Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
4 Major Activities
Caricato da
virgil mae taghapCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4 Major Activities
Caricato da
virgil mae taghapCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4 Major Activities
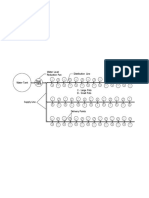
1. Animal Delivery
Reception-Off loading - Animals are transported from housing to abattoir.
Receiving area must have watering, feeding and animal inspection facilities.
Ante-Mortem Inspection - Animals are to be inspected by a Veterinarian.
Healthy animals are sent to lairage while sick and injured animals are to be sent
to isolation pen or slaughtered immediately. Ante-mortem inspection is any
method of inspection of animal health prior to slaughtering by official inspector
for consumers’ safety.
Lairage - Place where animals are provided rest before slaughter. Rest is to be
provided up to 24 hours to overcome the physiological stress involved in
transportation of animals.
Emergency Slaughtering - Immobility of pigs is a reason for emergency
slaughter. An emergency slaughter is a slaughter of a food animal that has a
disease, that is suspected to have one, or that is injured. These animals are
slaughtered in facilities designed for this purpose or in slaughterhouse sections
used for this purpose or on the premises of a regular slaughterhouse but at
separate times.
2. Slaughtering Activities
Stunning - renders an animal insensible before it is killed
Bleeding - remove as much blood from the carcass as possible before further
handling
Scalding - lowering of animal into steam to prepare skin for dehairing
Dehairing - removal of the hair of the carcass
Singeing - cleaning the carcass by burning the hair
Removal of heads and feet - head shall be removed by cutting through the
vertebral column behind the ear at the atlas joint.
Removal of hides
Brisket Splitting
Evisceraton - process of removing the internal organs in the abdominal and
thoracic cavities
Offal cleaning - wastes or the by-products after evisceration are cleaned and
are ready to be outloaded
3. Packaging and Cooling
Carcass Splitting - dividing carcass into parts
Post Mortem Inspection – means any methods of the inspection of carcass and
visceral organs by official inspector for consumers’ safety.
Final Wash
Deboning
Carcass Quartering
Carcass Quarter Transfer
Hanging
Chilling - The carcasses will be placed in chilled storage prior to dispatch. Meat
will be kept in chilled storage (at 2°C) for a minimum period of 24 hours before
dispatch.
4. Meat delivery
Outloading (Carcasses/Packaged Meat) – Carcasses are placed ready for
transporting from abattoir to market.
http://www.epa.ie/licences/lic_eDMS/090151b2800c1cdb.pdf - process flow w/ diagram
Life long learning:
As future Ag. Engr's, it is essential to be familiar in making a process flow chart or to interpret one.
Basic knowledge on a process flow charts can help an Engr or a business owner to improve the
efficiency of a workplace in accomplishing a task. Streamlining the processes within a business can
greatly help operators to increase their productivity, and more productivity means more sales, more
sales means greater profit. By providing flow charts on any services/business it will help avoid
technical errors and can give visitors an idea on how the operation works.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- (Julie K. Briggs, Valerie G.A. Grossman BSN CEN Emergency Nursing 5 Tier Triage ProtocolDocumento272 pagine(Julie K. Briggs, Valerie G.A. Grossman BSN CEN Emergency Nursing 5 Tier Triage ProtocolWulan Rahmadani FauziNessuna valutazione finora
- IEC Workshop PresentationDocumento5 pagineIEC Workshop Presentationvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- FinishDocumento1 paginaFinishvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- 04-AE199 Group Report 1 TemplateDocumento3 pagine04-AE199 Group Report 1 Templatevirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Agex1321 PDFDocumento5 pagineAgex1321 PDFMyrla Mae SintosNessuna valutazione finora
- ACRONYMSDocumento1 paginaACRONYMSvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Argie Sheet 4Documento1 paginaArgie Sheet 4virgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- 04-AE199 Group Report 1 TemplateDocumento3 pagine04-AE199 Group Report 1 Templatevirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Argie Sheet 2Documento1 paginaArgie Sheet 2virgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- MGMT 20 Case Study Template 2019 - HNBDocumento8 pagineMGMT 20 Case Study Template 2019 - HNBvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqua History PhilDocumento27 pagineAqua History Philvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- EdmodoDocumento1 paginaEdmodovirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqua FinalsDocumento3 pagineAqua Finalsvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Site PlanDocumento1 paginaSite Planvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Super FriendDocumento1 paginaSuper Friendvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Pork Consumption Is Increasing Due To The Demand of Our Growing PopulationDocumento1 paginaPork Consumption Is Increasing Due To The Demand of Our Growing Populationvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Industry 4.0Documento10 pagineIndustry 4.0virgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ReportDocumento9 pagineLab Reportvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Pechay ProductionDocumento17 paginePechay Productionemarie8panerio83% (6)
