Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Data Soldadura
Caricato da
Chiclla Quispe PercyCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Data Soldadura
Caricato da
Chiclla Quispe PercyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Welds (ANSI/AISC 360-10, CHAPTER J)
2. Fillet welds
2b. Limitations
The minimum size of fillet welds shall be not less than the size required to transmit calculated forces, nor the
size as shown in Table J2.4. These provisions do not apply to fillet weld reinforcements of partial- or complete-
joint-penetration groove welds.
The maximum size of fillet welds of connected parts shall be:
(a) Along edges of material less than 1/4-in. (6 mm) thick; not greater than the thickness of the material.
(b) Along edges of material 1/4 in. (6 mm) or more in thickness; not greater than the thickness of the
material minus 1/16 in. (2 mm).
The minimum length of welds designed on the basis of strength shall be not less than four times the nominal
weld size.
AWS D1.1/D1.1M, Complementary specifications.
2.3.3.7 Effective Throat of Skewed T-Joints.
The effective throat of a skewed T-joint in angles between 60 and 30 shall be the minimum distance from the
root to the diagrammatic face, less the Z loss reduction dimension. The effective throat of a skewed T-joint in
angles between 80 and 60 and in angles greater than 100 shall be taken as the shortest distance from the
joint root to the weld face.
4. Strength
The design strength, Rn of welded joints shall be the lower value of the base material strength determined
according to the limit states of tensile rupture and shear rupture and the weld metal strength determined
according to the limit state of rupture as follows:
Rn
For the base metal
For the weld metal
where
FnBM: Nominal stress of the base metal.
Fnw: Nominal stress of the weld metal.
ABM: Cross-sectional area of the base metal.
Awe: Effective area of the weld.
FEXX: Filler metal classification strength.
Fy: Specified minimum yield stress of the base metal.
Fu: Specified minimum tensile strength.
Available Strength of Welded Joints, Table J2.5
Load Type and Direction Relative to Weld Axis Pertinent Metal Resistance factor, Nominal Stress
Fillet welds including fillets in holes and slots and skewed T-Joints
Base 0.9 FnBM = 0.6 Fy
Shear
Weld 0.75 Fnw = 0.60 FEXX
Tension or compression in parts joined parallel to a
Tension or compression Parallel to weld axis weld need not be considered in design of welds
joining the parts.
6. Filler Metal Requirements
The choice of filler metal shall comply with the requirements for matching filler metals given in AWS
D1.1/D1.1M.
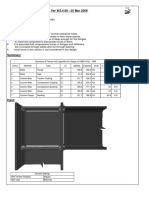
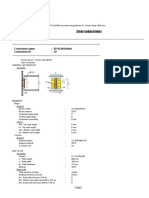
Geometric checks
Effective length Size
Description Type W.P. t
(mm) lmin l wmin wmax w
(mm) (mm) (mm) (mm) (mm)
Web weld Fillet SMAW 6 40 145 3 6 3
W.P.: Welding process.
t: Material thickness of thinner part joinned.
l: Effective length of the weld.
w: Weld leg size.
Strength Checks
Base
Electrode Shear (Weld Metal) Stresses (Base Metal) Resistance factor
Metal
Size
Description (mm) t l
(mm) (mm) Worst Worst
Fw Fy Resistant Use Resistant Use Base material Weld
(MPa) (MPa) case (MPa) (%) case (MPa) (%)
(MPa) (MPa)
E60XX
Web weld 3 6 145 250.0 49.8 186.8 26.65 35.2 135.0 26.07 0.90 0.75
(415.0)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Calculation For Base Plate ConnectionDocumento85 pagineCalculation For Base Plate ConnectionpriantomoNessuna valutazione finora
- CE319 Design of Steel StructureDocumento53 pagineCE319 Design of Steel StructureMD Mazharul Islam BappyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce 304 Lesson 6Documento5 pagineCe 304 Lesson 6Lester Khiets RoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teves, Eric Venz C. Bsce 3-4 Ce-Pc 325 Laboratory 1Documento71 pagineTeves, Eric Venz C. Bsce 3-4 Ce-Pc 325 Laboratory 1Teves, Eric Venz C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Column Base Plate (Fixed Type)Documento13 pagineColumn Base Plate (Fixed Type)KM YapNessuna valutazione finora
- BPOSDAGDocumento27 pagineBPOSDAGIndustry Standard Structural DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- 12F0011X0-Stainless-Steel-Fastener-Mechanical-PropertiesDocumento2 pagine12F0011X0-Stainless-Steel-Fastener-Mechanical-PropertiespkdscdubaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-Mechanics of TurningDocumento23 pagine3-Mechanics of TurningOKELLO JOB LAZARUSNessuna valutazione finora
- Column to Girder Connection CalculationDocumento15 pagineColumn to Girder Connection CalculationNitesh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Sambungan Las: Keuntungan dan Kerugian Las Serta Persoalan WeldingDocumento50 pagineSambungan Las: Keuntungan dan Kerugian Las Serta Persoalan WeldingMaruli SaragihNessuna valutazione finora
