Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit V: Z - Transforms and Difference Equations
Caricato da
poojaabanindran100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
144 visualizzazioni2 pagineTitolo originale
UNIT 5 ZT_WS .docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
144 visualizzazioni2 pagineUnit V: Z - Transforms and Difference Equations
Caricato da
poojaabanindranCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING(AUTONOMOUS)
DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MATHEMATICS
SUBJECT: MA16351 MATHEMATICS-III
UNIT V: Z -TRANSFORMS AND DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS
PART- A
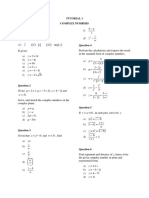
1. Define z-transform of the sequence x(n).
2. Find the Z transforms of the following:
1
(i) (ii) e iat (iii) (n 2) (iv) r n cos n & r n sin n .
( n 1)!
3. Find the Z transforms of the following:
an
(i) n 2 (ii) (n 1)( n 2) (iii) (iv) a n sin n (v) a n cosh n (vi) e t t 2
n!
(vii) e t sin 2t (viii) e 3t cos t .
4. State and prove Initial value theorem and First shifting theorem.
5. State convolution theorem on z-transforms.
z 1
z
6. Evaluate (i) Z 1 2 . (ii) Z 2
z 7 z 10 z 1
7. Form difference equation from (i) U n a 2 n 1 (ii) y n a b3 n (iii) y n a 2 n b(2) n
(iv) y ax bx 2 .
PART-B
1. Find the z-transform of cos n and hence find Z (n cos n ) .
1 n n n
2. Find the z-transform of , cos and a cos .
n 2 2
3. Find the Z-transform of a n , na n and a n cos .
1 z
4. Prove that Z z log .
n 1 z 1
1
5. Find the Z-transform of .
(n 1)( n 2)
2n 3
6. Find the Z-transform of f (n) .
(n 1)( n 2)
7. State and prove Final value theorem.
8. State and prove second shifting theorem.
z2 z2
9. Using Convolution theorem find inverse Z-transforms of (i) (ii)
( z a)( z b) ( z a) 2
8z 2 z2 12 z 2 z2
(iii) (iv) (v) (vi) .
(2 z 1)(4 z 1) ( z 1)( z 3) (3z 1)( 4 z 1) 1 1
( z )( z )
2 4
z 3 3z z ( z 2 z 2)
10. Using partial fractions find inverse Z-transforms of (i) (ii)
( z 1) 2 ( z 2 1) ( z 1)( z 1) 2
z3 z ( z 1) 2 z 2 3z 3z 2 18 z 26
(iii) (iv) (v) (vi) .
( z 1) 2 ( z 2) ( z 1)( z 2 1) ( z 2)( z 4) ( z 2)( z 3)( z 4)
z z ( z 2)
11. Using the method of long division find inverse Z-transforms of (i) (ii) 2
( z 1) 2
z 2z 4
10 z z2 z
(iii) (iv) .
( z 1)( z 2) ( z 1) 3
4z 2 2z z ( z 2 1)
12. Using the method of residues find inverse Z-transforms of (i) (ii)
z 3 5z 2 8z 4 ( z 2 1) 2
2z 3z
(ii) (iv) .
( z 1)( z 1)
2
( z 1)( z 2)
13. Solve the following difference equations using z-transforms:
(i) y(n 2) 6 y(n 1) 9 y(n) 2 n given that y (0) 0 and y (1) 0.
(ii) y (n) 3 y (n 1) 4 y (n 2) 0, n 2 given that y (0) 3 and y (1) 2.
(iii) y n 2 y n 2 given that y0 y1 0.
(iv) y n 2 4 y n 0.
(v) u n 2 2u n1 u n 3n 5.
(vi) u n 2 4u n 1 3u n 3 n With u 0 0, u1 1.
(vii) y (n 3) 3 y (n 1) 2 y (n) 0, y (0) 4, y (1) 0 and y (2) 8.