- Philrice HRDocumento1 paginaPhilrice HRvirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Parental Consent: (Signature Over Printed Name) (Signature Over Printed Name)Documento1 paginaParental Consent: (Signature Over Printed Name) (Signature Over Printed Name)virgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Parental Consent: (Signature Over Printed Name) (Signature Over Printed Name)Documento1 paginaParental Consent: (Signature Over Printed Name) (Signature Over Printed Name)virgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- ArgieDocumento1 paginaArgievirgil mae taghapNessuna valutazione finora
- Clayton & Willihnganz: Basic Pharmacology For Nurses, 17th EditionDocumento4 pagineClayton & Willihnganz: Basic Pharmacology For Nurses, 17th EditionabsianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethanol Injection Method Liposomes PDFDocumento2 pagineEthanol Injection Method Liposomes PDFElizabeth100% (1)
- 6 MonocytopoiesisDocumento8 pagine6 MonocytopoiesisVannisa Dwi NovianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pro Fitness Home Gym: Assembly & User Instructions - 237/4693Documento36 paginePro Fitness Home Gym: Assembly & User Instructions - 237/4693Aneta KochańskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chart of Starfinder Playable Races Through Alien Archive 3Documento8 pagineChart of Starfinder Playable Races Through Alien Archive 3Thallis ThawanNessuna valutazione finora
- YJBMT1198 - Proof PART 1-1Documento17 pagineYJBMT1198 - Proof PART 1-1Wanniely KussNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 9th Chapter 5 Cell Biology NotesDocumento4 pagineScience 9th Chapter 5 Cell Biology NotesavanishNessuna valutazione finora
- Lung Structure - BioNinjaDocumento2 pagineLung Structure - BioNinjaDaniel WalshNessuna valutazione finora
- Septic Shock: Stephen Trzeciak, R. Phillip Dellinger, and Joseph E. ParrilloDocumento14 pagineSeptic Shock: Stephen Trzeciak, R. Phillip Dellinger, and Joseph E. ParrilloMedranoReyesLuisinNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1 Cell BioDocumento7 pagineExperiment 1 Cell BioWinserng 永森Nessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Advances in HypertensionDocumento6 pagineRecent Advances in Hypertensionrudi saputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Fat OxidationDocumento10 pagineUnderstanding Fat OxidationPaulo CesarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Ciência Da Esgrima: Implicações Da Performance e Prevenção de LesõesDocumento18 pagineA Ciência Da Esgrima: Implicações Da Performance e Prevenção de LesõesDaniel GonçalvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mani Dweepa Varnana in TeluguDocumento165 pagineMani Dweepa Varnana in Telugukngane8878100% (4)
- Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocumento6 pagineChronic GlomerulonephritisIsak ShatikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mirror TracingDocumento8 pagineMirror TracingMichael CamusNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento7 pagineUrinary Tract InfectionCaressie BiscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ronald John Recio, M.A., Rpsy, Emdrprac. Mbpss Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Puso MoDocumento22 pagineRonald John Recio, M.A., Rpsy, Emdrprac. Mbpss Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Puso MoChunelle Maria Victoria EspanolNessuna valutazione finora
- англ 2023 мої відповідіDocumento8 pagineангл 2023 мої відповідіElena HyrychNessuna valutazione finora
- Gallus Gallus DomesticusDocumento4 pagineGallus Gallus DomesticusyvonneymNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Eukaryote Prokaryote Animal Plant 1.: Learning Packet No.2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocumento3 pagineCell Eukaryote Prokaryote Animal Plant 1.: Learning Packet No.2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsSean LestherNessuna valutazione finora
- Insecticide ClassificationDocumento10 pagineInsecticide ClassificationAnuragBhatnagarNessuna valutazione finora
- AB BC : Part ADocumento39 pagineAB BC : Part AApoorva GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullDocumento22 pagineUnit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullrynNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Areas of AssessmentDocumento10 pagine13 Areas of AssessmentNicole Anne TungolNessuna valutazione finora
- Knee Examination - OSCE SkillsDocumento3 pagineKnee Examination - OSCE Skillsfranksmith51Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetric & Gynecology Nursing: Topic-Physiological Changes During LabourDocumento54 pagineObstetric & Gynecology Nursing: Topic-Physiological Changes During LabourBhumi ChouhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eating DHEADocumento18 pagineEating DHEAYutt PlermpiromNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal's Circulartory System.Documento2 pagineAnimal's Circulartory System.CHANON KIATKAWINWONGNessuna valutazione finora