Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry - Salt Analysis PDF
Caricato da
Syed ArshadDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry - Salt Analysis PDF
Caricato da
Syed ArshadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.
com
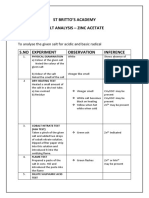
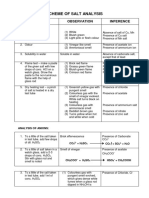
SALT ANALYSIS
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF INORGANIC SALT
Experiment Number. ------------
Date: --------------
AIM:
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION OF SAMPLE No: ………………
The sample is: Presence of:
m
Blue Cu2+ ions
Green Cu2+ or Ni2+ions
co
Dark yellow/Brown Fe3+ or Mn(NO3)2
1 Colour of the sample is noted
Flesh or light pink Mn2+ ions
y. Absence of
da
Colourless / White transition metal
cations.
Livid Blue flame Presence of Pb2+ ion
to
2 A thick paste of the sample is Presence of Cu2+
Green-edged blue flame
es
prepared in con. HCl and is shown ions.
to the non-luminous part of a Crimson flame Presence of Sr2+ ions
di
Bunsen flame with the help of a Presence of Ba2+
glass rod. Pale green flame
ions
tu
Brick red flame Presence of Ca2+ ion
.s
ANALYSIS OF ANIONS
w
3 A little of the sample is treated Colourless, odourless gas (CO2) is Presence of CO32—
w
with dil. HCl acid evolved with effervescence. ion
w
4 A little of the sample is treated
White fuming, pungent smelling gas
with con. H2SO4. (HCl) produces dense white fumes Presence of Cl— ion
when mouth of NH4OH bottle is
shown near the mouth of the test
tube.
Note: Warm/Heat if necessary
5 Reddish brown gas (NO2) on
A pinch of salt is heated with a
boiling the mixture with copper Presence of NO3—
few drops of conc. H 2SO 4 for
turnings and a few drops of ion.
10-15 seconds.
conc. H 2SO4
CONFIRMATORY TESTS FOR ANIONS
6 An aqueous solution of the
A white precipitate (BaSO4)
sample is acidified with
formed, which is insoluble in Presence ofSO42 – ion
dil.HCl followed by the
con.HCl
addition of BaCl2 solution.
7 An aqueous solution of the A white precipitate (PbSO4)
sample is acidified with dilute formed, which is soluble in SO42— ion is
acetic acid followed by the Ammonium acetate [CH3 COONH4] confirmed.
addition of lead acetate [(CH3- solution.
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
COO)2Pb] solution.
8
Pass the above gas through CO32— ion is
Lime water turns milky
clear limewater. confirmed.
9 An aqueous solution of the
Thick curd like white (AgCl)
sample is treated with dil.
precipitate dissolves in excess of Cl— ion is confirmed.
HNO3 followed by AgNO3
NH4OH solution.
solution.
10 A pinch of salt is heated
wthafew drops of conc. H2SO4 A reddish brown gas is released NO3- ion is confirmed
and a few copper turnings
Note:
Place the test tube containing the reaction mixture in beaker containing ~50 ml tap water and then
Mixing ratio: 1 ml of sample solution + 1ml dil.H 2SO4 + 2 ml FeSO4 (aq) and then add 1 ml of con.
only add con.H2SO4 to avoid temperature build up due to exothermic nature of the reaction.
If precipitation takes during this test, add more dil.H 2SO4 and then remove the precipitate by
Sulphuric acid drop by drop.
centrifugation.
ANALYSIS OF CATIONS
m
Confirmatory Tests For NH4+ ion
co
Agitate a pinch of the solid salt
Smell of ammonia (NH3), which
sample with NaOHsolution and note
produces dense white fumes when NH4+ ion
its smell.
(Note: Release the gas near your
the test tube. y.
Con. HCl is shown near the mouth of confirmed.
da
nose)
The solid salt sample is treated with
NH4+
to
NaOH solution followed by A brown precipitate is formed. ion
Nessler‘s reagent. (NH2.HgO.HgI) confirmed.
es
Note: Do not shake the mixture.
di
INTER-GROUP SEPARATION OF CATIONS
A true solution of the salt is prepared in distilled water.
tu
How to prepare? - Start with a pinch of sample + 4ml of solvent. If it dissolves completely,
Note:
.s
If the sample is insoluble in water; try dissolving it in dil.HCl or dil.HNO3
then gradually increase the concentration by dissolving more salt.
w
11 About 1 ml. of the sample
w
Presence of group – I
solution is treated with dil. White precipitate of PbCl2
cations
w
HCl
12 Black precipitate of Copper sulphide
Through the above solution Presence of group –
(CuS)
H2S gas is passed. II cations
H2S WORK: Dirty H2S gas delivery tube & its washing water can cause contamination
Note:
Reject any black precipitate obtained if the sample is not blue or green in colour
of your work. Students should ensure that they are neat and clean before use.
