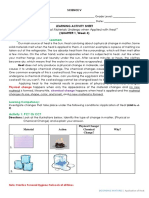
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
3rd Quiz
Caricato da
Ian Cleo TiapeDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
3rd Quiz
Caricato da
Ian Cleo TiapeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SECOND QUARTER
THIRD SUMMATIVE TEST
SCIENCE – 5
Name: ______________________________________________ Score:_______________
Section: _____________________________________________ Date:_______________
DIRECTION: Read and analyze each item carefully. Encircle the letter of the correct answer.
1. What do all female flowers have?
A. petals B. pollen C. pistil D. stamen
2. Which is the colourful part of most flowers?
A. sepals B. petals C. stamen D. pistil
3. Which part is NOT present in an imperfect flower?
A. petal or sepal B. pollen or sepal C. anther or filament D. pistil or stamen
4. Which describes a papaya flower?
A. complete and perfect C. incomplete but perfect
B. complete and imperfect D. incomplete and imperfect
5. What type of pollination happens when the pollen grains are transferred from the anther
of a flower to the stigma of another flower in the same plant?
A. Cross pollination B. Imperfect pollination
C. Self-pollination D. perfect pollination
6. In which part of the plant does the embryo develop?
A. seed B. flower C. leaf D. stem
7. The corn grain is a monocot. How many cotyledons does it have?
A. one B. two C. none D. many
8. Why do we say that the mango reproduces sexually?
A. It develops suckers C. It can be propagated by grafting.
B. It grows from a seed. D. Its cuttings can develop into new plants
9. From which structure can potato be propagated asexually?
A. corn B. rhizome C. tuber D. bulb
10. Which members of the following pairs are NOT matched?
A. testa - seed B. anther – filament C. pollen – ovule D. calyx – sepals
11. Flowers like sunflowers make large amounts of tiny, light pollen grains that are mostly
pollinated by ____________.
A. Wind B. animals C. humans D. insects
12. Which of the following plants is grown from a bulb?
A. onion B. ginger C. potato D. kangkong
13. What is the colourful parts of flowers that protects the lower parts where seeds are made?
A. Petals B. pistil C. sepals D. stamen
14. Where does the seed get its food supply?
A. cotyledon B. embryo C. endosperm D. radicle
15. Which of the following reproduce by means of spores?
A. fern B. mango C. pine tree D. banana
16. When is the intertidal zone covered with water?
A. at high tide B. at low tide C. during night time hours D. during daylight hours
17. In which tidal zones do eel grass, algae, fish, shrimps, dolphin and more survive?
A. Supratidal zone B. Subtidal zone C. Intertidal zone D. Both A and B
18. Why do birds abundant in estuaries?
A. Birds can rest and look for food in estuaries.
B. It is their habitat.
C. It is their breeding places.
D. It is the place where they can get their mate.
19. Which is not considered a challenge in the intertidal zone?
A. moisture B. waves C. salinity D. water level
20. Animals in the intertidal zone have different adaptation for them survive, which of these
uses a root-like structure that attach to rocks or mussels thus keeping it in place?
A. Snail B. kelp C. crab D. sponge
21. Salinity in the intertidal zone is higher as compared to other tidal zone. What could be the
reason for this?
A. Salt trapped in rocks pools evaporates, leaving behind salt deposits.
B. More salt solution in the intertidal zone than any other area.
C. Higher concentration of salt is carried by tides.
D. Animals contribute to salt production.
22. Which of this water environment considered as “brackish water”?
A. estuary B. ocean C. pool D. sea
23. What can damage life in estuary?
I. Land development III. Agricultural wastes
II. Industrial wastes IV. Proper wastes management
A. I only B. I, II and III C. II, III and IV D. I, II, III and IV
24. Why would it be advantageous to burrow oneself into the sand if you live in an intertidal
zone?
A. So you would not be carried away by the tide B.So you can make a bigger home
B. C.So you can get more oxygen D. So you can get food.
25. In many desert regions, water is diverted from streams and rivers to people in cities. How
does this affect the animals in the area?
