Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Intro To Cell Bio BIOL 2021
Caricato da
RobertTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Intro To Cell Bio BIOL 2021
Caricato da
RobertCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Intro to Cell Bio (Cells and Genomes)
Unity of life
Cell is basic unit of life
o Unicellular
o Multicellular
All cellular life has these characteristics in common
o DNA as its genetic material
o Several RNAs
o Proteins
Enzymes
Cell membrane
Reproduction
Energy (ATP)
Diversity of Living Organisms
Cell Size
Cell Structure
o Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic
o Prokaryotic
Nucleus: no
RNA Processing: no
Organelles: no
Cell Wall: yes
Temperature
Grows best below 20C: psychrophiles
Grows best between 20-50C: mesophiles
Grows best above 50-80C: thermophiles
Grows best 80-120C: Hyperthermophiles
PH (acidic or basic)
Grows well at pH 1 to 2: acidophiles
o Helicobacter pyloric in the stomach
o Peptic ulcer and gastric cancer
Grows best near neutral pH: neutrophile
Chapter 1
Grows well at basic pH: alkaliphile
Water
Most cells require a min moisture content
Some bacteria can make spores: cells that survive in the near absence of
water
Salt
Most cells require a moderate level of salt
Some cells can exist in a very high salt concentrations: halophiles
Oxygen availability
Require o2 for growth: aerobic
Require lack of o2 for growth: anaerobic
Nutrient availability
Most microorganisms require organic and inorganic nutrients to grow
and survive
Cyanobacteria grow in the absence of key nutrient: e.g. can convert co2
from air into organic cellular molecules
o Eukaryotic
Nucleus: yes
RNA Processing: yes
Organelles: yes
Cell Wall: no
Fungi
A fungi, eukaryotic unicellular organism
Most commonly used in the food industry
o Under aerobic conditions used as a baker’s yeast
o Under anaerobic conditions used for alcohol production
Involved in human diseases
o Yeast infections
o Opportunistic infections (e.g. AIDS)
Molds
Filamentous fungi with a mycelial structure
o Mycelium is a highly branches system of tubes that contain
mobile cytoplasm with many nuclei
Molds are used for production of citric acid and antibiotics.
o The mold penicillium produces penicillin
Protozoa
Unicellular eukaryotes lack cell wall
They cause a number of human diseases
o e.g. malaria
But may have beneficial roles
o Digestion
o Removing bacteria from wastewater
Chapter 1
o Viruses
Viruses are complexes of nucleic acids and proteins
Use functions of the host cells on which they are parasites
They are not cellular life
The viral parasite cause changes int eh cell
Directing the host cells metabolism to the production of new virus particles may
cause cellular death
What are viruses?
Nucleic acid genome
o DNA or RNA
Protein coat
o Protection, entry into the cell
Lipid envelope in some viruses
o Archaea
Morphologically, the two kingdoms of prokaryotes appear similar. However, the
have major biochemical/genomic differences
Most archaea live in extreme environments
Thermoacidophiles
o Expand
Methanophiles
o Expand
Halophiles
o Expand
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Astm D 1418 PDFDocumento3 pagineAstm D 1418 PDFseeralan_198667% (3)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Lesson StructureDocumento19 pagineLesson Structurer karthickNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous Organic Extraction Using Soxhlet MethodDocumento5 pagineContinuous Organic Extraction Using Soxhlet MethodMaria Harianja0% (1)
- Ethanol Amine Production PDFDocumento8 pagineEthanol Amine Production PDFFatih FıratNessuna valutazione finora
- Om Prakash PPT BiologyDocumento11 pagineOm Prakash PPT BiologyOm Prakash100% (1)
- AOCS Ca 5a-40Documento2 pagineAOCS Ca 5a-40Bimmo Dwi Hartono100% (15)
- Alcohol, Ether and Phenol PDFDocumento66 pagineAlcohol, Ether and Phenol PDFAniruddha KawadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimensionamento FlangeDocumento12 pagineDimensionamento FlangeAlessio Di BellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols, Phenols, Ehers PDFDocumento15 pagineAlcohols, Phenols, Ehers PDFHarsh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical in TextileDocumento36 pagineChemical in TextileAhmed IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Organomineral Fertilizer Application On The Performance of Chili Pepper (Capsicum Annuum)Documento38 pagineEffect of Organomineral Fertilizer Application On The Performance of Chili Pepper (Capsicum Annuum)Hamid Fruqon Abiola FaruqNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle and Carbon Fixation PathwaysDocumento8 paginePhotosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle and Carbon Fixation PathwaysVaan ChinNessuna valutazione finora
- Davis 2019Documento20 pagineDavis 2019AnaisFNessuna valutazione finora
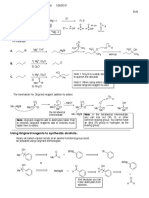
- Using Grignard Reagents To Synthesize Alcohols:: O H C CHDocumento3 pagineUsing Grignard Reagents To Synthesize Alcohols:: O H C CHSankar AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
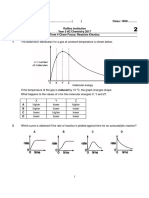
- 2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsDocumento4 pagine2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsxmxmxmxmxmNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 6 Edition ©2003Documento41 pagineAlkenes: Structure and Reactivity: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 6 Edition ©2003hei chuNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm D1258 - 1 (En)Documento2 pagineAstm D1258 - 1 (En)svvasin2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trade Effluent Discharge RequirementsDocumento6 pagineTrade Effluent Discharge RequirementsNor AzilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wells Plastics Additives For Polyethylene ExtrusionDocumento4 pagineWells Plastics Additives For Polyethylene ExtrusionmohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- H2o2 MSDSDocumento14 pagineH2o2 MSDSHoàng Minh ĐườngNessuna valutazione finora
- Muhammad Wajid: Institute of Pharmacy Gulab Devi Educational Complex, LahoreDocumento36 pagineMuhammad Wajid: Institute of Pharmacy Gulab Devi Educational Complex, LahoreAhmed ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Rope and Rope Works, Knots, Ties, and SplicesDocumento3 pagineRope and Rope Works, Knots, Ties, and SplicesJj GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Gel Electrophoresis GuideDocumento16 pagineDNA Gel Electrophoresis GuideNasrullah RoslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Biofertilizer On Growth, Productivity, Quality and Economics of Rainfed Organic Ginger (Zingiber Officinale Rosc.) Bhaisey Cv. in North-Eastern Region of IndiaDocumento96 pagineEffect of Biofertilizer On Growth, Productivity, Quality and Economics of Rainfed Organic Ginger (Zingiber Officinale Rosc.) Bhaisey Cv. in North-Eastern Region of IndiaIsroi.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Viva QuestionsDocumento4 pagineSome Viva Questionsseru100% (1)
- FermentationDocumento7 pagineFermentationSyed D Kings'Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0196890422012195 MainDocumento16 pagine1 s2.0 S0196890422012195 MainAlex SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- IS 3025-5 (1983): Methods of sampling and test (physical and chemical) for water and wastewater, Part 5: OdourDocumento5 pagineIS 3025-5 (1983): Methods of sampling and test (physical and chemical) for water and wastewater, Part 5: OdourKrishna ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Logger - Acid Base TitrationDocumento9 pagineData Logger - Acid Base TitrationHidayah NurNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Pollution CharacteristicsDocumento34 pagineAir Pollution CharacteristicsLeonor BagnosNessuna valutazione finora