13 To about 2ml. (If the sample
is insoluble in water; try Gelatinous white precipitate of
dissolving it in dil.HClor Aluminium hydroxide {Al(OH)3}
dil.HNO3) of the salt solution
2 ml of saturated NH4Cl
Presence of group –
solution is added. Shake the
III cations
mixture well and then add Brown precipitate Ferric hydroxide
7ml of NH4OH solution and {Fe(OH)3}
agitate.
Note: This solution may be
called group-III solution
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
14 Dirty white precipitate of Zinc
sulphide (ZnS)
Through 2 ml of the of the
Buff precipitate of Manganese Presence of group –
above solution (group –III
sulphide (MnS) IV cations
solution) H2S gas is passed
Black precipitate of Nickel sulphide
(NiS)
Note: Reject any black precipitate obtained if the sample is not green in colour
15 White precipitate of
To 2ml of the group – III
Bariumcarbonate (BaCO3) Presence of group
solution (NH4)2CO3 (Little
Strontium carbonate (SrCO3) or V cations
excess) solution is added
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
Confirmatory test for Magnesium (Mg2+) ion
16 To 2ml of the group –III
solution Di-sodium hydrogen
phosphate is added. (Note: White crystalline precipitate of Presence of Mg2+
Scratch the sides of the test Magnesium phosphate ion
tube with a glass rod if
necessary)
CONFIRMATORY TEST FOR CATIONS
ANALYSIS OF GROUP – I CATION
m
Confirmatory Tests For Lead (Pb2+) Ion
co
17 To one portion of the sample
solution add few drops of Yellow precipitate of Lead chromate Presence of Pb2+
Potassium chromate (K2CrO4) (PbCrO4) ion confirmed
solution.
y.
da
18 To another portion of the
sample solution add few Yellow precipitate of Lead iodide Presence of Pb2+
to
drops of Potassium iodide (PbI2) ion confirmed
(KI) solution.
es
ANALYSIS OF GROUP – II CATIONS
di
Confirmatory Tests For Copper (Cu2+) Ion
19 To one portion of the sample
tu
Presence of Cu2+
solution add excess of Deep blue solution, [Cu(NH3)4](OH)2
ion confirmed
.s
NH4OH solution
20 Treat one portion of the above
w
deep blue solution with dil.
Acetic acid followed by few Chocolate coloured precipitate Presence of Cu2+
w
drops of K4[Fe(CN)6] Cu2[Fe(CN)6] ion confirmed
w
(Potassium Ferro cyanide)
solution
ANALYSIS OF GROUP – III CATIONS
Confirmatory Tests For Aluminium (Al3+) Ion
21 To one portion of the sample
White precipitate, Al(OH)3, dissolves Presence of Al3+
solution NaOH solution is
in excess of NaOH ion confirmed
added drop by drop.
22 Another portion of the sample
solution is acidified with
dil.HCl followed by the
addition of blue litmus
A floating blue precipitate is formed (It Presence of Al3+
solution. Shake the mixture
is called the “Floating blue lake) ion confirmed
well to get a pink coloured
solution. To this solution
NH4OH solution is added
drop wise without shaking.
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
ANALYSIS OF GROUP – III CATIONS.
Confirmatory Tests for Ferric (Fe3+) Ion
23 To one part of the A Prussian blue colouration Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 Fe3+ ion
diluted salt solution confirmed.
K4[Fe(CN)6] (Potassium
ferrocyanide) solution is
added.
24 To 2nd part of the diluted A blood red colouration Fe(CNS)3 Fe3+ ion
salt solution Potassium confirmed.
thiocyanate (KCNS)
solution is added.
ANALYSIS OF GROUP – IV CATIONS.
Confirmatory Tests for Zinc (Zn2+) Ion
25 To one portion of the
sample solution NaOH White precipitate {Zn(OH)2} dissolves in Zn2+ ion
solution is added drop excess of NaOH(aq) confirmed.
wise without shaking.
