Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
PRECAL
Caricato da
Jerwin Fernandez TorralbaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PRECAL
Caricato da
Jerwin Fernandez TorralbaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
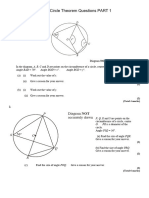
Axis: It’s a straight line which runs from the apex of the cone to the centre of the base.
Conic: It’s the locus of a point which moves in a plane, such that: the ratio of its distance from a
fixed point to its perpendicular distance from a fixed straight line is always constant.
Centre: The point which bisects every chord of the conic passing through it, is called the centre.
Double ordinate: It’s a straight line which is perpendicular to the axis and terminated at both
ends of the curve.
Latus rectum: It’s the double ordinate which passes through the focus.
Vertex: An extreme point on a conic section.
Asymptote: A straight line which a curve approaches arbitrarily closely as it goes to infinity.
Locus: The set of all points whose coordinates satisfy a given equation or condition.
Focus: A point used to construct and define a conic section, at which rays reflected from the
curve converge (plural: foci).
Conic section: Any curve formed by the intersection of a plane with a cone of two nappes.
Directrix: A line used to construct and define a conic section; a parabola has one directrix;
ellipses and hyperbolas have two (plural: directrices).
Radius- It's the distance around acircle. A radius can be a line from any point on the
circumference to the center of the circle. If you put two radii together, edge to edge, going
through the center of acircle, you would get a diameter.
Circle- is the set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point. The distance
from the center is called the radius, and the point is called the center. Twice the radius is
known as the diameter.
Parabola- is the set of all points whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus,
is equal to the distance from a fixed line, called the directrix. The point halfway between the
focus and the directrix is called the vertex of the parabola.
Ellipse- is the set of all points for which the sum of the distances from two fixed points (the
foci) is constant. In the case of an ellipse, there are two foci, and two directrices.
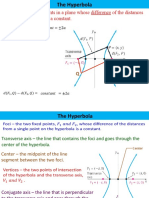
Hyperbola- is the set of all points where the difference between their distances from two
fixed points (the foci) is constant. In the case of a hyperbola, there are two foci and two
directrices. Hyperbolas also have two asymptotes.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Summative Assessment 2 Pre CalDocumento1 paginaSummative Assessment 2 Pre CalAbby Gayle NacinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 33 Common Literary Devices: Definitions, Examples, and Exercises September 22, 2020 by Sean GlatchDocumento3 pagine33 Common Literary Devices: Definitions, Examples, and Exercises September 22, 2020 by Sean GlatchJerwin Fernandez TorralbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Why The Earth'S Interior Is Hot?: Mangaldan National High School Science, Technology, Engineering, MathematicsDocumento7 pagineWhy The Earth'S Interior Is Hot?: Mangaldan National High School Science, Technology, Engineering, MathematicsJerwin Fernandez TorralbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Speech ActDocumento57 pagineSpeech ActJerwin Fernandez TorralbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Powerpoint Level OneDocumento24 pagineMicrosoft Powerpoint Level OneJerwin Fernandez TorralbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth's InteriorDocumento3 pagineEarth's InteriorJerwin Fernandez Torralba100% (2)
- Troubleshooting Computer ErrorsDocumento4 pagineTroubleshooting Computer ErrorsJerwin Fernandez TorralbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 1 (Q20)Documento2 pagineTest 1 (Q20)Mitadru DattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Me 418 (Correlation) : Analytic GeometryDocumento1 paginaMe 418 (Correlation) : Analytic GeometryLegna LegnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions On ConicsDocumento14 pagineQuestions On ConicsNilansh RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiitjee: AES Venue AddressDocumento20 pagineFiitjee: AES Venue Addressarnavanand3009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorem Part 1Documento4 pagineCircle Theorem Part 1saishaalva777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Section 10.3 Ellipses: NameDocumento2 pagineSection 10.3 Ellipses: Namesarasmile2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Review 2Documento23 pagineReview 2Syed Raheel AdeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 MathDocumento355 pagineClass 11 MathAryanNessuna valutazione finora
- EllipseDocumento13 pagineEllipsebonifacio gianga jrNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry - PresentationDocumento70 pagineAnalytic Geometry - PresentationAdrian PrinceNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 10Documento8 pagineMathematics 10Eden GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ellipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AsDocumento18 pagineEllipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AseL LeahNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperbola (Conic Sections)Documento14 pagineHyperbola (Conic Sections)Ann CandidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Parabola Exercise 2 - ADocumento19 pagineParabola Exercise 2 - AAtharva Sheersh PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Math12doc PDFDocumento12 pagineMath12doc PDFLester John PrecillasNessuna valutazione finora
- Conic Section: Case - II:-If The Plane Does Not Pass Through The Vertex O (0,0)Documento13 pagineConic Section: Case - II:-If The Plane Does Not Pass Through The Vertex O (0,0)Anupama NiroulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Identifying The Conic Sections by InspectionDocumento19 pagineIdentifying The Conic Sections by InspectionIan VillamorNessuna valutazione finora
- Conic SectionsDocumento21 pagineConic SectionsFree lancerNessuna valutazione finora
- Conic Sections WorksheetDocumento2 pagineConic Sections WorksheetAudie T. MataNessuna valutazione finora
- Ellipse Theory eDocumento18 pagineEllipse Theory ethinkiit100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry Ellipse ProblemsDocumento12 pagineAnalytic Geometry Ellipse ProblemsOjit QuizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Test-1 (Circles & Parabola)Documento4 pagineTest-1 (Circles & Parabola)Ishaan ShandilyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 (Hyperbola and Focus Directrix Equation)Documento84 pagineLecture 7 (Hyperbola and Focus Directrix Equation)Clarisson Rizzie P. CanluboNessuna valutazione finora
- PRE - CALCULUS 1st Quarter TEST QUESTIONSDocumento6 paginePRE - CALCULUS 1st Quarter TEST QUESTIONSgarryNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 05 Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFDocumento2 pagineChapter 05 Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFKamalesh Shenoy100% (1)
- Alangalang National High School: Department of EducationDocumento4 pagineAlangalang National High School: Department of EducationShy KwonNessuna valutazione finora
- Conic Sections WorksheetDocumento2 pagineConic Sections WorksheetbhartNessuna valutazione finora
- Inter 2nd Year Maths IIB (English Medium) 2024 Guess Paper-1Documento2 pagineInter 2nd Year Maths IIB (English Medium) 2024 Guess Paper-1kalyani0875Nessuna valutazione finora