Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
University of Makati: J.P. Rizal Extension Brgy. West Rembo, Makati City WWW - Umak.edu - PH
Caricato da
Franz Mecaela0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni4 paginesampling techniques
Titolo originale
Types of Sampling
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentosampling techniques
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni4 pagineUniversity of Makati: J.P. Rizal Extension Brgy. West Rembo, Makati City WWW - Umak.edu - PH
Caricato da
Franz Mecaelasampling techniques
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
UNIVERSITY OF MAKATI
J.P. Rizal Extension Brgy. West Rembo, Makati City
www.umak.edu.ph
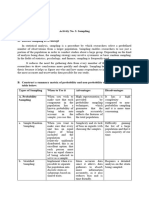
Sampling Techniques Definition Strengths Weaknesses When to Use
A sampling method of
gathering representative
data from a group. As
opposed to random
sampling, quota
sampling requires that
representative
individuals are chosen Insures some degree of Degree of When strata are present
Quota Sampling out of a specific representativeness of all generalizability is and stratified sampling is
subgroup. For example, the strata in the questionable not possible
a researcher might ask population
for a sample of 100
females, or 100
individuals between the
ages of 20-30.
Purposive sampling Proportionality is a When Your research
has 7 different problem. objective is to determine
A purposive sample is a primary types. This Purposive sampling the patterns of use of
non-probability sample allows researchers to does not account for social media by global
that is selected based on find homogenous proportionality as IT consulting companies
characteristics of a samples, perform one of its primary based in the US. Rather
Purposive Sampling population and the typical case sampling, concerns. The goal is than applying random
objective of the study. seek out deviant case to find a range of sampling and choosing
Purposive sampling is sampling, or look at cases to provide as subjects who may not be
also known as characteristics from an much insight as available, you can use
judgmental, selective, or entire population. possible in the purposive sampling to
subjective sampling. It reaches a targeted fastest amount of choose IT companies
sample quickly. time whose availability and
Purposive sampling attitude are compatible
provides options. When It is prone to with the study.
a targeted sample needs researcher bias.
to be reached quickly, Purposive sampling is
the different types of based on the
sampling make it researcher. That
possible to make means their conscious
generalizations from the or unconscious bias
results that are being goes into the data
studied. being collected. That
bias may make the
data seem to be valid,
but it can also
influence the data and
provide false results.
Judgement sampling It is unscientific;
is noble to provide
Judgment sample, or detailed information
Expert sample, is a type about the difficulties It is wasteful and
of random sample that is in obtaining the usually too large
selected based on the distinction. A random samples are selected; when there is no time
opinion of an expert. sample would provide to do a proper study.
Judgment Sampling Results obtained from a less bias, but
judgment sample are potentially less raw You cannot
subject to some degree information. extrapolate the results
of bias, due to the frame The auditor is given to the population as a if small sites are
and population not being an opportunity to whole as the samples involved and no
identical. The frame is a bring his judgement are not representative; estimate of accuracy
list of all the units, and expertise into is needed
items, people, etc., that play. No special
define the population to knowledge of Personal bias in
be studied. statistics is required; selecting the sample is
unavoidable;
Availability of Data Possible Bias in Data When the population
subjects for this type Gathering This is just too large that it
of study can be just method can get the is impossible to
within the researcher views of a specific include every
Convenience sampling group of people and individual.
(also known as not the whole
availability sampling) is Saves Precious population In pilot studies
a specific type of non- Time this is because it Possibility of
probability sampling doesn’t need to Sampling Error in documenting that a
method that relies on acquire an exhaustive Since the selection particular quality of a
Convenience Sampling data collection from research for the whole process is already substance or
population members population biased, there are phenomenon occurs
who are conveniently inaccuracies that are within a given
available to participate bound to set in. sample. Such studies
in study. Facebook polls Saves Previous No Generalized are also very useful
or questions can be Money With this Results Using this for detecting
mentioned as a popular option though, you method will lead to the relationships among
example for convenience can just collect data difficulty of acquiring different phenomena.
sampling. with the use of generalized
sampling technique conclusions that have
been drawn from the
research.
