Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
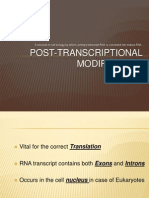
Post Translational Modification
Caricato da
Saira Dogar0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
95 visualizzazioni4 paginePost-translational modification refers to covalent or enzymatic changes that occur to proteins after or during their synthesis. Translation is the process by which mRNA is used to produce proteins with the help of ribosomes. There are several types of post-translational modifications, including trimming, covalent attachment, protein folding, and protein degradation. Common covalent attachments include phosphorylation, methylation, glycosylation, sulfation, hydroxylation, and more. These modifications regulate protein function and increase diversity.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Post translational modification.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoPost-translational modification refers to covalent or enzymatic changes that occur to proteins after or during their synthesis. Translation is the process by which mRNA is used to produce proteins with the help of ribosomes. There are several types of post-translational modifications, including trimming, covalent attachment, protein folding, and protein degradation. Common covalent attachments include phosphorylation, methylation, glycosylation, sulfation, hydroxylation, and more. These modifications regulate protein function and increase diversity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
95 visualizzazioni4 paginePost Translational Modification
Caricato da
Saira DogarPost-translational modification refers to covalent or enzymatic changes that occur to proteins after or during their synthesis. Translation is the process by which mRNA is used to produce proteins with the help of ribosomes. There are several types of post-translational modifications, including trimming, covalent attachment, protein folding, and protein degradation. Common covalent attachments include phosphorylation, methylation, glycosylation, sulfation, hydroxylation, and more. These modifications regulate protein function and increase diversity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
Post translational modification can be defined as
The covalent or generally enzymatic modifications of proteins
durig of after the synthesis of the proteins.
Before understanding about it, first of all we
must have information about what is translation.
In molecular biology ,translation refrs to the formation of
proteins from mrna with the help of ribosomes present in the
cytoplasm of the cell in the case of prokaryotes while in
eukaryotes it is carried in the membrane of rer or in the
cytosol. the mrna then decoded from dna is migrated in to the
cytoplasm for the synthesis of protein that then fold, acquire
a tertiary conformation and perfom their perspective
functions.
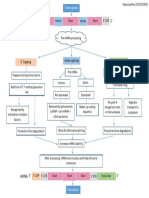
Steps In post translational modifications:_
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Types of post translational modifications are involved in
modifying the protein structure after they have been
translated according to information on the mRNA.
The post-translational modifications can be covalent or
enzymatic.
In the human body these ptms increase the diversity and
accuracy of proteins.
The types of post translational modifications are:
Trimming
Covalent attachment
Protein folding
Protein degradation
Trimming:-
Insulin is synthesized in the cells in the inactive form.for
proper functioning of insulin its past translational
modification occurs that involves the removal of the part of
the protein to convert it into a three dimensional and fully
active form.
Covalent attachment:
Refers to the addition or the transfer of the
polypeptide chain that acts as atn acceptor region. In this way
proteins are modified for the diversity of functions. It
includes:
Phosphorylation
Methylation
Glycosylation
Sulfation
Hydroxylation
Phosphorylation: is the addition of one or more phosphate
groups to the protein. Post translational phosphorylation is
one of the most common protein modifications that occur in
animal cells. The vast majorities of phosphorylation occur as a
mechanism to regulate the biological activity of a protein and
such are transient.
In animal cells, serine tyrosine and thereonine are the amino
acids that are subjected to this method.
Glycosylation:- is the addition of carbohydrate molecules to
the polypeptide chain and modifying it into glycoproteins.
Many of the proteins that are destined to be a part of the
plasma membrane or to b secreted from the cell, have
carbohydrate chains attached to the amide nitrogen of the
asparagine or the hydroxyl groups of sereine , threonine. N
glycosylation occurs in ER and O glycosylation in the Golgi
Complex.
Sulfation :- sulfate modification takes place by the addition
of the sulfate molecules and these modifications of proteins
occur at tyrosine residues. Tyrosine sulfation is accomplished
by the activity of TPSTs (tyrosylprotein sulfotransferases)
wich are membrane assosciated enzymes of trans-golgi
network. There are two tpsts :
Tpst 1
Tpst 2
The universal phosphate donor is 3 phosphoadenosyl 5 o
phosphosulphate (pspa).
METHYLATION:- the transfer of one carbon methyl group to
nitrogen or oxygen to amino acid side chains o the
hydrophobicity of the protein and can neutralize a negative
amino acid charge when bound to carbdoxylic acids. It is
mediated by methyltransferases and S- adenosyl methionine
is the primary methyl group donor.
HYDROXYLATION:- IS THE biological process of addition of
hydroxyl group to a protein amino acid. It is the type of ptm
that involves the conversion of a –CH group into –COH group
and hese hydroxylatedn amino acids are involved in the
regulation of some important factors called transcription
factors. Among 20, the two
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bacterial TransposonsDocumento36 pagineBacterial TransposonsShweta SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Silencing: An In-Depth Look at Mechanisms and ApplicationsDocumento18 pagineGene Silencing: An In-Depth Look at Mechanisms and ApplicationsNAMRA RASHEEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Fibrinogen and Platelets: An Overview of Primary HemostasisDocumento11 pagineFibrinogen and Platelets: An Overview of Primary HemostasisElyza L. de GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocumento12 pagineCell Cycle and Cell DivisionMajid Al-hachami100% (1)
- Cell Cycle RegulationDocumento4 pagineCell Cycle RegulationSomNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento9 pagineTranscription and TranslationlinhNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA ReplicationDocumento55 pagineDNA ReplicationZainab Jamal Siddiqui100% (1)
- Linkage: Harshraj Subhash Shinde KKW, Cabt, NashikDocumento14 pagineLinkage: Harshraj Subhash Shinde KKW, Cabt, Nashiksivaram888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biotecnology and Its ApplicationDocumento87 pagineBiotecnology and Its ApplicationRangaswamyBiligiraiah100% (1)
- Molecular BiologyDocumento9 pagineMolecular Biologyrifat RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- GROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocumento24 pagineGROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Gene Regulation: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarDocumento39 pagineGene Regulation: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarmskikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Silencing: Presented by Aastha Pal M.Sc. 4 Semester (Biotechnology) Swami Rama Himalayan UniversityDocumento22 pagineGene Silencing: Presented by Aastha Pal M.Sc. 4 Semester (Biotechnology) Swami Rama Himalayan UniversityAmit NegiNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes: © John Wiley & Sons, IncDocumento65 pagineRegulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes: © John Wiley & Sons, IncRoberto CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- TranscriptionDocumento70 pagineTranscriptionkhan aishaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Manipulative EnzymesDocumento17 pagineDNA Manipulative EnzymesZain Ul AbedienNessuna valutazione finora
- General Translation MechanismDocumento15 pagineGeneral Translation MechanismAishwarya KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key 2Documento3 pagineAnswer Key 2SharyproNessuna valutazione finora
- Genomes in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocumento46 pagineGenomes in Prokaryotes and EukaryoteskityamuwesiNessuna valutazione finora
- Post-Translational Modification: Dr. Md. Imtaiyaz HassanDocumento61 paginePost-Translational Modification: Dr. Md. Imtaiyaz Hassanbiotechnology2007100% (1)
- Regulation of the lac Operon in E. coliDocumento32 pagineRegulation of the lac Operon in E. coliAlina RafiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- ReplicationDocumento45 pagineReplicationAleena MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocumento13 pagineRegulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsMifta KhuljannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Eukaryote Translation PDFDocumento21 pagineEukaryote Translation PDFChandra Mohan Meena100% (1)
- Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocumento75 pagineReplication - Transcription - TranslationJason FryNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocumento3 paginePost Transcriptional ModificationLubainur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- RNA ProcessingDocumento23 pagineRNA Processingsaeed313bbtNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Post Translational Modification - PPT RDocumento38 pagineProtein Post Translational Modification - PPT RPranav NakhateNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocumento31 paginePost Transcriptional ModificationranasiddharthNessuna valutazione finora