A. The animals become more active in daylight hours.
B. The animals migrate to tropical rainforest.
C. The animals move closer to cities to get food
D. The animals stop searching for food and water
26. There are five major types of estuaries. How do they are classified?
A. based on how they are formed. B. based on their shape.
C. based on their location D. Both A and B
27. Which is one of the effects of global warming in estuaries?
A. water temperature increases B. water temperature decreases
C. water level decreases D. water level increases
28. When is intertidal zone exposed to air?
A. at high tide B. at low tide C. at rainy days D. at sunny day
29. Why is it important to protect the estuaries and intertidal environment?
A. It provides places for habitat of valuable species of plants and animals.
B. It attracts tourists. C. It gives people work to do.
D. It is a mandate to give importance from the town mayor.
30. As a grade five pupil, how can you contribute in the preservation and conservation of our
estuaries?
A. Join in a stream or beach cleanup in our community or in school.
B. Advise your town mayor to conduct an orientation.
C. Do not use pesticides.
D. Keep more fishes alive
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division of Bulacan
Baliwag North District
JOSEFA V. YCASIANO MEMORIAL SCHOOL
San Roque, Baliwag Bulacan
FIRST QUARTER
THIRD SUMMATIVE TEST
TABLE OF SPECIFICATION
SCENCE - 5
Item Placement & Bloom’s
Taxonomy
No. of Days Taught
No. of Items
Percentage
Understanding
Remembering
Evaluating
Analyzing
Applying
Creating
Objectives
1. Describes the 1-6
3 9 30% 10
reproductive parts in plants 13-14
and their functions
2. Describes the different
7-9,
modes of reproduction in
2 6 20% 11-12
flowering and non-flowering
plants such as moss, fern, 15
mongo and others
3. Discusses the interactions
among living things and 5 15 50% 16-30
non-living things in estuaries
and intertidal zones
TOTAL 10 30 100 29 1
Submitted by :
SHERMA C. ANTONIO
Teacher
Noted:
MA.LUISA E. SANTOS
Principal II
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- EPP-TLE G6 Q1 W5-PrintableDocumento11 pagineEPP-TLE G6 Q1 W5-PrintableAlexis LinaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cot Lesson Plan Science 5 Quarter 3 Week 1Documento5 pagineCot Lesson Plan Science 5 Quarter 3 Week 1Kim Ramos100% (1)
- Secondperiodicaltestenglishgrade3 141011072305 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocumento5 pagineSecondperiodicaltestenglishgrade3 141011072305 Conversion Gate02 PDFelsa catacutanNessuna valutazione finora
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocumento6 pagineMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogLeahNNa vetoricoNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Cycle of Selected AnimalsDocumento26 pagineLife Cycle of Selected AnimalsJoey PatalinghugNessuna valutazione finora
- English Diagnostic TosDocumento2 pagineEnglish Diagnostic TosCarinaJoy Ballesteros Mendez DeGuzman100% (1)
- Art 2 MakilingDocumento7 pagineArt 2 MakilingAnnabelle Poniente HertezNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - English 6 - Q2 - W8Documento5 pagineDLL - English 6 - Q2 - W8Tess DelacNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 4 DLL English Q1 W2Documento8 pagineGrade 4 DLL English Q1 W2Teacher JennetNessuna valutazione finora
- English: Types of Viewing MaterialsDocumento10 pagineEnglish: Types of Viewing MaterialsEthan Lance CuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Three Wishes of The WoodcutterDocumento4 pagineThe Three Wishes of The WoodcutterRenee FeridoNessuna valutazione finora
- SLK Grade 6 Mathematics (Dividing Fractions)Documento10 pagineSLK Grade 6 Mathematics (Dividing Fractions)Rommel YabisNessuna valutazione finora
- Identifying Whether The Materials Are Useful and Harmful.: Performance Tasks in Science 5 First QuarterDocumento4 pagineIdentifying Whether The Materials Are Useful and Harmful.: Performance Tasks in Science 5 First QuarterMichael Edward De Villa50% (2)
- 2ND Periodical Test - Science 5Documento6 pagine2ND Periodical Test - Science 5Eugel Garedo50% (2)
- Bow Mapeh 5Documento4 pagineBow Mapeh 5Micah DejumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cot Science 4 q2 w3Documento54 pagineCot Science 4 q2 w3Frit ZieNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 4 PPT Week 1-Lesson 1-3-Absorb Water-Float and Sink-Undergo Decayed Materials - Melcs Code - S4mt-Ia-1Documento55 pagineScience 4 PPT Week 1-Lesson 1-3-Absorb Water-Float and Sink-Undergo Decayed Materials - Melcs Code - S4mt-Ia-1Jay B. Blanco IVNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Body Adaptation and SurvivalDocumento64 pagineFinal Body Adaptation and SurvivalCatherine Lagario Renante100% (1)
