Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lec24 PDF
Caricato da
Ihab OmarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lec24 PDF
Caricato da
Ihab OmarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Heat Transfer Third Year Dr.Aysar T.
Jarullah
Radiation Heat Transfer
Thermal radiation is that electromagnetic radiation emitted by a body as a result of its
temperature.
Radiation Properties
When radiant energy strikes a material surface, part of the radiation is reflected, part is
absorbed, and part is transmitted.
If
ρ = the fraction reflected = Reflectivity
α = the fraction absorbed = absorptivity
τ = the fraction transmitted = transmissivity
This mean
ρ + α + τ =1
For most solid, τ = 0
ρ + α =1
For black body ρ = 0
Reflection is of Two Types
1- Specular reflection, when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Heat Transfer Third Year Dr.Aysar T. Jarullah
2- Diffuse reflection, when an incident beam is distributed uniformly in all directions
after reflection.
………………………………………………………………………..
The emissive power of a body E is defined as the energy emitted by the body per unit area and
per unit time.
Black body is a body which absorbs all the incident radiation falling upon it. Thus, Eb is the
emissive power of a black body.
E
Є =
Eb
For black body, Є =1
and Eb T 4
Where T is the absolute temperature of a body (K).
The constant proportion (σ) is called Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.669 × 10-8 W/m2.K4
q net A (T14 T24 )
Radiation Shape Factor
Heat Transfer Third Year Dr.Aysar T. Jarullah
Consider two black surfaces A1 and A2, as shown in Figure. The radiation shape factors are
defined as:
F1 − 2 = fraction of energy leaving surface 1 that reaches surface 2
F2 − 1 = fraction of energy leaving surface 2 that reaches surface 1
Fi − j = fraction of energy leaving surface i that reaches surface j
The calculations of shape factors for a few geometries are given in figures 8.12 to 8.16 (also
table 8.2).
The energy leaving surface 1 and arriving at surface 2 =
The energy leaving surface 2 and arriving at surface 1 =
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- RadiationDocumento31 pagineRadiationtristan_aNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat and Mass Transfer ManualDocumento30 pagineHeat and Mass Transfer ManualSushil ThakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 1Documento4 pagineLec 1Anonymous XwZa9BRWBWNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat TransferDocumento72 pagineHeat TransferMontuKumar100% (1)
- Radiation 1Documento26 pagineRadiation 1Malek Marry AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 States of Matter Handout 2Documento6 pagineGrade 10 States of Matter Handout 2Dexter TorringtonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocumento26 pagineChapter 1 IntroductionGeraldine ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Residue (Conradson) TestDocumento17 pagineCarbon Residue (Conradson) TestAi ToolNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiling and Condensation PDFDocumento11 pagineBoiling and Condensation PDFYeditha Satyanarayana MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITDocumento47 pagineGas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITmohan govindasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Actual Indicator Diagram For A Two Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineDocumento3 pagineActual Indicator Diagram For A Two Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN75% (4)
- Basic Principles Basic Transformer Parameters and Construction Construction Conclusion BibliographyDocumento17 pagineBasic Principles Basic Transformer Parameters and Construction Construction Conclusion BibliographySHANKAR PRINTINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Friction and LubricationDocumento7 pagineEngine Friction and Lubricationdzh513Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alkylation PDFDocumento7 pagineAlkylation PDFVasthadu Vasu Khanan DLNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical SystemDocumento75 pagineElectrical SystemS Bharadwaj Reddy67% (3)
- Continuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingDocumento4 pagineContinuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingAnnissa Nur HidayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Illumination1Documento37 pagineChapter 4 Illumination1GurusumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Counting Principles PDFDocumento50 pagineCounting Principles PDFEmir Privado100% (2)
- Basics of Transformer RatingsDocumento2 pagineBasics of Transformer Ratingsavandetq15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transfer - SK MondalDocumento97 pagineHeat Transfer - SK MondalMiguelaTayNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 6Documento5 pagineLec 6Abderrahim HAMDAOUINessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Machines Lab-II ManualDocumento41 pagineElectrical Machines Lab-II Manualsuresh270Nessuna valutazione finora
- Boiling and CondensationDocumento12 pagineBoiling and CondensationKarthik SadasivuniNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocumento16 pagineInternal Combustion EnginesAshton SelokaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-1 Nozzles PDFDocumento69 pagineCh-1 Nozzles PDFCh. Muhammad UsamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Fault CalculationsDocumento124 pagine03 Fault Calculationsfdsfs2131Nessuna valutazione finora
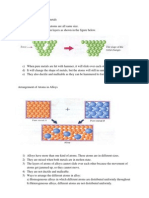
- Arrangement of Atoms in MetalsDocumento12 pagineArrangement of Atoms in MetalsNada AliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Mixtures and CombustionDocumento7 pagineProperties of Mixtures and CombustionKhairul NajmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Me Lab 2Documento14 pagineMe Lab 2Lennin John CaguioaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Chapter 1Documento23 pagineHeat Chapter 1Kale DireNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Friction PDFDocumento24 pagineEngine Friction PDFsushil.vgiNessuna valutazione finora
- HMT - 2 Marks PDFDocumento29 pagineHMT - 2 Marks PDFFaiyu MechNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdocuments - in 1 Introduction To Heat TransferDocumento12 pagineFdocuments - in 1 Introduction To Heat TransferShafqat HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 RadiationDocumento47 pagineChapter 4 RadiationKamal JamaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Convection: Its Free, No Operating Cost! .. Its Natural .Documento34 pagineFree Convection: Its Free, No Operating Cost! .. Its Natural .zeeshanahmad111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Qip Ice 23 Lubrication SystemsDocumento24 pagineQip Ice 23 Lubrication SystemsMohan Kumar SNessuna valutazione finora
