Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Form Space Order
Caricato da
Anthony June Asa0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
44 visualizzazioni66 pagineSummary
Titolo originale
Form space order
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoSummary
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
44 visualizzazioni66 pagineForm Space Order
Caricato da
Anthony June AsaSummary
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 66
FORM, SPACE, ORDER
NOTES FROM DK CHING
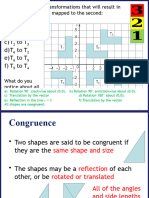
What does the Figure at right show?
a. Symmetry
b. Rhythm
c. Balance
d. Asymmetry
What Form was used in the given figure at right?
a. Central
b. Grid
c. Radial
d. Cluster
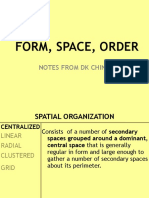
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR
RADIAL
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a number of secondary
LINEAR
spaces grouped around a dominant,
RADIAL central space that is generally
CLUSTERED regular in form and large enough to
gather a number of secondary
GRID
spaces about its perimeter.
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR
RADIAL
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a number of secondary
LINEAR
spaces grouped around a dominant,
RADIAL central space that is generally
CLUSTERED regular in form and large enough to
gather a number of secondary
GRID
spaces about its perimeter.
The Rotonda: Villa Capra
Andrea Palladio
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a series of spaces that can
LINEAR
either be directly related to one
RADIAL another or be linked through a
CLUSTERED separate and distinct linear space.
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a series of spaces that can
LINEAR
either be directly related to one
RADIAL another or be linked through a
CLUSTERED separate and distinct linear space.
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a series of spaces that can
LINEAR
either be directly related to one
RADIAL another or be linked through a
CLUSTERED separate and distinct linear space.
GRID Usually consists of repetitive spaces
which are alike in size, form, and
function.
May also consist of a single linear
space that organizes along its length
a series of spaces that differ in size,
form or function.
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR
RADIAL
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a central space from which
LINEAR
a number of linear organizations
RADIAL extend in a radial manner.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a central space from which
LINEAR
a number of linear organizations
RADIAL extend in a radial manner.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a central space from which
LINEAR
a number of linear organizations
RADIAL extend in a radial manner.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
Consists of a central space from which
LINEAR
a number of linear organizations
RADIAL extend in a radial manner.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR Relies on physical proximity to relate
RADIAL its spaces to one another.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR Relies on physical proximity to relate
RADIAL its spaces to one another.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR Relies on physical proximity to relate
RADIAL its spaces to one another.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR Relies on physical proximity to relate
RADIAL its spaces to one another.
CLUSTERED
GRID
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR Consists of forms and spaces whose
RADIAL position in space and relationship
with one another are regulated by
CLUSTERED three – dimensional grid pattern or
GRID field.
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR Consists of forms and spaces whose
RADIAL position in space and relationship
with one another are regulated by
CLUSTERED three – dimensional grid pattern or
GRID field.
SPATIAL ORGANIZATION
CENTRALIZED
LINEAR
RADIAL
CLUSTERED
GRID
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY
DATUM
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY A line established by two
DATUM points in space, about
which forms and spaces
RHYTHM can be arranged in a
regular or irregular
manner.
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY A line established by two
DATUM points in space, about
which forms and spaces
RHYTHM can be arranged in a
regular or irregular
manner.
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY A line established by two
DATUM points in space, about
which forms and spaces
RHYTHM can be arranged in a
regular or irregular
manner.
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY
DATUM
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY
DATUM
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY
DATUM
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY
DATUM
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS Implies that in the most, if not all,
HIERARCHY architectural composition, real
difference exist among forms and
DATUM spaces that reflects their degree of
RHYTHM importance as well as the functional,
formal and symbolic role they play in
the organization.
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS Implies that in the most, if not all,
HIERARCHY architectural composition, real
difference exist among forms and
DATUM spaces that reflects their degree of
RHYTHM importance as well as the functional,
formal and symbolic role they play in
the organization.
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY
DATUM
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY
DATUM
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY A line, plane or volume to which
DATUM other elements in a composition
relate.
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY A line, plane or volume to which
DATUM other elements in a composition
relate.
RHYTHM
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY Refers to any movement
DATUM characterized by a patterned
recurrence of elements or motifs
RHYTHM at regular or irregular intervals.
