Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Health Teaching Plan Format
Caricato da
Alcie Laanan Bucayan0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
427 visualizzazioni3 pagineGuide on how to make a health teaching plan
Titolo originale
Health Teaching Plan format
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoGuide on how to make a health teaching plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
427 visualizzazioni3 pagineHealth Teaching Plan Format
Caricato da
Alcie Laanan BucayanGuide on how to make a health teaching plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Adventist medical Center College
San Miguel, Iligan City
DEVELOPING the TEACHING PLAN
Adventist Medical Center College
San Miguel, Iligan City
Teaching Plan
Topic: Wound care
General Objectives: After 30 minutes of nurse-patient interaction, the patient will be able to
acquire knowledge, skills and attitude regarding proper execution of wound care.
Venue:
Participants:
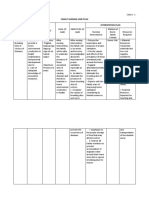
Learning Content Method of Timeframe Instructional Methods of
/Specific Outline/ Instruction/ (in mins.) Resources Evaluation/
Objectives Learning Teaching Allotment Evaluation
Outcome Learning Parameters
Activities
This refers to Outline of Techniques. Time allotted This deals This will
the desired the subject Strategies, for the ice- with depend on
learning or matter or instructional breakers and manpower, the learning
behavioral topic which ,materials introduction money, objectives of
attributes or should and media to the learning machine, etc. the session or
behaviors coincide with be used session, lesson.
that must be the learning activities,
shown at the or behavioral recap, open
end of the objective forum (if
session. any) etc.
EXAMPLES to the above parts of Teaching Plan
Within 30 Definition of Pre-Activity 5 minutes Visual Aids Q&A
mins of wound care Introduction such as
health Wound care of self (cartolina, 1. The
teaching the is the process Q&A pentel pen awareness
patient will of cleansing and scotch of the
be able to: and dressing tape) patient
1. Define wound in Lecture 5 minutes about the
correctly order to discussion procedure
the become free
wound from being
care. infection Lecture done.
discussion 2. Define
2. Describe Infection wound
signs and Sign and care in
symptoms symptoms your own
of wound include word
infection. wound warm correctly
to touch, 3. What are
misalignment the
of wound materials
edges, and to be used
purulent in wound
wound care?
drainage. 4. What are
Signs of the
systemic comments
infection or
include fever opinions
and body about the
malaise. procedure
being
thought?
Preparing the Teaching Plan
- A health education plan may emphasize a phase of the behavior-change process
that is related to the client’s health needs/problems.
- The plan may follow the sequence of that process, from pre-training to the
continued performance of a behavior that helps resolve a health need/problem.
- The written teaching plan represents a package of educational services provided to a
participant or consumer or student. The plan, therefore, should be written from the
participant’s viewpoint.
The process of generating a teaching plan helps the Health Educator:
a. Recognize and use methods of learning that involve the client as an active participant;
b. Include a list of specific actions or abilities that the client may perform at intervals
during the educational intervention and at the end;
c. Clarify what he expects the students to do when the educational intervention is over.
Health Educator preparing a teaching plan in primary health setting should:
A. Get background information about the client from the person’s record and any agency
reports that include description of the client’s population group(demographic data—
who, what, where)
B. Conduct needs assessment of the participants , the scope and content of the health
education class, possible actions/interventions to be undertaken to address the needs,
and the possible approaches, strategies or methodologies to be used.
STEPS I WRTING a HEALTH EDUCATION PLAN (Castro, 2011)
1. Assess the learning needs by answering the following:
a. What are the characteristics and learning capabilities of the learner or client?
- client’s age
- developmental stage in his or her lifestyle (Is there a health threat, deficit, need or
foreseeable crisis or stress point)
- use the Family assessment guide
-level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is the client situated
b. What needs have been identified and prioritized in terms of health promotion, risk
reduction and health problems?
- Consult epidemiological report, community needs assessment report, incident
report.
c. What knowledge does he or she already have in relation to the subject matter?
- Interview the client regarding knowledge of certain facts related to the subject
matter, administer pre-test and post-test questionnaires.
d. Is the client motivated to change unhealthy behaviors?
- Health educator must identify reasons for seeming resistance or indifference to
change which may be due to lack of knowledge or skills regarding the issue on hand,
environmental constraints or hindrances, cultural belief and practices.