- ASME Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) SummaryDocumento3 pagineASME Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) SummaryvenkateshNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation 1 Design ReportDocumento6 pagineFoundation 1 Design ReportDinesh RajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Base Plate CheckDocumento180 pagineBase Plate CheckHussain Mir100% (1)
- Bolted Connections 1Documento45 pagineBolted Connections 1Nicole ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard weld calculation for steel profilesDocumento11 pagineStandard weld calculation for steel profilesOvidiu MoraruNessuna valutazione finora
- Memoria Samet SimpleDocumento2 pagineMemoria Samet SimpleJuan Emanuel VenturelliNessuna valutazione finora
- Bolted Fin Plate Connection Title: Notes and AssumptionsDocumento6 pagineBolted Fin Plate Connection Title: Notes and AssumptionsJonAthan LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Base PlateDocumento6 pagineBase PlateShaikh ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Joining Module - 2 HR Recitation With Data For Lab ReportsDocumento4 pagineJoining Module - 2 HR Recitation With Data For Lab ReportsKarnati SatwikNessuna valutazione finora
- Cutting Forces and Surface Roughness in Hard Turning of Hot Work Steel X38Crmov5-1 Using Mixed CeramicDocumento6 pagineCutting Forces and Surface Roughness in Hard Turning of Hot Work Steel X38Crmov5-1 Using Mixed CeramicAnnada Prasad MoharanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam To BeamDocumento6 pagineBeam To BeamShaikh ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Base Plate Design for H-Shaped Steel ColumnDocumento9 pagineBase Plate Design for H-Shaped Steel ColumnharishduttNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation For Column Base Plate (H-Shape)Documento9 pagineCalculation For Column Base Plate (H-Shape)Syafiruddin CokiNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation 1 Design ReportDocumento7 pagineFoundation 1 Design ReportEdwinBastidasNessuna valutazione finora
- Tensile Strength Conversion Sheet For Slab On Grade Fiber Dosage CalculationsDocumento5 pagineTensile Strength Conversion Sheet For Slab On Grade Fiber Dosage Calculationsjana zongerNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of The Joint Connection of RC Pile From XinChuangDocumento13 pagineCalculation of The Joint Connection of RC Pile From XinChuangDier K-riboNessuna valutazione finora
- Slab Design OldDocumento14 pagineSlab Design Oldshreejay maneNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding Symbol 14 Nov 2023Documento24 pagineWelding Symbol 14 Nov 2023achmad kurniawan ZakariaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.0 Design For 5-Pile Group (Square Group)Documento1 pagina8.0 Design For 5-Pile Group (Square Group)afzal taiNessuna valutazione finora
- Resistance Welding: Indian Institute of Welding - ANB Refresher Course - Module 10Documento40 pagineResistance Welding: Indian Institute of Welding - ANB Refresher Course - Module 10dayalramNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of RC Plate Coupling BeamDocumento5 pagineDesign of RC Plate Coupling BeamJai ThakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam - Column Connection - Ver W2.4.00 - 25 Mar 2008 Title: Code of Practice: Created: Notes and AssumptionsDocumento2 pagineBeam - Column Connection - Ver W2.4.00 - 25 Mar 2008 Title: Code of Practice: Created: Notes and AssumptionsNyu123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- 50 CRV 4Documento2 pagine50 CRV 4saptotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 04-Nov-23 Design Code ENDocumento23 pagineProject Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 04-Nov-23 Design Code ENkheang amgNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Failure Analysis: M. Cerit, O. Kokumer, K. GenelDocumento8 pagineEngineering Failure Analysis: M. Cerit, O. Kokumer, K. GenelluisNessuna valutazione finora
- 16mm Rotary Type, Metal Shaft Series: Application FeatureDocumento6 pagine16mm Rotary Type, Metal Shaft Series: Application Featureromanbun1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3B. Welded Connections: CE4: Design of Steel Structures - Prof. Dr. A. VarmaDocumento14 pagineChapter 3B. Welded Connections: CE4: Design of Steel Structures - Prof. Dr. A. VarmaGNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam CalculationDocumento49 pagineBeam CalculationRobin Charles SamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah 5 Sambungan LasDocumento31 pagineKuliah 5 Sambungan LasAlifiaNessuna valutazione finora
- ETABS 2015 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2015 15.2.2 License # 1YTPN38NXMTW9BADocumento2 pagineETABS 2015 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2015 15.2.2 License # 1YTPN38NXMTW9BAjuanda sinagaNessuna valutazione finora