- Stefan's Law of RadiationDocumento7 pagineStefan's Law of RadiationHema AnilkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- RAC Assignments 24062016 091508AMDocumento37 pagineRAC Assignments 24062016 091508AMsakalidhasavasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium ChartsDocumento29 pagineEquilibrium ChartsanikfaisalNessuna valutazione finora
- Eme Question BankDocumento13 pagineEme Question Bankapi-315791751Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Harmonic Motion NotesDocumento9 pagineSimple Harmonic Motion Noteslouis parchmentNessuna valutazione finora
- TOP 250+ Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers 07 August 2021 - Thermodynamics Interview Questions - Wisdom Jobs IndiaDocumento23 pagineTOP 250+ Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers 07 August 2021 - Thermodynamics Interview Questions - Wisdom Jobs IndiaHELL RIDERNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Gas DynamicsDocumento12 pagineIntroduction To Gas DynamicsAswin Varghese TharakanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ideal and Practical TransformerDocumento8 pagineIdeal and Practical TransformerChintal.vinodNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuels and CombustionDocumento12 pagineFuels and CombustionAbhishek PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Power CycleDocumento44 pagineChapter 2 Power CycleBese Mat100% (1)
- Classification of Internal Combustion EnginesDocumento51 pagineClassification of Internal Combustion Engineskunkalamarru100% (1)
- Chap 012Documento50 pagineChap 012Nguyễn TúNessuna valutazione finora
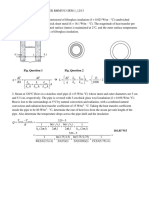
- L A K L A K L T RA T Q K K L K L Q T L: Fig. Question 1 Fig. Question 2 Fig. Question 3Documento2 pagineL A K L A K L T RA T Q K K L K L Q T L: Fig. Question 1 Fig. Question 2 Fig. Question 3Bi100% (1)
- Interview Questions (TD)Documento9 pagineInterview Questions (TD)anil gautamNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Week 1 CC PDFDocumento2 pagineAssignment Week 1 CC PDFPushparaj MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Circuits 3 QPDocumento7 pagineElectric Circuits 3 QPPREM OfFiCiAlNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbomachines Intro 1Documento22 pagineTurbomachines Intro 1Mukul Goyal0% (1)
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocumento9 pagineChapter 1 IntroductionNikko ManaleseNessuna valutazione finora
- FEA Interview Questions Module 1Documento22 pagineFEA Interview Questions Module 1Namit MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Free VibrationsDocumento27 pagineFree Vibrationshelllooo00Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 314 Lecture NoteDocumento47 pagineCHE 314 Lecture NoteojigbijojomayeNessuna valutazione finora
- HMT Module V Class NoteDocumento20 pagineHMT Module V Class NoteJithosh BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- HT Lecture 16 RadiationDocumento21 pagineHT Lecture 16 Radiationramasubbaiah vussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transport by RadiationDocumento19 pagineHeat Transport by RadiationLuizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 27Documento11 pagineLec 27Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 26Documento8 pagineLec 26Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Machines. Mr. Subhadeep Mandal. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Tutorial-8Documento8 pagineFluid Machines. Mr. Subhadeep Mandal. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Tutorial-8Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Machines. Professor Sankar Kumar Som. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-13. Draft TubeDocumento8 pagineFluid Machines. Professor Sankar Kumar Som. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-13. Draft TubeAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Machines. Mr. Sayan Das. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Tutorial-7Documento10 pagineFluid Machines. Mr. Sayan Das. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Tutorial-7Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Machines.: Mr. Sayan Das. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento11 pagineFluid Machines.: Mr. Sayan Das. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical EngineeringAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Machines. Mr. Sayan Das. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Tutorial-3Documento11 pagineFluid Machines. Mr. Sayan Das. Teaching Assistant. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Tutorial-3Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Correction Factor For Complex H.E (F) : T AUF QDocumento4 pagineCorrection Factor For Complex H.E (F) : T AUF QAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 12Documento10 pagineLec 12Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- LECTURE 5 - Stress-Strain DiagramDocumento5 pagineLECTURE 5 - Stress-Strain DiagramAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 38Documento10 pagineLec 38Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 3Documento4 pagineLec 3Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 7Documento4 pagineLect 7Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Across Cylinder and SpheresDocumento4 pagineFlow Across Cylinder and SpheresAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Across Tube Banks: PR - ReDocumento3 pagineFlow Across Tube Banks: PR - ReAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 10Documento6 pagineLec 10Anonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 8Documento4 pagineLec 8Anonymous 2BJgxbxJ0% (1)
- Lec10 PDFDocumento3 pagineLec10 PDFAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
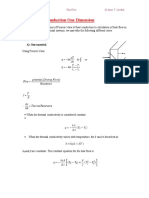
- Heat Source Systems: 1-Plane Wall With Heat SourcesDocumento5 pagineHeat Source Systems: 1-Plane Wall With Heat SourcesAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- The Overall Heat Transfer CoefficientDocumento5 pagineThe Overall Heat Transfer CoefficientAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transfer Third Year DR - Aysar T. JarullahDocumento2 pagineHeat Transfer Third Year DR - Aysar T. JarullahAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Conductivity: Gases Liquids SolidsDocumento4 pagineThermal Conductivity: Gases Liquids SolidsAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Introduction To CompressorsDocumento6 pagine2 Introduction To CompressorsAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 KG of Air Is Compressed PolytropicallyDocumento1 pagina1 KG of Air Is Compressed PolytropicallyAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora