Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Engineering Physics
Caricato da
Faraaz Qureshi0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
14 visualizzazioni24 pagineEngineering physics
Titolo originale
100201 Engineering Physics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoEngineering physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
14 visualizzazioni24 pagineEngineering Physics
Caricato da
Faraaz QureshiEngineering physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 24
ROI NOssssessesssseeenseee
MADHAV INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE GWALIOR-05
1° Yr. Bech Examination (Sem- If) Jan-Jun2019
Subject Code: 100201
Subject: Engineering Physies (AU/BT/CE/CM/ME)
Time: 3 hrs. Max Marks:70
‘Note:
1. Answer all 05 questions. Al questions carry equal marks.
2. In each question a,b,c are compulsory & part d has internal choice. Out of which, part a carry 2 mark, b carry 2 marks, e carry
3 marks and part d or e carry 7 marks.
3. Allparts of each questions are to be attempted at one place.
4. Assume suitable value for missing data, any
Question No. OF Marks | COs
a | Define phase velocity and group velocity. a hi
b_ | State and prove Heisenberg’s Uncertainty principle. @ 2
¢ | Show that the de-Broglie wavelength for an electron is found to be equal to (12.26/VV) A. 03 zy
‘@_| Explain the construction and working of a Cyclotron with a well labeled diagram. oF fas
1 or
@ | Derive Schrodinger’s Time Dependent equation, 7 fae
‘Question No, 02
dently the difference between constructive and destructive interference. 2 {Tt
6
‘When thin films are exposed to white Tight, beautiful colors are observed. Give reasons to [02 | 2
Justify your answer.
¢ | Ina Newion’s ring experiment, the diameter of the 10 ring changes from 1.40 em to 1.27 em | 03 3
‘when a liquid is introduced between the lens and the plate, Calculate the refractive index of the
liquid.
a [Discuss the Newion's Ring experiment for detennining the wavelength of incident }O7 [45
‘monochromatic light along with a well labeled diagram,
or
| Explain Brewster's Law. Use this law to prove that when light is incident on a transparent [07 | 4.6
substance at the polarizing angle; the reflected and refracted rays are at right angles.
‘Question No. 03
| \a__| Distinguish between p-type and n-type semiconductors. T
‘| Define the term Critical Temperature in Superconductors. 7) 2
¢ | Define Fermi Level. Draw the Fermi Level diagrams for P-Type and N-type semiconductors. 03 3
@_| Explain how a Zener diode can be used to maintain a constant voltage across the Toad along | 07 | 45
with a circuitry diagram.
SRE “ffs
pro
] ‘Question No, 04 7 I
| Siate the principle of a photodiode. oO T
|
b _| Distinguish between Top-Down and Bottom-Up approach in formation of nano-materials; ro 2
¢ | Fora solar cell, V,.=0.54 Volts, 0.024 Amperes. The open-cirouit voltage is 0.62 Volts and | 03 3
the short circuit photocurrent is 25 milli-Ampere. Calculate the Fill Factor,
d_ | Explain the construction and working of a Light Emitting Diode with a well labeled diagram, 07 45
oF
Explain the construction and working of a Liquid Crystal Display Also draw a wall Tabeled | 07 46
diagram,
Question No. 05
a | Define the terms Coherence and Monochromaticity 02 L
b ifferentiate between spontaneous and stimulated emission Process, 02 2
e- | For an optical fiber refractive index of the core is ny= 1.55, reftactive index of the ‘Cladding | 03 3
,=1.50. Determine the Numerical Aperture.
d_ | Explain the construction and working of a Ruby laser using a well labeled diagram. 07 45
oF
€ | Derive the correlation between Einstein's A and B coefficients, 07 46
MADHAV INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Cwarior-os-
BPE See eteet ee : = ia
PY Sear B Tech Examninaton ( Sern DL) Jan-Jun 2019
neering Phy sit
Sobdion of by
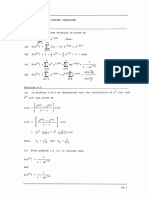
Edu A. (0) Phase Vetecilly: Gy we cpiolton , the vaca amgulan 4 wane Co)
Yo the propegahon coniland’ k is the plore velocity (wane weloccty )
Op
Tha, phae eT eloclty «f- polomnen af- contort hase. wheel.
4 a pone
advances Rapsre'n sy prada:
Growh Velocity : this velouty the vilrolty of emuclope athe
Pork of wowters re, uf isthe velocity af the wore pocleel (pene group):
bw
ial
(b) Hergen! bog 's Uncertainty rine:
Accrcing o underly riaripley uf is dnpornble 4 daeiining
Siomultowonvslig. the ayo peittion and momuationn Ga kena!
mnsasig pantiule- Pees
Jjthe wnerrleday in portion Ax awe we ss
phe diternivatiion af promecdnon a AP cere
Dx APe phe
: o px Apex
roo: voned >
eee @ hn OE kx)
bya e a Sty (art - ke)
fen ef Phare Tie wenees
é
ye yit te eee ,
= 2aSsh( cot oky) ean [SMe Sx]
@
ATT ope aA.
‘tf pall D>
cae wll din omy betiveon vhs noclis
Whe caretcbinn of hs eformeciton of roele prom “putin Uy) bs
oo Sx] =O
Ak ye Qnent ate
a SE ells
ee)
2» ee
Bsiond Ha be the abs of finn op Li nod cmnecnbin
thin
4m 4 Bh, = Gone ae Cy
aay 7
awd Oy ha = OMT ————_¢
fon (18) anne) fie
Dk (ar ee 7
2
ne
or db Dk
bt be By pr amp
> wp Ok
hy (Ax Op=h]
> AX> pp > P
More accurtt measnrenirts shows
At Ab
oy
4.0)
drm hb
scouts
aol
Jone
for an -eleten moving in potemcinf offence ot V vet,
Eo+V
h ———s
> ok
D> Be
+
vhf 6TH” Ses
me ql ae)
nT celta
Fating all “these voles wr meget, ce get
D = 12:26 x10"
Jv
Dd 2 ia28 f
Jv : i
1d). He cyclotron 0 a poecliclt accelindler, 7
Lawirenct in 149. A eyelovon commits of fo Sarge dlapo magrslt
depict te poder a gem) Cirondan. heen of uniform
rag rete “pod Thane nt call Dees
We MY ar oseilting vl tnge across Di, Pkt, which one
injected ito He mr dguadie “vale region op @ D, tree out a
somicirenlor path unchih Hy yeah We ges wane thoy one,
accedinarteel by The cliche {veld - After. gosming energy thant
a aan i) y
PpowkLies Pye Sn
Aged difrendiobins, egret (i) went A, ome,
oe
a a. & fo
> fysig gh ————
at
Mujahy og YL, both sites gage ay
ewe PvE Vew = —4Y
30
fom equation Gy (7¥) aea(v)
th 2% = 4 2% 2 Vey WY
at Bm 9x
dn 3-Dimewnlows
rane ak a ATi) Veo
aw
ee
eet = “a WV y +Ven¥]
i
Thiscs th cir dapendond Cbidgan. evan
(9
Exe. 2. (a) Consfructive Intinforence -
pores, med on Larne Phase 07 Howaing hore
Gf votinferiny
durante af an tT, whl me Oia, Bos Than HA
mnoppna oe obfedvad
a
Linay = (tit)
meat cach other. fa ofeonte phones
Lag WHS
ITT with nr 3 ne)
When wtofows
th, posi” phaue cijfferunee Ge (204
ham mbit ore abternsel ta the PR poten -
a a bctehisht;
: ‘Whe
when Th lon iy mupprosed 42 Gen
ie “ a crburs arase dna To TOR
Col ant fen. 72
nae Lylt awd, reflcted fron ha Lf and
botlean vy th felon
The Liybt whek wr fom a
foot fn te supe sp |
well tebmeltfealowr. where. roaches the sotelyfes ths question
Qype = (Ont) vy anf enty his ocbowr op wbot Lyer
poll Le fret wnat dhs mami teal tnte replete
Lilt
(¢) Refractive taoleyt q a hip
~P ain = = 1.2192...
