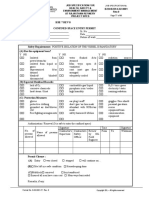
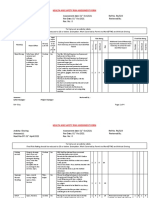
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Iso 45001 - 6.1.1
Caricato da
dnmuleTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Iso 45001 - 6.1.1
Caricato da
dnmuleCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Clause 6: Planning
This clause provides guidance on how to plan for the OH&S management system, including
identifying and assessing the risks and opportunities associated with the organization and its
workers, and the actions necessary to deal with these risks and opportunities.
Clause 6.1: Actions to address risks and opportunities
Clause 6.1.1 General
Planning is an integral part of all elements of an OH&S management system. Effective planning
is concerned with prevention by identifying, eliminating and controlling hazards and risks. This
is particularly important when dealing with health risks, which might only become apparent after
a long gestation period. Planning should be a collaborative effort involving personnel throughout
the organization. This co-operation is eminently suitable for demonstrating and gaining
commitment to continual improvement and promoting a positive health and safety culture
throughout the organization.
Planning for the OH&S management system is an ongoing process and is undertaken in order:
To determine the risks that can affect the OH&S performance of the organization;
To manage these risks;
To identify opportunities to improve OH&S performance and the OH&S management
system.
When planning for the OH&S management system, the organization should take into account the
following:
The organization and its context (clause 4.1);
The needs and expectations of workers and other interested parties (clause 4.2);
The scope of the OH&S management system (clause 4.3).
Planning should be proportionate to the level of risk identified.
While the organization should consider all potential risks to its OH&S performance it should
focus on those hazards which are most likely to occur and/or have the greatest impact.
The company should concentrate on those opportunities that can realistically be acted upon, with
priority given to those that are most likely to improve performance.
Examples of opportunities to improve OH&S performance include the following:
Identification of hazards, how they are communicated, analysed and controlled;
Enhancing the inspection and auditing functions;
Introduction of job safety analysis and task-related assessments;
Modification of working processes including the alleviation of monotonous and repetitive
work;
Implementation of permit-to-work processes;
Incident or nonconformity investigations and corrective actions;
Implementation of ergonomic and other injury prevention-related assessments;
Integration of occupational health and safety considerations at the earliest stage in the
design life cycle of plant and equipment;
Integration of occupational health and safety considerations at the earliest stage in
planning for facilities relocation, and/or process redesign;
Introduction of new technology;
Improvement of the occupational health and safety culture of the organization;
Enhancing the visibility of top management’s support for the OH&S management
system;
Enhancing the incident investigation process;
Improving worker consultation and participation;
Benchmarking of the organization’s OH&S performance against that of other
organizations;
Collaborating in forums that review issues relating to occupational health and safety.
The organization must maintain documented information on:
Risks and opportunities;
The process and actions needed to determine and address its risks and opportunities to the
extent necessary to have confidence that they are carried out as planned.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Iso 45001Documento10 pagineIso 45001sanjeev kumar0% (1)
- Health Safety Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandHealth Safety Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Building A Safety Culture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandBuilding A Safety Culture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 28000 A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandISO 28000 A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Guide Safety and Lean Trends 2022Documento32 pagineGuide Safety and Lean Trends 2022JOSEPH RIŇOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior-based safety A Clear and Concise ReferenceDa EverandBehavior-based safety A Clear and Concise ReferenceNessuna valutazione finora
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemDa EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- Occupational Safety and Legal Obligations: Property of STIDocumento8 pagineOccupational Safety and Legal Obligations: Property of STIKharylle P. Rivera100% (1)
- Safe System Of Work A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandSafe System Of Work A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Nebosh Igc1 Lesson Plan Day 1Documento2 pagineNebosh Igc1 Lesson Plan Day 1KarenNessuna valutazione finora
