Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Protein Synthesis
Caricato da
AbigailDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Protein Synthesis
Caricato da
AbigailCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Protein synthesis
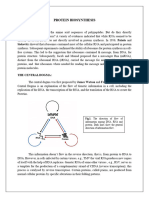
Protein synthesis is one of the most fundamental biological processes by which individuals cells build
their specific proteins. Within these processes involved both DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and there
difference in their function. The process is initiated in the cells nucleus where specific enzymes unwind
the needed section of DNA, which makes the DNA in these region accessible and a RNA copy can be
made. These RNA molecules then moves from the nucleus to the cell cytoplasm where the actual
process of protein synthesis takes place.
All cells functions through protein. Protein function is defined by their molecular function, localization
within cell and involvement in a particular biological process. All component of protein function are
defined by the exact composition, structure and conformation of the protein which when encrypted
within the DNA region called locus encoding that protein.
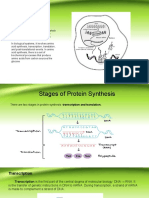
Transcription
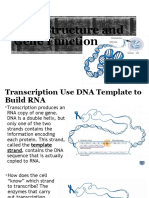
These is the first of overall two protein synthesis steps. During transcription the informatioin encoded in
the DNA is copied to a RNA molecule as one strand of the DNA double helix is used as the template. The
RNA molecule is sent to the cytoplasm, which helps to bring all component required for the actual
protein synthesis together. Amino acid transport RNAs, ribosomes etc. In the cytoplasm the protein
polymers are actually synthesized through chemical reactions i.e Why the process is known as protein
synthesis or even more precisely protein biosynthesis. The RNA copy of the protein genetic information
encoded in DNA molecule is produced in the nucleus and it’s called messenger RNA (mRNA). Each
mRNA encodes the information for a single protein and is much smaller in size compared to the DNA
molecule. These makes it possible for mRNA to exist in the nucleus through tiny opening called nuclear
pores. Once it exit the nucleus and enter the cytoplasm, the mRNA could interact with a cellular
structure known as the divisor which serves as the cells assembler within the process of protein
synthesis. When the mRNA interacts with the big ribosome subunit, these triggers the approach of
another RNA molecule called transfer RNA (tRNA) the tRNA molecule posses a specific sequence of 3-
bases(anti-codon) which has to complement a corresponding sequence within the mRNA sequence.
When it finds it, it attaches to the mRNA at the other end of the tRNA is loaded with an amino acids.
The first tRNA binds to a so called start codon which is the same for all proteins.
Translation
It occurs in the cytoplasm after leaving the nucleus, mRNA must undergo several modifications before
being translated. Sections of the mRNA that do not code for amino acid called introns are removed. A
poly-A tail consisting of several adenine bases is added to one end of the mRNA while the guanosine
triphosphate cap is added to the other end. These modifications remove unneeded sections and
protects the ends of the mRNA molecule
Translation consist of three primary stages
Initiation – ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA
Elongation – the ribosome moves along the mRNA molecule linking amino acid and forming a
polypeptide chain
Termination – the ribosome reaches a stop codon which terminates protein synthesis and
release the ribosome.