[DJs 1-27)
(6)
QAMA) thon a beam ¢
monoclremnadtic Lig le is
allawteal to fall nerrally
en a semictrawe S
Glass fol placed at om
amet 45° wath th usr zon
aod reflects Liybt from
to qloas pet is jfotl vormally
or a cphmor emrrsere tows plod on o Hat glois plat, dank ans
brigla dire rans eda veflectten betueon
stat tha ouncl allan dapers of ary ain cfm Canratructel
Upetivernn Hu plano cowie Lows anna ee gtors plate C45 1)
Dat differner ipolerma trkecferivg baanws
De amt wy +e.
dee the tef-Up :
MM oH ) yro
Pho eich
Canslitinn or mvaralna
4 atta s wr a) 2te (anlar i
fe 2 ‘
eee as yes Te
Cone for minima
2tad ,3,--. “NY
Potzna
eee
Dat us Conor the thtelenesy op the out
' ; é A Gas t
dard yar the ross of the renga qhet age than, Ate
ab rhe vastios wf Cuvveler 4 the darn (fy 2)
D
Hes Ret a
H@= % 7 ARR ig
jon Farhagaous Heron te pe
ae
cA CHG HA
ow hae 2kee to
Since Kv quite fang? 1h Lompertoor tet, thinafore t wt
be raglate!
—_— Gay
> ve 2k*
From —egra%ours (aed vi)
yrs Re era
? Dre 2(anrPR
Datermination F wiolelang te of hy ht
ese teeta
from aagaton (U5
ey
fens “fogothan. with dhe radinn Cunvratise og the Aend Ged
Hop LCP wortns alerse oririnla
ql L
wd the aree lory
(8)
20) + Brawten's Rowe
The Predtart aungle ast urbech othe pop eetel byt in
Completely prloateed ww Enswn as Browssten's anqlh oy
await + spedlants atin Ch).
Accarelly to IPressster + te rafrostice pnt a op #ht srustioam
Sin tp
is gen by Tar tentp] 2 Sine ty
Eee as :
Fa akove veltion in Enown oy Brewther's avr
t .
fn Tener (hy Ay)
bo tp= Shr = by ( Ter)
2 tpt
The v0 leboy
11 panes
te ples hat at the purrs’ snbg angle, 7he viflecled,
ofa oe
fee YOYS ake ot neple angls ts each other.
(4)
RB. (A) pr type Semeoncbetor
Iehing am acceptor ype prypern (trivalent) 43 adebd t. “Ke
Indriattl sempteondineter, 8 creates neni envpy Lael which
ake atte gop ta ty the nepbbeaksod of * Anh af vyalonce
tan of enrgalos . Ain apparent moemont o hobs tales
Place foam tre oncetfier Lovely de cthe Nolomee bowl: The energ ates
qe fly ont duyteat near the valimen hewel awal clecrcaae
Vert'ce apwors: 4 Couchoethion bam
Ba rey charge Coren,
- 4 eg ET =o BSL evel
Ey Valente bowel
thon 4 satlenaout of olonsr Ee. Corals a
(pertarvalert ) rieponaily is ; i eeeeeeotee ae ea ae
aided] te che errystel , of create b
cenit echo) wathovt adoliig-
ay rin babs This than EY anya
trocducnd now emvepy ervels inte the energy Leawsh pictus,
Thy Aecalion ofp thine row Levels attis slightly helo th bathe
of he canctncshing Gamal. Hance “jhe mage change carreers
Cb) Cvibiced Temper |
Ek efrical renisdnrly of Some mmatals, alloys and Cornrhovnncld clye|
Svalebenly to Zero x ant Cidleaf Lelsvra cerdtonkn ia
shew freraTRns This howe is lerewn ad surperter dancin
wal toe Tem pancl—e al Reh ag neymel mitinie tory ato
a erfereomainrting viata is called Cyoticel Aeonrporotune Te.