26 To 2nd part of the sample
m
solution K4[Fe(CN)6]
Greenish/bluish white [Zn2[Fe(CN)6] Zn2+ ion
(Potassium
co
precipitate. confirmed.
Ferrocyanide) solution is
added.
y.
ANALYSIS OF GROUP – IV CATIONS.
da
Confirmatory Tests for Manganese (Mn2+) Ion.
to
27 To one portion of the
sample solution add A white precipitate {Mn(OH)2} formed turns Mn2+ ion
es
NaOH solution drop to brown (MnO2) confirmed.
wise without shaking.
di
28 ¼ spatula of solid
sample is treated with ½
tu
ml of con.HNO3
followed by the addition
.s
A purple colour formed changes to brown on Mn2+ion
of 1 ml of Sodium
standing. confirmed.
w
bismuthate solution#.
Note: Add water to get
w
a colourless solution if
w
needed
ANALYSIS OF GROUP – IV CATIONS.
Confirmatory Tests for Nickel (Ni2+) Ion. (Note: All salts containing Ni are Greenish in colour)
29 To one portion of the
sample solution add 10
drops of Dimethyl glyoxime A scarlet red precipitate. Ni2+ ion confirmed
reagent followed by excess
of NH4OH solution.
30 To the 2nd portion of the
sample solution add Br2
water solution followed by A black precipitate. Ni2+ ion confirmed
NaOH solution, boil and
then keep aside.
ANALYSIS OF GROUP V CATIONS
Confirmatory Tests for Barium (Ba2+) ion
31 To one portion of the sample
Ba2+ ion
solution add a few drops of A yellow (BaCrO4) “precipitate‖.
confirmed.
Potassium chromate
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
(K2CrO4) solution.
32 To another portion of the
sample solution add a few
drops of Dil.H2SO4 acid.
Do this test only if
Note:
A white (BaSO4) precipitate. Ba2+ ion confirmed.
the K2CrO4 test is
Do this test only as
positive
the 2nd confirmatory
test for Ba2+.
Confirmatory Tests for Strontium (Sr2+) ion
33 A portion of the sample
solution is treated with
Scanty white (SrSO4) precipitate Sr2+ ion confirmed.
acetic acid followed by
ammonium sulphate solution
34 A thick paste of the sample
is prepared in con. HCl and
is shown to the non-
Sr2+ ion confirmed.
m
Crimson coloured flame
luminous part of a Bunsen
flame with the help of a
co
glass rod.
Confirmatory Tests Calcium (Ca2+) ion.
35 To one portion of the sample
y.
da
solution add a few drops of A white (CaC2O4) precipitate formed
Ca2+ ion confirmed.
Ammonium Oxalate dissolves in Con. HCl.
to
{(NH4)2C2O4 } solution.
36 A white (Ca(NH4)K[Fe(CN)6]
es
Another portion is made precipitate.
“neutral” by adding NH4OH Note:
Only a ‘neutral’ solution answers
di
followed by boiling till
smell of NH3 is gone. Cool
If the medium is acidic or
this test.
Ca2+ ion confirmed.
tu
this solution and then add 2
drops of NH4Cl and few
Allow the reaction mixture to
alkaline, the test fails.
.s
drops of K4[Fe(CN)6]
w
solution. stand and cool down for the
precipitate to be seen.
w
w
2 Drops of salt solution are
37
treated with 3 drops of
Blue precipitate / solution Mg2+ion confirmed
Magneson reagent and 3
drops of NaOH solution
REPORT:
The given sample no._______has: Cation: ……….……….………
Anion: ……….……………….
The salt is: …………………….
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Note: Use only ionic and molecular formulae for reporting
NOTES & USEFUL INFORMATION:
1. Always record the analysis in a tabular form. (i. e. draw three columns for recording
―Experiment‘, ‗Observation‘ and ‗Inference‘)
2. Give continuous serial numbers to tests while recording the analysis in your book.
3. ―Notes‖ given in this ‗analysis handout‘ are hints only, hence should not be written in the
journal.