(viii) u n2 4u n1 5u n 24n 8 given that u 0 3, u1 5.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Arfken Solutions Manual 7th Ed PDFDocumento524 pagineArfken Solutions Manual 7th Ed PDFBolaybalam84% (77)
- Cleaning Validation ProtocolDocumento6 pagineCleaning Validation ProtocolVega life sciences100% (1)
- Water TreatmentDocumento153 pagineWater Treatmentpoojaabanindran100% (1)
- Unit 4 Fourier Transforms Lecture Notes PDFDocumento30 pagineUnit 4 Fourier Transforms Lecture Notes PDFpoojaabanindran100% (1)
- MCQ 4 GroundwaterDocumento6 pagineMCQ 4 GroundwaterAnonymous EvbW4o1U7100% (4)
- IMP 2 Marks With AnswersDocumento6 pagineIMP 2 Marks With AnswersvimalNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 - MHZ5530 2017-18Documento2 pagineAssignment 2 - MHZ5530 2017-18Madusanka WeebeddaNessuna valutazione finora
- MA2002D - Tutorial Sheet 2-23.01.2023Documento2 pagineMA2002D - Tutorial Sheet 2-23.01.2023B SakethNessuna valutazione finora
- MP DPP Sheet 5Documento3 pagineMP DPP Sheet 5Kunish GargNessuna valutazione finora
- StupidDocumento12 pagineStupidLavan KapelNessuna valutazione finora
- Nta Net/Jrf Dec 2020Documento4 pagineNta Net/Jrf Dec 2020Kunish GargNessuna valutazione finora
- MP DPP Sheet 6Documento4 pagineMP DPP Sheet 6Kunish GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Important Facts and Formulae For JeeDocumento68 pagineMathematics Important Facts and Formulae For JeetestbangaloreNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 5 23Documento2 pagineAssignment 5 23Ahammad Mostafa HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- TpdeDocumento2 pagineTpdeAbhishekNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento2 pagineGujarat Technological UniversityVedant SonawaneNessuna valutazione finora
- ASG Sir Complex (Moderate)Documento8 pagineASG Sir Complex (Moderate)Atharv AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- S.E (2019 Pattern) - 2023-80-84Documento5 pagineS.E (2019 Pattern) - 2023-80-84somnath swamiNessuna valutazione finora
- BTMA 301: Quiz, Assignment & QB Unit - IDocumento20 pagineBTMA 301: Quiz, Assignment & QB Unit - IAnushkaNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Tutorial. 05 09 2023Documento2 pagine21 Tutorial. 05 09 2023abhimanyu.yadav2022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Complex IntegrationDocumento22 pagineComplex IntegrationSreeram VijapurapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Krishna Adithya: Department of Mathematics Unit Wise Question BankDocumento9 pagineSri Krishna Adithya: Department of Mathematics Unit Wise Question Bankrevathy100% (1)
- MATH 311: Midterm Review Questions Spring 2017Documento12 pagineMATH 311: Midterm Review Questions Spring 2017Anonymous ijsmXCn3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento2 pagineGujarat Technological UniversityYo Yo AkNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento2 pagineGujarat Technological UniversityVedant SonawaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento2 pagineGujarat Technological UniversityAnkitaNessuna valutazione finora
- SR MATHS IIA VSAQ SOLUTIONS Bfd62d0a A987 4635 Adb9 B4da28bf5d2eDocumento44 pagineSR MATHS IIA VSAQ SOLUTIONS Bfd62d0a A987 4635 Adb9 B4da28bf5d2eMohith NakkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Differentiation&Vector Integration QBDocumento4 pagineVector Differentiation&Vector Integration QBS AdilakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5, Tutorial 2 TBVP SRM TutorialDocumento1 paginaUnit 5, Tutorial 2 TBVP SRM Tutorialnobita upmanyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment MAL 201 Z-TransDocumento1 paginaAssignment MAL 201 Z-TransVijay GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Svce Maths Unit IIDocumento2 pagineSvce Maths Unit IIrangarajan691174Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment2 Sem2 IpuDocumento2 pagineAssignment2 Sem2 IpuVansh SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- BA224 Lec 9Documento11 pagineBA224 Lec 9selimhany10107575Nessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Class 11 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 5 (PDF)Documento22 pagineComplex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Class 11 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 5 (PDF)Dezma 0007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Numbers 02 - Practice Sheet - JEE Challengers 2023Documento7 pagineComplex Numbers 02 - Practice Sheet - JEE Challengers 2023ttojo7105Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 5 TPDE Z Transform LECTURE NOTES PDFDocumento30 pagineUNIT 5 TPDE Z Transform LECTURE NOTES PDFpoojaabanindran0% (2)