- Planned Safety InspectionDocumento104 paginePlanned Safety InspectionKirstie Lou Sales100% (1)
- Behaviour Based Safety: Presented byDocumento14 pagineBehaviour Based Safety: Presented bynasrul dracoNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandManufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated ISO 14001+18001 Awareness Training (1day)Documento95 pagineIntegrated ISO 14001+18001 Awareness Training (1day)Stephen Lim Kean Jin100% (3)
- GRI 403 - Occupational Health and Safety 2018 PresentationDocumento28 pagineGRI 403 - Occupational Health and Safety 2018 PresentationCostas JacovidesNessuna valutazione finora
- Quentic Whitepaper ISO 45001Documento18 pagineQuentic Whitepaper ISO 45001Miruna IliescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Safe Work Procedure A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandSafe Work Procedure A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- ObjectivityDocumento7 pagineObjectivityvaratharaj bNessuna valutazione finora
- Health And Safety A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandHealth And Safety A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandSafety Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 45001 2018 On Site Supplier Audit Checklist SampleDocumento4 pagineISO 45001 2018 On Site Supplier Audit Checklist SampleAmr EssamNessuna valutazione finora
- Health and Safety Policy and ProceduresDocumento5 pagineHealth and Safety Policy and ProceduresJalil JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- culture of safety A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa Everandculture of safety A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Environmental Conservation Rules, 1997 (ECR'97)Documento2 pagineEnvironmental Conservation Rules, 1997 (ECR'97)নরকেররাজপুত্রNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) A Clear and Concise ReferenceDa EverandBusiness Process Re-engineering (BPR) A Clear and Concise ReferenceNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Environmental Policy (PDR)Documento1 pagina1 Environmental Policy (PDR)nyan linNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand and Powertool Safety PDFDocumento8 pagineHand and Powertool Safety PDFJamal Uddin100% (1)
- OHS ResponsibilitiesDocumento5 pagineOHS ResponsibilitiesAce GreensNessuna valutazione finora
- Ergonomics Principles and GuidelinesDocumento18 pagineErgonomics Principles and GuidelinesArpan Gautam100% (1)
- Managing Safety and HealthDocumento6 pagineManaging Safety and HealthLexter CEmpronNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior Based SafetyDocumento27 pagineBehavior Based SafetySuresh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 45001:2018 Migration Self-Assessment Guide: How Ready Are You For ISO 45001?Documento16 pagineISO 45001:2018 Migration Self-Assessment Guide: How Ready Are You For ISO 45001?Vikas SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2 Unit GC2: Controlling Workplace Hazards: Learning OutcomesDocumento18 pagine4.2 Unit GC2: Controlling Workplace Hazards: Learning Outcomesnavin100% (2)
- Pressure Testing PR86POGC001Documento20 paginePressure Testing PR86POGC001naren_013Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5S Good HousekeepingDocumento24 pagine5S Good HousekeepingJohn Lloyd GenerosoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is An Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) Program?Documento18 pagineWhat Is An Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) Program?Varsha SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Checklist For ConcessionsDocumento10 pagineAudit Checklist For ConcessionsbangladragosNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrective And Preventative Action A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandCorrective And Preventative Action A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Training On ISO 14001, Clause No.: 6.1.2 Environmental Aspects (AI)Documento37 pagineTraining On ISO 14001, Clause No.: 6.1.2 Environmental Aspects (AI)sankusi_rkflNessuna valutazione finora
- My Safety Leadership ChecksDocumento8 pagineMy Safety Leadership ChecksVaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Occupational health and safety A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandOccupational health and safety A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- EHS in Pharmaceutical IndustryDocumento19 pagineEHS in Pharmaceutical IndustryARPITA MISHRANessuna valutazione finora
- Bosh1103 - 7.0 Chemical Health Risk AssessmentDocumento59 pagineBosh1103 - 7.0 Chemical Health Risk AssessmentAddry AlffianNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrective Action A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandCorrective Action A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Planned Job ObservationDocumento52 paginePlanned Job ObservationJohn Mark DulawanNessuna valutazione finora
- HSP AuditDocumento10 pagineHSP AuditslusafNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 14001 English PDFDocumento5 pagineIso 14001 English PDFkemalNessuna valutazione finora
