Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 7 - C F I D: Ontrol AND Ield Nstrumentation Ocumentation
Caricato da
Anonymous QucKa3TCBNTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 7 - C F I D: Ontrol AND Ield Nstrumentation Ocumentation
Caricato da
Anonymous QucKa3TCBNCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHAPTER 7 – CONTROL AND FIELD INSTRUMENTATION DOCUMENTATION 97
company that is designing a process normally has standards that they fol-
low in the creation of a loop diagram. These standards may be docu-
mented by the creation of a master template that illustrates how field
devices and nomenclature are used on the drawing.
The loop diagram typically contains a significant amount of detail. For
example, if a junction box is used as an intermediate wiring point, the loop
diagram will contain information on the wiring junctions from the field
device to the control system. An example of a loop diagram is shown in
Figure 7-4.
As is illustrated in this example, junction box connections are shown on
the line that shows the division between the field and the rack room. The
loop diagram shows the termination numbers used in the junction box
and the field device and for wiring to the control system input and output
cards. Also, the Display and Schematic portions of the loop diagram
provide information on how the field input and output are used in the
control system.
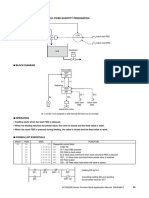
Figure 7-4 shows installation details for a two-wire level transmitter that is
powered through the control system analog input card. Also, connections
are shown between the control system analog output card and an I/P
transducer and pneumatic valve actuator. Details such as the 20 psi air
supply to the I/P and the 60 psi air supply to the actuator are shown on
this drawing. Based on information provided by the loop diagram, we
know that the I/P will be calibrated to provide a 3–15 psi signal to the
valve actuator. In addition, specific details are provided on the level mea-
surement installation. Since the installation shows sensing lines to the top
and bottom of the tank, it becomes clear that the tank is pressurized and
that level will be sensed based on the differential pressure.
In this particular installation, the instrumentation engineer has included
purge water to keep the sensing line from becoming plugged by material
in the tank. Even fine details such as the manual valve to regulate the flow
of purge water are included in the loop diagram to guide the installation
and maintenance of the measurement device.
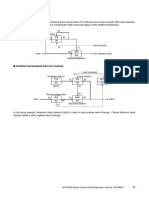
In this example, the loop diagram shows the installation of a rotameter. A
rotameter consists of a movable float inserted in a vertical tube and may
be used to provide an inexpensive mechanical means of measuring volu-
metric flow rate in the field.
As this example illustrates, the loop diagram provides information that is
critical to the installation, checkout, and maintenance of field devices. By
examining the loop diagram, it is possible to learn details that may not be
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Environmental Impact Assessment by L.W. CanterDocumento38 pagineEnvironmental Impact Assessment by L.W. CanterDewi Hadiwinoto33% (9)
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideDa EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (8)
- Substation Automation Systems: Design and ImplementationDa EverandSubstation Automation Systems: Design and ImplementationValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- IQOQGP8Documento10 pagineIQOQGP8Lautaro100% (2)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsDa EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- 7.5 Tagging Conventions: Chapter 7 - C F I DDocumento1 pagina7.5 Tagging Conventions: Chapter 7 - C F I DAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto 2 Finals Topic 3-Piping, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Diagrams-Converted1Documento20 pagineAuto 2 Finals Topic 3-Piping, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Diagrams-Converted1Reynee Shaira Lamprea MatulacNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrument DrawingDocumento12 pagineInstrument DrawinghbakriNessuna valutazione finora
- Ed - Lec09 Chapter 9 - PFD PidDocumento36 pagineEd - Lec09 Chapter 9 - PFD Pideja70Nessuna valutazione finora