- Z Transforms WorksheetsDocumento4 pagineZ Transforms Worksheetspilas_nikolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Taylor's Theorem: Suppose ThatDocumento101 pagineTaylor's Theorem: Suppose ThatShashwat RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex NumberDocumento3 pagineComplex Numberdeek_jNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers: L-1 M-14.1 Suggested ProblemsDocumento3 pagineAnswers: L-1 M-14.1 Suggested ProblemsSubrata KarmakarNessuna valutazione finora
- 478 - PHS 472 MathematicalDocumento14 pagine478 - PHS 472 MathematicalAyomikunNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Functions in Complex AnalysisDocumento26 pagineAnalytic Functions in Complex AnalysisJian's ShahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Tpde Z Transform 2015Documento26 pagineTpde Z Transform 2015MOHAMED FAIZALNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Assingment IIIDocumento1 paginaDigital Assingment IIIRudransh KatiyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign 2Documento1 paginaAssign 2R TharunishNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 - Complex Integration - Tutorial 1Documento1 paginaUnit 5 - Complex Integration - Tutorial 1tanishqsharma05112003Nessuna valutazione finora
- M11 Wk07 WS 2021 Complex Numbers 2 WS Studen - 1626347787297 - KirCgDocumento1 paginaM11 Wk07 WS 2021 Complex Numbers 2 WS Studen - 1626347787297 - KirCgRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANNessuna valutazione finora
- NCB 10103: Mathematics For Engineers 1 Complex Number Tutorial 5Documento5 pagineNCB 10103: Mathematics For Engineers 1 Complex Number Tutorial 5aNessuna valutazione finora
- MA5252 Engineering Mathematics II Unit IIDocumento3 pagineMA5252 Engineering Mathematics II Unit IIKarunambika ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 - Complex Number SystemDocumento8 pagineChapter-1 - Complex Number Systemajwa telNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 04 SET (31-34)Documento5 paginePart 04 SET (31-34)Amit AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- SUMSEM2022-23 MAT3003 TH VL2022230700106 2023-05-26 Reference-Material-IDocumento4 pagineSUMSEM2022-23 MAT3003 TH VL2022230700106 2023-05-26 Reference-Material-IRaunak SenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1000 Most Important Questions For Jee - Part 3: 1. The ValueDocumento34 pagine1000 Most Important Questions For Jee - Part 3: 1. The ValueraunitNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Analysis: 5.1 Basic Review of Complex NumbersDocumento22 pagineComplex Analysis: 5.1 Basic Review of Complex NumbersAnil karelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Set Unit-3 (Modefied)Documento3 paginePractice Set Unit-3 (Modefied)yedotanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics-Iia: S.No Nam of The Chapter Weightage MarksDocumento42 pagineMathematics-Iia: S.No Nam of The Chapter Weightage MarksMoscowNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT V - MA6351 TPDE - Z - Transform - LECTURE NOTES PDFDocumento30 pagineUNIT V - MA6351 TPDE - Z - Transform - LECTURE NOTES PDFRaghul TNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Note: Study Similar Model Problems With Different Data Values AlsoDocumento4 pagineImportant Note: Study Similar Model Problems With Different Data Values AlsoMr PerfectNessuna valutazione finora
- TBL Polar Coordinates QuestionDocumento2 pagineTBL Polar Coordinates QuestionMAISARAH BINTI ISHAK UnknownNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment PDEDocumento2 pagineAssignment PDESANGIT PRADHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1Documento2 pagineTutorial 1hockweng tanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1Documento2 pagineTutorial 1hockweng tanNessuna valutazione finora
- SR Maths - IiaDocumento12 pagineSR Maths - IiaNandhan MedaramittaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Da EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesDa EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesValutazione: 1.5 su 5 stelle1.5/5 (2)
- TrafficDocumento1 paginaTrafficpoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V: Z-Transforms and Difference Equations: Department of Applied Mathematics Sri Venkateswara College of EngineeringDocumento93 pagineUnit V: Z-Transforms and Difference Equations: Department of Applied Mathematics Sri Venkateswara College of EngineeringpoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- AnalysisDocumento6 pagineAnalysispoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- FourierDocumento3 pagineFourierpoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V: Z - Transforms and Difference EquationsDocumento2 pagineUnit V: Z - Transforms and Difference Equationspoojaabanindran100% (1)