Snowball sampling or It’s quicker to find Sampling bias and there is no
chain-referral sampling samples: Referrals margin of error: precalculated list of
is defined as a non- make it easy and Since people refer target population
probability sampling quick to find subjects those whom they details
technique in which the as they come from know and have there is immense pain
Snowball Sampling samples have traits that reliable sources. similar traits this involved in contacting
are rare to find. This is a Cost effective: This sampling method can members of the target
sampling technique, in method is cost have a potential population
which existing subjects effective as the sampling bias and members of the target
provide referrals to referrals are obtained margin of error. population are not
recruit samples required from a primary data inclined towards
for a research study. source. Lack of cooperation: contributing due to a
There are fair chances social stigma attached
Sample hesitant even after referrals, to them
subjects: Some people might not be the confidentiality of
people do not want to cooperative and the organization
come forward and refuse to participate respondents work for
participate in research in the research (CIA, FBI or terrorist
studies, because they studies. organization).
don’t want their
identity to be exposed.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Mental Survey (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Da EverandThe Mental Survey (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics and Statistical ThinkingDocumento6 pagineStatistics and Statistical ThinkingMarietoni PallanNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Unit 2Documento18 pagineResearch Unit 2Aarzu KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Pros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaDocumento4 paginePros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaKyla RodriguezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pros and Cons of Sampling-With-Cover-Page-V2Documento5 paginePros and Cons of Sampling-With-Cover-Page-V2musawar420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Data and WaysDocumento52 pagineUnderstanding Data and WaysWillie SosaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - Sampling - WordDocumento27 pagine4 - Sampling - WordAya MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- POLSCI 105 SamplingDocumento3 paginePOLSCI 105 SamplingcmaryjanuaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling WorksheetDocumento2 pagineSampling WorksheetMaedot HaddisNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Probability SamplingDocumento6 pagineNon Probability SamplingYoya LoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jasmin Grace Bustamante Stem 11-RadonDocumento3 pagineJasmin Grace Bustamante Stem 11-RadonJasmin grace BustamanteNessuna valutazione finora
- MethodologyDocumento27 pagineMethodologyAngela Maxine BajarNessuna valutazione finora
- PR2 - Reviewer Learning JournalDocumento2 paginePR2 - Reviewer Learning JournalImee Kaye RodillaNessuna valutazione finora
- PR2 - Q1 - Lesson 1B - Nature of ResearchDocumento30 paginePR2 - Q1 - Lesson 1B - Nature of ResearchMellanie CoracheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 MM402 First AssignmentDocumento19 pagineGroup 1 MM402 First Assignmentpriscilla hoveNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling - Methods With Cover Page v2Documento4 pagineSampling - Methods With Cover Page v2musawar420Nessuna valutazione finora
- AlisonJanePicka 2017 Chapter5Sampling ResearchMethodsInInfoDocumento12 pagineAlisonJanePicka 2017 Chapter5Sampling ResearchMethodsInInfoObinna UbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gate Scholorship Work - October: Sampling FundamentalsDocumento13 pagineGate Scholorship Work - October: Sampling Fundamentalssiva sankariNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes 1 To 3Documento12 pagineNotes 1 To 3leandro corditaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 6 - LongDocumento1 paginaLesson 6 - LongFrancine Nace HimpayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonprobability SamplingDocumento2 pagineNonprobability SamplingPartha BhattacharjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Population Sampling TechniquDocumento2 paginePopulation Sampling TechniquMuhammad QasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Bbij 10 00326Documento4 pagineBbij 10 00326Malika Ilma KautsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Population Research Convenience Sampling StrategiesDocumento2 paginePopulation Research Convenience Sampling StrategiesGabriel AgyemangNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Research ReviewerDocumento9 paginePractical Research ReviewerhatdognamalakiNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 12: Selecting A SampleDocumento2 pagineCHAPTER 12: Selecting A Samplealia.delareineNessuna valutazione finora