- Enhancer: Q1) What Is Role of Enhancers and Promoters in Transcription of Eukaryotes? AnsDocumento9 pagineEnhancer: Q1) What Is Role of Enhancers and Promoters in Transcription of Eukaryotes? AnsSudeep BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 3 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocumento50 pagineDay 3 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingAniket ParabNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocumento38 pagineTranscription and RNA ProcessingRishi Kumar100% (1)
- Purines, Pyrimidines and Nucleotides and the Chemistry of Nucleic AcidsDa EverandPurines, Pyrimidines and Nucleotides and the Chemistry of Nucleic AcidsNessuna valutazione finora
- Postranslational ModificationDocumento78 paginePostranslational ModificationnsjunnarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Translational ModificationDocumento11 paginePost Translational ModificationCynCyntya HarlyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Translational Control & Post-Translational ModificationsDocumento10 pagineTranslational Control & Post-Translational ModificationsBhaskar GangulyNessuna valutazione finora
- Eukaryote Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocumento35 pagineEukaryote Regulation of Gene ExpressiondewiulfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic RecombinationDocumento60 pagineGenetic RecombinationJeevan BasnyatNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Post-Translational Modification AnalysisDocumento2 pagineOverview of Post-Translational Modification AnalysisSteven4654Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Gene ExpressionDocumento35 pagine4 Gene ExpressionThảo ThảoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-mRNA: 5' Capping Polyadenylation Intron SplicingDocumento1 paginaPre-mRNA: 5' Capping Polyadenylation Intron SplicingKayoung HeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Translation in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocumento17 pagineTranslation in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesMuhammad Arslan YasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Translation in Prokaryotes: NEET 2020Documento1 paginaTranslation in Prokaryotes: NEET 2020ADIKKI ANOOHYANessuna valutazione finora
- RNA Modification: Post-Transcriptional Processing of RNADocumento4 pagineRNA Modification: Post-Transcriptional Processing of RNArustyryan770% (1)
- Genome Organization in ProkaryotesDocumento8 pagineGenome Organization in ProkaryotesVijay Kishore75% (4)
- Translation in ProkaryotesDocumento25 pagineTranslation in ProkaryotesNaomi Lamtiur0% (1)
- Answers PGR Week9 2016Documento11 pagineAnswers PGR Week9 2016kkk13whyNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocumento38 pagineDNA Replication Prokaryotes EukaryotesSudeep BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaDocumento51 pagineLecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaBakalJenazahNessuna valutazione finora
- Agrobacterium Mediated Gene Transfer BA3825 SWaghmareDocumento8 pagineAgrobacterium Mediated Gene Transfer BA3825 SWaghmareSubash Ragasudha100% (1)
- Genetic Engineering: Applications in Agriculture and BiotechnologyDocumento10 pagineGenetic Engineering: Applications in Agriculture and BiotechnologyDeepika KVNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription: RNA Polymerases and General Transcription FactorsDocumento77 pagineTranscription: RNA Polymerases and General Transcription FactorsmluluNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocumento7 pagineDNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotessmn416Nessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication: How DNA Is CopiedDocumento13 pagineDNA Replication: How DNA Is CopieddvdmegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Students Lecture 2 Transcription and TranslationDocumento28 pagineMaster Students Lecture 2 Transcription and Translationha88ial88Nessuna valutazione finora
- cDNA Libraries and Gene CloningDocumento8 paginecDNA Libraries and Gene CloningRoberto RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Histone ModificationsDocumento8 pagineHistone ModificationsAnna PurnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Post-Transcriptional Modification: An Overview of mRNA ProcessingDocumento20 paginePost-Transcriptional Modification: An Overview of mRNA ProcessingZain YaqoobNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Methods For The Detection of Pathogenic MicroorganismsDocumento16 pagineA Review of Methods For The Detection of Pathogenic MicroorganismsLuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstracts For 32nd Congrass of ZoologyDocumento350 pagineAbstracts For 32nd Congrass of ZoologySaima WaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- GE IV TH SemDocumento185 pagineGE IV TH Semrahul vivekNessuna valutazione finora