- ENGDocumento5 pagineENGJade ArguillesNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 5 DLL SCIENCE 5 Q4 Week 5Documento4 pagineGrade 5 DLL SCIENCE 5 Q4 Week 5Angelica W. PetinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in English 4Documento4 pagineLesson Plan in English 4Son YongNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuesday: Reference: Araling Panlipunan (Pilipinas Bilang Isang Bansa) Pahina 75-79Documento4 pagineTuesday: Reference: Araling Panlipunan (Pilipinas Bilang Isang Bansa) Pahina 75-79Gil Arriola100% (1)
- By: Rene VillanuevaDocumento14 pagineBy: Rene VillanuevaAlvin SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- TG - SCIENCE 5 Q2 S5LT-II - I-J 10Documento7 pagineTG - SCIENCE 5 Q2 S5LT-II - I-J 10jellyB Rafael100% (1)
- Moduele 5 - English (Differentiate Words With Different Medial Vowels)Documento16 pagineModuele 5 - English (Differentiate Words With Different Medial Vowels)Marisol de BelenNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP in English 4 Week 6 Day 1Documento4 pagineDLP in English 4 Week 6 Day 1John Carlo Dinglasan100% (1)
- MAPEH 6 Q4 Week 1Documento10 pagineMAPEH 6 Q4 Week 1Nicolle Klein100% (2)
- Grade 5 DLL Science 5 q4 Week 1Documento5 pagineGrade 5 DLL Science 5 q4 Week 1Jules Nikko Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Grade 4 DLL Quarter 3 Week 3 (Sir Bien Cruz)Documento45 pagineGrade 4 DLL Quarter 3 Week 3 (Sir Bien Cruz)Maria Ronavie Davalos Mantes100% (1)
- Sonny V. Matias TLE/EPP TeacherDocumento22 pagineSonny V. Matias TLE/EPP TeacherSonny MatiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 5 Quarter 1 Week 3Documento3 pagineScience 5 Quarter 1 Week 3Wex B. Lancee100% (2)
- Q1L5Health - Keeping Homes, Schools and Communities Healthy ThroughDocumento19 pagineQ1L5Health - Keeping Homes, Schools and Communities Healthy ThroughEra Mallari ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- MAPEH-HEALTH6 - Q2-WK4-D4 - Identify Different Types of WasteDocumento14 pagineMAPEH-HEALTH6 - Q2-WK4-D4 - Identify Different Types of WasteglaidzNessuna valutazione finora
- W5 Q1 Day 1-5 Grade 6 Science Module PDFDocumento24 pagineW5 Q1 Day 1-5 Grade 6 Science Module PDFVina LacapNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastery Test q3 w7 and w8Documento11 pagineMastery Test q3 w7 and w8Jo-Ann Santiago PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W7Documento10 pagineDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W7Geoffrey Tolentino-Unida100% (2)
- Tos Mapeh 6 Second Periodic Test 2022 2023 FinalDocumento3 pagineTos Mapeh 6 Second Periodic Test 2022 2023 FinalHero LaguitNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocumento3 pagineGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogJisbert Pablo AmpoNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Mathematics 5 q2 w8Documento8 pagineDLL Mathematics 5 q2 w8Quennee Ronquillo EscobilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Poem VertebratesDocumento1 paginaPoem VertebratesRICARDO ALCARAZ100% (1)
- First Periodical Test in English With TOSDocumento4 pagineFirst Periodical Test in English With TOSNica Joy HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 - Diseases Sickness Resulting From Exposure To Decaying MaterialsDocumento44 pagineLesson 4 - Diseases Sickness Resulting From Exposure To Decaying MaterialsCatherine Renante100% (1)
- DLL English Aug 29-Sept 2Documento2 pagineDLL English Aug 29-Sept 2IvanAbandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Melc - Grade 4 Health - Q3 and Q4Documento3 pagineMelc - Grade 4 Health - Q3 and Q4SALIHAH MARJANNAH SUBA100% (1)
- Grade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk6 - GLAKDocumento20 pagineGrade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk6 - GLAKMelanie TrinidadNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Quarter 2 Week 4 MATHEMATICS 3Documento3 pagineDLL Quarter 2 Week 4 MATHEMATICS 3CRISTILE ANN GESMAN100% (1)
- Science 5 - Q2 - W8Documento6 pagineScience 5 - Q2 - W8Mathleen DescalzoNessuna valutazione finora
- English 5Documento25 pagineEnglish 5Menchie Salvana BaringNessuna valutazione finora