4. Some Manganese salts show sparking flame when flame test is conducted.
5. ―DANGER!‖ Hot concentrated reagents should not be thrown into sink. {Cool the out side of
the test tube to room temperature under running tap water and then carefully dilute the
mixture by adding tap water little by little. Once the mixture is safely diluted, it may be washed
normally.}
6. Whenever solubility of a precipitate formed is tested, a small amount (a drop) of the precipitate
should be transferred to another test tube and dissolve in excess amount of solvent. (Always
show two test tubes for attestation of the work)
7. When chloride ion is detected with Cu2+ or Mn2+ions, AgCl will not give a clear transparent
solution with excess of NH4OH (Solubility part of the 2nd confirmatory test). This may be
avoided by washing the precipitate: [Centrifuge the mixture and discard the rest of the solution
m
to separate AgCl. Add distilled water to the centrifuge tube, shake well to wash AgCl.
Centrifuge again and discard water. Use the washed AgCl to do solubility test with NH4OH.]
co
8. Nessler’s reagent test should be conducted only after identifying the presence of NH4+ ion using
NaOH test. (Zn2+& Mn2+ ions can also give brown precipitate with Nessler‘s reagent)
y.
9. Confirmatory tests for cations can also be done using true solutions made from the precipitate
obtained during Inter-group separation of the cation in suitable solvents.
da
10. Only Green or Blue salts will give black precipitate with H2S gas. If black precipitate is obtained
with salts that are not blue or green it is due to contamination of the solution and should be
to
11. # Sodium Bismuthate solution: The reagent shows tendency to settle as it is sparingly soluble
rejected.
es
in distilled water. So whenever the reagent is used, do shake the reagent bottle well before
transferring the reagent. Otherwise only supernatant water will get transferred to the test tube.
di
12. Second confirmatory test for Ni2+ ion may fail if Br2 water used is weak.
13. If chloride ion is confirmed with Calcium ion: Neutralisation has to be compulsorily done as
tu
CaCl2 shows acidic character.
14. 2nd confirmatory test for Ca2+ ion: If the sample does not dissolve in distilled water, the true
.s
solution made should be properly neutralised as per the instruction given.
w
15. Write completed salt work in the Journal only after getting it corrected in the observation book.
w
16. You are requested to refer to laboratory guide books kept in the Library to learn Viva
questions.
w
**********************************************************************************
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Business Policy FormulationDocumento21 pagineBusiness Policy FormulationWachee Mbugua50% (2)
- Identifying Anions and Cations in a Salt Through Chemical TestsDocumento4 pagineIdentifying Anions and Cations in a Salt Through Chemical Testsmohnish83% (6)
- Salt Analysis - Iv Barium ChlorideDocumento3 pagineSalt Analysis - Iv Barium ChlorideNAN100% (6)
- Proposal For Funding of Computer Programme (NASS)Documento6 pagineProposal For Funding of Computer Programme (NASS)Foster Boateng67% (3)
- Shore Activities and Detachments Under The Command of Secretary of Navy and Chief of Naval OperationsDocumento53 pagineShore Activities and Detachments Under The Command of Secretary of Navy and Chief of Naval OperationskarakogluNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Viva Questions With AnswersDocumento5 pagineBasic Viva Questions With AnswersGovind Singh KhatiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Identify Organic Compound Functional GroupDocumento2 pagineIdentify Organic Compound Functional Groupmohnish50% (2)
- Operations Management Success FactorsDocumento147 pagineOperations Management Success Factorsabishakekoul100% (1)
- Salt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsDocumento19 pagineSalt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsPreetam Kalyaan100% (1)
- Identify Anion and Cation in Mysterious SaltDocumento2 pagineIdentify Anion and Cation in Mysterious SaltRohit Sur60% (52)
- Salt Analysis ChartDocumento7 pagineSalt Analysis ChartZulfiquar Hadi82% (359)
- SALT ANALYSIS - Chemistry Practical XII PDFDocumento12 pagineSALT ANALYSIS - Chemistry Practical XII PDFDr. Md. Tanweer Alam80% (5)
- Budokon - Mma.program 2012 13Documento10 pagineBudokon - Mma.program 2012 13Emilio DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- The Philippine Army Doctrine DevelopmentDocumento10 pagineThe Philippine Army Doctrine DevelopmentRy PomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment - Salt Analysis Calcium Chloride 2223Documento2 pagineExperiment - Salt Analysis Calcium Chloride 2223ARYAN GOELNessuna valutazione finora