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSITION
AXIS
HIERARCHY Refers to any movement
DATUM characterized by a patterned
recurrence of elements or motifs
RHYTHM at regular or irregular intervals.
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
POP QUIZ !!!
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 1
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 1
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 1
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 2
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 2
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 2
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 3
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 3
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 3
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 4
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 4
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 4
REVELATIONS !
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 1
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 1
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 2
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 2
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 3
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 3
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 4
ADDITIVE FORMS
A. SPATIAL TENSION
B. EDGE TO EDGE
C. FACE TO FACE
D. INTERLOCKING VOLUME
NUMBER 4
What does the Figure at right show?
a. Symmetry
b. Rhythm
c. Balance
d. Asymmetry
What does the Figure at right show?
a. Symmetry
b. Rhythm
c. Balance
d. Asymmetry
What Form was used in the given figure at right?
a. Central
b. Grid
c. Radial
d. Cluster
What Form was used in the given figure at right?
a. Central
b. Grid
c. Radial
d. Cluster
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Form Space OrderDocumento28 pagineForm Space OrderJuan Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Spatial Organization TypesDocumento46 pagineSpatial Organization TypesAndrea PazNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Elements of Design Focusing On FormsDocumento19 pagineIntroduction To Elements of Design Focusing On FormsXxx05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Rhythm and Balance in ArchitectureDocumento31 paginePrinciples of Rhythm and Balance in ArchitectureEesha NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Arch-Tectonics: Spatial OrganizationsDocumento22 pagineApplications of Arch-Tectonics: Spatial OrganizationsKalsoom RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Composition PDFDocumento100 paginePrinciples of Composition PDFMary Nicole Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure Geometry ScriptDocumento3 pagineStructure Geometry ScriptEfferel GoodsNessuna valutazione finora
- Group6 HyperlinkDocumento41 pagineGroup6 HyperlinkJamilla V. FestinNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of DesignDocumento100 paginePrinciples of DesignTheja Mae SarrozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spatial OrganizationDocumento64 pagineSpatial OrganizationTesfuGebreslassieNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 6 C8, 8.1 Identifying Symmetry of 2D ShapesDocumento42 pagineGrade 6 C8, 8.1 Identifying Symmetry of 2D ShapesJustin Jumar B. AceronNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Architecture - IIDocumento59 pagineTheory of Architecture - IILokesh JangirNessuna valutazione finora
- GENED4Documento19 pagineGENED4Ashley DumpNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Design Essentials of The StructureDocumento65 pagine2 - Design Essentials of The StructureJaelaurence DiosanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid FigureDocumento25 pagineSolid FigureKathleen FrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Groups and Its Application to Physical ProblemsDa EverandTheory of Groups and Its Application to Physical ProblemsNessuna valutazione finora
- FashionDocumento30 pagineFashionJudith AlmendralNessuna valutazione finora
- Architectural CompositionDocumento58 pagineArchitectural CompositionPai Lang ZhenNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles and Elements of DesignDocumento2 paginePrinciples and Elements of DesignFABIENNE MARIE DUPIANONessuna valutazione finora