Initiation – during translation, a small ribosomal subunit attaches to a mRNA molecule. At the
same time an initiator tRNA molecule recognizes and binds to a specific coding sequence on
the same mRNA molecule. A large ribosomal subunit then joins the newly formed complex. The
initiator tRNA resides in the p sitpermission leaving the second binding site called the A site
open. Once the new tRNA molecule recognizes the next codon sequence on the mRNA, it
attaches to the open A site. A peptide bond forms connecting the amino acid of tRNA in the p
site to a amino acid of tRNA on the A site
Elongation
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineProtein SynthesisArlan AbraganNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A449Documento1 paginaAstm A449Vitor Rigueira de GodoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi-Mechanical Pulping of Napier GrassDocumento98 pagineSemi-Mechanical Pulping of Napier GrassAmelyate NamatNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineProtein SynthesisArlan AbraganNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocumento17 pagineProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- Acetone Production ReportDocumento83 pagineAcetone Production Reportpravalchauha89% (9)
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocumento65 pagineQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Particle Test (MT) : Level IiDocumento18 pagineMagnetic Particle Test (MT) : Level IiAhmed El Morsy100% (1)
- SilaneCouplingAgents eDocumento24 pagineSilaneCouplingAgents eElisabeth Kurnia Bloom100% (1)
- From Gene To ProteinDocumento9 pagineFrom Gene To ProteincrookedspookNessuna valutazione finora
- TranscriptionDocumento25 pagineTranscriptionYamunaa ElencovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Translation 1Documento9 pagineTranslation 1akarshsingh111111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento4 pagineProtein Synthesisyossifwaleed611Nessuna valutazione finora
- AziyatDocumento7 pagineAziyatASHFAQ AHMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein BiosynthesisDocumento21 pagineProtein BiosynthesisMyrrh Tagurigan TrainNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisDocumento3 pagineWhat Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisJennifer JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocumento20 pagineCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocumento8 pagineLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Theme 2 Module 3 Script Slide 1: Slide 2: Your Summary NotesDocumento10 pagineTheme 2 Module 3 Script Slide 1: Slide 2: Your Summary NotesRush KlassyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4Documento3 pagineLab 4Roben CasiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Translation Group 4Documento4 pagineTranslation Group 4Mehboob Ur RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Translation: Protein Biosynthesis Mrna Amino AcidsDocumento4 pagineTranslation: Protein Biosynthesis Mrna Amino AcidsMalick AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.05 - DNA ReplicationDocumento3 pagine3.05 - DNA ReplicationGaurav Chaudhuri100% (1)
- Protein Biosynthesis - 070214Documento7 pagineProtein Biosynthesis - 070214LakshmipriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ribosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Documento16 pagineRibosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Atikatul MutmainahNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Studying BiologyDocumento62 pagineStudying BiologyNicolas AliasNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene ExpressionDocumento58 pagineGene ExpressionJunirose PanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 ReviewerDocumento2 pagineGrade 10 ReviewerLanie De la TorreNessuna valutazione finora
- Kanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyDocumento12 pagineKanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyMuhammad FarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah 9 Gene Expression THB 2022Documento28 pagineKuliah 9 Gene Expression THB 2022Dea puspita DewiNessuna valutazione finora
- S5 Biology (Protein Synthesis)Documento9 pagineS5 Biology (Protein Synthesis)Mwesigwa HannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription: Protein Biosynthesis Is The Process by Which BiologicalDocumento4 pagineTranscription: Protein Biosynthesis Is The Process by Which BiologicalAnand RajNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Structure and Gene Function Part 2Documento12 pagineDNA Structure and Gene Function Part 2Jiro SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio AssignmentDocumento9 pagineBio AssignmentMOHAMMAD IMRAN BIN KASHEMNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein BiosynthesisDocumento7 pagineProtein BiosynthesisOlusola OtasanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Documento13 pagineThe Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Rocelyn VillegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaDocumento13 pagineProtein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaTere CantikkNessuna valutazione finora
- Translation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanDocumento30 pagineTranslation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanCristie Ann GuiamNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineWhat Is Protein SynthesisVaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento2 pagineTranscription and TranslationMary Rose Bobis VicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocumento26 pagine05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 3 - Ribosome - Gavrila Lucian-IonutDocumento3 pagineTema 3 - Ribosome - Gavrila Lucian-IonutIonut ManolescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcript and TranslateDocumento19 pagineTranscript and TranslateSaya AtulNessuna valutazione finora
