTERNAL EXTERNAL
POWER POWER
RECEPTACLE PLUGGED IN
NOT IN AVAIL
USE
Contactor Base
Contactor
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
AC/DC Ground Service Network Operation/Control and Indicating
AC ground/flight distribution network can be supplied: Supply selection for ground service network is controlled from panel 2000VU,
• either normally from the aircraft network, MAINT BUS switch: - one position corresponds to the normal supply configuration.
- the other position controls the ground service network supply from the ground
• or directly by the ground power unit upstream of the external power contactor,
power unit. This position is electromagnetically latched.
in ground service configuration. In ground service configuration this network
can be supplied without energizing the whole aircraft network. The switch returns to the normal position in case of voluntary or automatic (GPCU
protections) unlatching of the ground power unit. The normal supply configuration
The AC ground/flight network comprises the sub-busbars:
takes precedence over the ground service configuration.
• 212XP,
NOTE: Overheat of TR2 results in the automatic unlatching of MAINT BUS switch.
• 214XP,
This entails the cut-off of the ground distribution network.
• 216XP-C.
Figure 3: Ground Service Network
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 4: AC/DC Ground Service Control and Distribution
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
DC Ground Service Network • 601PP,
DC ground flight distribution network can be supplied: • 602PP.
• either normally from the aircraft network, These sub-busbars are supplied directly from the ground power unit through the
• or directly by the ground power unit upstream of the external power contactor. contactor 14XX via the TR2. The contactor 14XX is controlled by the MAINT BUS
This is via the TR2 in ground service configuration, without energizing the control switch 5XX located on panel 2000VU.
whole aircraft network. Figure 5: DC Ground Service Network
The DC ground/flight network comprises the following 28 VDC service busses:
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-7
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 6: Parts Location
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-8
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Enhanced Electrical Power Generating System er Control Unit (GAPCU) which activates the indicator lights. With such indications
the ground cart can supply the aircraft network. As soon as the EXT PWR P/B is
(EEPGS) External Power pressed in, the on blue legend illuminates and the GAPCU closes the External
Power Contactor (EPC) to supply the aircraft electrical network. The Bus Tie Con-
External Power Control tactor (BTCs) 1 and 2 close if no engine driven generator is on line.
Normal Parameter Abnormal Parameter
If the external power parameters are correct, the indicator lights on the external If any external power parameter is not correct, the indicator lights stay off. The ex-
power panel and the EXT PWR AVAILable light on the cockpit overhead panel ternal power cannot be connected to the aircraft network.
come on. The power parameters are monitored by the Ground and Auxiliary Pow-
Figure 7: EEPGS External Power Control
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-9
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
External Power Supply Operation
EXT PWR not in use (available)
The Ground Power Unit (GPU) supplies the Transfer Circuit through the External
Power Contactor (EPC). The closed PRR connects power from the internal supply via the PTC sensor to
the distribution bus and from there:
A Ground and Auxiliary Power Control Unit (GAPCU) controls and protects the
• to the solenoid of EPC auxiliary relay. The auxiliary relay cannot be energized
connection and disconnection of the GPU and the APU generator to the network.
until it gets a ground from the flip/flop. The ground is supplied when the EXT
Ground Power CTL & MON PWR switch is pushed ON.
• to the EXT PWR NOT IN USE white light via the contactor 12XX provided that
The 115V AC, 400 Hz, 3 phase output of the GPU is connected to the aircraft net-
the MAINTenance BUS switch is OFF.
work through the EPC and Bus Tie Contactors (BTCs).
• directly to te EXT PWR AVAIL amber light.
The GAPCU monitors permanently the quality of the delivered ground power. At
least one faulty parameter automatically disconnects the ground power from the Figure 8 shows GAPCU operation with external power available but not in use.
transfer line. The monitoring and control of the connection and disconnection is
made by two internal relays. The Interlock Monitoring Relay (IMR) and the Power
Ready Relay (PRR).
PRR and IMR Power Supply
The IMR is energized when:
• The GPU DC control power sensed on the interlock circuit is less than 42V DC.
• The voltage sensed on the interlock circuit is less than 13V AV.
• All external power parameters checked by the internal Control and Protection
circuit are correct.
The PRR is energized when:
• The external power interlock is valid,
• And all parameters are correct.
The annunciators NOT IN USE and AVAILABLE located on the ground power re-
ceptacle are ON.
PTC Protection
If a short circuit occurs on the PRR output line sensed by the Positive Temperature
Coefficient (PTC) sensor, the red PTC TRIP LED on the front face of the GAPCU
comes on and a BITE message is sent to the Centralized Fault Display System
(CFDS).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-10
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 8: GAPCU (External Power Module) Operation
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-11
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
EXT PWR in use (on)
When the External Power (EXT PWR ) P/B switch is pressed (momentary switch
action), the flip/flop provides a ground signal to the solenoid of the EPC auxiliary
relay 5XG.
The relay connects power from 104XG to the GLC/BTC logic. Depending on the
supply status the logic will authorize the closure of the EPC.
At the receptacle:
• The NOT IN USE light will extinguish
• The AVAIL light remains ON.