Fr Hy tt ums Mere a olistemee an pr time df, dhe
Mk OM Ws eB dy > 26 dt
God we bins thet efor porte ialecrty in-egual @ Hh gporfi
elon a oe By
_
(4
of Ep AW dk po aecrmeierere
Thin chose in ennyy well be equal wha wertle deme
ae uy dk
> ey 20
qk, 2 E
oeO«wK
v
2
3d). Zener diode as voltage regulato
‘The Zener Diode ot “Breakdown Diode”, as they are sometimes referred too, are basically
the same as the standard PN junction diode but they are specially designed to have a low and
specified Reverse Breakdown Voltage which takes advantage of any reverse voltage applied
to it.
Zener Diodes can be used to produce # stabilised voltage output with low ripple under
varying load current conditions. By passing a small current through the diode from a voltage
Source, via a suitable current limiting resistor (Rs), the zener diode will conduct sufficient
current to maintain a voltage drop of Vout.
Ig
Ww
B.C. input voltage
from rectifier or
smoothing circuit
Vin (Vs)
“The resistor, Re is connected in series with the zener diode to limit the current flow through
the diode with the voltage source, Vs being connected across ‘the combination. The stabilised
tutput voltage Vis taken from across the zener diode. The zener diode is connected with is
carpatde emninal connected to the positive rail of the DC supply so itis reverse biased and
will be operating in its ‘preakdown condition. Resistor Rg js selected so to limit the maximum
current flowing in the circuit With no load connected to the circuit, the load current will be
zero, (Iu=0), and all the circuit current passes through the zener diode which in tum
dissipates its maximum power. ‘Also a small value of the series resistor Rs will result in a
greater diode current when the load resistance Ry, is connected and large as this will increase
sre power dissipation requirement of the diode so care must be taken when selecting the
tnpropriate value of series resistance so that the zener's maximum power rating i5 not
exceetied under this no-load or high-impedance condition.
‘The load ig connected in parallel with the zener diode, so the voltage aeross Ry is always the
same as the zener voltage, (Vr = Vz).
Q.4 (a). Photodiode: A special type of PN junction device that generates current when
exposed to light is known as Photodiode. It is also known as photodetector or photosensor. It
operates in reverse biased mode and converts light energy info electrical energy.
Principle of Photodiode
It works on the principle of Photoelectric effect.
“The operating principle of the photodiod> is such that when the junction ofthis ewo tering
Semiconductor device is illuminated then electric current starts flowing through it. Only
uinosity current flows through the device when the certain reverse potential is applied to
4b).
Breaks the massive problem into Solves the fundamental low-level
smaller sub problems. problem and integrates them into
a larger one.
Sub modules are solitarily analysed.
oriented Object-oriented programming
Stracture/procedural
programming languages Le, C) languages (like C++, Java, ete.)
follows the bottom-up approach.
follows the top-down approach.
Module documentation, test . case
creation, code implementation. and
debugging.
ue
»), Fill factor = 22%
4c) Fill factor = Fa = 5
4(@). Construction of Light Emitting Diode
‘The construction of light emitting diode is so much simple, it is made by depositing the three
layers of semiconductor material on a substrate. These three semiconductor material layers
are made three regions which are called a P-type region which is top one, active region which
is middle one and N-type region which is bottom one. The figure 2 shows all of three
semiconductor material regions.
Free stectron
photo credit
Figure 2 The Construction
Diagram of Light Emitting Diode
As Per the figure 2 the P-type region have the holes, N-type region have the elections and
active region have both electron and holes. In normal condition when there are no any
voltages are applied at anode and cathode then all the holes and electrons are present at their
places but when the voltages are applied at this light LED then it is forward biased. Then the
holes from p-type region and electrons from n-type region are pushed up towards the active
region, which is also called the depletion region. Because the holes have positive charge and
electron have negative charge then the light is produced by the recombination of these
opposite polarity charges.