- Cot-1-English 3-Sy23-2024Documento4 pagineCot-1-English 3-Sy23-2024Joyz MadrediñosNessuna valutazione finora
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocumento5 pagineMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogMarichanLooc100% (2)
- Science GR 345 2nd Quarter MG Bow 1Documento7 pagineScience GR 345 2nd Quarter MG Bow 1api-359551623Nessuna valutazione finora
- DLP - Q1 - Week 3Documento9 pagineDLP - Q1 - Week 3IVY MALENessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 03 31 Basa Pilipinas Quarter 3 Grade 1 English Teacher's Guide (Second Edition) PDFDocumento186 pagine2016 03 31 Basa Pilipinas Quarter 3 Grade 1 English Teacher's Guide (Second Edition) PDFIris SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Relative PronounDocumento2 pagineRelative PronounDina RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Objectives:: B.ReferencesDocumento33 pagineI. Objectives:: B.ReferencesKairuz Demson AquilamNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Test in Filipino: Education Program Supervisor/LRMS ManagerDocumento5 paginePost Test in Filipino: Education Program Supervisor/LRMS ManagerFia Jean Nadonza Pascua100% (1)
- Science 5 Quarter 2 Week 6Documento60 pagineScience 5 Quarter 2 Week 6Rhona Liza CanobasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan COT1Documento8 pagineLesson Plan COT1lea mae bayaNessuna valutazione finora
- English 5 Q4 Test & TOSDocumento9 pagineEnglish 5 Q4 Test & TOScristine joy andresNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Culture: Customers CapitalistDocumento9 pagineTypes of Culture: Customers CapitalistIan Cleo TiapeNessuna valutazione finora
- LonganizaDocumento1 paginaLonganizaIan Cleo TiapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Facts About The Population of The Philippines: The Debate On The MethodDocumento10 pagineQuick Facts About The Population of The Philippines: The Debate On The MethodIan Cleo TiapeNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.also Known As Ballroom Dances.: Test IV - EnumerationDocumento1 pagina12.also Known As Ballroom Dances.: Test IV - EnumerationIan Cleo TiapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Caraga Institute of Technology Prelim Exam NSTP 101 Test I.Multiple Choice - Select The Letter of The Correct Answer.3 Pts EachDocumento2 pagineCaraga Institute of Technology Prelim Exam NSTP 101 Test I.Multiple Choice - Select The Letter of The Correct Answer.3 Pts EachIan Cleo TiapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Caraga Institute of Technology Prelim Exam NSTP 101 Test I.Multiple Choice - Select The Letter of The Correct Answer.3 Pts EachDocumento2 pagineCaraga Institute of Technology Prelim Exam NSTP 101 Test I.Multiple Choice - Select The Letter of The Correct Answer.3 Pts EachIan Cleo TiapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem of Myanmar ??Documento8 pagineEcosystem of Myanmar ??aungkhaingmoemyintNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Pollutants On Humans and Other LivingDocumento29 pagineEffects of Pollutants On Humans and Other LivingM.SohailNessuna valutazione finora
- Roxhill Stewardship Report 2007Documento160 pagineRoxhill Stewardship Report 2007WWRHAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Activity # 2 Energy Flow in Ecosystems: The Trophic Pyramids IntroductonDocumento6 pagineLaboratory Activity # 2 Energy Flow in Ecosystems: The Trophic Pyramids IntroductonMAY UNIDANessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Invasive India-Jan08Documento35 pagineAssessment Invasive India-Jan08xyogeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Env InteractionsDocumento16 pagineHuman Env InteractionsPablo XIA HUA PIAO PIAONessuna valutazione finora
- Republic Act No. 7611Documento27 pagineRepublic Act No. 7611Paul John Page PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- GED104 - Science AdvocacyDocumento3 pagineGED104 - Science AdvocacyDian Lovely ManalacNessuna valutazione finora
- Een House Monitoring and Spray Water SystemDocumento2 pagineEen House Monitoring and Spray Water SystemDinesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Aquaculture SystemsDocumento17 pagineIntegrated Aquaculture SystemsArif Dwi NurhudaNessuna valutazione finora
