Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Labex8 Epithelial Tissues
Caricato da
Julian SobremisanaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Labex8 Epithelial Tissues
Caricato da
Julian SobremisanaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Laboratory Exercise
8
Epithelial Tissues
membrane. The cells readily divide and lack blood vessels
Pre-Lab (are avascular).
Epithelial cells always have a free (apical) surface
11. Carefully
Carefull read the introductory material and exposed to the outside or to an open space internally and
examine the entire lab content. a basal surface that attaches to the basement membrane.
2. Be familiar with epithelial tissues (from lecture or Many shapes of the cells, like squamous (flat), cuboidal, and
the textbook). columnar, exist that are used to name and identify the varia-
tions. Epithelial cell functions include protection, filtration,
3. Visit www.mhhe.com/martinseries1 for pre-lab
secretion, and absorption. Many of the prepared slides con-
questions.
tain more than the tissue to be studied, so be certain that your
view matches the correct tissue. Also be aware that stained
colors of all tissues might vary.
The slides you observe might have representative tis-
Materials Needed
sue from more than one site, but the basic tissue structure
will be similar to those represented in this laboratory exer-
C
Compound light microscope cise. Simple squamous epithelium is located in the air sacs
Prepared slides of the following epithelial tissues: (alveoli) of the lungs and inner linings of the heart and blood
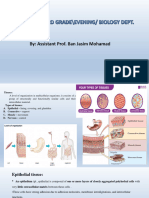
Simple squamous epithelium (lung) vessels. Simple cuboidal epithelium is situated in kidney
Simple cuboidal epithelium (kidney) tubules, thyroid gland, liver, and ducts of salivary glands.
Simple columnar epithelium (small intestine) A nonciliated type of simple columnar epithelium is located
Pseudostratified (ciliated) columnar epithelium in the linings of the uterus, stomach, and intestines, and a
(trachea) ciliated type lines the uterine tubes. A ciliated type of pseu-
Stratified squamous epithelium (esophagus) dostratified columnar epithelium is positioned in the linings
Transitional epithelium (urinary bladder) of the upper respiratory tubes. A keratinized type of stratified
squamous epithelium is found in the epidermis of the skin,
For Learning Extension Activity:
and a nonkeratinized type in the linings of the oral cavity,
Colored pencils esophagus, vagina, and anal canal. Transitional epithelium
lines the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra.
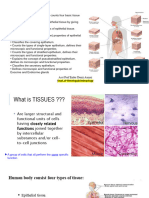
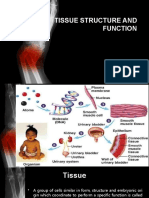
A tissue is composed of a layer or group of cells
similar in size, shape, and function. Within the human body, Purpose of the Exercise
there are four major types of tissues: (1) epithelial, which To review the characteristics of epithelial tissues and to
cover the body’s external and internal surfaces and most observe examples.
glands; (2) connective, which bind and support parts; (3)
muscle, which make movement possible; and (4) nervous, Learning Outcomes
which conduct impulses from one part of the body to another
After completing this exercise, you should be able to
and help to control and coordinate body activities.
Epithelial tissues are tightly packed single (simple) to 1 Identify and sketch six examples of epithelial tissues on
multiple (stratified) layers of cells that provide protective microscope slides.
barriers. The underside of this tissue layer contains an acellu- 2 Differentiate the special characteristics of each type of
lar basement membrane layer of adhesives and collagen with epithelial tissue.
which the epithelial cells anchor to an underlying connective 3 Indicate a location and function of each type of epithe-
tissue. A unique type of simple epithelium, pseudostratified lial tissue.
columnar, appears to be multiple cells thick. However, this 4 Inventory the general characteristics of epithelial tissues
is a false appearance because all cells bind to the basement that you were able to observe.
69
mar73044_ch05-08.indd 69 1/13/09 5:02:46 PM
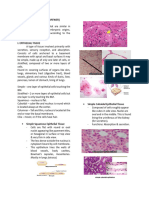
FIGURE 8.1 Micrographs of epithelial tissues. Note: The brackets to the right of each micrograph indicate the tissue.
Free (apical) surface of tissue (side view)
Lumen
Nucleus
Basement membrane Nucleus
Basement membrane
Connective tissue
Free surface of tissue
Connective tissue
(a) Simple squamous epithelium (side view)
(b) Simple cuboidal epithelium (from kidney)
Cilia (on free surface of tissue)
Nucleus in basal Microvilli Cytoplasm
portion of cell Free surface of tissue Goblet cell
Goblet cell
Nuclei
Basement membrane
Connective tissue
Basement membrane
Connective tissue
(c) Simple columnar epithelium (from intestine)
(d) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia (from trachea)
Free surface of tissue
Free surface of tissue
Squamous cells
Layer of dividing cells
Basement membrane
Nuclei
Connective tissue
(e) Stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized)
(from esophagus)
Procedure—Epithelial Tissues Basement membrane
1. Review the introductory material and complete Part A Connective tissue
of Laboratory Report 8.