- SimplingDocumento3 pagineSimplingajaramilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8: Quantitative SamplingDocumento5 pagineChapter 8: Quantitative SamplingWahyu HidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Socio 3-2Documento12 pagineSocio 3-2panda 0909Nessuna valutazione finora
- SamplingDocumento13 pagineSamplingOnycha SyNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 02Documento7 pagineActivity 02Guzman T. John WayneNessuna valutazione finora
- PR2 ReviewerDocumento4 paginePR2 ReviewerHoney Mae CarolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- PRAC2 Midterm 2Documento3 paginePRAC2 Midterm 2biancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 1 AnalysisDocumento3 pagineTask 1 AnalysisSithu AungNessuna valutazione finora
- Patton1990 PDFDocumento10 paginePatton1990 PDFMohd Ariffin AliNessuna valutazione finora
- DavisGallardo 200X SamplingDocumento18 pagineDavisGallardo 200X SamplingYassin KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- MethodologyDocumento35 pagineMethodologyhoormohameed2019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Q3 Prac1 Lecture Lesson2Documento2 pagineQ3 Prac1 Lecture Lesson2Synd WpNessuna valutazione finora
- PSYCHOLOGY - PAPER - 3 - STUDY - GUIDE by Yusra#6578Documento5 paginePSYCHOLOGY - PAPER - 3 - STUDY - GUIDE by Yusra#6578ndballoutNessuna valutazione finora
- STATS ReviewerDocumento3 pagineSTATS ReviewerDianne BarceloNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Research 2 Humss 4Documento13 paginePractical Research 2 Humss 4Oliver CarsolemNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 - Sampling TechniquesDocumento34 pagineTopic 2 - Sampling TechniquesCarlyne Guiang FijerNessuna valutazione finora
- Research II SLM - q3 w1-2 Module 1 With PTDocumento3 pagineResearch II SLM - q3 w1-2 Module 1 With PTEvelyn SuNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methodology NotesDocumento5 pagineResearch Methodology Notesapi-409521281Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2GPRL Day1Documento9 pagine2GPRL Day10000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Feby PPT Marketing Research FixDocumento18 pagineFeby PPT Marketing Research FixRike DesiliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Socio 7Documento20 pagineSocio 7panda 0909Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Quantitative ResearchDocumento25 pagineLesson 1 Introduction To Quantitative ResearchJunilyn SamoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Probability SamplingDocumento7 pagineNon-Probability SamplingUMAR IJAZNessuna valutazione finora
- Q:-Explain The Probability and Nonprobability Sampling TechniquesDocumento3 pagineQ:-Explain The Probability and Nonprobability Sampling TechniquesSuraj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- + PR2 Reviewer 1st QuarterDocumento11 pagine+ PR2 Reviewer 1st QuarternamieNessuna valutazione finora
- SAS - Session-23-Research 1Documento6 pagineSAS - Session-23-Research 1ella retizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Collection of Data Week 2 (Prelim)Documento31 pagineCollection of Data Week 2 (Prelim)Jovialis LlanitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Module 1 4th QuarterDocumento4 pagineResearch Module 1 4th QuarterAngel PicazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sapres1 CM4Documento11 pagineSapres1 CM4ace mabutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Population Sampling Probability and Non Probability TechniquesDocumento2 paginePopulation Sampling Probability and Non Probability TechniquesIsmael LozanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Handour Research 2Documento8 pagineLast Handour Research 2Maria ElizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strengths and Weaknesses of Quantitative Research 2Documento23 pagineStrengths and Weaknesses of Quantitative Research 2Kristine AsuncionNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 MethodsDocumento42 pagine6 MethodsSaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling Assignment Biostats.Documento7 pagineSampling Assignment Biostats.ahtishamakhtar01Nessuna valutazione finora