On the EXT PWR switch in the cockpit:
• The ON light comes ON
• The AVAIL light extinguishes.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-12
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 9: GAPCU Operation EXT PWR ON
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-13
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
GAPCU D/O Interlock
The Ground and Auxiliary Power Control Unit (GAPCU) controls the APU Gener- The Interlock Monitoring Relay (IMR) closes when:
ator (GEN) and the External Power (EXT PWR) System. The APU Generator Line The 28V DC control voltage from the Ground Power Unit (GPU) to the GAPCU, is
Contractor (AGLC), the External Power Contractor (EPC) and their related Auxil- within limits (<45V DC and <60V AC),
iary Relays can only close when the correct conditions exist. They are opened
The phase voltage (115V AC) at the Point Of Regulation (POR), is accepted by
manually or automatically, by the control and protection circuits.
the Control and Protection Module.
The GAPCU also performs BITE analysis and communication and interface with
other systems: The closed IMR connects 28V DC to the GPU. This interlock voltage is a ''hold on''
supply for the GPU contactor and is one of the PRR and the EPC close. If the IMR
• Generator Control Units (GCUs), opens, the AND gate is disqualified, the PRR trips and the EPC opens.
• APU Electronic Control Box (ECB),
• Centralized Fault Display Interface Unit (CFDIU), EPC Control
• System Data Acquisition Concentrators (SDACs), The closed PRR provides 28V DC to the solenoid of the solenoid of the EPC AUX
• Landing Gear Control and Interface Unit (LGCIU) 1. relay (5XG). The AUX relay is responsible for opening and closing the main con-
tactor (EPC) The EPC AUX relay is also responsible for the priority switching, i.e.
Power Supply the External Power over the APU GEN.
The GAPCU internal power supply module can be supplied by the external power When the EXT PWR P/BSW is pressed the FLIP/FLOP provides a ground to close
or the APU GEN via internal Transformer/Rectifiers (TRs). The supply module the EPC AUX relay. Depending on the network supply status (sensed by the Gen-
also has a back-up supply from the Bat BUS. erator Line Contactor (GLC)/Bus Tie Contactor (BTC) logic) the EPC AUX relay
connects power via the open APU GLC (AGLC) to the EPC. The EPC then con-
EXT PWR Control nects the GPU to the transfer line. When the EXT PWR P/BSW is pressed again,
The GAPCU performs the following functions for the external power control and the FLIP/FLOP removes the ground so that the AUX relay and EPC open.
BITE:
• monitoring,
APU P/BSW
• interlock function, The APU GEN P/BSW is used to connect or disconnect the APU GEN and reset
the APU GEN control system. After a fault detection (tripping of the generator), the
• External Power Contactor (EPC) control,
control must be reset by setting the P/BSW to OFF and back to ON.
• protection,
• BITE function, AGLC Control and Monitoring
• communication and interface. The AGLC is under control of the AGLC AUX relay and the GLC/BTC logic. If all
APU GEN parameters are correct, the AGLC connects the GEN to the transfer
Monitoring line.
The GAPCU permanently monitors the quality of the external power supply. A
faulty parameter automatically disconnects the external power from the transfer
line opening the Power Ready Relay (PRR) hence the EPC. In some GAPCU fail-
ure conditions the back-up card can control the PRR, so that the external power
can still be connected to the aircraft. In these cases, after a ''cold reset'' the PRR
closes and the external power is supplied to the aircraft with limited protection.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-14
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 10: GAPCU Communication & Interface
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-15
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Protection Overheat Protection
The GAPCU performs the following protection functions for the external power: An oil temperature bulb is installed in the APU GEN. The bulb is directly connected
• over and under voltage, to the APU Electronic Control Box (ECB). In case of oil temperature above 185°C,
• over and under frequency, the ECB commands an immediate shutdown of the APU:
• over current, Communication and Interface
• EXT PWR interlock,
The GAPCU communicates with the GCUs, the CFDIU and the SDACs.
• Incorrect Phase Sequence (IPS),
• open cable or open/short circuit, With the GCU
• EPC failure. The GAPCU communicates with the two GCUs via MIL-STD 1553 links. The
The Over Voltage (OV) protection is accomplished by monitoring the highest GAPCU always initiates the transfer of information from the GCUs and communi-
phase voltage at the POR. An OV condition exist when the highest phase voltage- cates in two modes: normal and interactive mode. In normal mode, the GAPCU
exceeds 130 +/- 1,5V AC. After an inverse delay, the IMR, PRR and EPC are periodically interrogates each GCU for channel status, fault status and LRU iden-
tripped. tification. In interactive mode (only on ground when requested from the CFDIU),
the normal mode is interrupted by a self-test command. The GAPCU will request
The Under Voltage (UV) is sensed in the same way as OV. An UV condition exists a self-test of each GCU and will perform its own test routine.
when the lowest phase voltage is less than 101,5 +/- 1,5V AC. After a 4,5 second
time delay max, the PRR, IMR and EPC are tripped. With the CFDIU
An over current on the wiring between the PRR and the aircraft bus (1000XG) will The GAPCU communicates with the CFDIU via arinc 429 links. During normal
change the status of the Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) sensor (high im- mode of transmission, the GAPCU continuously sends its own and the two GCUs
pedance). The sensor then provides a signal to switch on the red PTC LED on the fault data, to the CFDIU.
front face of the GAPCU and sends a BITE message to the Centralized Fault Dis-
play System (CFDS). With SDAC
The PTC and the PTC LED are only supplied if the EXT PWR remains connected The GAPCU continuously communicates with the SDACs via arinc 429 links. The
to the receptacle (i.e. PRR is still closed). The LED is not a ''latched'' status signal. SDACs provide system data to the ECAM and fault data to the FWCs.