- Codon ChartDocumento3 pagineCodon ChartMymy SalgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- TranscriptionDocumento4 pagineTranscriptionkaiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Translation - DNA To mRNA To Protein - Learn Science at ScitableDocumento11 pagineTranslation - DNA To mRNA To Protein - Learn Science at ScitableKen KyoushiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Expression and Regulation-TRFDocumento6 pagineGene Expression and Regulation-TRFAnanya PriyadarsineeNessuna valutazione finora
- FROM Gene To Protein  Translation1cDocumento41 pagineFROM Gene To Protein  Translation1cTiffany GordonNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurul Aina HakimaDocumento23 pagineNurul Aina HakimaAdam AdemNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis DefinitionDocumento5 pagineProtein Synthesis Definitioncatherinebitkerrochester100% (2)
- Protein SynthesisDocumento7 pagineProtein SynthesisCreznin YapNessuna valutazione finora
- From Gene To Protein,: Cellular and Sub-Cellular Protein ExpressionDocumento25 pagineFrom Gene To Protein,: Cellular and Sub-Cellular Protein ExpressionPUBG HackerNessuna valutazione finora
- From Dna To ProteinDocumento6 pagineFrom Dna To ProteinMadona BadoevNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento14 pagineProtein SynthesisOginda MokoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento4 pagineProtein SynthesisAvaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento4 pagineProtein SynthesisEvans MogakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft 1Documento11 pagineDraft 1Afiah LutfiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah 9. Translation (Oke)Documento35 pagineKuliah 9. Translation (Oke)Sinta DosiNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis StepsDocumento8 pagineProtein Synthesis Stepsgjga9bey100% (2)
- Lecture 5Documento27 pagineLecture 5Animikh RayNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology - Chapter 17Documento3 pagineAP Biology - Chapter 17Hamin GilNessuna valutazione finora
- TranslationDocumento1 paginaTranslationmeccha ella sojorNessuna valutazione finora
- Bits F111-Course HandoutDocumento3 pagineBits F111-Course HandoutPPNessuna valutazione finora
- 02.01.23 SR - Star Co-Sc (Model-A & B) Jee Main Ctm-2 QPDocumento20 pagine02.01.23 SR - Star Co-Sc (Model-A & B) Jee Main Ctm-2 QPTanay1 MitraNessuna valutazione finora
- F748669CT Process TechnologyDocumento6 pagineF748669CT Process Technologyতুহিন ভট্টাচার্য্যNessuna valutazione finora
- EXPERIMENT 1 DETERMINATION OF REACTION HEAT (Physical Chem)Documento17 pagineEXPERIMENT 1 DETERMINATION OF REACTION HEAT (Physical Chem)siti irdinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Simulation of Intelligent Building FacadesDocumento291 pagineComputer Simulation of Intelligent Building FacadesDobri StefNessuna valutazione finora
- AQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1Documento9 pagineAQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1joeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alloy 6201 Product Specification Rev.4Documento3 pagineAlloy 6201 Product Specification Rev.4Ly PhongNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Boiling and Pool BoilingDocumento9 pagineFlow Boiling and Pool BoilingShivani SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science10 Q4 M3 W5 6 1Documento10 pagineScience10 Q4 M3 W5 6 1Reyydell DelimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Remediation Project 1Documento26 pagineRemediation Project 1api-508660724Nessuna valutazione finora
- ElemeNtS-Technical Offer 2020.5Documento36 pagineElemeNtS-Technical Offer 2020.5jawed iqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento9 pagineChemistryAbhey GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Pollen AllergyDocumento13 pagineWhat Is A Pollen AllergyHuria MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Book 2 Chapter - 15 (Common Chemical Industries in Pakisten)Documento55 pagineChemistry Book 2 Chapter - 15 (Common Chemical Industries in Pakisten)Rana Hassan TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (CHM4301) : Alkenes and AlkynesDocumento19 pagineAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry (CHM4301) : Alkenes and AlkynesAnonymous lClX1bNessuna valutazione finora
- Benzene: Training On The Hazards of Benzene in The WorkplaceDocumento26 pagineBenzene: Training On The Hazards of Benzene in The WorkplaceAgung RahmadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mixtures and Separations-Lecture#1Documento15 pagineMixtures and Separations-Lecture#1victoria0% (1)
- Question Paper CodeDocumento4 pagineQuestion Paper CodeBalaji ArunNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By: Group C Sanjay Kr. Yadav Deepankar Ghosh Natraj S. AdhikariDocumento40 paginePresented By: Group C Sanjay Kr. Yadav Deepankar Ghosh Natraj S. AdhikariBandameedi RamuNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 3025 - 31 - 1 - 2022Documento16 pagineIs 3025 - 31 - 1 - 2022Ruby MalhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuffseald 2G MSDSDocumento12 pagineTuffseald 2G MSDSVijayKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ETPDocumento3 pagineETPSanaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simplified Method For The Cultivation of Extreme Anaerobic Archaea Based SULFIDE 2000 !!!!Documento6 pagineA Simplified Method For The Cultivation of Extreme Anaerobic Archaea Based SULFIDE 2000 !!!!Vera Brok-VolchanskayaNessuna valutazione finora
- ks3 Acids and Alkalis Whats Your Idea PowerpointDocumento11 pagineks3 Acids and Alkalis Whats Your Idea PowerpointManha abdellahNessuna valutazione finora
- Device Turns Air Pollution Into InkDocumento2 pagineDevice Turns Air Pollution Into InkAnonymous izrFWiQNessuna valutazione finora