- Health and Safety Manual 2023Documento36 pagineHealth and Safety Manual 2023habiba rais100% (1)
- NEBOSH Diploma in Environmental Management Unit ED1 (2010 Specification)Documento5 pagineNEBOSH Diploma in Environmental Management Unit ED1 (2010 Specification)Raz BiophyNessuna valutazione finora
- BODC Contractor Health Safety Handbook Version 16Documento25 pagineBODC Contractor Health Safety Handbook Version 16Rooja BajracharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operational Risk Management Plan A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandOperational Risk Management Plan A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Management CommitmentDocumento18 pagineModule 2 Management CommitmentKavin Raj100% (1)
- Safety And Health A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandSafety And Health A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Safety InspectionDocumento7 pagine1 - Safety InspectionTawfik Mohamed Abu ZaidNessuna valutazione finora
- RISQS Core Sentinel CDM Compliance MatrixDocumento36 pagineRISQS Core Sentinel CDM Compliance MatrixSaurabh GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scaffoliding Training R1Documento69 pagineScaffoliding Training R1Farrukh AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessment Checklist For New and Expectant MothersDocumento2 pagineRisk Assessment Checklist For New and Expectant MothersDave NalugonNessuna valutazione finora
- General Description of Your Company: Upplier Nformation ORMDocumento2 pagineGeneral Description of Your Company: Upplier Nformation ORMdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Carrier Information FormDocumento6 pagineCarrier Information FormdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Change Request FormDocumento4 pagineChange Request Formdnmule0% (1)
- Supplier Non-Conformity FormDocumento1 paginaSupplier Non-Conformity FormdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Notification of AuditDocumento1 paginaNotification of AuditdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Udit Eport: Document N°: QUA-F-0019 Rev 3Documento1 paginaUdit Eport: Document N°: QUA-F-0019 Rev 3dnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Carrier Evaluation FormDocumento1 paginaCarrier Evaluation FormdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Improvement Action Form: Branch: Form Number: ActivityDocumento1 paginaImprovement Action Form: Branch: Form Number: ActivitydnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Trip Lashing Inspection ChecklistDocumento1 paginaPre-Trip Lashing Inspection Checklistdnmule100% (1)
- Date: Subject: Participants: Issues of The Meeting: Status PDCA (Plan - Do - Check - Act) Person in Charge Deadlines Status at Meeting M+1Documento1 paginaDate: Subject: Participants: Issues of The Meeting: Status PDCA (Plan - Do - Check - Act) Person in Charge Deadlines Status at Meeting M+1dnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Operation Defined, Planed and Monitored Under Control (Effective) Optimized (Efficient)Documento2 pagineBasic Operation Defined, Planed and Monitored Under Control (Effective) Optimized (Efficient)dnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Meeting Attendance FormDocumento1 paginaMeeting Attendance FormdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Audits Planning: Auditees ActivitiesDocumento1 paginaAnnual Audits Planning: Auditees ActivitiesdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Review MinuteDocumento8 pagineManagement Review MinutednmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Q-HSE Weekly Report: Country: Entity: WeekDocumento4 pagineQ-HSE Weekly Report: Country: Entity: WeekdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensitivity of Neighbourhood RatingDocumento2 pagineSensitivity of Neighbourhood RatingdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Aspects Severity Rating InstructionsDocumento1 paginaEnvironmental Aspects Severity Rating InstructionsdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Aspects Frequency Rating InstructionsDocumento2 pagineEnvironmental Aspects Frequency Rating InstructionsdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Aspects Severity Rating InstructionsDocumento1 paginaEnvironmental Aspects Severity Rating InstructionsdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Employees Present On SiteDocumento1 paginaList of Employees Present On SitednmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Management System Procedure: Nvironmental NalysisDocumento5 pagineManagement System Procedure: Nvironmental NalysisdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- HSE Regulatory Watch Follow-Up: Person in Charge of The Follow-Up Date of UpdateDocumento1 paginaHSE Regulatory Watch Follow-Up: Person in Charge of The Follow-Up Date of UpdatednmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- FOLIO 1 (To Be Retained by Site) : Document N°: HSE-F-0518 Rev 07Documento2 pagineFOLIO 1 (To Be Retained by Site) : Document N°: HSE-F-0518 Rev 07dnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Intervention