Thus, if a short circuit exist, and the LED is illuminated, it will off as soon as the
external power is removed from the receptacle. Interface with the LGCIU
The GAPCU receive a flight/ground discrete signal from LGCIU 1. It enables the
APU GEN Control interactive mode of communication between the GAPCU and the CFDIU.
The main functions are:
• control of the field excitation through the Generator Control Relay (GCR),
• voltage regulation,
• control of the AGLC through the PRR in conjunction with the BTC/GLC logic,
• control and protection of the APU GEN and the network.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-16
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
AC/DC Ground Service Distribution D/O
EXT PWR P/B ON
The whole aircraft electrical network is supplied including the AC and DC GND/
FLT busses
Figure 11: Ground Service Distribution with EXT PWR On
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-17
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 12: MAINT BUS SW ON
EXT PWR is available but
not ON (14PU and 12XN
open) and the MAINT BUS
SWITCH switched to ON. AC
BUS 2 and 202XP are not en-
ergized, so relay 7XX is de-
energized and supplies relay
14XX via relay 14PU and re-
lay 12XX via relay 12XN.
With these two relays ener-
gized, the DC GND/FLT bus
(6PP) is supplied via TR2 and
the AC GND/FLT busses
(212XP, 216XP and 214XP
via 12XX and 14XX).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-18
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 13: TR 2 Failure with EXT PWR On
If TR2 fails the GND/FLT
busses are automatically
supplied from the TR1 via
DC BUS 1, BAT BUS and
DC
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-19
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
Figure 14: TR 2 Failure with MAINT BUS SW On
If the GND/FLT busses are
supplied (MAINT BUS
SWITCH ON) and TR2 has an
internal overheat (T>172°C)
the MAINT BUS switch trips
OFF because relay 6XX is de-
energized. Thus, relays 12XX
and 14XX are also de-ener-
gized so there is no power sup-
ply to any of the AC and DC
GND/FLT busses.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-20
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
AC/DC Sheddable Bus Supply the DC ESS BUS and the battery 1 supplies the STATic INVerter, which supplies
the AC ESS BUS.
Normal Configuration In this condition, the AC and DC SHED BUSSES are not supplied because relays
The AC and DC ESSential BUSses supply the AC and DC ESSential SHEDdable 8XH and 8PH are open due to the BAT ONLY relays 2XB and 6XB being ener-
BUSes via the control relays 8XH and 8PH. The open or closed position of the re- gized.
lays 8XH and 8PH depends on the network supply status. Note that the AC and DC SHED ESS BUSSES are also shed during an EMER
GEN TEST, because relays 16XE and 21XE are energized.
Emergency Configuration
If there is an electrical emergency and the Constant Speed Motor Generator
(CSM/G) is not available, the aircraft is on battery power only. Battery 2 supplies
Figure 15: Emergency Configuration
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-21
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
GALY & CAB SYS and Commercial Load
Figure 16: Galley & Cabin System and Commercial Load
In normal supply configuration
(GALY & CAB and COMMER-
CIAL P/BSWs pushed in), all
the galleys and the cabin and
commercial sub-busbar are
supplied.
When the GALY & CAB P/
BSW is set to OFF (OFF leg-
end on) all the galleys and the
cabin systems sub-busbars
(218XP, 220XP and 210PP,
212PP) are OFF. When the
COMMERCIAL P/BSW is set
to OFF (OFF legend on) all the
galleys and all the sub-bus-
bars are off.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-22
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
TR1 or 2 Loss
Figure 17: TR 1 or 2 Loss
GALY & CAB and COM-
MERCIAL P/BSWs are in
normal supply configura-
tion. When TR 1 or TR 2 is
lost the relay 1PC2 is en-
ergized, the DC sub-bus-
bars 210PP and 212PP
are not supplies.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-23
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-40 External Power
IDG 1 or 2 Loss
Figure 18: IDG 1 or 2 Loss
When IDG 1 or IDG 2 is
lost, BTC 1 and 2 are
closed and the relay
10XA is de-energized,
this sheds the cabin-re-
lated sub-busses. If the
APU GENerator is lost
due to a current overload
on the ground, all Galleys
& Cabin related sub-
busses are off.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-40-24
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
24-50 Load Distribution
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-1
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
AC Electrical Power Distribution System Description
The galley general supply is controlled from flight compartment overhead panel
The AC electrical power distribution on board is carried out in several steps corre- 35VU by means of GALLEY pushbutton switch (normal operation when the push-
sponding to: button is pressed in).
• Power distribution:
– from the different sources towards the main AC busbars located in panel A320 EDW
120VU, The galley general supply is controlled from the cockpit ELEC panel 35VU by
– then, from the main AC busbars, either directly towards important consum- means of the GALY & CAB pushbutton switch (normal operation when the push-
ers (pumps, galleys...), or towards the associated distribution sub-busbars button is pressed in).
located in the circuit breaker panels.
