Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Economics Overview
Caricato da
mkpatidarDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Economics Overview
Caricato da
mkpatidarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mahendra K Patidar / PGDM BIF / 017 / 091604 86684
BASIC ECONOMICS: AN OVERVIEW
Economics is originated from a Greek term ‘OIKONOMIKOS’, which means house
management.
Every economic system, irrespective of its nature, is required to face three kind of economic
problems:
What to produce and in what Quantities?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
Economics: “Economics is the science which studies human behavior as a relationship
between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses”.
The term ‘Micro Economics’ and ‘Macro Economics’ were first coined and used by Ragnar
Frisch.
‘Micro Economics was popularized by Alfred Marshall
‘Macro Economics’ was popularized by JM Keynes.
Micro Economics is also called ‘Price Theory’, because it explains pricing in factor market
and product market.
Macro Economics is also called ‘Income and Employment Theory’.
‘Micro Economics’ concerned with the economic activities of economic units as consumers,
resource owners and business units. ---LeftWitch
‘Macro Economics’ studies national income not individual income, general price level
instead of individual prices and national output instead of individual output. ---KE Boulding
Equilibrium refers to a situation in which economics agents satisfy with the existing
allocation of resources and do not want any further change.
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: HH Gossen was the first economist to esplain the law
of diminishing marginal utility in 1854. In the words of Prof Boulding “As a consumer
increases the consumption of any one commodity, keeping constant the consumption of all
other commodities, the marginal utility of the variable commodity must eventually
(ultimately) decline”.
Elasticity of Demand: The degree to which quantity demanded responds to change in price
is known as Elasticity of Demand.
1
Page
Mahendra K Patidar / PGDM BIF / 017 / 091604 86684
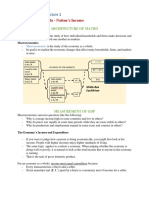
Gross National Product (GNP): It is the total value of all final goods and services produced in
the economy in one year.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): The market value of the total goods and services produces in
a country in one particular period usually in a year. If net foreign income deducted from
GNP, we get GDP.
Net National Product (NNP) = GNP - Depreciation
Net Domestic Product (NDP) = GDP - Depreciation
Methods for measurement of National Income:
Output Method
Expenditure method
Income Method
2
Page
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Train Your GirlfriendDocumento124 pagineTrain Your GirlfriendRobin Graham70% (10)
- General Insurance GlossaryDocumento50 pagineGeneral Insurance GlossarymkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Controls Matrix v3 0 1Documento1.304 pagineCloud Controls Matrix v3 0 1IT SecurityNessuna valutazione finora
- (DOH HPB) PA5 Playbook - Peer Support Groups For The YouthDocumento88 pagine(DOH HPB) PA5 Playbook - Peer Support Groups For The YouthKaren Jardeleza Quejano100% (1)
- Macroeconomics Basic ConceptsDocumento20 pagineMacroeconomics Basic Conceptsneo0157Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Suspense Practice Q HDocumento5 pagineChapter 6 Suspense Practice Q HSuy YanghearNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Introduction To EconomicsDocumento24 pagine1 Introduction To Economicsrommel legaspiNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Economics and Financial Analysis: Unit - 1Documento42 pagineBusiness Economics and Financial Analysis: Unit - 1Mohd YounusNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics Notes Unit I & IIDocumento13 pagineMacroeconomics Notes Unit I & IISwathi PabbathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Macro Economics-PPT..1Documento72 pagineMacro Economics-PPT..1Taposh Sarkar100% (1)
- Financial, Cost and Management AccountingDocumento82 pagineFinancial, Cost and Management Accountingmkpatidar100% (1)
- Introduction To Economic AnalysisDocumento18 pagineIntroduction To Economic AnalysiskrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- CondrenDocumento303 pagineCondrenbebelizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cassino To The Alps - US Army Center of Military HistoryDocumento625 pagineCassino To The Alps - US Army Center of Military HistoryBootlead BootleadingNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Considerations For A Successful Hyperion Planning ImplementationDocumento45 pagineKey Considerations For A Successful Hyperion Planning Implementationayansane635Nessuna valutazione finora
- National IncomeDocumento129 pagineNational IncomeBabli PattanaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment Planning (Asset Allocation - Concepts & Practices)Documento40 pagineInvestment Planning (Asset Allocation - Concepts & Practices)mkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester 2Documento761 pagineSemester 2kajal goyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Join The Following Sentences Using A Relative PronounDocumento2 pagineJoin The Following Sentences Using A Relative PronounIsabel SoteleNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 27001Documento84 pagineIso 27001sboukhal100% (2)
- RP FinalDocumento125 pagineRP FinalAditya SoumavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Compendium: Economics and FinanceDocumento14 pagineCompendium: Economics and Financegaurav jainNessuna valutazione finora