- DetailsDocumento1 paginaDetailsJansen SjaklifNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathcad - Dead - Load - Hanger - FixingDocumento12 pagineMathcad - Dead - Load - Hanger - FixingtonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Spread Sheet of Plate Girder-Is800-2007Documento3 pagineSpread Sheet of Plate Girder-Is800-2007yedida v r aviswanadhNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation 1 Design ReportDocumento7 pagineFoundation 1 Design ReportEdwinBastidasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ongc WPS 1 of 2Documento4 pagineOngc WPS 1 of 2Kiran NikateNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation 1 Design ReportDocumento5 pagineFoundation 1 Design Reportyug draciNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding Procedure Specification for ASME Section IXDocumento4 pagineWelding Procedure Specification for ASME Section IXRahul MoottolikandyNessuna valutazione finora
- ETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.2.0 License # 1BHL6PNMMMVATF7Documento2 pagineETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.2.0 License # 1BHL6PNMMMVATF7Anonymous 6R10dB2RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation 1 Design ReportDocumento7 pagineFoundation 1 Design Report“Lava Gamers” ahmet akmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem-Wps - PQR - WPQ-004 CS-SS 08-08 GtawDocumento5 pagineChem-Wps - PQR - WPQ-004 CS-SS 08-08 Gtawvijay padaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis Professional 2017 for Perfil "CDocumento2 pagineAutodesk Robot Structural Analysis Professional 2017 for Perfil "CJuan Emanuel VenturelliNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam To Column Web UC254Documento2 pagineBeam To Column Web UC254gunasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam To Column Web UC254.Documento2 pagineBeam To Column Web UC254.gunasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 04-Nov-23 Design Code ENDocumento13 pagineProject Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 04-Nov-23 Design Code ENkheang amgNessuna valutazione finora
- TEORI - Bolted & Welded ConnectionsDocumento95 pagineTEORI - Bolted & Welded Connectionsmelanie amalia zahra100% (1)
- Project Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 04-Nov-23 Design Code ENDocumento20 pagineProject Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 04-Nov-23 Design Code ENkheang amgNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter (5) Design of Bolted ConnectionDocumento9 pagineChapter (5) Design of Bolted ConnectionAhmed BarakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Links MasterDocumento1 paginaLinks MasterChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Data SoldaduraDocumento2 pagineData SoldaduraChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance LogDocumento1 paginaPerformance LogChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- CloudDocumento2 pagineCloudChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- ManufacturerDocumento2 pagineManufacturerChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- LibrosDocumento1 paginaLibrosChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- 251515Documento1 pagina251515Chiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculo ConexionDocumento7 pagineCalculo ConexionChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cuentas ActualizadasDocumento1 paginaCuentas ActualizadasChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Rodamiento Bielas: Manufacturer Description Part Number MassDocumento1 paginaRodamiento Bielas: Manufacturer Description Part Number MassChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- HTTP QuechuaDocumento1 paginaHTTP QuechuaChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- CloudDocumento2 pagineCloudChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas engine parameters and performance resultsDocumento3 pagineGas engine parameters and performance resultsChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- HTTPDocumento1 paginaHTTPChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- First PartDocumento1 paginaFirst PartChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Web Extractor EolicoDocumento1 paginaWeb Extractor EolicoChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Angels or DevilsDocumento1 paginaAngels or DevilsChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas engine parameters and performance resultsDocumento3 pagineGas engine parameters and performance resultsChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Angels or DevilsDocumento1 paginaAngels or DevilsChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- MatlabDocumento1 paginaMatlabChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Infinite SkillsDocumento1 paginaInfinite SkillsChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Separador