• Power distribution from sub-busbars: A320E Swiss Sun (IJU, IJV, IJW)
– the distribution from these sub-busbars towards the different AC consum- If the OFF legend of COMMERCIAL pushbutton switch (commercial load shed) is
ers. off (pushbutton switch pressed in), galley general supply can be controlled from
flight compartment overhead panel 35VU by means of GALLEY pushbutton switch
This chapter deals only with power distribution. This can be broken down as fol-
(normal operation when the pushbutton is pressed in).
lows:
• the AC main distribution connected to 115 VAC busses 1XP and 2XP Operation/Control and Indicating
• the AC essential distribution connected to 115 VAC ESS bus 4XP and 115
VAC SHED bus 8XP Galley Automatic Shedding
If only one generator is available, galley(s) (primary feeders controlled by the relay
System Description 6XA) is (are) automatically shedded. White GALLEY SHED indication appears on
The distribution busbars are supplied according to various configurations depend- the ELEC page of the lower ECAM display unit (no light on GALLEY pushbutton
ing on: switch).
• the procedures applied by the crew members in the different failure configura-
tions, Overload detected by a GCU
• the availability of the various power sources. • amber FAULT legend illuminates on GALLEY pushbutton switch,
• auto display of the ELEC page on the lower ECAM display unit,
The possible configurations are:
• MASTER CAUT light + single chime + amber message on the upper ECAM
• normal flight configuration
display unit confirm the overload.
• emergency configuration corresponding to the loss of the two main generators
with the auxiliary generator not available The crew has to release GALLEY pushbutton switch on the UPPER ECAM DU
(white OFF legend illuminates). This action results in shedding of all galleys.
• smoke configuration
GALLEY indication is displayed on the lower ECAM DU, STATUS page.
NOTE: These configurations are dealt with in their respective ATA chapter.
NOTE: On ground, it is possible to supply all galleys:
Galley Power • either with the APU GEN: If I > 277 A, galleys automatic shedding,
The galley assembly is divided into several parts: • or with the EXT PWR: without galleys automatic shedding.
• Aft galley,
• Forward galley
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-2
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Figure 1: Generation and Distribution
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-3
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Circuit Breaker Panels Circuit Breaker Panel 2000VU
The front circuit breaker panel 2000VU faces the FWD passenger/crew door (841)
Overhead Circuit Breaker Panel 49VU and is located in the center of the cabin ceiling. The circuit breakers are connected
The overhead circuit breaker panel 49VU is accessible to the Captain and First Of- to either an AC or a DC power source.
ficer. The circuit breakers are connected either to an AC or a DC power source. AC Power Supply. - 115 VAC - 26 VAC / DC Power Supply. - 28 VDC
AC Power Supply. - 115 VAC - 26 VAC / DC Power Supply. - 28 VDC Each circuit breaker head is marked with the FIN and not with the rating. This is to
On the aircraft, the Functional Item Number (FIN) is shown on the rear side of the help to identify circuit breakers when they are opened during aircraft maintenance
VU panel. procedures.
NOTE: On the aircraft, the FIN is shown on the rear side of the VU panel.
Circuit Breaker Panel 105VU
The circuit breaker panel 105VU (Battery Power Center) is located in the avionics Circuit Breaker Panel 2001VU
compartment next to access door 822. You must open the access door from the The circuit breaker panel 2001VU faces the aft passenger door (842) and is locat-
panel 105VU. The circuit breakers are connected to BAT 1(2) power source. ed in the center of the cabin ceiling. The circuit breakers are connected to either
BAT power supply. - 28 VDC an AC or a DC power source.
On the aircraft, the FIN is marked below the head of each circuit breaker. AC Power Supply. - 115 VAC - 26 VAC / DC Power Supply. - 28 VDC
Circuit Breaker Panel 106VU Configuration of Circuit Breakers
The circuit breaker panel 106VU (AC/DC emergency power center) is located in Black head circuit breaker: This type of circuit breaker does not have an auxiliary
the avionics compartment next to access door 812. You must open the access contact. It is standard.
door from the panel 106VU. The circuit breakers are connected either to an AC or
a DC power source. Green head circuit breaker: This type of circuit breaker holds an auxiliary contact
connected to SDAC when it is tripped.
AC Power Supply. - 115 VAC - 26 VAC / DC Power Supply. - 28 VDC
Circuit breaker with a red threaded bush: For safety reasons, to avoid that the
On the aircraft, the labels and the FINs are marked behind the access door of the crew resets it in flight, the C/B is guarded. If it is necessary to open it, the red
panel 106VU opposite the circuit breaker panel. threaded bush must first be removed, unscrewed with a standard wrench. (WTB)
Rear Circuit Breaker Panel 120VU Circuit breaker with a yellow collar: Some circuit breakers have a yellow collar to
help the crew to find them more easily on the circuit breaker panel. (Emerg.
It comprises the following panels: - 121VU, - 122VU, - 123VU, - 124VU, -
Checklist) For clipped circuit breaker, there are two types of collars, metallic or
125VU. These circuit breaker panels are located on the rear panel 120VU. The plastic, secured by lockwire.
circuit breakers are connected either to an AC or a DC power source.