2. Use the microscope to observe the prepared slides of types
of epithelial tissues. As you observe each tissue, look for (f) Transitional epithelium (unstretched) (from urinary bladder)
its special distinguishing features such as cell size, shape,
and arrangement. Compare your prepared slides of epi-
thelial tissues to the micrographs in figure 8.1.
70
mar73044_ch05-08.indd 70 1/13/09 5:02:59 PM
3. As you observe the tissues in figure 8.1 and the prepared FIGURE 8.2 Three possible cuts of a banana:
slides, note characteristics epithelial tissues have in com- (a) longitudinal section; (b) cross section; (c) oblique
mon. List characteristics you were able to observe in Part section. Sections through an organ, as a body tube,
B of the laboratory report. frequently produce views similar to the cut banana.
4. As you observe each type of epithelial tissue, prepare a
labeled sketch of a representative portion of the tissue in
Part C of the laboratory report.
5. Test your ability to recognize each type of epithelial
tissue. To do this, have a laboratory partner select one
of the prepared slides, cover its label, and focus the
microscope on the tissue. Then see if you can correctly
identify the tissue. 1
6. Complete Parts B and C of the laboratory report.
Learning Extension Activity
As you observe histology slides, be aware that tissues
and some organs may have been sectioned in longi- (a)
tudinal (lengthwise cut), cross section (cut across),
or oblique (angular cut) ways. Observe figure 8.2 for
how this can be demonstrated on cuts of a banana. The
direction in which the tissue or organ was cut will result
in a certain perspective when it is sectioned, just as the
banana was cut three different ways. Often a tissue slide
has more than one tissue represented and has blood
vessels or other structures cut in various ways. Locate
an example of a longitudinal section, cross section, and
oblique section of some structure on one of your tissue
slides.
(b)
(c)
71
mar73044_ch05-08.indd 71 1/13/09 5:03:15 PM
NOTES
72
mar73044_ch05-08.indd 72 1/13/09 5:03:32 PM
Name
Laboratory Report Date
8 Section
The corresponds to the Learning Outcome(s) listed at the beginning of the
laboratory exercise.
Epithelial Tissues
Part A Assessments
Match the tissues in column A with the characteristics in column B. Place the letter of your choice in the space provided. (Some
answers may be used more than once.) 2
Column A Column B
a. Simple columnar epithelium f
_______ 1. Consists of several layers of cube-shaped, elongated, and irregular
b. Simple cuboidal epithelium cells
c. Simple squamous epithelium d
_______ 2. Commonly possesses cilia that move dust and mucus out of the
d. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium airways
e. Stratified squamous epithelium c
_______ 3. Single layer of flattened cells
f. Transitional epithelium
d
_______ 4. Nuclei located at different levels within cells
c
_______ 5. Forms walls of capillaries and air sacs of lungs
d
_______ 6. Forms linings of trachea and bronchi
e
_______ 7. Younger cells cuboidal, older cells flattened
f
_______ 8. Forms inner lining of urinary bladder
b
_______ 9. Lines kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands
a
_______ 10. Forms lining of stomach and intestines
a
_______ 11. Nuclei located near basement membrane
e
_______ 12. Forms lining of oral cavity, anal canal, and vagina
Part B Assessments
As you examined each specific epithelial tissue, you should have noted some of the general characteristics that they possess as
described in the introduction of the laboratory exercise. List any of these you were able to observe. 4
Answers will vary.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
73
mar73044_ch05-08.indd 73 1/13/09 5:03:34 PM
Part C Assessments
In the space that follows, sketch a few cells of each type of epithelium you observed. For each sketch, label the major charac-
teristics, indicate the magnification used, write an example of a location in the body, and provide a function. 1 2 3
(sketches)
Simple squamous epithelium (____×) Simple cuboidal epithelium (____×)
Location: __________________________________________ Location: __________________________________________
Function: __________________________________________ Function: __________________________________________
Simple columnar epithelium (____×) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia (____×)
Location: __________________________________________ Location: __________________________________________
Function: __________________________________________ Function: __________________________________________
Stratified squamous epithelium (____×) Transitional epithelium (____×)
Location: __________________________________________ Location: __________________________________________
Function: __________________________________________ Function: __________________________________________
Critical Thinking Activity
C Learning Extension Activity
As a result of your observations of epithelial tissues, Use colored pencils to differentiate various cellu-
which
hi h one(s)
( provide(s) the best protection? Explain lar structures in Part C. Select a different color for a
Stratified squamous epithelium
your answer. _________________________________ nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, basement mem-
brane, goblet cell, and cilia whenever visible.
would have excellent protection as it is several
____________________________________________
cells thick. Pseudostratified columnar
____________________________________________
epithelium with cilia would provide good
____________________________________________
movement of mucus and trapped particles
away from the lungs.