- T Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectDocumento10 pagineT Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectPayal DhameliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposed Format For Research Proposal For MPhill and PHDDocumento3 pagineProposed Format For Research Proposal For MPhill and PHDNaoman ChNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 4 Template Quantitative Article Qualitative Article: NSG3029 W4 Project Research Template Wildaliz ColonDocumento4 pagineWeek 4 Template Quantitative Article Qualitative Article: NSG3029 W4 Project Research Template Wildaliz ColonMikey MadRatNessuna valutazione finora
- Brancati Dawn PDFDocumento15 pagineBrancati Dawn PDFLibertadRmrTNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Research Design? A Research Design Is A Plan or Strategy ForDocumento55 pagineWhat Is A Research Design? A Research Design Is A Plan or Strategy ForAngelika BandiwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ia WorkbookDocumento11 pagineIa Workbookapi-188978784Nessuna valutazione finora
- Validity N Reliability PDFDocumento19 pagineValidity N Reliability PDFGurpreet Singh Walia100% (1)
- Chapter 6Documento61 pagineChapter 6asmelash gideyNessuna valutazione finora
- ANOVA of Unequal Sample SizesDocumento7 pagineANOVA of Unequal Sample SizesSHARMAINE CORPUZ MIRANDANessuna valutazione finora
- Hasil Output SPSSDocumento4 pagineHasil Output SPSSFitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide For Election Officials in BelizeDocumento32 pagineGuide For Election Officials in BelizeMyrtle PalacioNessuna valutazione finora
- P12resources Item Analysis and InstructionDocumento17 pagineP12resources Item Analysis and InstructionShai ReenNessuna valutazione finora
- Starr, Martha A. (2014), Qualitative and Mixed - Methods Research in Economics. Surprising Growth, Promising FutureDocumento27 pagineStarr, Martha A. (2014), Qualitative and Mixed - Methods Research in Economics. Surprising Growth, Promising FutureNahuel Aranda EjarqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Utah Voter Turnout HistoryDocumento1 paginaUtah Voter Turnout HistoryMcKenzie StaufferNessuna valutazione finora
- GradesDocumento1 paginaGradesAngelo Henry AbellarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electoral College Argumentative EssayDocumento4 pagineElectoral College Argumentative EssayTechnoTato100% (1)
- Scientific Method Experiment Rubric Q Q: ProblemDocumento2 pagineScientific Method Experiment Rubric Q Q: Problemjsencion977Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Specification Table: AnalysisDocumento1 paginaTest Specification Table: AnalysismaiarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychometric Evaluation of The PSSUQ Using Data FRDocumento28 paginePsychometric Evaluation of The PSSUQ Using Data FRyuliani indahNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Programs and Quality Systems For The Food IndustryDocumento36 pagineQuality Programs and Quality Systems For The Food IndustryHaile GetachewNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Operations and Supply Chain Management, Binder Ready VersionDocumento38 pagineTest Bank For Operations and Supply Chain Management, Binder Ready VersionDivya AhujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adavanced Qualitative Research Methods Versus Advanced Quantitative Research MethodsDocumento13 pagineAdavanced Qualitative Research Methods Versus Advanced Quantitative Research MethodsMr. Laban Kipkemoi RotichNessuna valutazione finora
- PR2 Lesson3Documento25 paginePR2 Lesson3Celestial LacambraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonparametric Methods: Analysis of Ranked Data: AnswerDocumento20 pagineNonparametric Methods: Analysis of Ranked Data: AnswerShekhar MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics Survey ProjectDocumento3 pagineStatistics Survey ProjectSarahEvans100% (1)
- Total Quality Management Multiple Choice Questions HighlightsDocumento6 pagineTotal Quality Management Multiple Choice Questions HighlightshemantNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 (5671)Documento16 pagineAssignment 1 (5671)faiza sadaf100% (1)
- Jadwal Jaga IgdDocumento9 pagineJadwal Jaga IgdsasaqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation WPS OfficeDocumento3 pagineEvaluation WPS OfficeMery IsabellaNessuna valutazione finora
- AMSM Ch4Documento24 pagineAMSM Ch4Aticha KwaengsophaNessuna valutazione finora