AC Power Supply. - 115 VAC - 26 VAC / DC Power Supply. - 28 VDC Reset of the Circuit Breaker
On the aircraft, the FIN is marked below the head of each circuit breaker. • in flight, it is not permitted to close a tripped circuit breaker,
NOTE: Panels 121VU/122VU and their placards are not customized. Therefore, • on ground, you must not close a tripped circuit breaker without trouble shooting
there can be placards for circuit breakers that are not installed on a given aircraft. of the related system.
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-4
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Galley Power Figure 2: Galley Components
The power supply provides the galleys with 115 V AC. There are 50 KVA available
for all galleys. This power is divided into two parts, the AFT galley power with 30
KVA and the FWD galley power with 20 KVA. The galleys are electrically connect-
ed with cable lugs to the aircraft terminal blocks.
System Description
The power supply provides the galley assemblies with 115 V AC through the three
phase normal busbars 1XP and 2XP. Six triple core wires (feeders A to F) distrib-
ute the power to terminal blocks in the forward and aft galley area. Vendor wiring
distributes the power to the galley units. The wiring is connected to the terminal
blocks by the electrical connector.
The maximum available load for all galleys is 50 KVA. The load is distributed as
follows:
• Network 1 = feeder A, B and E with 30 KVA,
• Network 2 = feeder C, D and F with 20 KVA.
Circuit breakers protect the feeders. Power contactors switch the power.
Operation/Control & Ind
The power contactors for the galleys are controlled through control relays as fol-
lows:
With the APU generator running or with external power supplied you can supply
all feeders with power (on the ground). With both engine driven generators run-
ning, you can supply all feeders with power (on the ground or in flight). With only
engine 1 driven generator running, only feeders B and D is supplied. Feeders A,
C, E and F are shed automatically (on the ground or in flight). You can manually
shed all the feeders to the galley with the pushbutton switch 2XA GALLEY OFF in
the cockpit (on the overhead panel 35VU).
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-5
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Figure 3: Galley Power A318
The galleys are electrically supplied by
the AC normal busbars. Note that extra
cabin systems load busses can be add-
ed. The power supply is controlled from
the GAL & CAB and COMMERCIAL P/
BSWs, connected in series
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-6
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Figure 4: Galley Power A320
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-7
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Figure 5: Galley Power A321
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-8
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
GALY & CAB and Commercial P/BSW (A318) galley busses are supplied. When the main landing gear is compressed, all the
galleys can be electrically supplied, either by the external power, the APU gener-
If either the GALY & CAB P/BSW or the COMMERCIAL P/BSW is OFF, all galley
ator or both Integrated Drive Generators (IDGs).
power is removed. If the COMMERCIAL P/BSW is ON and the GALY & CAB P/
BSW is OFF, all galley power is removed but the commercial busses are still sup- If only one generator source is available in flight, the Bus Tie Contactors (BTCs)
plied. Related messages are sent to the ECAM. The GALY & CAB P/BSW amber are energized and relay 6XA is de-energized. Most of the galley loads are auto-
legend comes on if a generator overload is detected. matically shed. There is an ECAM message but no GAL & CAB FAULT indication.
With the aircraft on ground and electrically supplied by the APU only, all galley
Operation loads will be automatically shed if an APU generator overload is detected by the
With the GALY & CAB and COMMERCIAL P/BSWs ON and normal electrical con- Ground and Auxiliary Power Control Unit. The GALY & CAB FAULT light comes
figuration, relays 5XA, 6XA and 9XA control the galley feeder contactors and all on until the P/BSW is released OFF.
Figure 6: A318 Normal Operation on Ground
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-9
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Figure 7: One IDG Operation in Flight (A318)
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-10
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Figure 8: Overload Operation on Ground (A318)
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-11
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Load Monitoring (A318) message is triggered. Manually switch off the galley power to unload the genera-
tor. On the ground, an APU Generator overload automatically sheds all the galley
The GALY & CAB P/BSW FAULT light comes on if a Generator Control Unit
power.
(GCU) detects an IDG overload or the GAPCU detects an APU Generator over-
load. An IDG overload does not automatically shed galley power, but an ECAM
Figure 9: IDG Overload (A318)
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-12
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
Refueling on Batteries • 28 VDC service bus 601PP if at least ground service busses are energized,
The network consists of busbars 501PP and 502PP (28 VDC). It is supplied as • 28 VDC hot bus 701PP (directly linked to battery 1) if no other power is avail-
soon as the refuel door located on the fuselage below the right wing is opened. able on board.
Two supplies are then possible: NOTE: Refueling power supply is automatically cut off ten minutes after.
Figure 10: Refueling on Batteries Schematic
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-13
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Electrical Power
A318/A319/A320/A321 24-50 Load Distribution
January06/Technical Training for training purposes only
24-50-14
Copyright by SRTechnics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
24-Study Questions
24-00 General 4. What is the purpose of the BUS TIE pushbutton?
1. The AC bus is normally supplied from:
5. What is the priority sequence of the AC power sources to the AC busses?
2. The DC battery bus can be supplied by the:
6. Is the ground power control unit powered in flight?
3. Bus tie contactor enable AC buses:
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-1
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
24-01 System Report / Test 24-22 AC Main Generation
7. Where can the generator system be tested? 10. When does the IDG fault light illuminate?
8. Log entry:"GEN FAULT ECAM message". Describe the fault isolation proce- 11.How is an IDG disconnected?
dure?
12.When does the IDG cooler bypass open?
9. How and where is it possible to reset a disabled TRU?
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-2
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
13.What happens if an IDG disconnect pushbutton is pressed with engine not run- 16.What is the purpose of the differential protection for the generator system?
ning?
17.How is a differential protection trip reset?
14.How is the generator output voltage regulated to 115V AC?
18.What happens if a parallel feeder becomes open?
15.What happens when a generator fault is detected?
19.What is the configuration if both BTC,s are open?
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-3
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
20.When are both BTC,s (Bus Tie Contactors) closed? 24-24 AC Emergency Generation
24.Where is the CSM/G installed and how is it driven?
24-23 AC Auxiliary Generation 25.Which conditions are required for an auto-deployment of the RAT?
21.Are the APU and engine generators identical in their construction?
22.Are there any differences between an IDG-GCU and an APU-GCU? 26.How can the CSM/G be tested on ground?
23.Where is the APU generator oil outlet temperature sent to?
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-4
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
27.On the ground in cold aircraft configuration what does the activation of the RAT 24-30 DC Generation
& EMER GEN MAN ON pushbutton cause?
30.Where and under which conditions is it possible to read the voltage of the air-
craft batteries?
28.In emergency configuration with aircraft speed below 50kts what is the condi-
tion of the aircraft elelctrical network? (BATT. P/B IN)
31.When does the BATT FAULT light come on?
29.Which precautionary measures are required prior to an emergency generator
test?
32.When does the low battery voltage detection system operate?
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-5
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
33.Under what conditions is the static inverter in operation? 36.What happens if a TRU fails?
34.Which TRU,s are active with engine generators operating? 37.What is the basic operation of the BCL (battery charge limiter) system?
35.How is a TRU protected?
24-40 External Power
38.With the engine generators on line what does the EXT PWR ON light indicate
when lit?
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-6
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
39.What does the EXT PWR AVAIL light indicate when lit? 42.How many generators are required for an entire galley power supply?
24-50 Load Distribution
40.Describe the function of the GEN 1 LINE pushbutton :
41.Why does the GALLEY FAULT light illuminate following GEN OVERLOAD?
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-7
Copyright by SR Technics
Training Manual Study Questions
A318/A319/A320/A321 Electrical Power
January06/Technical Training For training purposes only
Study Questions 24-8
Copyright by SR Technics
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 21 BeamerDocumento184 pagine21 BeamerMrityunjay Kumar Jha100% (1)
- 25 BeamerDocumento50 pagine25 BeamerMrityunjay Kumar Jha100% (1)
- 22 BeamerDocumento216 pagine22 BeamerMrityunjay Kumar Jha100% (1)
- 00-20 BeamerDocumento130 pagine00-20 BeamerMrityunjay Kumar Jha100% (2)
- Airbus NotesDocumento128 pagineAirbus NotesmartinbutlerNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Manual A 318: ATA 21 Air ConditionDocumento17 pagineTraining Manual A 318: ATA 21 Air ConditionbnolascoNessuna valutazione finora
- 27 BeamerDocumento226 pagine27 BeamerashufriendluckyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ata 36Documento52 pagineAta 36Geovanni Riquelme LooNessuna valutazione finora
- Ata 21 (Cat A)Documento161 pagineAta 21 (Cat A)Kiet La100% (1)
- Vdocument - in A320 FLT CTRL Laws and ProtectionsDocumento37 pagineVdocument - in A320 FLT CTRL Laws and ProtectionsRobert LautierNessuna valutazione finora
- A320 Ramp and Transit Ata 70 - Powerplant PW6000Documento354 pagineA320 Ramp and Transit Ata 70 - Powerplant PW6000Cassiano CapellassiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Reference Guide General Pneumatic: SR TechnicsDocumento2 pagineQuick Reference Guide General Pneumatic: SR TechnicsPanagiotis Diakidis0% (1)
- Vragen VACBI A330-200Documento7 pagineVragen VACBI A330-200Arkadiy ChernovNessuna valutazione finora
- A318/A319/A320/A321 (CFM56) : CommunicationsDocumento124 pagineA318/A319/A320/A321 (CFM56) : CommunicationsRaby AbidiNessuna valutazione finora
- 38 Water & WasteDocumento108 pagine38 Water & WasteHeber CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Bleed Air Supply Technical ManualDocumento14 pagineEngine Bleed Air Supply Technical ManualAnas Abandeh100% (1)
- 04 A330 Ata 45Documento96 pagine04 A330 Ata 45OwenNessuna valutazione finora
- Boeing 757 200/300 General FamiliarisationDocumento209 pagineBoeing 757 200/300 General FamiliarisationCatts Admin100% (1)
- ATA 28 Fuel Level 3Documento128 pagineATA 28 Fuel Level 3miguel angel camargo chevel0% (1)
- FAST52Documento21 pagineFAST52Vahid AlimoradiNessuna valutazione finora
- A330Documento79 pagineA330Dipendra Sen100% (1)
- TTM Single Aisle Line & Base Ata 24Documento474 pagineTTM Single Aisle Line & Base Ata 24Jia DuoduoNessuna valutazione finora
- A320 Center Pedestal R1Documento1 paginaA320 Center Pedestal R1wenjukwaxNessuna valutazione finora
- 23 CommunicationsDocumento238 pagine23 CommunicationsMaher Abu-ElolaNessuna valutazione finora
- A380 Lights Maintenance ManualDocumento90 pagineA380 Lights Maintenance ManualGuyNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Aisle Technical Training Manual T1+T2 (CFM 56) (LVL 2&3) CommunicationsDocumento238 pagineSingle Aisle Technical Training Manual T1+T2 (CFM 56) (LVL 2&3) CommunicationsHark DarkNessuna valutazione finora
- A 320321 Mel CDLDocumento765 pagineA 320321 Mel CDLMustafa Direk100% (2)
- FAC B1 - B2 - B2redDocumento1 paginaFAC B1 - B2 - B2redPanagiotis DiakidisNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 A330 Ata 28Documento152 pagine16 A330 Ata 28Owen100% (1)
- A334e 31D L3 D-Ne PDFDocumento54 pagineA334e 31D L3 D-Ne PDFAaron Harvey100% (1)
- Practical Element Ramp and Transit A330Documento16 paginePractical Element Ramp and Transit A330Edison Vianney Cardona MontoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Manual B 737-300/400/500: ATA 26 Fire ProtectionDocumento68 pagineTraining Manual B 737-300/400/500: ATA 26 Fire ProtectionGeovanni Riquelme LooNessuna valutazione finora
- Ata 49 ApsDocumento89 pagineAta 49 ApsGeovanni Riquelme LooNessuna valutazione finora
- Airbus A300-600/A310 Landing Gear SystemsDocumento190 pagineAirbus A300-600/A310 Landing Gear SystemsRaph 1123Nessuna valutazione finora
- A320 Modification ListDocumento1.336 pagineA320 Modification ListAhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- ATA 36 Level 1 PNEUMATICSDocumento25 pagineATA 36 Level 1 PNEUMATICSjimbokhepelNessuna valutazione finora
- A320 Communications Systems OverviewDocumento450 pagineA320 Communications Systems OverviewNizar HarbNessuna valutazione finora
- Leaflet FCPCDocumento2 pagineLeaflet FCPCAshraf BadawiNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 A330 Ata 35Documento32 pagine08 A330 Ata 35Owen100% (1)
- Pneumatics System OverviewDocumento30 paginePneumatics System Overviewbelinda koyaiyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Airbus A318/319/320/321: Auto Flight ATA 22Documento130 pagineAirbus A318/319/320/321: Auto Flight ATA 22Geovanni Riquelme LooNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Conditioning Systems OverviewDocumento101 pagineAir Conditioning Systems OverviewA Wong100% (1)
- A320 ATA 24 Electrical PowerDocumento474 pagineA320 ATA 24 Electrical PowerDavid MF CocNessuna valutazione finora
- A320 Landing Gear Technical TrainingDocumento34 pagineA320 Landing Gear Technical TrainingDuvan Cardona SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 A330 Ata 51 - 57Documento124 pagine06 A330 Ata 51 - 57Owen100% (1)
- AIR CONDITIONING TRAINING MANUAL OVERVIEWDocumento129 pagineAIR CONDITIONING TRAINING MANUAL OVERVIEWA WongNessuna valutazione finora
- LEVEL III - ATA 25 Equipment - FurnishingDocumento72 pagineLEVEL III - ATA 25 Equipment - Furnishingwagdi0% (1)
- A318/A319/A320/A321 Landing Gear: Lufthansa Technical TrainingDocumento32 pagineA318/A319/A320/A321 Landing Gear: Lufthansa Technical TrainingBELISARIONessuna valutazione finora
- Esquema 320Documento9 pagineEsquema 320Paco Iglesias CubilesNessuna valutazione finora
- A319/A320/A321 Technical Training Manual 27 Flight Controls Mechanics / Electrics & Avionics CourseDocumento3 pagineA319/A320/A321 Technical Training Manual 27 Flight Controls Mechanics / Electrics & Avionics CourseDavid OwenNessuna valutazione finora
- WISE SA HPV Trouble Shooting ATA 36Documento12 pagineWISE SA HPV Trouble Shooting ATA 36Anonymous U7NCvevMvNessuna valutazione finora
- CTC-232 Fda PDFDocumento205 pagineCTC-232 Fda PDFashufriendluckyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ata 32 L1 Landing GearDocumento33 pagineAta 32 L1 Landing GearjimbokhepelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Crash of an Alaska Airlines Boeing 727 Juneau, Alaska September 4, 1971Da EverandThe Crash of an Alaska Airlines Boeing 727 Juneau, Alaska September 4, 1971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group 30 Electrical System: Marine Diesel Engines D9A2A MP - D9A2A MH D12D-B MPDocumento1 paginaGroup 30 Electrical System: Marine Diesel Engines D9A2A MP - D9A2A MH D12D-B MPuser1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 05 A330 Ata 24Documento204 pagine05 A330 Ata 24Owen100% (4)
- Manual Iq Dataplus IIDocumento47 pagineManual Iq Dataplus IIArmando HuarayaNessuna valutazione finora
- UPSSG3525Documento66 pagineUPSSG3525nourtal2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Bulletin: User's GuideDocumento74 pagineInstruction Bulletin: User's GuideHdhm TdhNessuna valutazione finora
- 1100G JM LBM 02 - Engine ConstructionDocumento66 pagine1100G JM LBM 02 - Engine ConstructionMrityunjay Kumar Jha100% (3)
