Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Retest 1 (Unit 5)
Caricato da
Attagasam ArjunDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Retest 1 (Unit 5)
Caricato da
Attagasam ArjunCopyright:
Formati disponibili
K. RAMAKRISHNAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING K. RAMAKRISHNAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING K.
RAMAKRISHNAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
RETEST I-UNIT V- EE6702- PSG VII EEE B RETEST I-UNIT V- EE6702- PSG VII EEE B RETEST I-UNIT V- EE6702- PSG VII EEE B
Part-A (Answer ALL questions) Part-A (Answer ALL questions) Part-A (Answer ALL questions)
1. What are the drawbacks of oil circuit breaker? 1. What are the drawbacks of oil circuit breaker? 1. What are the drawbacks of oil circuit breaker?
2. What are the two theories explaining the current zero 2. What are the two theories explaining the current zero 2. What are the two theories explaining the current zero
interruption? interruption? interruption?
3.What are the advantages of air blast circuit breaker? 3.What are the advantages of air blast circuit breaker? 3.What are the advantages of air blast circuit breaker?
4. On what factors RRRV depends? 4. On what factors RRRV depends? 4. On what factors RRRV depends?
5. Define recovery voltage. 5. Define recovery voltage. 5. Define recovery voltage.
6. What is meant by electro negativity of SF6 gas? 6. What is meant by electro negativity of SF6 gas? 6. What is meant by electro negativity of SF6 gas?
7. What are the factors to be considered while selecting the type 7. What are the factors to be considered while selecting the type 7. What are the factors to be considered while selecting the type
of circuit breaker. of circuit breaker. of circuit breaker.
8. Define breaking capacity of circuit breaker. 8. Define breaking capacity of circuit breaker. 8. Define breaking capacity of circuit breaker.
9. Define short time rating of circuit breaker. 9. Define short time rating of circuit breaker. 9. Define short time rating of circuit breaker.
10. List the problems encountered during DC circuit breaking. 10. List the problems encountered during DC circuit breaking. 10. List the problems encountered during DC circuit breaking.
PART B (8 X10 =80) PART B (8 X10 =80) PART B (8 X10 =80)
11.Derive the expression for restriking voltage and rate of rise 11.Derive the expression for restriking voltage and rate of rise 11.Derive the expression for restriking voltage and rate of rise
of restriking voltage(RRRV). of restriking voltage(RRRV). of restriking voltage(RRRV).
12.Describe the principle and construction of vacuum circuit 12.Describe the principle and construction of vacuum circuit 12.Describe the principle and construction of vacuum circuit
breaker. Also state the advantage and disadvantages of vacuum breaker. Also state the advantage and disadvantages of vacuum breaker. Also state the advantage and disadvantages of vacuum
CB. CB. CB.
13.With the block diagram, explain the construction, operating 13.With the block diagram, explain the construction, operating 13.With the block diagram, explain the construction, operating
principle and advantages of SF6 circuit breaker. principle and advantages of SF6 circuit breaker. principle and advantages of SF6 circuit breaker.
14(a)Explain in detail the various ratings on circuit breaker. 14(a)Explain in detail the various ratings on circuit breaker. 14(a)Explain in detail the various ratings on circuit breaker.
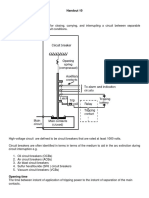
14(b)Draw the schematic of HVDC circuit breaker and explain 14(b)Draw the schematic of HVDC circuit breaker and explain 14(b)Draw the schematic of HVDC circuit breaker and explain
its functions. its functions. its functions.
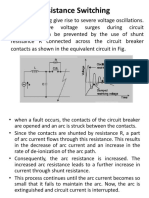
15 Explain the resistance switching for arc interruption in 15 Explain the resistance switching for arc interruption in 15 Explain the resistance switching for arc interruption in
circuit breaker. Also explain the following: Current chopping circuit breaker. Also explain the following: Current chopping circuit breaker. Also explain the following: Current chopping
& capacitive current interruption. & capacitive current interruption. & capacitive current interruption.
16. Explain with a neat sketch the construction and working of 16. Explain with a neat sketch the construction and working of 16. Explain with a neat sketch the construction and working of
minimum oil circuit breaker. Also give its merits and demerits. minimum oil circuit breaker. Also give its merits and demerits. minimum oil circuit breaker. Also give its merits and demerits.
17. A 50Hz, 11KV 3-phase alternator with earthed neutral has a 17. A 50Hz, 11KV 3-phase alternator with earthed neutral has a 17. A 50Hz, 11KV 3-phase alternator with earthed neutral has a
reactance of 5 ohms per phase and is connected to a bus-bar reactance of 5 ohms per phase and is connected to a bus-bar reactance of 5 ohms per phase and is connected to a bus-bar
through a circuit breaker. The distributed capacitance upto through a circuit breaker. The distributed capacitance upto through a circuit breaker. The distributed capacitance upto
circuit breaker between phase and neutral is 0.01 microfarad. circuit breaker between phase and neutral is 0.01 microfarad. circuit breaker between phase and neutral is 0.01 microfarad.
Determine Determine Determine
1.Peak restriking voltage across the contacts of the circuit 1.Peak restriking voltage across the contacts of the circuit 1.Peak restriking voltage across the contacts of the circuit
breaker breaker breaker
2.frequency of oscillation 2.frequency of oscillation 2.frequency of oscillation
3.The average rate of rise of restriking voltage upto the first 3.The average rate of rise of restriking voltage upto the first 3.The average rate of rise of restriking voltage upto the first
peak peak peak
18. A three phase alternator has the line voltage of 12KV. The 18. A three phase alternator has the line voltage of 12KV. The 18. A three phase alternator has the line voltage of 12KV. The
generator is connected to a circuit breaker. The inductive generator is connected to a circuit breaker. The inductive generator is connected to a circuit breaker. The inductive
reactance up to the circuit breaker is 5 /phase. The distributed reactance up to the circuit breaker is 5 /phase. The distributed reactance up to the circuit breaker is 5 /phase. The distributed
capacitance up to circuit breaker between phase and neutral is capacitance up to circuit breaker between phase and neutral is
capacitance up to circuit breaker between phase and neutral is
0.011 µf. Determine peak restriking voltage across the CB, 0.011 µf. Determine peak restriking voltage across the CB,
0.011 µf. Determine peak restriking voltage across the CB, frequency of restriking voltage, frequency of restriking voltage,
frequency of restriking voltage, average rate of restriking voltage up to peak restriking voltage, average rate of restriking voltage up to peak restriking voltage,
average rate of restriking voltage up to peak restriking voltage, maximum RRRV. maximum RRRV.
maximum RRRV.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Full Download Ebook PDF System Dynamics 4th Edition by William Palm PDFDocumento41 pagineFull Download Ebook PDF System Dynamics 4th Edition by William Palm PDFdorothy.jackson594100% (33)
- Theory of Circuit BreakingDocumento45 pagineTheory of Circuit Breakingthangalakshmiprakash100% (1)
- Installation Form - Submersible Pump of SAERDocumento2 pagineInstallation Form - Submersible Pump of SAERHary FadlyNessuna valutazione finora
- SGP Question Bank 1-3Documento2 pagineSGP Question Bank 1-3vsasaankNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 4 - Second PartDocumento34 pagineCH 4 - Second PartNasser AlmofariNessuna valutazione finora
- Bus-Bar Modules: Modular Components Fitted in Bus-Bar Lengths and BaysDocumento32 pagineBus-Bar Modules: Modular Components Fitted in Bus-Bar Lengths and BaysMahmoud MoezNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & AnswerDocumento4 pagineUnit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & Answerpriyadarshini212007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unitwise QuestionsDocumento2 pagineUnitwise QuestionsSdalthafNessuna valutazione finora
- BEE 42 AssignmentDocumento3 pagineBEE 42 AssignmentVikesh gondNessuna valutazione finora
- Switchgear Unit 4 QuestionsDocumento1 paginaSwitchgear Unit 4 Questionslovegupta891Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rider-Resonance and Alignment - John F. RiderDocumento95 pagineRider-Resonance and Alignment - John F. RidermplennaNessuna valutazione finora
- 18EE73Documento3 pagine18EE73abhinav vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Circuit AnalysisDocumento121 pagineDC Circuit AnalysisChaudhry Muhammad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank - Unit 5 (Circuit Breaker)Documento2 pagineQuestion Bank - Unit 5 (Circuit Breaker)suryavanshivipin2709Nessuna valutazione finora
- AIC 2 Marks Q & ADocumento38 pagineAIC 2 Marks Q & ASriramNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient VoltageDocumento20 pagineTransient VoltageAshish ParasharNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Power and ResonanceDocumento77 pagineComplex Power and Resonanceconference RequirementsNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions & Answers On Real Transformer and Equivalent CircuitDocumento18 pagineQuestions & Answers On Real Transformer and Equivalent Circuitkibrom atsbha100% (1)
