Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Arteries of The Spinal Cord and Brainstem
Caricato da
Dr.G.Bhanu PrakashTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Arteries of The Spinal Cord and Brainstem
Caricato da
Dr.G.Bhanu PrakashCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Arteries of the Spinal Cord and Brainstem
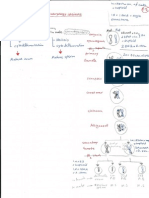
The brainstem and upper spinal cord are supplied by the vertibrobasilar system.
The vertebral artery is a branch of the subclavian artery. The connections of the
vertibrobasilar system from caudal to rostral are as follows:
Vertebral artery → posterior spinal artery (PSA), posterior inferior cerebellar arteries
(PICA), and the anterior spinal artery (ASA).
Both vertebral arteries fuse → basilar artery.
The basilar artery runs along the center of the anterior/ventral pons. Its branches are:
1) The anterior inferior cerebellar arteries (AICA)
2) Multiple pontine arteries
3) The superior cerebellar artery
Superiorly, the basilar artery ends by branching into both posterior cerebral arteries.
The anterior spinal artery and bilateral posterior spinal arteries supply the spinal cord.
The anterior spinal artery supplies all the spinal cord except for the dorsal columns.
The dorsal columns are supplied by the posterior spinal arteries.
The vertebral artery supplies the inferior olivary complex.
The PSA supplies the cuneate and gracile nuclei in the medulla.
Lateral medullary (Wallenberg) syndrome results from damage to structures supplied
by the PICA.
Within the medulla:
1) Nucleus ambiguous (CN IX, X, XI)
2) Lateral spinothalamic tract (anterolateral pathway)
3) Spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus
4) Vestibular nuclei
5) Solitary nuclei and tract
Also supplies the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
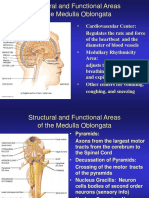
Medial medullary (Dejerine) syndrome results from damage to the following structures
supplied by the ASA.
Structures within the medulla supplied by the ASA:
1) Pyramids
2) Medial lemniscus
3) CN XII (hypoglossal) nerve and nucleus
Branches of the basilar artery supplies the pons. Pontine arteries supply the entire pons,
and some regions receive additional blood supply from either the AICA or superior
cerebellar artery.
The cochlear nucleus (within the medulla) is supplied by the AICA.
Structures within the pons supplied by pontine arteries and the AICA:
1) Facial (CN VII) nerve and nucleus
2) Vestibular nuclei (CNVIII)
3) Trigeminal (CN V) nuclei and nerve
4) Spinal trigeminal tract
5)Inferior and middle cerebellar peduncles
The superior cerebellar artery contributes blood flow to the superior cerebellar
peduncle.
Other structures within the pons supplied only by pontine arteries:
1) Abducent (CN VI) nucleus and nerve
2) Corticospinal fibers
3) Medial leminscus
4) Medial longitudinal fasciculus
Occlusion of the basilar artery results in locked-in syndrome.
The midbrain receives blood supply mostly from branches of the posterior cerebral
artery.
The exception is the superior colliculus, which receives blood via the superior cerebellar
artery.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Arteries of The BrainDocumento2 pagineArteries of The BrainDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigeminal SystemDocumento4 pagineTrigeminal SystemDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventricular SystemDocumento2 pagineVentricular SystemDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- The Spinal CordDocumento3 pagineThe Spinal CordDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- USMLE Step 1 Course DetailsDocumento3 pagineUSMLE Step 1 Course DetailsDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditory SystemDocumento2 pagineAuditory SystemDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- USMLE Step 1 Course DetailsDocumento3 pagineUSMLE Step 1 Course DetailsDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor LesionsDocumento8 pagineMotor LesionsDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolic Enzyme Regulation: GlycolysisDocumento4 pagineMetabolic Enzyme Regulation: GlycolysisBigBoostingNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertensive EmgerenciesDocumento16 pagineHypertensive EmgerenciesDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- The Blood - Physiology DetailedDocumento27 pagineThe Blood - Physiology DetailedDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (2)
- The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: AnatomyDocumento76 pagineThe Cardiovascular System: The Heart: AnatomyadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology Hand Written NotesDocumento22 pagineEmbryology Hand Written NotesDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (1)
- Respiratory Physiology Hand Written NotesDocumento12 pagineRespiratory Physiology Hand Written NotesDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac CycleDocumento38 pagineCardiac CycleDeepika KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Usmle Medical BiochemistryDocumento27 pagineUsmle Medical BiochemistryDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (1)