- 1100G-JM-LBM - 00 - Front Matter PDFDocumento6 pagine1100G-JM-LBM - 00 - Front Matter PDFPkjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- A318 Diffs B1 & 2 PT 2 of 2Documento364 pagineA318 Diffs B1 & 2 PT 2 of 2Mrityunjay Kumar JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyd SynopticsDocumento10 pagineHyd SynopticsMrityunjay Kumar JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Level 2 3 ATA 34Documento224 pagineLevel 2 3 ATA 34Mrityunjay Kumar JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- A318 Technical Training Manual Part 1 Aircraft DimensionsDocumento216 pagineA318 Technical Training Manual Part 1 Aircraft DimensionsMrityunjay Kumar JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- 23 BeamerDocumento262 pagine23 BeamerMrityunjay Kumar Jha100% (1)
- MK6 Golf GTI Wiring Diagrams & Component Locations PDFDocumento1.165 pagineMK6 Golf GTI Wiring Diagrams & Component Locations PDFMorarescu Andrei100% (5)
- Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Tesla TurbineDocumento13 pagineFabrication and Performance Analysis of Tesla TurbineAmal ShajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahan Bio Kerosene Ke 2Documento20 pagineBahan Bio Kerosene Ke 2Damianus tri handokoNessuna valutazione finora
- HVAC Air Filters Catalogue Provides Clean Air SolutionsDocumento6 pagineHVAC Air Filters Catalogue Provides Clean Air SolutionssemoyapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Third Quarter-Module 4: Week 4Documento11 pagineThird Quarter-Module 4: Week 4SHERLA PERENANessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis of Aqeous SolutionDocumento6 pagineElectrolysis of Aqeous Solutionanon_383714618Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Outlook: U.S. Public Finance Sector ProfilesDocumento35 pagine2011 Outlook: U.S. Public Finance Sector ProfilesSam BlanshardNessuna valutazione finora
- ManualDocumento1 paginaManualBorza DorinNessuna valutazione finora
- DTC P1B77 High Voltage Precharging Fault - SonataHybrid 2015Documento12 pagineDTC P1B77 High Voltage Precharging Fault - SonataHybrid 2015Auto DiagNessuna valutazione finora
- "Electrons in Atoms": Chemistry Atlantic Bilingual School Christian Campbell MDDocumento75 pagine"Electrons in Atoms": Chemistry Atlantic Bilingual School Christian Campbell MDusmcdoc113597Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plumbing Pre-Board Exam-Answer KeyDocumento18 paginePlumbing Pre-Board Exam-Answer KeyKrizia Charish MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 700r4 Cable Adjustment InstructionsDocumento3 pagine700r4 Cable Adjustment InstructionsTito Tales100% (1)
- Spectra Printing Division 2006 AccessoriesDocumento16 pagineSpectra Printing Division 2006 Accessoriesironma71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Instructions: MFP RangeDocumento12 pagineInstallation Instructions: MFP RangeSoheil GhasemiNessuna valutazione finora
- Especificaciones MAGNUM MMG55Documento5 pagineEspecificaciones MAGNUM MMG55DAVNIALNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobil Delvac MX 15W-40Documento3 pagineMobil Delvac MX 15W-40Rachit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.8L Cac Parts Book 20sept13Documento37 pagine8.8L Cac Parts Book 20sept13Silver SilverNessuna valutazione finora
- BOQ - SIPIL GI 150 KV RAJAPAKSIDocumento14 pagineBOQ - SIPIL GI 150 KV RAJAPAKSIReinhard Jesaya SimbolonNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Pipe DesignDocumento12 pagineEng Pipe DesignEsapermana Riyan100% (1)
- Solar Micro InverterDocumento23 pagineSolar Micro InverterHassan SouleymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of IndonesiaDocumento73 pagineHandbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of IndonesiaWanali AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chvcm4 Instructions NaDocumento1 paginaChvcm4 Instructions NaCarlos CabralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling of Subcooled Flow Boiling Heat Transfer of Water Through A Vertical Heated PipeDocumento4 pagineModelling of Subcooled Flow Boiling Heat Transfer of Water Through A Vertical Heated PipeDr Mohammed AzharNessuna valutazione finora
- NABL 104 Guide for Electrical Testing LabsDocumento122 pagineNABL 104 Guide for Electrical Testing LabsMani Dhamodharan100% (1)
- TANTRANSCO Cost Data 2020-2021Documento27 pagineTANTRANSCO Cost Data 2020-2021Lingaraj Suresh LingaianNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Green EconomyDocumento11 pagineIntroduction To Green Economyvineet soodNessuna valutazione finora
- Cre S16Documento4 pagineCre S16vikas patheNessuna valutazione finora
- Gissa Navira SevieDocumento31 pagineGissa Navira SevieGissa SevieNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions: Penberthy Model Tme MixerDocumento4 pagineInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions: Penberthy Model Tme MixerGuillermo MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Carburetor Troubleshooting Guide: Cold Starting ProblemDocumento1 paginaCarburetor Troubleshooting Guide: Cold Starting ProblemhemaNessuna valutazione finora