- Unit 5-Dimension and Model Analysis PDFDocumento40 pagineUnit 5-Dimension and Model Analysis PDFA.s. MahasreerajhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Fourier Transforms PDFDocumento69 pagineUnit 4 Fourier Transforms PDFpoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IV Fourier Transform: D.Meiyappan Department of Applied Mathematics SvceDocumento69 pagineUnit IV Fourier Transform: D.Meiyappan Department of Applied Mathematics SvcepoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V: Z - Transforms and Difference EquationsDocumento2 pagineUnit V: Z - Transforms and Difference Equationspoojaabanindran100% (1)
- MSW - 2 - 2016 Municipal Solid Waste Management Rules - 2016 - Vol-2Documento604 pagineMSW - 2 - 2016 Municipal Solid Waste Management Rules - 2016 - Vol-2nimm196267% (3)
- FourierDocumento2 pagineFourierpoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 CE 6304Documento40 pagineUnit 1 CE 6304Pavan Kumar ArigiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Partial Differential EquationsDocumento153 pagineUnit 1 Partial Differential Equationspoojaabanindran100% (2)
- Four Series Unit IDocumento32 pagineFour Series Unit IkausikraamNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Tpde & Pde Lecture Notes PDFDocumento36 pagineUnit 1 Tpde & Pde Lecture Notes PDFpoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 5 TPDE Z Transform LECTURE NOTES PDFDocumento30 pagineUNIT 5 TPDE Z Transform LECTURE NOTES PDFpoojaabanindran0% (2)
- Unit 1 Fluid Properties and Hydrostatic ForcesDocumento115 pagineUnit 1 Fluid Properties and Hydrostatic ForcespoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Fourier SeriesDocumento195 pagineUnit 2 Fourier Seriespoojaabanindran100% (1)
- Unit 1a Fluid PropertiesDocumento57 pagineUnit 1a Fluid PropertiespoojaabanindranNessuna valutazione finora
- (M1 Technical) Cpe0011lDocumento12 pagine(M1 Technical) Cpe0011lJoel CatapangNessuna valutazione finora
- D 6988 - 03 Medicion de CalibreDocumento7 pagineD 6988 - 03 Medicion de CalibreMiguelAngelPerezEsparzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Flow GraphDocumento38 pagineSignal Flow Graphgaurav_juneja_4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Hydrostatic PressureDocumento25 paginePrinciples of Hydrostatic PressureJherhamy BaguilatNessuna valutazione finora
- Metering - Manual - Eastern - RegionDocumento65 pagineMetering - Manual - Eastern - RegionAmit PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 RheologyDocumento32 pagineLecture 3 Rheologybattal eduNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Signal AnalysisDocumento4 pagineSmall Signal Analysissamaiyasamp3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Umfluxus F808 809v1-2-1enDocumento186 pagineManual Umfluxus F808 809v1-2-1endu lich clipNessuna valutazione finora
- Niosh Lift Push PullDocumento15 pagineNiosh Lift Push Pullahuan huanNessuna valutazione finora
- HCLDocumento8 pagineHCLlalit shakhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hy30 3300 Uk PDFDocumento96 pagineHy30 3300 Uk PDFDragan LazicNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter V Beam Deflections 5.4Documento3 pagineChapter V Beam Deflections 5.4Joshua John JulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus - ME 512 Airconditioning and Ventilation Systems - Not DetailedDocumento2 pagineSyllabus - ME 512 Airconditioning and Ventilation Systems - Not DetailedallovidNessuna valutazione finora
- Prefixes and SuffixesDocumento15 paginePrefixes and SuffixesRita Otero100% (1)
- Marine Hydrodynamics - J. N. Newman PDFDocumento450 pagineMarine Hydrodynamics - J. N. Newman PDFfarazali2919100% (4)
- Csi ReferDocumento502 pagineCsi Referrenzo wilber bernedo beltranNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Life TablesDocumento6 pagineTypes of Life TablesMarielle DelfinNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculating The Heating Value of BiogasDocumento5 pagineCalculating The Heating Value of BiogasAnonymous MVHQ97KEoPNessuna valutazione finora
- DatumsDocumento22 pagineDatumsAlberto LobonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogo Cadenas de Ingenieria PDFDocumento136 pagineCatalogo Cadenas de Ingenieria PDFGlicerio Bravo GaticaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vectors 05 Notes PDFDocumento21 pagineVectors 05 Notes PDFADSaksoulNessuna valutazione finora
- PT Flash Handout 2010Documento24 paginePT Flash Handout 2010Zahraa DakihlNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Stress MonitoringDocumento78 pagineThermal Stress MonitoringSIVA KAVYANessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment N1Documento9 pagineAssignment N1Rania ChNessuna valutazione finora
- Gasket Selection GuideDocumento42 pagineGasket Selection GuideDGWNessuna valutazione finora
- Hass English LatheDocumento318 pagineHass English LathePrabhu Subbiah RamdossNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocumento15 pagineMathematics in The Modern WorldMikaela MelegritoNessuna valutazione finora