Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Preparation of Pure Hydrogen
Caricato da
Muhammad IlhamTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Preparation of Pure Hydrogen
Caricato da
Muhammad IlhamCopyright:
Formati disponibili
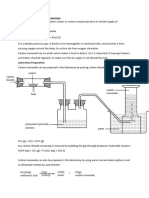
Hydrogen gas is manufactured by
(1) Electrolysis of NaOH solution with Ni or Fe electrode:
2H2O 2H2 + O2
(2) Catalytic reduction of steam by coke, or by CO using Fe2O3 catalyst (Bosch
process):
750 K
C + H2O CO + H2 (water gas)
670-770 K
CO + H2O CO2 + H2
Fe2O3
(3) Catalytic oxidation of hydrocarbons with steam at 1200 K in the presence
of nickel catalyst, followed by oxidation of CO to CO2 by steam at 670 K:
Ni, 1200 K
CnH2n+2 + nH2O nCO + 2nH2
Natural gases are mainly mixtures of CH4, C2H6 and H2. The alkanes are
oxidized to CO with steam using alumina as catalyst. The product is called
syntetic fuel gas. CO is oxidized further to CO2 as in Bosch process.
Al2O3
CH4 + H2O CO + 3H2O
Al2O3
C2H6 + 2H2O 2CO + 5H2
(4) Cracking of petroleum, in which higher alkanes and cycloalkanes give
lower hydrocarbons abd aromatic compounds with the release of hydrogen
(reaction (6) above).
(5) As a hydroproduct in other industrial operations like manufacture of
NaOH, or of Cl2 from saturated NaCl.
Preparation of Pure Hydrogen
Pure hydrogen is prepared by (i) dissolving pure magnesium metal in pure
dilute HNO3, or (ii) electrolysis of warm Ba(OH)2 solution with nickel
electrodes in a U-tube.
Commercial hydrogen has H2S, CO, CO2, and O2 as the main impurities. It
is purified as follows:
(a) Caustic potash (KOH) solution absorbs H2S and other sulphur com-
pounds
H2S + 2KOH K2S + 2H2O
(b) Ammoniacal copper formate absorbs CO completely:
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ + HCOO- + 2CO [Cu(CO)2(OOCH)]+ + 4NH3
(c) CO2 is removed by absorption in water under pressure to obtain soda
water. Residual CO2 is absorbed in aqueous ethanolamine solutions:
2HOCH2CH2NH2 + CO2 + H2O (HOCH2CH2NH3+)2CO32-
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsDa EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNessuna valutazione finora
- All Chemical ReactionsDocumento29 pagineAll Chemical ReactionsManeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid BaseDocumento18 pagineAcid BasechaitanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxygen: HalcogensDocumento18 pagineOxygen: HalcogensDhirNessuna valutazione finora
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Documento29 pagineAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Compounds of Carbon: (I) Per, Nonocarhonic Acid, (Ii) Perdicarbonic AcidDocumento72 pagineCompounds of Carbon: (I) Per, Nonocarhonic Acid, (Ii) Perdicarbonic Acidsant venkatakrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- ReactionsDocumento2 pagineReactionspushpa121yajaNessuna valutazione finora
- One Shot JA Block Chem Part 1 12 March FINAL Pankaj Sir FINAL MergedDocumento181 pagineOne Shot JA Block Chem Part 1 12 March FINAL Pankaj Sir FINAL Mergedsuvendu shekhar MahakudNessuna valutazione finora
- S Block NotesDocumento7 pagineS Block NotesSiddharth SangaiNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE Main Hydrocarbons Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocumento20 pagineJEE Main Hydrocarbons Revision Notes - Free PDF Downloadpurple youNessuna valutazione finora
- OTflp OX7 NL790 DT 4 I 4 YEDocumento26 pagineOTflp OX7 NL790 DT 4 I 4 YESubhashakti BeheraNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of HydrogenDocumento9 paginePreparation of HydrogenDavies Masumba50% (2)
- Oxyg en Fa Mily: OxygenDocumento26 pagineOxyg en Fa Mily: Oxygendevli falduNessuna valutazione finora
- Salt Analysis (XII)Documento18 pagineSalt Analysis (XII)Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 12S-2023 Chemistry 9Documento9 pagine12S-2023 Chemistry 9Alumbwe MubondaNessuna valutazione finora
- With Metals: Metals Gold Platinum Iridium Oxides Oxidation StateDocumento3 pagineWith Metals: Metals Gold Platinum Iridium Oxides Oxidation StatevibhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon allotropes and propertiesDocumento5 pagineCarbon allotropes and propertiesMandeep ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento11 pagineChemistryEttaNessuna valutazione finora
- CPI Notes 2Documento3 pagineCPI Notes 2HELLONessuna valutazione finora
- Oxygen Family: Preparation and Properties of Oxygen, Ozone and Hydrogen PeroxideDocumento26 pagineOxygen Family: Preparation and Properties of Oxygen, Ozone and Hydrogen PeroxideGudia kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision notes on p-block elements group 13 to 16Documento20 pagineRevision notes on p-block elements group 13 to 16Bharadwaj SubramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocumento5 pagineHydrogen and Its CompoundsAngela Jones100% (1)
- Important Chemical Reactions for Class 10 ChemistryDocumento9 pagineImportant Chemical Reactions for Class 10 ChemistryManish SainNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers For REINFORCEMENT EXERCISEDocumento5 pagineAnswers For REINFORCEMENT EXERCISEAbgyyg LuRf UNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen: (I) From WaterDocumento3 pagineHydrogen: (I) From WaterSnehin PoddarNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonates and bicarbonates reactions properties usesDocumento3 pagineCarbonates and bicarbonates reactions properties usesMaulida CitrifoliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocumento4 pagineWeek 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDenzel MusaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Chemistry CH-4NotesDocumento6 pagine12th Chemistry CH-4NotesMajid HafeezNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen and Its Compounds: ChapterDocumento24 pagineHydrogen and Its Compounds: ChapterBharatNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic-Chemistry (As Level)Documento8 pagineOrganic-Chemistry (As Level)Pirate HunterNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrogen & PhosphorusDocumento30 pagineNitrogen & PhosphorusSachin KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chlorine and Its CompoundsDocumento19 pagineChlorine and Its Compoundskakembo hakimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeDocumento12 pagineChemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeSooryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 30-32-Class 11-Chapter 4-ChemistryDocumento9 pagineDay 30-32-Class 11-Chapter 4-Chemistryjatin nayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol, Ester, Carboxylic Acid PDFDocumento17 pagineAlcohol, Ester, Carboxylic Acid PDFJustin LukmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen's Position and Compounds in the Periodic TableDocumento6 pagineHydrogen's Position and Compounds in the Periodic TableSharoon JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Inorganic ChemistryDocumento17 pagineIndustrial Inorganic ChemistryMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen ChlorideDocumento3 pagineHydrogen Chloriderkjoseph1410Nessuna valutazione finora
- S.3 Chemistry MR SsemugoomaDocumento9 pagineS.3 Chemistry MR SsemugoomalionlioneenjohnsmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem f4 NotesDocumento56 pagineChem f4 Notesmayogebukapuka2Nessuna valutazione finora
- P Block2012 457Documento145 pagineP Block2012 457AaravNessuna valutazione finora
- (Game Changer 1.0) - P Block, D & F Block - 6 JanDocumento102 pagine(Game Changer 1.0) - P Block, D & F Block - 6 JanRama KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry HSC FormulasDocumento6 pagineChemistry HSC Formulashpgc101100% (1)
- Syn Gas: Nomula Devadeekshith B130943Ch Omprakash Hada B130980Ch Poluparthi Jagadish B130322ChDocumento16 pagineSyn Gas: Nomula Devadeekshith B130943Ch Omprakash Hada B130980Ch Poluparthi Jagadish B130322ChkamauNessuna valutazione finora
- CopperDocumento26 pagineCopperShirjak ThokarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulphuric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)Documento3 pagineSulphuric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)the lillyNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon OxidesDocumento12 pagineCarbon Oxidesprateek gangwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon OxidesDocumento12 pagineCarbon Oxidesprateek gangwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- P Block2012 457Documento143 pagineP Block2012 457Abhishek Bansal100% (1)
- Topic 9.3 2009 Group VII Prelim SolnDocumento8 pagineTopic 9.3 2009 Group VII Prelim SolndeadbeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Transiton metal chemistryDocumento15 pagineTransiton metal chemistryazabokennedy09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non - MetalsDocumento3 pagineNon - MetalsAlex noslenNessuna valutazione finora
- 03.hydrogen & Its Compounds (Theory) Module-2-1Documento8 pagine03.hydrogen & Its Compounds (Theory) Module-2-1Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- InorganicDocumento137 pagineInorganicShaswata Roy50% (2)
- Anorganic Chemistry: You Want To Gain The "Prize", The B. EngDocumento44 pagineAnorganic Chemistry: You Want To Gain The "Prize", The B. EngArinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogen Family ChemistryDocumento16 pagineHalogen Family ChemistryDhirNessuna valutazione finora
- Co - Co2Documento2 pagineCo - Co2quynhnnp234101eNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry:halogensDocumento11 pagineGeneral Chemistry:halogensMarvin IdigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulfuric Acid Manufacture: Analysis, Control and OptimizationDa EverandSulfuric Acid Manufacture: Analysis, Control and OptimizationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- LT 2662a Brochure Design Guide For Bonding Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers Volume 3 2011Documento82 pagineLT 2662a Brochure Design Guide For Bonding Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers Volume 3 2011OzkanNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Antioxidant Capacities of Raw and Cooked Meats Arda Serpen, Vural Gökmen, Vincenzo FoglianoDocumento16 pagineTotal Antioxidant Capacities of Raw and Cooked Meats Arda Serpen, Vural Gökmen, Vincenzo FoglianoMuh Mirza LegawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Mobile Biodiesel Production PlantDocumento137 pagineDesign of A Mobile Biodiesel Production PlantDinhtai NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- IFARS generic drugsDocumento5 pagineIFARS generic drugsOky Spinola IdroosNessuna valutazione finora
- Iron and Steel Manufacturing ProcessDocumento28 pagineIron and Steel Manufacturing ProcessMarnel Roy Mayor78% (32)
- Human Physiology An Integrated Approach 6th Edition Silverthorn Test BankDocumento25 pagineHuman Physiology An Integrated Approach 6th Edition Silverthorn Test BankLauraMitchellfgie100% (56)
- High Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyDocumento69 pagineHigh Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyAliefanugerahsani Attabe100% (1)
- Oils and Pigments - 2012 - Jan EsmannDocumento37 pagineOils and Pigments - 2012 - Jan Esmannancadors100% (1)
- Periodic TableDocumento23 paginePeriodic Tabled anjilappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymatic Treatments Improve Textile PropertiesDocumento24 pagineEnzymatic Treatments Improve Textile PropertiesKhandaker Sakib FarhadNessuna valutazione finora
- Fragmentation of Organic Compounds in EI-MSDocumento18 pagineFragmentation of Organic Compounds in EI-MSMoustafa ElsadanyNessuna valutazione finora
- JECFA Monograph 22Documento169 pagineJECFA Monograph 22Yiyi ArayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 7 Parallel Test 2021-2022Documento6 pagineScience 7 Parallel Test 2021-2022malifi ciadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1Documento14 pagineModule 1Harsha MayankNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid SolutionDocumento8 pagineLiquid SolutionAyush KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSAB Tool Steel Performance Comparison ChartDocumento1 paginaASSAB Tool Steel Performance Comparison ChartNugroho Faris Sudrajat100% (2)
- 10 - Suvg 27 - F.G. - 69-78Documento10 pagine10 - Suvg 27 - F.G. - 69-78Valentina AnutaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Engineering MaterialsDocumento6 pagineMock Engineering MaterialsJohn AsokNessuna valutazione finora
- General Characteristic of Crude OilDocumento20 pagineGeneral Characteristic of Crude Oildassi99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ijftr 29 (2) 239-259Documento21 pagineIjftr 29 (2) 239-259aymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic CompoundsDocumento19 pagineNomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic CompoundsH to O ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 5 - Liquefaction - 2015 PDFDocumento6 pagineLect 5 - Liquefaction - 2015 PDFAnonymous oqlnO8e100% (1)
- Choosing the Right Fire Extinguisher for Your NeedsDocumento2 pagineChoosing the Right Fire Extinguisher for Your Needsfaisalhotline9500Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gulf Hydraulic Oil Guide for System Selection & PerformanceDocumento30 pagineGulf Hydraulic Oil Guide for System Selection & PerformanceRAJ SAURABH PANDEYNessuna valutazione finora
- NCES Fuel Cell McqsDocumento9 pagineNCES Fuel Cell Mcqsdr.Sabita shresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vacuum Soldering Using Formic Acid PaperDocumento6 pagineVacuum Soldering Using Formic Acid PaperZine-Eddine BoutaghouNessuna valutazione finora
- Carechlor BCDocumento2 pagineCarechlor BCAdrian FlorinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No 70, 71 Formulation of Semi Solids and Gels and JelliesDocumento34 pagineLecture No 70, 71 Formulation of Semi Solids and Gels and JelliesAdinath ShirsatNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubber Properties Chart PDFDocumento1 paginaRubber Properties Chart PDFArasarethina KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sliding TB 105mmDocumento42 pagineSliding TB 105mmSaud AffanNessuna valutazione finora