- Field Testing of Fan SystemsDocumento4 pagineField Testing of Fan Systemsnedduc20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design Project LabDocumento80 pagineDesign Project Labkaushikei22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Guide For Calculating Pump Flow Rate and Power Consumption For Large Solar Water HeatersDocumento4 pagineGuide For Calculating Pump Flow Rate and Power Consumption For Large Solar Water HeatersMoeNessuna valutazione finora
- AICHE - PFD - PID - Lectura No 1 EGOYP 2015Documento8 pagineAICHE - PFD - PID - Lectura No 1 EGOYP 2015Yuldor LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- HVACT10 Mhlogo FanDocumento8 pagineHVACT10 Mhlogo FanjameeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow 7 DiagramsDocumento12 pagineFlow 7 DiagramsIne Florez PalaciozNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Balancing - AgDocumento8 pagineAir Balancing - AgHai Le100% (2)
- Engineering STD DWGDocumento6 pagineEngineering STD DWGvyroreiNessuna valutazione finora
- EPF4802 - Chapter 7 (Part 1) Instrumentation and Control - NoteDocumento27 pagineEPF4802 - Chapter 7 (Part 1) Instrumentation and Control - NotehidayantiemNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Loop HardwareDocumento56 pagineControl Loop Hardwarecharleselitb92Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) 2.4 Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID)Documento34 pagine2.3 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) 2.4 Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID)Sofea Izyan100% (1)
- Design of Sprinkler System by Engr. MarianoDocumento29 pagineDesign of Sprinkler System by Engr. MarianoJhobs Besmonte100% (15)
- Designing A Process Flowsheet-Mayo 2009 PDFDocumento7 pagineDesigning A Process Flowsheet-Mayo 2009 PDFKathy SandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- Duct Sizing - Circular DuctDocumento18 pagineDuct Sizing - Circular DuctbalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping and Instrumentation Drawings in Aspen HYSYSDocumento278 paginePiping and Instrumentation Drawings in Aspen HYSYSmahmoud38140% (1)
- PUMP A Spreadsheet Program For The Calculation of Piping Systems andDocumento12 paginePUMP A Spreadsheet Program For The Calculation of Piping Systems andmsaadullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumatic Circuits DesignDocumento20 paginePneumatic Circuits DesignyassinNessuna valutazione finora
- Question BankDocumento2 pagineQuestion BankSanatan DharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Air Inlet System Features On Automotive Turbocharger Compressor PerformanceDocumento19 pagineThe Effect of Air Inlet System Features On Automotive Turbocharger Compressor Performancestefan.vince536Nessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Pressure Drop CalculationDocumento9 pagineLiquid Pressure Drop CalculationMichaelMahonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Flow Diagram (PFD) & Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&id)Documento29 pagineProcess Flow Diagram (PFD) & Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&id)Mohd Nor Ariffin100% (2)
- Deliverable ListDocumento4 pagineDeliverable ListbaigprodNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 P&ID Guide PDFDocumento9 pagine02 P&ID Guide PDFcharleselitb92Nessuna valutazione finora
- 17ME754 Mechatronics PLC and 8085Documento9 pagine17ME754 Mechatronics PLC and 8085Abhishek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Line SizingDocumento12 pagineLiquid Line Sizinglolofm25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hyena: Hydraulic Analysis of Fire Sprinkler and Hydrant SystemsDocumento6 pagineHyena: Hydraulic Analysis of Fire Sprinkler and Hydrant SystemsacidoanimalNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrument Hookup DiagramDocumento1 paginaInstrument Hookup DiagramAbhayy Dev0% (1)
- Flow DiagramsDocumento12 pagineFlow DiagramsLuis PullasNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Design and EconomicsDocumento16 pagineProcess Design and EconomicsNigel MitchellNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping Workbook PIDesignDocumento73 paginePiping Workbook PIDesignUrsula MoeringsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Ieee Test System Methods: Reliability ofDocumento11 pagineThe Ieee Test System Methods: Reliability oftinazdrilicNessuna valutazione finora
- Partic Spec DMA & BC-Part B-Ver Feb 2016Documento29 paginePartic Spec DMA & BC-Part B-Ver Feb 2016sathishNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumatic SymbolsDocumento11 paginePneumatic Symbolsaa23XbNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Aspects of Numerical Simulation of Control Valves For Steam TurbinesDocumento1 paginaSome Aspects of Numerical Simulation of Control Valves For Steam TurbinesSharat ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressor Performance Map Generation and Testing Per SAE J1723Documento40 pagineCompressor Performance Map Generation and Testing Per SAE J1723DoctorObermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Level ControllerDocumento3 pagineLevel ControllerPriasmoro Galih SantosoNessuna valutazione finora