- M E Final 1 IntroDocumento12 pagineM E Final 1 IntroNikhil LathiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Macroeconomic ActivityDocumento3 pagineIntroduction To Macroeconomic ActivityTrisha RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- MacroDocumento3 pagineMacroMay AnNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter No:02: National Income Accounting & Its MeasurementsDocumento34 pagineChapter No:02: National Income Accounting & Its MeasurementsIhtisham AfridiNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomic Data - Nation's Income: Macroeconomics: Lecture 1Documento6 pagineMacroeconomic Data - Nation's Income: Macroeconomics: Lecture 1АдамNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec2 06 AugDocumento23 pagineLec2 06 AugPragya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- MacroeconomicsDocumento212 pagineMacroeconomicschichipmunk1225Nessuna valutazione finora
- PBD Module 1 NotesDocumento13 paginePBD Module 1 Notesafshots422Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7 National Income PART I: National Income Accounting: Macro./ Topic 7 / P.1Documento6 pagine7 National Income PART I: National Income Accounting: Macro./ Topic 7 / P.1ishan_mNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics 12TH NotesDocumento18 pagineEconomics 12TH NotesVinothini SridhaarNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Macro EconomicsDocumento20 pagineSummary of Macro EconomicsYogesh JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Economies by Dr. K. S.Narayana Introduction To Economies by Dr. K. S.NarayanaDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Economies by Dr. K. S.Narayana Introduction To Economies by Dr. K. S.NarayanaRajKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- KTEE203Documento8 pagineKTEE203Nhi Nguyễn Trần LiênNessuna valutazione finora
- For An Economy As A Whole, Income Must Equal ExpenditureDocumento3 pagineFor An Economy As A Whole, Income Must Equal ExpenditureGianne AbcedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics BestDocumento73 pagineEconomics BestMuzamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of National IncomeDocumento72 pagineTheory of National IncomeAlex RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Macro Economics 1Documento9 pagineMacro Economics 1Deepak SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Marathon Class (Part 1) - Indian Economy For UPSC EPFODocumento41 pagineMarathon Class (Part 1) - Indian Economy For UPSC EPFOdiwakarj7_310135942Nessuna valutazione finora
- Economics by Nitesh SirDocumento73 pagineEconomics by Nitesh SirKhalid gowharNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics For Final PDFDocumento14 pagineMacroeconomics For Final PDFFahima Jahan AyeshaNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT I - The Realm of MacroeconomicsDocumento7 pagineUNIT I - The Realm of MacroeconomicsAkeem TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncert Notes For Economics: 12th StandardDocumento39 pagineNcert Notes For Economics: 12th StandardNagaraj MulgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Institute of Plantation Management, Bengaluru: A Report OnDocumento12 pagineIndian Institute of Plantation Management, Bengaluru: A Report OnGOWRI SHANKARNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro of MacroDocumento3 pagineIntro of MacroSam LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics: Principles ofDocumento56 pagineMacroeconomics: Principles ofKogo VickNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring National Income and Output: Group 3Documento64 pagineMeasuring National Income and Output: Group 3Jester de ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- EconomicsDocumento19 pagineEconomicsrajdino80Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Part ADocumento38 pagineUnit 1 Part Avansh.meghawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Macro Economics For Business DecisionsDocumento86 pagineMacro Economics For Business DecisionsViraja GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- 5th Semester EconomicsDocumento64 pagine5th Semester EconomicsVivaan BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- National Income-Zunaira AhmedDocumento31 pagineNational Income-Zunaira AhmedMuhammad AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- (Macro) SlidesDocumento212 pagine(Macro) SlidesMinh NgọcNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Economics For OrganisationsDocumento25 pagineManagerial Economics For OrganisationsAbhishek ModakNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Meaning and Approaches of National Income AccountingDocumento20 pagine2.1 Meaning and Approaches of National Income Accountingabadi gebruNessuna valutazione finora
- C1,2,3,4 (Updated)Documento59 pagineC1,2,3,4 (Updated)Châu Nguyễn Hoài ThùyNessuna valutazione finora
- MACRO 1 NotesDocumento33 pagineMACRO 1 NotesPride ChinonzuraNessuna valutazione finora
- National Income Accounting Lesson 1Documento12 pagineNational Income Accounting Lesson 1Tension Dene kaNessuna valutazione finora
- National IncomeDocumento45 pagineNational IncomeAnil LouraNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1Documento3 pagineTopic 1Benard BettNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4-National Income 1Documento26 pagineUnit 4-National Income 1tempacc9322Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 and Lesson 2Documento21 pagineLesson 1 and Lesson 2Qui BuiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Following Are Some of The Important Uses of National Income StatisticsDocumento11 pagineThe Following Are Some of The Important Uses of National Income StatisticsMarilyn BasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Macro EconomicsDocumento22 pagineSummary of Macro EconomicsAk GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics 2022Documento212 pagineMacroeconomics 2022duy phamNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Economy Notes by Anish Mohan (Updated)Documento122 pagineComplete Economy Notes by Anish Mohan (Updated)Chinmay JagtapNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics IDocumento213 pagineMacroeconomics IchiNessuna valutazione finora