in The Event of Accidental Spillage of Hazardous MaterialsDocumento2 pagineIntervention in The Event of Accidental Spillage of Hazardous MaterialsdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Carrying Out An Accident InvestigationDocumento2 pagineCarrying Out An Accident InvestigationdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Actions in Case of A FireDocumento1 paginaActions in Case of A FirednmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Control OrganisationDocumento1 paginaEmergency Control OrganisationdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Wastes Tracking FormDocumento1 paginaWastes Tracking FormdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Waste Monthly Report: Report N° .. / 201 Site: DateDocumento1 paginaWaste Monthly Report: Report N° .. / 201 Site: DatednmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Yard Operations ChecklistDocumento1 paginaYard Operations ChecklistdnmuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil Water Separator Operators ManualDocumento13 pagineOil Water Separator Operators Manualabcde100% (1)
- BarrièreDocumento24 pagineBarrièreanas.novacimNessuna valutazione finora
- (PAPER) Trbojevic, V. M. (2009) Another Look at Risk and Structural Reliability Criteria.Documento6 pagine(PAPER) Trbojevic, V. M. (2009) Another Look at Risk and Structural Reliability Criteria.O SNessuna valutazione finora
- NH4OH MsdsDocumento6 pagineNH4OH MsdsZoelFikar FahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Safety Work Practices PlanDocumento5 pagineElectrical Safety Work Practices PlanAlbin LoyolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modularization Chemical PlantDocumento4 pagineModularization Chemical Plantmora287Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Damper - FAQDocumento6 pagineFire Damper - FAQNedunuri.Madhav MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Advisory Circular 102-37Documento12 pagineRevised Advisory Circular 102-37ASD GACANessuna valutazione finora
- PM Handbook (Full PDFDocumento88 paginePM Handbook (Full PDFGary LoNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Checklist of Audit For Issuing Interim ISSC: Record NoDocumento7 pagineSelf-Checklist of Audit For Issuing Interim ISSC: Record NoalberioNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical SafetyDocumento31 pagineElectrical SafetyDennis BallantyneNessuna valutazione finora
- Eil Confined Space Entry PermitDocumento1 paginaEil Confined Space Entry PermitAvesh ChauahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Checklist ISM AuditDocumento14 pagineChecklist ISM AuditIonut Neamtu100% (6)
- Operating Manual - FeederDocumento74 pagineOperating Manual - Feedermarkus_stark3137Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum QT-740 & QT-750 Service ManualDocumento101 pagineQuantum QT-740 & QT-750 Service ManualIzzeldin ZakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Health and Safety Risk Assessment FormDocumento4 pagineHealth and Safety Risk Assessment Formbasil aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Jakarta, 16 Desember 2019 Disetujui Oleh, Disiapkan Oleh,: Presentasi Akhir Di SiteDocumento1 paginaJakarta, 16 Desember 2019 Disetujui Oleh, Disiapkan Oleh,: Presentasi Akhir Di SiteAnonymous AKniLO9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rules For Classification and Construction IV Industrial ServicesDocumento68 pagineRules For Classification and Construction IV Industrial ServicesMohamed FouadNessuna valutazione finora
- Sur Stik MsdsDocumento2 pagineSur Stik MsdsJessNessuna valutazione finora
- Sigunit L535 AF - SDSDocumento8 pagineSigunit L535 AF - SDSMuh. Agung Triady PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- PD Delta OutD V Outdoor Cabinet en Rev.00Documento34 paginePD Delta OutD V Outdoor Cabinet en Rev.00bousseyf100% (1)
- Microbiological Quality and Safety in Dairy Industry BookDocumento216 pagineMicrobiological Quality and Safety in Dairy Industry Bookziza20 ZizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gigabeam G1.25 Installation and Operations Manual 031706Documento158 pagineGigabeam G1.25 Installation and Operations Manual 031706Santosh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unsafe Act & Unsafe ConditionDocumento9 pagineUnsafe Act & Unsafe ConditionGoldie Mae Abad100% (1)
- An Introduction To Haccp Food SafetyDocumento24 pagineAn Introduction To Haccp Food SafetypeterlimttkNessuna valutazione finora
- Exec. Order 03-19 - BDRRMCDocumento7 pagineExec. Order 03-19 - BDRRMCnorie garcesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nebosh Igc-1 Important Questions and AnswersDocumento9 pagineNebosh Igc-1 Important Questions and AnswersWafula RobertNessuna valutazione finora
- Am Iso 45001 Gap Analysis Us 2pp PrintDocumento2 pagineAm Iso 45001 Gap Analysis Us 2pp PrintDavid Mora VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessment Form: ChemicalsDocumento2 pagineRisk Assessment Form: ChemicalsabubakreNessuna valutazione finora
- Fsra 5 Step Checklist PDFDocumento1 paginaFsra 5 Step Checklist PDFMaria Lisdiana100% (1)