Working Principle Light Emitting Diode
‘The light LED works on the same principle of simple PN junction diode means when the
anode is connected to positive terminal of de supply and cathode is connected to the negative
terminal of de supply then the PN junction is forward biased. When the PN junction is
forward biased then the holes’ form P-type region and electrons from N-type region are
recombined then the conduction band is formed for emitting the light energy in the form of
light energy photons. This whole phenomenon is called electroluminescence phenomena and
this light energy depends upon the amount of current absorbed by the LED. In other words,
this light energy is directly proportional to the absorbing current means when it absorbs more
current then the light would be high similarly when it absorbs low current then the Tight
would be low. All the absorbing current not converted into light energy some of the portion
of this current is converted into heat which is dissipated by the light emitting diode during
light emitting into external environment. This heat is known as electron dissipate energy and
this dissipate energy also depends upon the semiconductor material of light emitting diode.
The inner working diagram of this light emitting diode is also shown in figure 3.
\
conduction band
== Fermi tevel
end gay
‘ferkidden band)
‘aleniee band
4. (©. Aliquid crystal display or LCD draws its definition from its name itself. It is
combination of two states of matter, the solid and the liquid, LCD uses a liquid crystal to
produce a visible image. Liquid crystal displays are super-thin technology display screen that
are generally used in laptop computer screen, TVs, cell phones and portable video games.
LCD's technologies allow displays to be much thinner when compared to cathode ray tube
(CRI) technology.
Liquid crystal display is composed of several layers which include two polarized panel filters
and electrodes. LCD technology is used for displaying the image in notebook or some other
electronic devices like mini computers. Light is projected from a lens on a layer of liquid
crystal. This combination of colored light with the grayscale image of the crystal (formed as
electric current flows through the crystal) forms the colored image.
‘This image is then displayed on the screen.
LCD Layered Diagram
‘How LCDs are constructed?
Simple facts that should be considered while making an LCD:
hanye the polarized light
visa} both ofthe operation to wansmit also able
s mentigned above that we need to fake two polarized lass pieces filter in the malking of
the liquid erysta
rubbed with a speeial polymer
The glass which does not have a polarized film on the surface of j1 must be
luich ill ereate microscopi
‘coves on the surface of the
polarized slass Hltet
The proves must be in the same direction of the polarized film. Now
c have to add a coating of pneumatic Hiquid polarized filter of
ter
th
ized el
orientation. W!
en the right any
appears at the first laver piece, we should add a second
piece of glass with the polarized film, The fist filter will be naturally polarized as the light
strikes it at the starting stage.
Thus the fight travels through each layer and guided on the next with the help of molecule.
The molecule tends to change its plane of vibration of the light in order to match their angle
When the light reaches to the far end of the liquid crystal substance, it vibrates at the same
that of the final layer of the molecule vibrates. The light
allowed to enter into the
device only if the second layer of the polarized glass matches with the final layer of the
molecule,
How LCDs Work?
‘The principle behind the LCD's is that when an electrical eurrent is applied to the Hauid
crystal molecule, the molecule tends to untwist, This causes the angle of light which is
passing through the molecule of the polarized glass and also cause a change in the angle of
the top polarizing filter. As a result a litle light is allowed to pass the polarized glass through
a particular area of the LCD. Thus that particular area will become dark compared to other.
“The LCD works on the principle of blocking light. While constructing the LCD's, a reflected
tmitror is arranged at the back. An electrode plane is made of indium-tin oxide which is kept
on top and a polarized glass with a polarizing film is also added on the bottom of the device.
‘The complete region of the LCD has to be enclosed by a common electrode and above it
should be the liquid erystal matter.