- MathematicsDocumento1 paginaMathematicsmanojchavan21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shape & Form: Shape Form Transformation of Form Organization of FormDocumento45 pagineShape & Form: Shape Form Transformation of Form Organization of FormBereket KassahunNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantifying The Strength of Bivariate Relationships: Ben BaumerDocumento46 pagineQuantifying The Strength of Bivariate Relationships: Ben BaumertesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Slides SymmetricPatterns KikoDocumento97 pagineSlides SymmetricPatterns KikoSeth Holden DiesmosNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Warmup M&G 2Documento82 pagineMaths Warmup M&G 2MNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizing and Ordering Principles in DesignDocumento94 pagineOrganizing and Ordering Principles in DesignJulia IngallaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4elementsofdesign 140422015503 Phpapp01Documento46 pagine4elementsofdesign 140422015503 Phpapp01Sunil TalekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 GMATH PDFDocumento66 pagineChapter 1 GMATH PDFAsri AlNessuna valutazione finora
- Circles and ChordsDocumento32 pagineCircles and ChordsJoshua Tirao100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Nature of MathematicsDocumento32 pagineLesson 1 Nature of MathematicsDanna Christine HARINANessuna valutazione finora
- Form and SpaceDocumento4 pagineForm and SpaceRjNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Intro Stats 4 e 4th Edition 0321891244Documento17 pagineTest Bank For Intro Stats 4 e 4th Edition 0321891244DanielleHawkinsrosta100% (24)
- Projection of SolidsDocumento28 pagineProjection of SolidsSruthi ChallapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Subhash Dey's B.St XII Textbook Part ADocumento72 pagineSubhash Dey's B.St XII Textbook Part AvikramNessuna valutazione finora
- Architecture of The SpaceDocumento5 pagineArchitecture of The SpaceSinduja KanagarajNessuna valutazione finora
- SymmetryDocumento96 pagineSymmetryshaangakharNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento13 pagine1Pervez alamNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading A Line GraphDocumento3 pagineReading A Line GraphJoseph YeshewasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Principles of CompositionDocumento10 pagineThe Principles of CompositionEA Kev Ramos50% (2)
- Introduction To Fischer Projections: Rotated by 180 Degrees Without Changing ItsDocumento10 pagineIntroduction To Fischer Projections: Rotated by 180 Degrees Without Changing ItsJohn RavenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Congruent Triangles v3 030919Documento29 pagineLesson 1 Congruent Triangles v3 030919Jhenny Rose PahedNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic Field Theory Lec3Documento15 pagineElectromagnetic Field Theory Lec3Sourabh GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay ClassificationDocumento7 pagineEssay Classificationcjawrknbf100% (2)
- 5 Ways To Arrange & Organize Space: Centralized Linear Radial Clustered GridDocumento6 pagine5 Ways To Arrange & Organize Space: Centralized Linear Radial Clustered GridJoseph AlcoranNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mathematical System Undefined and Defined TermDocumento56 pagineThe Mathematical System Undefined and Defined Termkylaomac0408Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4.lecture # 04, (Th+Lab)Documento74 pagine4.lecture # 04, (Th+Lab)liaqt zaib khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Relations and DigraphsDocumento2 pagineRelations and DigraphsKarl FajardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jazz_harmony__pitch-class_set_genera,-_2012_roamDocumento13 pagineJazz_harmony__pitch-class_set_genera,-_2012_roamskydonopoulosNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles and Elements of DesignDocumento14 paginePrinciples and Elements of DesignLiezel Jane SimblanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Spatial OrganizationDocumento15 pagineSpatial OrganizationNeil H. CancanNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 1 WorkbookDocumento4 pagineProject 1 Workbookfarah syamilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 3 - PPT - Patterns - DiagramsDocumento76 pagineGroup 3 - PPT - Patterns - DiagramsJosyn CABELTESNessuna valutazione finora
- Spatial Organization and Spatial Relationship PDFDocumento17 pagineSpatial Organization and Spatial Relationship PDFGokulNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulæ: Formulæ Triangle Equilateral Triangle Triangle Triangle Base Altitude Square Rectangle Rhombus DiagonalsDocumento2 pagineFormulæ: Formulæ Triangle Equilateral Triangle Triangle Triangle Base Altitude Square Rectangle Rhombus Diagonalsk2LAINessuna valutazione finora
- Assertion 5Documento4 pagineAssertion 5MiitNessuna valutazione finora
- Correlation & Regression Analysis in 40 CharactersDocumento13 pagineCorrelation & Regression Analysis in 40 CharactersPaurnima RaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature of MathematicsDocumento5 pagineNature of MathematicsMikaela Althea BorromeoNessuna valutazione finora
- SLHT Math9 Q3 Wk1aDocumento7 pagineSLHT Math9 Q3 Wk1aErica BecariNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test AllDocumento141 pagineSummative Test AllLairepmi EmjaneNessuna valutazione finora