- HevcaDocumento3 pagineHevcavirtechNessuna valutazione finora
- Nomographs For Preliminary Design A Useful Set of NomoDocumento5 pagineNomographs For Preliminary Design A Useful Set of NomoMaximiliano ScarlatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Valve OcrDocumento14 pagineControl Valve OcrpathakshashankNessuna valutazione finora
- 07-264 1896-1901 PDFDocumento6 pagine07-264 1896-1901 PDFSugianto BarusNessuna valutazione finora
- Tek 7633Documento320 pagineTek 7633Brian FishNessuna valutazione finora
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesDa EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Variable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersDa EverandVariable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignDa EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants: Volume 1Da EverandApplied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants: Volume 1Valutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aerospace Actuators 2: Signal-by-Wire and Power-by-WireDa EverandAerospace Actuators 2: Signal-by-Wire and Power-by-WireNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Rail Fuel Injection Technology in Diesel EnginesDa EverandCommon Rail Fuel Injection Technology in Diesel EnginesNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Predictive Control of High Power Converters and Industrial DrivesDa EverandModel Predictive Control of High Power Converters and Industrial DrivesNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationDa EverandDesign Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationNessuna valutazione finora
- How to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesDa EverandHow to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorDa EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled 123 PagesDocumento1 paginaUntitled 123 PagesAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages330Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages330Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 - C F I D: Figure 7-8. ISA-5.1 Tag Number ConventionDocumento1 paginaChapter 7 - C F I D: Figure 7-8. ISA-5.1 Tag Number ConventionAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages37Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages37Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.8.2 Example - Basic Column Control: Chapter 7 - C F I DDocumento1 pagina7.8.2 Example - Basic Column Control: Chapter 7 - C F I DAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.4 Loop Diagram: C L F: B A C PDocumento1 pagina7.4 Loop Diagram: C L F: B A C PAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages2 PDFDocumento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages2 PDFAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages33Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages33Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages13Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages13Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Flow Diagram - Drawing That Shows The General: 7.3 Piping and Instrumentation DiagramDocumento1 paginaProcess Flow Diagram - Drawing That Shows The General: 7.3 Piping and Instrumentation DiagramAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages2 PDFDocumento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages2 PDFAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.5.2 Flow Batch Control Loop Configuration Example: Fixed Quantity PreparationDocumento1 pagina5.5.2 Flow Batch Control Loop Configuration Example: Fixed Quantity PreparationAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages23Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages23Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages14Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages14Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- SC100/200 Series Function Block Application Manual EM-6460-CDocumento1 paginaSC100/200 Series Function Block Application Manual EM-6460-CAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages25Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages25Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages22Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages22Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuration Audit Trail: Deltav Distributed Control System Product Data SheetDocumento1 paginaConfiguration Audit Trail: Deltav Distributed Control System Product Data SheetAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages13Documento1 paginaUntitled Extract Pages13Anonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- SC100/200 Series Function Block Application Manual EM-6460-CDocumento1 paginaSC100/200 Series Function Block Application Manual EM-6460-CAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2 Pid Control: SC100/200 Series Function Block Application Manual EM-6460-CDocumento1 pagina4.2 Pid Control: SC100/200 Series Function Block Application Manual EM-6460-CAnonymous QucKa3TCBNNessuna valutazione finora
- JSW SteelDocumento44 pagineJSW Steelauttyhubli100% (1)
- Wind Tunnel Calibration: Name: Animesh Phatowali Roll No: 17AE30005 Group: 6 Experiment:7Documento8 pagineWind Tunnel Calibration: Name: Animesh Phatowali Roll No: 17AE30005 Group: 6 Experiment:7Animesh PhatowaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Materials Alternator 200mw Power PlantDocumento31 pagineTraining Materials Alternator 200mw Power PlantLio MessiNessuna valutazione finora
- TC FLS Sihi Leh 1200 1500 1800 enDocumento10 pagineTC FLS Sihi Leh 1200 1500 1800 enGustavo ZavalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of Oil Skimmer RobotDocumento46 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Oil Skimmer RobotSathiya Udumalpet100% (2)
- ISO SymbolsDocumento167 pagineISO SymbolskillimakilliNessuna valutazione finora
- Eurocode 8-1-3Documento18 pagineEurocode 8-1-3joaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Mr. Harsh PanchalDocumento46 paginePrepared By: Mr. Harsh PanchalKáûshàl PãtëlNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing Cellular Glass Insulation Block: Standard Test Methods ofDocumento4 pagineTesting Cellular Glass Insulation Block: Standard Test Methods ofArun UdayabhanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Part-2Documento14 paginePhysics Part-2Thor hmNessuna valutazione finora
- Teikin Catalog Vol 18-Automotive FiatDocumento6 pagineTeikin Catalog Vol 18-Automotive FiatJuan Esteban Ordoñez BonillaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nuclear Matters Handbook PDFDocumento350 pagineThe Nuclear Matters Handbook PDFGene SevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Steel MakingDocumento26 pagineBasics of Steel MakingakshukNessuna valutazione finora
- Aiims PG May 2019Documento108 pagineAiims PG May 2019MarcelNessuna valutazione finora
- 118 - Package Boiler BrochureDocumento8 pagine118 - Package Boiler BrochureBayu Pramana PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Turret & Installation Challenges: Espirito Santo FPSODocumento26 pagineTurret & Installation Challenges: Espirito Santo FPSOUthanmalliah NagarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Defense Parcon 1Documento19 pagineMock Defense Parcon 1Nash Gemar Braga EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aquarea Split Systems Installation Handbook 2013 (A2W-SPX-130305-012)Documento80 pagineAquarea Split Systems Installation Handbook 2013 (A2W-SPX-130305-012)Anonymous ec2P0F5iKXNessuna valutazione finora
- SAPPHIRE® PLUS 70-BarDocumento2 pagineSAPPHIRE® PLUS 70-BarAyhan ÖZKALNessuna valutazione finora
- Target MonetaryDocumento9 pagineTarget MonetaryKuldeep RupareliaNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemiTek SOLARWASHPROTECT DATASHEETDocumento2 pagineChemiTek SOLARWASHPROTECT DATASHEETPhani ArvapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- EasyLabs CE AmplifierDocumento15 pagineEasyLabs CE AmplifierAvish KabraNessuna valutazione finora
- TwingoDocumento26 pagineTwingoDumitru-Lucian PurcaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Operacion RENR3037!03!01 - ALLDocumento60 pagineElectric Operacion RENR3037!03!01 - ALLRaúl Alberto Zang100% (1)
- The Effect of Financial Development On Renewable Energy Consumption. A Panel Data ApproachDocumento9 pagineThe Effect of Financial Development On Renewable Energy Consumption. A Panel Data ApproachArnawan Hasibuan, ST., MT Arnawan Hasibuan, ST., MTNessuna valutazione finora
- of Gatorade..Documento29 pagineof Gatorade..Jay ThakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- IC ENGINES NOTES Unit 2Documento41 pagineIC ENGINES NOTES Unit 2Satya NarayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- TM 5-9028 Lubricator, TRL MTD, MDL 2430, 1943Documento186 pagineTM 5-9028 Lubricator, TRL MTD, MDL 2430, 1943Advocate100% (1)