de RodamientosDocumento1 paginaSeparador de RodamientosChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Asd Steel Detailing Manual Eng 2010Documento170 pagineAsd Steel Detailing Manual Eng 2010MURTY69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Infinite SkillsDocumento1 paginaInfinite SkillsChiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP2000 Frame Element Forces Report535353535454545454555555555556565656565757575757585858ENERCOMPage 4 of 7-144.520.000.000.0010703.3410701.1410698.950.000.000.000.000.000.000.00Documento7 pagineSAP2000 Frame Element Forces Report535353535454545454555555555556565656565757575757585858ENERCOMPage 4 of 7-144.520.000.000.0010703.3410701.1410698.950.000.000.000.000.000.000.00Chiclla Quispe PercyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7-Work, Energy UpdatedDocumento43 pagineChapter 7-Work, Energy UpdatedNoor BlNessuna valutazione finora
- Simplified Method For Calculating He Active Earth Pressure On Retaining Walls of Narrow Backfi..Documento13 pagineSimplified Method For Calculating He Active Earth Pressure On Retaining Walls of Narrow Backfi..Naim AburayyamNessuna valutazione finora
- OpenSees Implementation Final PDFDocumento18 pagineOpenSees Implementation Final PDFHasan AyoubyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gunpowder RocketsDocumento4 pagineGunpowder RocketsMartin EcheverriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Heat TransferRishabh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- DYNA6 Manual With ExamplesDocumento227 pagineDYNA6 Manual With ExamplesDeepmalaJayesh100% (1)
- Rigid Bodies Dinamic SolutionsDocumento11 pagineRigid Bodies Dinamic SolutionsElle LawlietNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus I - Solutions #4Documento10 pagineCalculus I - Solutions #4anhducgmc2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of MaterialsDocumento4 pagineStrength of MaterialsAbi Nesh100% (1)
- Stress Analysis of Rectangular BracketDocumento28 pagineStress Analysis of Rectangular BracketArun prakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap10no1 PDFDocumento2 pagineChap10no1 PDFTajiriMollel23% (13)
- Design of Embeded Plate (INDIAN STANDARD)Documento3 pagineDesign of Embeded Plate (INDIAN STANDARD)Shubham Verma100% (2)
- Ujian 1 BNJ 20103 Dinamik SEMESTER 1 SESSI 2017/2018: Answer All QuestionsDocumento3 pagineUjian 1 BNJ 20103 Dinamik SEMESTER 1 SESSI 2017/2018: Answer All QuestionsJimmy KudiNessuna valutazione finora
- CH11 2Documento20 pagineCH11 2Usaid KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGR1003 Finals Week 1Documento40 pagineENGR1003 Finals Week 1celinewinchester7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Earthquake Waves ExplainedDocumento3 pagineTypes of Earthquake Waves ExplainedBobby WskNessuna valutazione finora
- Article Vilebrequin F8L413Documento12 pagineArticle Vilebrequin F8L413Maarten BaanNessuna valutazione finora
- RHEOLOGYDocumento39 pagineRHEOLOGYraju niraulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrodynamic Journal BearingDocumento4 pagineHydrodynamic Journal BearingEbe Nezer GNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 4Documento5 pagineExp 4alebachewNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear Drives Vs Belt DrivesDocumento17 pagineGear Drives Vs Belt DrivesAaryan MahakalkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 6-2Documento3 pagineTutorial 6-2Chandrali DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotex SpecDocumento30 pagineRotex SpecspringkimNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Lifting Hook: Earth Fill Load (Dl2)Documento21 pagineDesign of Lifting Hook: Earth Fill Load (Dl2)Asaru DeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Student Dorothy Kam: Laboratory Report Myp 5Documento10 pagineName of Student Dorothy Kam: Laboratory Report Myp 5api-336598674Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Material Machine DesignDocumento98 pagineStudy Material Machine DesignOxy GenNessuna valutazione finora
- Static & Kinetic Friction ExprementDocumento7 pagineStatic & Kinetic Friction ExprementBishoy GirgisNessuna valutazione finora
- AISC Basic Steel Design Session 6 - Stability Analysis and Design I 10-29-2013Documento28 pagineAISC Basic Steel Design Session 6 - Stability Analysis and Design I 10-29-2013Eric RicoNessuna valutazione finora
- MEBS6008 Environmental Services II Fluid Network AnalysisDocumento60 pagineMEBS6008 Environmental Services II Fluid Network Analysisahtin618Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS 102 - General Physics II Midterm Exam 1: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 03 March 2018, 10:00Documento3 paginePHYS 102 - General Physics II Midterm Exam 1: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 03 March 2018, 10:00Nano SuyatnoNessuna valutazione finora