- History 4 - Early Philippine SheltersDocumento2 pagineHistory 4 - Early Philippine SheltersAnthony June AsaNessuna valutazione finora
- IM - HISTORY 4 - Precolonial Vernacular Architecture PDFDocumento31 pagineIM - HISTORY 4 - Precolonial Vernacular Architecture PDFAnthony June AsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Art App ImsDocumento63 pagineArt App ImsAnthony June AsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Agreement For Condo Project (CAD) - UpdatedDocumento8 pagineService Agreement For Condo Project (CAD) - UpdatedAnthony June AsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Curricula Bachelor of Science in Architecture PDFDocumento40 pagineSample Curricula Bachelor of Science in Architecture PDFwanamariNessuna valutazione finora
- Estimating Guide For ArchitectsDocumento56 pagineEstimating Guide For ArchitectsChristopher Balbuena100% (2)
- Topic 2 PEDAGOGICAL PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING YOUNG LEARNERS (LGA)Documento13 pagineTopic 2 PEDAGOGICAL PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING YOUNG LEARNERS (LGA)Charles ComptonNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring resonances between dance and philosophyDocumento14 pagineExploring resonances between dance and philosophySandro Gibbon RattoNessuna valutazione finora
- Derek D. Attridge - Moving Words - Forms of English PoetryDocumento253 pagineDerek D. Attridge - Moving Words - Forms of English PoetryAnonymous 3V6h56rb100% (5)
- Learning Objectives For SingingDocumento1 paginaLearning Objectives For SingingmelindamiguelNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhajan BookDocumento201 pagineBhajan BookMarian Gi100% (1)
- Music PedagoguesDocumento24 pagineMusic PedagoguesDipesh TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Education 2Documento24 paginePhysical Education 2Francis PJ BegasoNessuna valutazione finora
- Deconstructing Chris PotterDocumento121 pagineDeconstructing Chris PotterTie Pereira100% (15)
- Chris Boucher - Doctor Who - Psi-Ence FictionDocumento149 pagineChris Boucher - Doctor Who - Psi-Ence FictionFelipe Andrés RibaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Raisin in The Sun EssayDocumento6 pagineA Raisin in The Sun EssayerinNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYED Final Exam - Attempt Review PDFDocumento11 paginePHYED Final Exam - Attempt Review PDFDwights ChristianNessuna valutazione finora
- DMIT Sample ReportDocumento33 pagineDMIT Sample ReportgkreddiNessuna valutazione finora
- Jazz Style and ArticulationDocumento8 pagineJazz Style and ArticulationChristina Syriopoulou100% (1)
- Downloaded From Manuals Search Engine: User Guide 18Documento1 paginaDownloaded From Manuals Search Engine: User Guide 18REYEYQETUNessuna valutazione finora
- Brenda Wristen PDFDocumento13 pagineBrenda Wristen PDFMatthew MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Edensor 2010Documento12 pagineEdensor 2010Marcela Del CampoNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento13 pagineUntitledAdriansyah KatiliNessuna valutazione finora
- Musical InvestigationDocumento4 pagineMusical InvestigationGermanTejadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 3 EnglishDocumento18 pagineYear 3 EnglishAhmad FadzilNessuna valutazione finora
- Debussy: Prelude To "The Afternoon of A Faun" (Prélude À L' Après-Midi D'un Faune)Documento2 pagineDebussy: Prelude To "The Afternoon of A Faun" (Prélude À L' Après-Midi D'un Faune)José PinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dance Appreciation and Composition: Lesson 3: Elements of DanceDocumento5 pagineDance Appreciation and Composition: Lesson 3: Elements of DancesasNessuna valutazione finora
- Formenlehre Arnold SchoenbergDocumento6 pagineFormenlehre Arnold SchoenbergLenin Estrella100% (1)
- Parametric Composition (First Draft)Documento31 pagineParametric Composition (First Draft)Olivier Pasquet100% (7)
- Combined P.E 2Documento34 pagineCombined P.E 2FfsafsafsavcxNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Schillinger's Theory of RhythmDocumento30 pagineGuide To Schillinger's Theory of RhythmConstantin Popescu100% (3)
- SCHICK Developing An Interpretive Context - Learning Brian Ferneyhoughs Bone AlphabetDocumento23 pagineSCHICK Developing An Interpretive Context - Learning Brian Ferneyhoughs Bone AlphabetLaura CalabiNessuna valutazione finora
- The ABCs of Bebop OrnamentationDocumento12 pagineThe ABCs of Bebop OrnamentationTroyNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements of DanceDocumento10 pagineElements of DanceClara Sabado CastillonesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Art Teaching Piano PDFDocumento280 pagineThe Art Teaching Piano PDFMichael Thanh Truong100% (5)
- Music: Quarter 1 - Module 3Documento39 pagineMusic: Quarter 1 - Module 3Harlyn May Geriane50% (2)