Next comes to the second piece of glass with an electrode in the form of the rectangle on the
bottom and, on top, another polarizing film. It must be considered that both the pieces are
kept at right angles. When there is no current, the light passes through the front of the LeDit
will be reflected by the mirror and bounced hack. As ihe electrode is connected to a baitery
the current from it wil cause the liquid crystals between the common-plane electrode and the
an
electrode shaped like a rectangle to untwist. Thus the light is blocked from passing through.
‘That particular rectangular area appears blank.
Q
5. (a) Coherence: two wave sources are perfectly coherent if they have a constant phase
difference and the same frequency, and the same waveform. Coherence is an ideal property
of waves that enables stationary (i.e. temporally and spatially constant) interference.
Monochromaticity: Monochromaticity represents the single color. If a light (radiation) have
only one wavelength, It is called as monochromatic light. Ex. — Sodium lamp.
5(b). Difference between spontaneous emission and stimulated emissi
Spontaneous emission does not require an external electromagnetic stimulus to release
energy, whereas stimulated emission does requite extemal electromagnetic stimuli to release
energy.
+ During spontaneous emission, only one energy wave is released, but during stimulated
emission two energy waves are released.
+ The probability of stimulated emission to take place is higher than the probability for
spontaneous emission to take place as extemal electromagnetic stimuli increases the
probability of attaining the dipole transition state.
« By properly matching the energy gaps and incident frequencies, stimulated emission can be
used to greatly amplify the incident radiation beam; whereas this is not possible when
spontaneous emission takes place.
5(0).
7 2
NABL= PNA)" = (No) = [CL 55)* — 50)? = 0.1525
5,(d). Ruby Laser: A ruby laser is a solid-state laser that uses the synthetic ruby erystal as its
laser medium, Ruby laser is the first successful laser developed by Maiman in 1960.
Ruby laser is one of the few solid-state lasers that produce visible light. It emits deep red light
of wavelength 694.3 nm.
Construction of ruby laser
|A raby laser consists of three important elements: laser medinm, the pump souree, and the
optical resonator.
Ww
Laser medium or gain median in ruby laser
Ina ruby laser, a single crystal of ruby (AlzO3: Cr) in the form of cylinder acts as a laser
medium or active medium. The laser mediuin (ruby) in the ruby laser is made of the host of
sapphire (AlOs) whieh is doped with small amounts of chromium ions (Cr). The ruby has
good thermal properties.
Fully
reflecting Partially
mirror reflecting
mirror
Laser output
Laser medium
(Ruby) ©
‘Pump source or energy source in ruby laser
‘The pump source is the clement of a ruby laser system that provides energy to the laser
medium, In a ruby laser, population inversion is required to achieve laser emission.
Population inversion is the process of achieving the greater population of higher eneray ste
then the lower energy state. In order to achieve population inversion, we need to supply
‘energy to the laser medium (ruby).
In aruby laser, we use feshtube as the energy souree of pump source, The Mashtube supplies
energy to the laser medium (ruby). When lower energy state electrons in the laser medium
nin sufficient energy from the feshtube, they jump into the higher energy state or excited
state.
Optical resonator
‘The ends of the cylindrical ruby rod are flat and parallel. The cylindrical ruby rod is placed
etween two mitrors. The optical coating is applied to both the mirrors, The process of
depositing thin layers of metals on glass substrates to make minor surfaces is called
silvering. Each mirror is coated or silvered differently.
‘At one end of the rod, the mirror ig fully silvered whereas, at another end, the mirror is
partially silvered.
iw
The fully silvered mirror will completely reflect the light whereas the partially silvered mirror
will reflect most part of the light but allows a small portion of light through it to produce
output laser light.
Working of ruby laser
The ruby laser is a three level solid-state laser, In a ruby laser, optical pumping technique is
used to supply energy to the laser medium. Optical pumping is a technique in which light is
used as energy source to raise electrons from lower energy level to the higher energy level.
Consider a ruby laser medium consisting of three energy levels Ey, Eo, Es with N number of
electrons.