- N13 2013 Intro To Economics Chapter 12 - Macro IntroDocumento16 pagineN13 2013 Intro To Economics Chapter 12 - Macro IntroRick DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Notes MA 1Documento164 pagineClass Notes MA 1Nagesh KambleNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics I-2009Documento205 pagineMacroeconomics I-2009Nguyễn Dung100% (1)
- CircularDocumento10 pagineCircularsebaresearchNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Of "The Economic System" By Armando Fastman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESDa EverandSummary Of "The Economic System" By Armando Fastman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNessuna valutazione finora
- Inventure: Mahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, HyderabadDocumento21 pagineInventure: Mahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, HyderabadmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Markets: Mahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, HyderabadDocumento22 pagineFinancial Markets: Mahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, HyderabadmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hedge Funds ShowDocumento33 pagineHedge Funds ShowmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Public PolicyDocumento8 paginePublic PolicymkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, HyderabadDocumento12 pagineMahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, Hyderabadmkpatidar100% (1)
- Financial and Credit Analysis: Mahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, HyderabadDocumento58 pagineFinancial and Credit Analysis: Mahendra K Patidar Pgdmbif Institute of Public Enterprise, HyderabadmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Commodity MarketsDocumento24 pagineCommodity MarketsmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Madhya PradeshDocumento4 pagineMadhya PradeshmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Am It Hi PaperDocumento10 pagineOperations Am It Hi PapermkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Economic IndicatorsDocumento2 pagineEconomic IndicatorsmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Insurance GlossaryDocumento25 pagineInsurance GlossarymkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental AnalysisDocumento7 pagineFundamental AnalysismkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Equity DerivativeDocumento2 pagineEquity DerivativemkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- BANKING A Placement PerspectiveDocumento8 pagineBANKING A Placement PerspectivemkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- ComputerDocumento12 pagineComputermkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- DesktopDocumento8 pagineDesktopmkpatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Demystifying Sheikh AbdullahDocumento4 pagineDemystifying Sheikh Abdullahveeraragavan.nNessuna valutazione finora
- WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT of The Ultra Light Technology. VidishaDocumento49 pagineWORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT of The Ultra Light Technology. Vidishasai projectNessuna valutazione finora
- Balance and Safety Mechanism PDFDocumento11 pagineBalance and Safety Mechanism PDFKhesmin KapilNessuna valutazione finora
- Affidavit of Probable Cause: ArresteeDocumento3 pagineAffidavit of Probable Cause: ArresteeMcKenzie StaufferNessuna valutazione finora
- Conflicts of IntrestDocumento11 pagineConflicts of IntrestDRx Sonali TareiNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant HR Business Partner in Chicago IL Resume David AndreDocumento2 paginePlant HR Business Partner in Chicago IL Resume David AndreDavidAndreNessuna valutazione finora
- School Teacher Profile DetailsDocumento17 pagineSchool Teacher Profile Detailskn.sateeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Contemporaries of ChaucerDocumento3 pagineContemporaries of ChaucerGarret RajaNessuna valutazione finora
- September 12 2023 Meeting MinutesDocumento5 pagineSeptember 12 2023 Meeting Minutesapi-156333616Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 PDFDocumento39 pagineUnit 2 PDFNoorie AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal 6 (Current Account Deficit) PDFDocumento24 pagineJournal 6 (Current Account Deficit) PDFdaniswara 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- End Of: Memory, Countermemory, and The The MonumentDocumento15 pagineEnd Of: Memory, Countermemory, and The The MonumentveidtNessuna valutazione finora
- 202 CẶP ĐỒNG NGHĨA TRONG TOEICDocumento8 pagine202 CẶP ĐỒNG NGHĨA TRONG TOEICKim QuyênNessuna valutazione finora
- MABX 2014 Construction Buyers GuideDocumento158 pagineMABX 2014 Construction Buyers Guidemabx_PANessuna valutazione finora
- Journey of The Company:: Carlyle Group Completes 10 % Exit in SBI Card Through IPODocumento3 pagineJourney of The Company:: Carlyle Group Completes 10 % Exit in SBI Card Through IPOJayash KaushalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Invention of The Female Mind - Women, Property and Gender Ideology in Archaic GreeceDocumento2 pagineThe Invention of The Female Mind - Women, Property and Gender Ideology in Archaic GreecegfvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Curso Inglés Desde CERO - Nivel Básico - 21-25Documento11 pagineCurso Inglés Desde CERO - Nivel Básico - 21-25david morrisonNessuna valutazione finora
- English Silver BookDocumento24 pagineEnglish Silver BookQamar Asghar Ara'inNessuna valutazione finora
- SEEBURGER WebEDI Wilo ENDocumento1 paginaSEEBURGER WebEDI Wilo ENmarketingNessuna valutazione finora