- Chapter 2Documento26 pagineChapter 2Dr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Obgyn MnemonicsDocumento4 pagineObgyn Mnemonicsapi-3700579100% (17)
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocumento52 pagineAnatomy MnemonicsDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (2)
- Important Points GyeneDocumento9 pagineImportant Points GyeneDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (3)
- Clinical MnemonicsDocumento15 pagineClinical Mnemonicsdr whitegamis100% (2)
- Biochemistry I (CliffsQuickReview) - 193pagDocumento193 pagineBiochemistry I (CliffsQuickReview) - 193pagmcbenze1607100% (5)
- Gims Mbbs Tuition1Documento6 pagineGims Mbbs Tuition1Dr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- GIMS - PLAB Training InstituteDocumento92 pagineGIMS - PLAB Training InstituteDr.G.Bhanu Prakash0% (2)
- Axilla Brachial PlexusDocumento25 pagineAxilla Brachial PlexusDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- ENT McqsDocumento21 pagineENT McqsDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (8)
- ECG DetailedDocumento151 pagineECG DetailedDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Physio UsmleDocumento61 pagineRespiratory Physio UsmleDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (2)
- Usmle Live Classes IndiaDocumento105 pagineUsmle Live Classes IndiaDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Structural and Functional Areas of The BrainDocumento29 pagineStructural and Functional Areas of The BrainRatna PratiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuro SnellDocumento10 pagineNeuro SnellDoodsDiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsurgical Anatomy Brainstem Safe Entry Zones, Jns 2016Documento18 pagineMicrosurgical Anatomy Brainstem Safe Entry Zones, Jns 2016Andrés SeguraNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaDocumento37 pagineIntroduction and Organization of Nervous System: Presented by Dr. Amen FatimaShanailNessuna valutazione finora
- ANAT3411Documento51 pagineANAT3411Kai Dong ChoongNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain StemDocumento4 pagineBrain StemHeart Of Ayurveda Beatrice DNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of Brainstem Pons and MidbrainDocumento4 pagineHistology of Brainstem Pons and MidbrainQairul Azman100% (2)
- J Neurosurg Article p1462Documento15 pagineJ Neurosurg Article p1462Patus QuakusNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Supply of BrainDocumento54 pagineBlood Supply of Brainsaniasddq1110Nessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology of Cns and AnomaliesDocumento111 pagineEmbryology of Cns and AnomaliesBaguma MichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrapyramidal Disorders, OedemaDocumento104 pagineExtrapyramidal Disorders, OedemaAyman RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual Sheep BrainWithDefinitionsDocumento64 pagineLab Manual Sheep BrainWithDefinitionsJJNessuna valutazione finora
- Powerpoint Decompressive CraniectomyDocumento33 paginePowerpoint Decompressive CraniectomySyarif HidayatullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Damasio (2000)Documento8 pagineDamasio (2000)yukos300100% (4)
- COMADocumento30 pagineCOMAnontapat paesarochNessuna valutazione finora
- SHADOWRUN Supplement Issue 06Documento31 pagineSHADOWRUN Supplement Issue 06Danthrall100% (1)
- Anastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockageDocumento5 pagineAnastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockagemcwnotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Twelve Cranial Nerves and Their FunctionsDocumento9 pagineTwelve Cranial Nerves and Their FunctionsKim JacintoNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1 Sleep & Rest-PatternDocumento57 pagineUNIT 1 Sleep & Rest-Patternab tubeNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of Tracts NCSDocumento3 pagineTable of Tracts NCSLuis Manuel Vegas IsasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet Q1 Week 6 The Powers of The MindDocumento3 pagineWorksheet Q1 Week 6 The Powers of The MindKent PesidasNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional NeuroanatomyDocumento23 pagineFunctional NeuroanatomyDaniela GrigoraşNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 1 Mental Health NursingDocumento62 pagineDocument 1 Mental Health NursingHardeep KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Practice Questions Gross Anatomy Neurology Neuroanatomy MCQDocumento68 pagine100 Practice Questions Gross Anatomy Neurology Neuroanatomy MCQAdmin Duties100% (1)
- Blink Reflex: AnatomyDocumento5 pagineBlink Reflex: AnatomyedelinNessuna valutazione finora
- Adults MidbrainDocumento2 pagineAdults MidbrainRightBrain PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Brain: Muh - Iqbal BasriDocumento40 pagineThe Brain: Muh - Iqbal Basrinurul rezki fitrianiazisNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroanatomy Notes PDFDocumento66 pagineNeuroanatomy Notes PDFfatimaabeer083% (6)
- Subcortical 1Documento46 pagineSubcortical 1IRSHAD SHAN KNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of CerebellumDocumento25 pagineAnatomy of CerebellumMaysa MasriNessuna valutazione finora