- Salt Analysis With EquationsDocumento12 pagineSalt Analysis With Equationsabhikhya aryaNessuna valutazione finora
- BtuDocumento39 pagineBtuMel Vin100% (1)
- Identify Salt Anion and Cation Using Preliminary TestsDocumento3 pagineIdentify Salt Anion and Cation Using Preliminary Testsmohnish67% (3)
- Lead Nitrate Chemistry Cbse 12 AnalysisDocumento8 pagineLead Nitrate Chemistry Cbse 12 AnalysisA.n. Surya50% (12)
- Aluminium Sulphate 1Documento2 pagineAluminium Sulphate 1Bimal Krishna Biswas60% (5)
- Biology Practical FileDocumento34 pagineBiology Practical FileBrain Food67% (6)
- Ammonium CarbonateDocumento1 paginaAmmonium CarbonateSophieNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 CaCO3Documento3 pagine6 CaCO3Abhi Suresh100% (3)
- Copper SulphateDocumento4 pagineCopper Sulphatesumathi siva50% (2)
- 1.SALT ANALYSIS Ammonium PhosphateDocumento3 pagine1.SALT ANALYSIS Ammonium Phosphatemohnish25% (8)
- Zinc SulphateDocumento2 pagineZinc Sulphategumtamm100% (1)
- Experiment Salt Analysis Ammonium Bromide 2223Documento2 pagineExperiment Salt Analysis Ammonium Bromide 2223ARYAN GOELNessuna valutazione finora
- Volumetric Analysis Class 11Documento3 pagineVolumetric Analysis Class 11Hemant Thakur100% (1)
- Zinc AcetateDocumento4 pagineZinc AcetateAbinaya chettiappanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminium Bromide Salt AnalysisDocumento3 pagineAluminium Bromide Salt AnalysisShanmuganathan100% (1)
- Identification of Cations and Anions in a SaltDocumento3 pagineIdentification of Cations and Anions in a SaltSarthika Gaulkar0% (1)
- Calcium CarbonateDocumento1 paginaCalcium CarbonateShreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lead Nitrate Chemistry Cbse 12 AnalysisDocumento7 pagineLead Nitrate Chemistry Cbse 12 Analysis2066 Harini Manickam 12 C100% (1)
- 5.SALT ANALYSIS Nickel SulphateDocumento4 pagine5.SALT ANALYSIS Nickel SulphatemohnishNessuna valutazione finora
- Lead NitrateDocumento1 paginaLead NitrateSophie100% (3)
- 3.SALT ANALYSIS Cobalt NitrateDocumento4 pagine3.SALT ANALYSIS Cobalt Nitratemohnish100% (1)
- Salt Analysis - Barium NitrateDocumento2 pagineSalt Analysis - Barium NitrateSwarnabha Bhattacharyya100% (2)
- Salt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2Documento7 pagineSalt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2piyush rajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Simple Salt - (Copper Nitrate) : Dry TestsDocumento3 pagineAnalysis of Simple Salt - (Copper Nitrate) : Dry TestsSarvan SankaranNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.SALT ANALYSIS Ferric NitrateDocumento3 pagine4.SALT ANALYSIS Ferric Nitratemohnish100% (1)
- Salt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2Documento7 pagineSalt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2piyush rajput100% (3)
- Systematic Analysis of SaltDocumento9 pagineSystematic Analysis of SaltvarshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Analyze Simple SaltDocumento6 pagineAnalyze Simple SaltDrGaurav Rajput50% (10)
- Analysis of Simple Salt-II-magnesium Nitrate For Record and ReferenceDocumento6 pagineAnalysis of Simple Salt-II-magnesium Nitrate For Record and Referencenikil saibaba100% (1)
- Salt Analysis - Xii PDFDocumento9 pagineSalt Analysis - Xii PDFहर्ष सैनी. कक्षा::बारहवीं 'द'Nessuna valutazione finora
- Salt analysis reveals calcium chlorideDocumento3 pagineSalt analysis reveals calcium chlorideAmythNessuna valutazione finora
- Detection of Ketone GroupDocumento7 pagineDetection of Ketone GroupRA.RAMESHNessuna valutazione finora
- Lead Nitrate Salt AnalysisDocumento2 pagineLead Nitrate Salt AnalysisSantosh Kumar Sahu0% (1)
- Strontium ChlorideDocumento5 pagineStrontium ChlorideAbinov Kumar KTNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheme of Salt AnalysisDocumento8 pagineScheme of Salt AnalysisAz Ahmed100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet Chemistry Salt Analysis 12th CBSEDocumento5 pagineCheat Sheet Chemistry Salt Analysis 12th CBSETammanurRaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Salt AnalysisDocumento12 pagineSalt AnalysisAditya Verma50% (4)