We assume that the energy levels will be E: < Ex < Es. The energy level E, is known as
ground state or lower energy state, the energy level Ez is known as metastable state, and the
energy level Es is known as pump state,
Let us assume that initially most of the electrons are in the lower energy state (E1) and only a
tiny number of electrons are in the excited states (Ep and Es)
@ @
eee E 2 ABB S2. 5,
Photons enema Ex
at
Selee cae c,
{
t
t
Population
Physics and Radio-Electronics oe
‘When light energy is supplied to the laser medium (ruby), the electrons in the lower energy
state or ground state (E1) gains enough energy and jumps into the pump state (Es),
‘The lifetime of pump state E3 is very small (10° sec) so the electrons in the pump state do not
stay for long period. After a short period, they fall into the metastable state Bz by releasing
radiationless energy. The lifetime of metastable state Fz is 10° see which is much greater
than the lifetime of pump state Es, Therefore, the electrons reach E2 much fester than they
leave E>. This results in an increase in the number of electrons in the metastable state E> and
hence population inversion is achieved.
Dy
@
Afier some period, the electrons in the metastable state E) falls into the lower energy state
E; by releasing energy in the form of photons. This is called spontaneous emission of
radiation,
When the emitted photon interacts with the electron in the metastable state, it forcefully
makes that electron fall into the ground state E). As a result, two photons are emitted. This is
called stimulated emission of radiation.
‘When these emitted photons again interacted with the metastable state electrons, then 4
photons are produced. Because of this continuous interaction with the clectrons, millions of
photons are produced.
Iman active medium (ruby), a process called spontaneous emission produces light. ‘The light
produced within the laser medium will bounce back and forth between the two mirrors. This
stimulates other electrons to fall into the ground state by releasing light energy. This is called
stimulated emission. Likewise, millions of electrons are stimulated to emit light. Thus, the
light gain is achieved.
‘The amplified light escapes through the partially reflecting mirror to produce laser light.
Ask ph avd Now bee mob of clin at ama teva” yy the,
shat awh 2, respectively: Te probabil 4 obraer tien
Fremaition for naumber. of siwn cfr stalk Ltn 2 per
Untt bine bo aieen by (u wn thadent -eninay dowert )
WA v= M Bru) ——
Thy btaf Jrrcbab lily op tranvttion we number of ales tem
Shit 2 Ted, 2tthin by spowkmeowsly or by shill
ews, wrt twa 1 guen by a
fe 7 Ne far uy) a
Gy armel agp tbilovisen ob emp Ty the abyerfattn oat
}
~|
emnot Thos
mewisvton prebabr liters ane 14
NA, = Ne Al
3 NBa uw) = Ne[Arit Baud] 7
Na Avi
DP Uw =
Ny) Bia 7 Ne Boy
U)= Ay
a, (f ) (iyE)-1
£ Bud according to Eras
By > Bes
> ume 4 7H) ee (Y
%, (Ls C7
Acad Le belbomann's toot
M (Ee eT
a
le eT
Aenu food again Gy
7 / ——oooe mo
vores & rw
Ba, eft}
Plunk’s yadialion he yualeds
Ue - ee E enh,
ee]
Conpooy (yet
[far , Bebe
Let eo
&
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Iso 25101-2009 PDFDocumento24 pagineIso 25101-2009 PDFADAM SYAHPUTRANessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Assignment IIDocumento23 pagine03 Assignment IIAnurag AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Forces On Large Steam Turbine Blades: RWE NpowerDocumento5 pagineForces On Large Steam Turbine Blades: RWE Npowermimoune lamraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress and Strain - Plane Stress and Plane StrainDocumento5 pagineStress and Strain - Plane Stress and Plane StrainPretheesh Paul CNessuna valutazione finora
- MITRES 6 008S11 Sol04 PDFDocumento9 pagineMITRES 6 008S11 Sol04 PDFsowNessuna valutazione finora
- Fenper Lanjut #4TurbulentTransport 2020Documento26 pagineFenper Lanjut #4TurbulentTransport 2020Aji Ridho PangestuNessuna valutazione finora