- S.S.T WORKSHEET-4 STD - 4thDocumento2 pagineS.S.T WORKSHEET-4 STD - 4thTejas ShigvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental and Social Impacts HighwayDocumento5 pagineEnvironmental and Social Impacts Highwayjanani004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento4 pagineDaftar PustakaI Gde Dharma AtmajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exhaust Impeller For Hot Mix PlantDocumento3 pagineExhaust Impeller For Hot Mix PlantAarti Varma100% (1)
- Checklist and Conservation Status of Ferns and Lycophytes in AmagDocumento4 pagineChecklist and Conservation Status of Ferns and Lycophytes in AmagPerlita CaneteNessuna valutazione finora
- BESS Report-1Documento2 pagineBESS Report-1AVANTIKA SAXENA Student, Jaipuria LucknowNessuna valutazione finora
- Cropwat SoftwareDocumento9 pagineCropwat SoftwareBuocahgendenk ToekankngapusiNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Readings 2Documento5 pagine11 Readings 2peejay gallatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Urban Agriculture in BostonDocumento32 pagineUrban Agriculture in BostonKathrynEntnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Science & TechnologyDocumento3 pagineEnvironmental Science & Technologymaria glayza corcueraNessuna valutazione finora
- NSTP NotesDocumento4 pagineNSTP NotesVance TansNessuna valutazione finora
- Published-Pdf-327-6-10. IJZAB ID No. 327 PDFDocumento6 paginePublished-Pdf-327-6-10. IJZAB ID No. 327 PDFIJZABNessuna valutazione finora
- Final End2 - Mathayom 2 ScienceDocumento7 pagineFinal End2 - Mathayom 2 ScienceAbdullohNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposed Sanitary Landfill, Its Management and Maintenance in Barangay Bula, Mambusao CapizDocumento44 pagineProposed Sanitary Landfill, Its Management and Maintenance in Barangay Bula, Mambusao CapizIcz FuentesNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Ecology?: Key PointsDocumento7 pagineWhat Is Ecology?: Key PointsMaryam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDocumento20 pagineEcosystem and Its ComponentsarunbvijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Paper Project For E-NurseryDocumento7 pagineReview Paper Project For E-Nurseryanon_64879265350% (2)
- Ritu Thakur Paper 2017 With A K SinghDocumento11 pagineRitu Thakur Paper 2017 With A K SinghRitu ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Date: Time: Location: Speakers:: Points ConcernDocumento1 paginaDate: Time: Location: Speakers:: Points ConcernXuân Quốc TrầnNessuna valutazione finora
- Reasons Against Deforestation - Argumentative Essay - (Essay Example), 668 Words GradesFixerDocumento2 pagineReasons Against Deforestation - Argumentative Essay - (Essay Example), 668 Words GradesFixerTashiNessuna valutazione finora
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDa EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (52)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (393)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDa EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (397)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldDa EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (597)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDa EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (111)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDa EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (116)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (517)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDa EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDa EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNessuna valutazione finora
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDa EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (216)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsDa EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (3)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDa EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (66)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDa EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (812)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouDa EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (62)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignDa EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (19)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueDa EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (38)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessDa EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (18)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignDa EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (39)