- Dry Test For Basic Radical: Experiment Observation InferenceDocumento6 pagineDry Test For Basic Radical: Experiment Observation InferenceJoy DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ammonium Sulphate Salt Analysis TestDocumento2 pagineAmmonium Sulphate Salt Analysis TestSantosh Kumar SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ammonium CarbonateDocumento4 pagineAmmonium Carbonatesumathi sivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Viva Voce QuestionsDocumento2 pagineViva Voce QuestionsBhavesh Desai100% (1)
- Titration (Mohrs Salt, Oxalic Acid) - XiiDocumento6 pagineTitration (Mohrs Salt, Oxalic Acid) - Xiisuraj mani das100% (1)
- Coin Investigatory)Documento19 pagineCoin Investigatory)Saumya Kharya70% (10)
- Comprehensive Chem Class12Documento16 pagineComprehensive Chem Class12iGadgetPro67% (3)
- XII Chemistry Practical-22Documento23 pagineXII Chemistry Practical-22Anbuchelvan VKNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Viva QuestionsDocumento4 pagineSome Viva Questionsseru100% (1)
- Chemistry Salt ChartDocumento3 pagineChemistry Salt ChartAnup NavaleNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Write a Physics Practical File in 40 StepsDocumento2 pagineHow to Write a Physics Practical File in 40 Stepspratibha1007100% (2)
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry - Salt AnalysisDocumento6 pagineCBSE Class 11 Chemistry - Salt AnalysisAneek PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple SaltDocumento9 pagineSystematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple SaltNisha VethigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheme of Analysis of Inorganic SaltDocumento11 pagineScheme of Analysis of Inorganic SaltHemsuta S.BNessuna valutazione finora
- Qualitative Inorganic Analysis: I. Physical Examination of The Salt Experiment Observation InferenceDocumento9 pagineQualitative Inorganic Analysis: I. Physical Examination of The Salt Experiment Observation InferenceAarohiNessuna valutazione finora
- Engb546 NP RevisedDocumento5 pagineEngb546 NP RevisedRafaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluetooth Mobile Based College CampusDocumento12 pagineBluetooth Mobile Based College CampusPruthviraj NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Elderly Suicide FactsDocumento2 pagineElderly Suicide FactsThe News-HeraldNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of SimilesDocumento10 pagineImportance of Similesnabeelajaved0% (1)
- Ass 3 MGT206 11.9.2020Documento2 pagineAss 3 MGT206 11.9.2020Ashiqur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- ProbabilityDocumento2 pagineProbabilityMickey WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Students Playwriting For Language DevelopmentDocumento3 pagineStudents Playwriting For Language DevelopmentSchmetterling TraurigNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 1Documento2 pagineClass 11 English Snapshots Chapter 1Harsh彡Eagle彡Nessuna valutazione finora
- Legend of GuavaDocumento4 pagineLegend of GuavaRoem LeymaNessuna valutazione finora
- Veerabhadra Swamy MantrasDocumento6 pagineVeerabhadra Swamy Mantrasगणेश पराजुलीNessuna valutazione finora
- Econometrics IntroductionDocumento41 pagineEconometrics IntroductionRay Vega LugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Modbus Quick StartDocumento3 pagineModbus Quick StartNash JungNessuna valutazione finora
- MOTOR INSURANCE TITLEDocumento5 pagineMOTOR INSURANCE TITLEVara PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Downloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Documento12 pagineDownloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Iqioo RedefiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5 ADHAVANDocumento29 pagineExperiment 5 ADHAVANManoj Raj RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 RDL2Documento101 pagineGroup 1 RDL2ChristelNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay A Level Drama and Theatee Studies A LevelDocumento2 pagineEssay A Level Drama and Theatee Studies A LevelSofia NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Newtons First LawDocumento14 pagineNewtons First LawcaitlyntreacyNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Listening Integrated Hkdse2022 UmayDocumento21 pagineEng Listening Integrated Hkdse2022 UmayHoi TungNessuna valutazione finora
- Dmat ReportDocumento130 pagineDmat ReportparasarawgiNessuna valutazione finora
- Khin Thandar Myint EMPADocumento101 pagineKhin Thandar Myint EMPAAshin NandavamsaNessuna valutazione finora
- PbisDocumento36 paginePbisapi-257903405Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ocimum Species Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological ImportanceDocumento13 pagineOcimum Species Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological ImportanceManika ManikaNessuna valutazione finora