- Magneto-Hydro Dynamic Generator: Hannes AlfvénDocumento34 pagineMagneto-Hydro Dynamic Generator: Hannes AlfvénHuzaifa WasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Iit RPR Ma201Documento2 pagineIit RPR Ma201atggregNessuna valutazione finora
- Question bank-MASS TRANSFER-II MECDocumento10 pagineQuestion bank-MASS TRANSFER-II MECkishore.21uchNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Structures Study Book 3Documento14 pagineSteel Structures Study Book 3ELMER EDINSON FLORES PONCENessuna valutazione finora
- Mekanika Rekayasa 1Documento2 pagineMekanika Rekayasa 1Rizqina AriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pump Performance Datasheet: Operating Conditions LiquidDocumento1 paginaPump Performance Datasheet: Operating Conditions LiquidFabian A NeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Free FallDocumento24 pagineFree FallNoob KidNessuna valutazione finora
- PHME16 CM Bearing FinalDocumento18 paginePHME16 CM Bearing Finalowais khanNessuna valutazione finora
- MMP 2 Mansoor Sultan: First PortionDocumento6 pagineMMP 2 Mansoor Sultan: First PortionMansoor AslamNessuna valutazione finora
- R1116010-00000-CI-SPC-0003-0-Anchor BoltDocumento16 pagineR1116010-00000-CI-SPC-0003-0-Anchor BoltLNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM D 638 - 14 Standard Test Method For Tensile Properties of PlasticsDocumento1 paginaASTM D 638 - 14 Standard Test Method For Tensile Properties of PlasticsGustavoNessuna valutazione finora
- Molle Per Stampi Die Springs Schraubendruckfedern Ressorts de Compression Muelles para Moldes Molas para EstamposDocumento40 pagineMolle Per Stampi Die Springs Schraubendruckfedern Ressorts de Compression Muelles para Moldes Molas para EstamposclaudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Tyco Quality Manual 1654241-1CrimpBroGBDocumento28 pagineTyco Quality Manual 1654241-1CrimpBroGBdamirNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFDocumento23 pagine1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFMARVIN DELA CRUZNessuna valutazione finora
- (Engineering Materials) Murat Bengisu (Auth.) - Engineering Ceramics-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2001)Documento629 pagine(Engineering Materials) Murat Bengisu (Auth.) - Engineering Ceramics-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2001)Prosenjit DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Air-Cooling Battery Thermal Management System For Formula Student CarDocumento19 pagineAnalysis of Air-Cooling Battery Thermal Management System For Formula Student Carleone.martellucciNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Solved TestDocumento10 pagineMathematics Solved TestShayan FarrukhNessuna valutazione finora
- Probabilistic Structural Dynamics: Parametric vs. Nonparametric ApproachDocumento39 pagineProbabilistic Structural Dynamics: Parametric vs. Nonparametric Approachejzuppelli8036Nessuna valutazione finora
- EOS Tuning 1671172242Documento34 pagineEOS Tuning 1671172242ASKY PNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Cite An Honors Thesis ApaDocumento4 pagineHow To Cite An Honors Thesis Apamonroeandertonsaltlakecity100% (2)
- Pinned Base Plate-ECPLUS Design-ExampleDocumento4 paginePinned Base Plate-ECPLUS Design-ExampleNivarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics and Its HistoryDocumento3 pagineMathematics and Its HistoryZlatni PresekNessuna valutazione finora
- An Intuitive Guide To Linear Algebra - BetterExplainedDocumento25 pagineAn Intuitive Guide To Linear Algebra - BetterExplainedvkk intensiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Probe Measurements of Electron-Energy Distributions in Plasmas: What Can We Measure and How Can We Achieve Reliable Results?Documento32 pagineProbe Measurements of Electron-Energy Distributions in Plasmas: What Can We Measure and How Can We Achieve Reliable Results?muhammad usmanNessuna valutazione finora