- Series RC Circuit: Fundamentals of Electricity II LABDocumento10 pagineSeries RC Circuit: Fundamentals of Electricity II LABMustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Snubber Circuit Design AnalysisDocumento27 pagineSnubber Circuit Design Analysisetmatsuda100% (1)
- Batangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentDocumento15 pagineBatangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentKarenMacalaladTanangNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3 Three Phase AlternatorDocumento2 pagineTopic 3 Three Phase AlternatorNo nameNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing TransformerDocumento14 pagineTesting TransformerBudhaditya GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- S.Y.B.Sc. Electronics (Ele - 211) Question BankDocumento51 pagineS.Y.B.Sc. Electronics (Ele - 211) Question BankPrakash SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Agsie - Johnmark Exp1Documento7 pagineAgsie - Johnmark Exp1CloudFarmInnovations IncorporatedNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE Guide For SR SwitchingDocumento7 pagineIEEE Guide For SR Switchingraza239100% (1)
- Rating of The Circuit BreakersDocumento19 pagineRating of The Circuit BreakersRoopa ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- QB To Exam Cell SGP First Series 2015Documento3 pagineQB To Exam Cell SGP First Series 2015finifathimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Niraj Mishra Question Bank Paper-1Documento6 pagineNiraj Mishra Question Bank Paper-1Arun SamyalNessuna valutazione finora
- SGP - Question Bank - Unit 1&2Documento1 paginaSGP - Question Bank - Unit 1&2rahul.joshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec8261 Lab ManualDocumento94 pagineEc8261 Lab ManualJayamani Krishnan0% (1)
- High Voltage Engineering PDFDocumento2 pagineHigh Voltage Engineering PDFShweta KhadseNessuna valutazione finora
- 19MO504-IE 2 MarksDocumento40 pagine19MO504-IE 2 MarksSaranya. M SNSNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements of Electronics Engineering Question Bank Unit - 1Documento5 pagineElements of Electronics Engineering Question Bank Unit - 1rahul vadhyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Breaker Thesis PDFDocumento121 pagineBreaker Thesis PDFKarthik SriramakavachamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18Documento28 pagineChapter 18dyalatalal225Nessuna valutazione finora
- EC2251 2 MarksDocumento15 pagineEC2251 2 MarksDeepan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- RRB Jobs Question Bank Junior Engineer Non Ac Write Short NotesDocumento6 pagineRRB Jobs Question Bank Junior Engineer Non Ac Write Short Noteskunalg293Nessuna valutazione finora
- Write Short Notes:: Question Bank For Jee Non - AcDocumento6 pagineWrite Short Notes:: Question Bank For Jee Non - Ackunalg293Nessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 54 DP2 DocumentationDocumento5 pagineEEE 54 DP2 DocumentationDarl John MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyristors PDFDocumento41 pagineThyristors PDFAvegeil Faye Rubio GamitNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Solution MachineDocumento2 pagineNumerical Solution Machinenimesh patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment #1 Thyristor Familiarization - Part 1Documento14 pagineExperiment #1 Thyristor Familiarization - Part 1Justin CorreNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Power Electronics DevicesDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To Power Electronics DevicesahmedsaeedobiedNessuna valutazione finora
- Double Freq TransientDocumento22 pagineDouble Freq TransientMelissa Miller100% (1)
- 33/11 KV Sub StationDocumento61 pagine33/11 KV Sub StationRatnesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Questions or MCQ On SCR or Thyristor 4 - Electrical Study App by Saru TechDocumento4 pagineObjective Questions or MCQ On SCR or Thyristor 4 - Electrical Study App by Saru TechAmirSaeed0% (1)
- Circuit Breakers (CBS) (52) : Handout 10Documento8 pagineCircuit Breakers (CBS) (52) : Handout 10Hubaib KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- TransformersDocumento7 pagineTransformersMoawiah Al-HawajrehNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocumento112 paginePower Electronics Lab ManualdiegosendoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- TY SWP Question BankDocumento4 pagineTY SWP Question Bankafatab SheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- OscillatorsDocumento14 pagineOscillatorsSoundararajan RajagopalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee Exp 4Documento7 pagineBee Exp 4Dhwani PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 2 Marks QuestionsDocumento13 pagineEc2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 2 Marks QuestionsSumathy SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Mark Questions With AnswersDocumento10 pagineTwo Mark Questions With AnswerssenthilNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheme Eee Unit3 QBDocumento35 pagineScheme Eee Unit3 QBMaaz S100% (2)