74
mar73044_ch05-08.indd 74 1/13/09 5:03:37 PM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals - Textbook and Colour Atlas (2004)Documento703 pagineVeterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals - Textbook and Colour Atlas (2004)Adina Constantin100% (1)
- Full Download Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineFull Download Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manualberthasauflyvski1j100% (27)
- LeukemiaDocumento47 pagineLeukemiaRaghav Oberoi100% (1)
- Microsoft Word Document جديدDocumento3 pagineMicrosoft Word Document جديدHisham EssamNessuna valutazione finora
- Resolving Negative Life ExperiencesDocumento19 pagineResolving Negative Life ExperiencessoriboNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesDocumento13 pagineBIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesdonnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy ReviewerDocumento32 pagineAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- A-P Chapter 4 TissueDocumento21 pagineA-P Chapter 4 TissueMONIQUE VELASCONessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Gen Bio ReviewerDocumento9 pagineTissue Gen Bio ReviewerAlfred CariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues Lab ProtocolDocumento39 pagineTissues Lab Protocol284161Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 ReviewerDocumento10 pagineChapter 4 ReviewerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity No. 5 TISSUES GANDocumento7 pagineActivity No. 5 TISSUES GANTORRES, EFRAIM MATTHEW S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- English Task 2 Pask SyafrizalDocumento5 pagineEnglish Task 2 Pask Syafrizalkhanya ayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDocumento8 pagineHuman Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualKevinHarrisoncatjn100% (12)
- Histology ReviewerDocumento11 pagineHistology ReviewerMaryell Denize LandichoNessuna valutazione finora
- LEC ACTIVITY4 TISSUES SilveroDocumento10 pagineLEC ACTIVITY4 TISSUES SilveroGeia Marie SilveroNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction Epithelial TissueDocumento64 pagineIntroduction Epithelial TissueKubun Ginta GintingNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Classification of Tissues (1) - 1Documento3 pagineLab - Classification of Tissues (1) - 1Jada NelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento18 pagineTissuesAndrea Elaine Joy TorrentoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell 4Documento80 pagineCell 4jocajoldinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHDocumento6 pagineLesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHLoraine Andrei DeLeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manual PDFDocumento27 pagineDwnload Full Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manual PDFcapsicum.imprison0fwm100% (9)
- Part 3 - Laboratory ManualDocumento50 paginePart 3 - Laboratory ManualBianca AnguloNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento40 pagineTissuesInsatiable CleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 1Documento2 pagineExercise 1Sheba Victoria RabagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Types Simple Epithelia: ObjectivesDocumento5 pagineTypes Simple Epithelia: ObjectivesSheba Victoria RabagoNessuna valutazione finora
- English Task 2Documento3 pagineEnglish Task 2Tiara ArmiliaNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2Documento15 pagineBIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2iuventasNessuna valutazione finora
- GenBio CellTypes Q1ReviewerDocumento8 pagineGenBio CellTypes Q1ReviewerSTO. DOMINGO, Aneka MaghintayNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy - Tissue - Part 1Documento5 pagineAnaphy - Tissue - Part 1Aileen DemaguilaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 EpithelialtissueDocumento84 pagine1 EpithelialtissueDeniz asmazNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Tissue of Human Body NotesDocumento11 pagine3 Tissue of Human Body Notesghanshyam agnihotryNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento6 pagineTissuesyes noNessuna valutazione finora
- AnaPhyLec Midterms TissueDocumento4 pagineAnaPhyLec Midterms TissueSoul YuNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy Chapter 4Documento4 pagineAnaphy Chapter 4Riy KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Bagian IsiDocumento16 pagineBagian IsiKeyla AishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Zoo Animal TissuesDocumento84 pagineGen Zoo Animal TissuesDale Gil JuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento78 pagineTissuesElaine Victoria ElizanNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita DirgantaraDocumento30 pagineAnimal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita Dirgantarahafiz amriNessuna valutazione finora
- TissueDocumento27 pagineTissueemilpauloquibilanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment # 4: Tissues Explore: 1.: Tissues Descriptions Functions Location AppearanceDocumento8 pagineAssignment # 4: Tissues Explore: 1.: Tissues Descriptions Functions Location AppearanceKassandra Shayne CaballeroNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 9 SM3 23-24pDocumento11 pagineBIO 9 SM3 23-24pNandini Pritesh PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual - TissuesDocumento14 pagineLab Manual - Tissues46bwilson100% (2)
- Tissue Level of Organisation: Unit IiDocumento15 pagineTissue Level of Organisation: Unit IiIyappan SubramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues and CellsDocumento14 pagineTissues and Cellsstormigirl017Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab1 Histology Bios E1b 2016cDocumento13 pagineLab1 Histology Bios E1b 2016cwekrjbhweiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue of The BodyDocumento12 pagineTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Histology Presentation PDFDocumento67 pagineHistology Presentation PDFAbd ElNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocumento16 pagine3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento98 pagineAnimal Tissuesfit3akmal100% (3)
- Kebo 107Documento23 pagineKebo 107Manu MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology LecDocumento258 pagineHistology LecBan JMNessuna valutazione finora
- Kebo107 PDFDocumento23 pagineKebo107 PDFbashraaNessuna valutazione finora
- TISSUEDocumento4 pagineTISSUEzairazapanta001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue ReviewerDocumento3 pagineTissue ReviewerFayena JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Characteristics of Most Types of Epithelial Tissue AreDocumento2 pagineCommon Characteristics of Most Types of Epithelial Tissue AreGwen Llanes AmbronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Level ReviewerDocumento9 pagineTissue Level ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Body TissueDocumento59 pagineBody TissueAbdul RaufNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento17 pagineAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocumento74 pagineTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Study Guide Tissues and MembraneDocumento19 pagineStudy Guide Tissues and MembraneSheam MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues & HistologyDocumento57 pagineTissues & Histologyruthdaisy507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissueDocumento14 pagineAnimal TissueSagar GavasNessuna valutazione finora
- Antifungal AgentsDocumento16 pagineAntifungal AgentstheintrovNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Pemarkahan: Tingkatan 5 Bahasa Inggeris 1119 Kertas 1 Dan 2Documento12 pagineSkema Pemarkahan: Tingkatan 5 Bahasa Inggeris 1119 Kertas 1 Dan 2nurmalajamaludinNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study DengueDocumento11 pagineCase Study DengueCarl Julienne MasangcayNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial Base ScottDocumento30 pagineCranial Base ScottShirley AliagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gambar Usg TestisDocumento28 pagineGambar Usg TestisIrfan YHNessuna valutazione finora
- Goat Housing and Fencing PDFDocumento43 pagineGoat Housing and Fencing PDFmary anthoneth bayle100% (1)
- Zoology MCQDocumento15 pagineZoology MCQeesha iqbal67% (3)
- Veterinary Reproductive UltrasonographyDocumento255 pagineVeterinary Reproductive Ultrasonographylenn chand100% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology PDFDocumento51 pagineAnatomy and Physiology PDFalexenneth canilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ear InfectionDocumento7 pagineEar Infectionbhatti19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Test For Endocrine DisordersDocumento4 pagineDiagnostic Test For Endocrine DisordersjesperdomincilbayauaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Manual of Otolaryngology Clear ScanDocumento283 pagineClinical Manual of Otolaryngology Clear ScanAyman Yakout100% (4)
- Istory of Jellyfish Envenomation: 3.1.1. Class Cubozoa - Cubozoan JellyfishDocumento16 pagineIstory of Jellyfish Envenomation: 3.1.1. Class Cubozoa - Cubozoan JellyfishRangsiyo BeabeoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Natural History of Human Poliomyelitis IDocumento23 pagineThe Natural History of Human Poliomyelitis IFitria Ayu LestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Neck TrianglesDocumento6 pagineNeck TrianglesJay-arh SebusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acupuncture ChartsDocumento7 pagineAcupuncture Chartsdoringrama50% (2)
- BIOLOGY (0610) s03 QP 3 Model Answer FinalDocumento15 pagineBIOLOGY (0610) s03 QP 3 Model Answer FinalDON-thegreat100% (8)
- Nervous System Concept MapDocumento12 pagineNervous System Concept MapJo BrackenNessuna valutazione finora
- Antonio Damasio, Hanna Damasio - Fear and The Human AmigdalaDocumento13 pagineAntonio Damasio, Hanna Damasio - Fear and The Human AmigdalaAna Victoria Casillas ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of NoseDocumento32 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of NoseBinita ShakyaNessuna valutazione finora
- A History of Isolator and Containment Technology论文Documento27 pagineA History of Isolator and Containment Technology论文Chendi SunNessuna valutazione finora
- THE URINARY SYSTEM Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento29 pagineTHE URINARY SYSTEM Anatomy and PhysiologyYatuwa LydiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Equine Tetanus 202CDocumento4 pagineEquine Tetanus 202Cvah5018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of The Horse's Foot by Reeks, Harry CaultonDocumento282 pagineDiseases of The Horse's Foot by Reeks, Harry CaultonGutenberg.org100% (1)
- Maternal QuestionsDocumento7 pagineMaternal Questionsjhae_darilayNessuna valutazione finora
- The Soul According To The Ethnolinguistic Groups of The PhilippinesDocumento4 pagineThe Soul According To The Ethnolinguistic Groups of The PhilippinesEarl SantosNessuna valutazione finora