- Third Sharif Ministry - Wikipedia PDFDocumento18 pagineThird Sharif Ministry - Wikipedia PDFSaira DogarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pakistan 21st Constitutional AmendmentDocumento3 paginePakistan 21st Constitutional AmendmentSaira DogarNessuna valutazione finora
- Third Sharif Ministry - Wikipedia PDFDocumento18 pagineThird Sharif Ministry - Wikipedia PDFSaira DogarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pakistan 21st Constitutional AmendmentDocumento3 paginePakistan 21st Constitutional AmendmentSaira DogarNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins BIOC2069 #1Documento36 pagineProteins BIOC2069 #1erica williamsNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Protein-Ligand DockingDocumento13 pagine2 Protein-Ligand DockingFhadliZilIkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Rapid Actions of Steroid Receptors in Cellular Signaling PathwaysDocumento12 pagineRapid Actions of Steroid Receptors in Cellular Signaling PathwaysJulio SantanaNessuna valutazione finora
- NPB 107 SyllabusDocumento2 pagineNPB 107 SyllabusApril MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- No Dance No Partner! A Tale of Receptor Flexibility in Docking and Virtual ScreeningDocumento55 pagineNo Dance No Partner! A Tale of Receptor Flexibility in Docking and Virtual ScreeningSelim sarıgülNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample PreparationDocumento88 pagineSample PreparationFrans Grovy NaibahoNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acids, Peptides & Proteins Structures FunctionsDocumento42 pagineAmino Acids, Peptides & Proteins Structures FunctionsLejNessuna valutazione finora
- Chaperone Plasmid Set: Table of ContentDocumento8 pagineChaperone Plasmid Set: Table of Contentrgon999Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.03 Secondary HemostasisDocumento8 pagine1.03 Secondary HemostasisShiena ArchividoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Lab Expt 5-Denaturation of ProteinsDocumento3 paginePre-Lab Expt 5-Denaturation of ProteinsMaria Isabella Francesca C. BargayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Perhitungan TenagaDocumento18 paginePerhitungan Tenagaramadhan syahputraNessuna valutazione finora
- LU2 Cell Structure and Function: Lect. 3: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Documento32 pagineLU2 Cell Structure and Function: Lect. 3: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Ahmat AmrinNessuna valutazione finora
- Analyze The Data: Protein PurificationDocumento3 pagineAnalyze The Data: Protein PurificationQuan ThieuNessuna valutazione finora
- Index - 2022 - Advances in Chemical ProteomicsDocumento7 pagineIndex - 2022 - Advances in Chemical ProteomicsPœta OciosoNessuna valutazione finora
- A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrixDocumento63 pagineA guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrixEduardo MullerNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins: Medical UsesDocumento8 pagineProteins: Medical UsesnotanintellectualNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Activity: Introduction To BioinformatcsDocumento18 pagineLab Activity: Introduction To Bioinformatcsreema amynNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of Cytochrome C in Electron TransportDocumento10 pagineThe Role of Cytochrome C in Electron TransportMohibNessuna valutazione finora
- Mecanismo Molecular de La AutofagiaDocumento14 pagineMecanismo Molecular de La Autofagiajohari salgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell CycleDocumento11 pagineCell CycleLydia Angelia YanitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytology CytoskeletonDocumento48 pagineCytology CytoskeletonMitzel Sapalo0% (1)
- CC Bishop QuestionsDocumento3 pagineCC Bishop QuestionsJohanna Kate DiestroNessuna valutazione finora
- Peptida Susu (Pengawet Alami)Documento11 paginePeptida Susu (Pengawet Alami)Silvia FebryNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Protein Mind Map PDFDocumento1 paginaChapter 4 Protein Mind Map PDFCynthia LingNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam II Review QuestionsDocumento9 pagineExam II Review QuestionsEmmanuel JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Small Globular ProteinsDocumento75 pagineBook Small Globular ProteinscaropsNessuna valutazione finora
- Kling 2017Documento63 pagineKling 2017jainigNessuna valutazione finora
- s15 Miller Chap 5b LectureDocumento22 pagines15 Miller Chap 5b LecturesilviaNessuna valutazione finora