- 2019-20 - 5EEU07 - Power Electronics LabDocumento42 pagine2019-20 - 5EEU07 - Power Electronics LabGautam AcharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec 1251 Electronics Circuits IIDocumento17 pagineEc 1251 Electronics Circuits IIainugiri100% (1)
- 2 Resistance and Resistivity - 1Documento9 pagine2 Resistance and Resistivity - 1Genesis MenesesNessuna valutazione finora
- EMT Quiz - 1 Type A Answers UnderlinedDocumento3 pagineEMT Quiz - 1 Type A Answers UnderlinedAbhishekKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Metacentric HeightDocumento4 pagineMetacentric HeightVrushiket PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular MotionDocumento14 pagineCircular MotionTran Phuong LinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Fe Simulation and Experiment of A Self Excited Synrel Generator Based On Comsol SoftwareDocumento7 pagineFe Simulation and Experiment of A Self Excited Synrel Generator Based On Comsol SoftwareboucharebNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDCDocumento5 pagineHVDCAlluri Appa RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Newtons Law of Universal GravitationDocumento10 pagineNewtons Law of Universal Gravitationdheerajr97Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion: 1a. (4 Marks)Documento21 pagine4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion: 1a. (4 Marks)xNessuna valutazione finora
- MSEG 667: 3: Guided Wave OpticsDocumento26 pagineMSEG 667: 3: Guided Wave OpticsJuan Carlos GarayNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems Lift DragDocumento3 pagineProblems Lift DragMuhammad HasdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 12: Shobrat Hasan Alvi Mehedi Hasan AkashDocumento10 pagineGroup 12: Shobrat Hasan Alvi Mehedi Hasan AkashTahsin AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Rail Structure Interaction For Multiple Span Railway Viaducts With Direct FIXED TRACKDocumento10 pagineRail Structure Interaction For Multiple Span Railway Viaducts With Direct FIXED TRACKsandeep tanavadekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Test 2-Force and Motion (P2) : 1. EmailDocumento8 paginePhysics Test 2-Force and Motion (P2) : 1. EmailSyed Muhammad Ali BokhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Assembly Instructions ECblue Basic Version ULDocumento45 pagineAssembly Instructions ECblue Basic Version ULMatei DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Word Problems in ScienceDocumento3 pagineSolving Word Problems in ScienceChrisel Luat LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsDocumento10 pagineH2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungNessuna valutazione finora
- Statics Assgnmnt)Documento20 pagineStatics Assgnmnt)Mohammed AdemNessuna valutazione finora
- MST 2Documento4 pagineMST 2Neha Prashant VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- TSDOS Adv Diag Testing DW PDFDocumento61 pagineTSDOS Adv Diag Testing DW PDFDhammika Dharmadasa100% (1)
- Ohmega BrochureDocumento12 pagineOhmega Brochurevenkat_060Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Physics NotesDocumento115 pagineClass 12 Physics NotesAiden Pearce100% (1)
- Simple Harmonic Motion by Edward AbellaDocumento50 pagineSimple Harmonic Motion by Edward AbellaEdward Amoyen AbellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Note: Connection Between Gate Driver and ControllerDocumento4 pagineApplication Note: Connection Between Gate Driver and ControllerEdsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Victor BrochureDocumento8 pagineVictor BrochureSanjay MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Week 3 EE462L Diode Bridge Rectifier PDFDocumento18 pagineLab Week 3 EE462L Diode Bridge Rectifier PDFFrew FrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of HVDC and FACTS Devices: Lecture NotesDocumento22 pagineFundamentals of HVDC and FACTS Devices: Lecture NotesKiran KunchamNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind Code Evaluation Caribbean Islands (Caricom) : Name of Document: Caribbean Uniform Building Code (Cubic)Documento13 pagineWind Code Evaluation Caribbean Islands (Caricom) : Name of Document: Caribbean Uniform Building Code (Cubic)Jayant LakhlaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Branch Circuits and FeedersDocumento28 pagineBranch Circuits and FeedersgteklayNessuna valutazione finora