- Health educator must create a “learning climate” during the pre-training phase to
encourage the client to decide to undergo health behavior change.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Health Education PlanDocumento3 pagineHealth Education PlanCamille VegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching PlanDocumento4 pagineTeaching PlanPagodNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Plan - Wound CareDocumento1 paginaTeaching Plan - Wound CareJemma Ganda100% (3)
- Npi Format For Rle 1Documento9 pagineNpi Format For Rle 1Patricia VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge PlanningDocumento3 pagineDischarge Planningfjhjhkyu50% (2)
- Teaching Plan For LaborDocumento2 pagineTeaching Plan For LaborSte Ward0% (1)
- Nutrition HTPDocumento3 pagineNutrition HTPAdriene Fay DominguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Plan FormDocumento3 pagineHealth Teaching Plan FormChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Family NCPcorrectDocumento6 pagineFamily NCPcorrectapi-3832358100% (11)
- Teaching Plan For Breast FeedingDocumento4 pagineTeaching Plan For Breast FeedingKramSenarevolNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Nursery BGHDocumento7 pagineHealth Teaching Nursery BGHAmira Fatmah QuilapioNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento2 pagineHealth Teaching PlanShedrann JohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento10 pagineHealth Teaching PlanAsterlyn Coniendo100% (2)
- Health Teaching Plan FormDocumento3 pagineHealth Teaching Plan FormEric EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- CVA-Health Teaching PlanDocumento5 pagineCVA-Health Teaching PlanAna100% (4)
- Teaching Plan Gerontologic NursingDocumento3 pagineTeaching Plan Gerontologic NursingJoan AbardoNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB Calculating Diets and Meal Planning Module 1Documento15 pagineLAB Calculating Diets and Meal Planning Module 1Angelica PalacNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERDocumento4 pagineHealth Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERJaic Ealston D. TampusNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Plan Group 1 CDocumento2 pagineHealth Teaching Plan Group 1 CKirstie CapitanNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Plan For Unang YakapDocumento3 pagineHealth Teaching Plan For Unang YakapSamantha sanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Plan - Wound Care and DressingDocumento6 pagineHealth Teaching Plan - Wound Care and Dressingp_dawg100% (2)
- Sample Health Teaching PlanDocumento1 paginaSample Health Teaching PlanGia Espinosa OcbeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Workplan Rle JuneDocumento18 pagineWorkplan Rle JuneQueeny Anne Apil33% (3)
- HEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Documento3 pagineHEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Asterlyn ConiendoNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised NCPDocumento8 pagineRevised NCPKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing: Unit 1, Module 1 Week 1Documento7 pagineCommunity Health Nursing: Unit 1, Module 1 Week 1Angel Joy CatalanNessuna valutazione finora
- ANGELICA M.docx HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FOR MATERNAL AND CHILD RLEDocumento7 pagineANGELICA M.docx HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FOR MATERNAL AND CHILD RLEAngelica Malacay RevilNessuna valutazione finora
- Micronutrients and Pregnancy Outcome: A Review of The LiteratureDocumento1 paginaMicronutrients and Pregnancy Outcome: A Review of The LiteratureDenisse Shazz Mae MaretNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP SmokingDocumento1 paginaNCP SmokingRuby GuarinNessuna valutazione finora
- HTP FinalDocumento3 pagineHTP Finalאורזלין לנזוןNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Education Plan - Case StudyDocumento7 pagineHealth Education Plan - Case StudyRenzy Mayven Pedriña LobatonNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching PlanDocumento92 pagineTeaching Plangladz25100% (3)
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineActivity IntoleranceDiane AbanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento6 pagineHealth Teaching PlanShara Lailanie A. AzisNessuna valutazione finora
- LFD CommunityDocumento1 paginaLFD Communityjai2x100% (1)
- Teaching Plan On Wound CareeeDocumento2 pagineTeaching Plan On Wound Careeeaambroce100% (1)
- Teaching Plan On Proper HygieneDocumento1 paginaTeaching Plan On Proper HygieneMA. LOUIMAR CATU0% (1)
- Teaching Plan Fo Cord Car1Documento15 pagineTeaching Plan Fo Cord Car1jaden1233Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases Associated in Carbohydrates 3Documento2 pagineDiseases Associated in Carbohydrates 3Mary Joy FalcesoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Mod9Documento3 pagineNCP Mod9Francis ChloeNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Plan Group 1 DDD Family Planning PDFDocumento5 pagineHealth Teaching Plan Group 1 DDD Family Planning PDFNathanielle Keith PENASONessuna valutazione finora
- FNCP CHNDocumento4 pagineFNCP CHNMariaNessuna valutazione finora
- TLGDocumento1 paginaTLGKylie GolindangNessuna valutazione finora
- Soapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINDocumento7 pagineSoapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINAna100% (2)
- Developing The Family Nursing Care PlanDocumento20 pagineDeveloping The Family Nursing Care PlanJahara Aiko PandapatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento8 pagineHealth Teaching PlanAbuMaryamBurahimAmlihNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento3 pagineHealth Teaching Plangracey sam67% (3)
- Home Visit PlanDocumento3 pagineHome Visit PlanKym HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumFrederene JavelonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xiii. Discharge Planning: Carbohydrates NutrientsDocumento4 pagineXiii. Discharge Planning: Carbohydrates Nutrientsgroupbsection1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento4 pagineActivity IntoleranceShermane Criszen F. SallanNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Plan - Breastfeeding Chris - PDFDocumento10 pagineTeaching Plan - Breastfeeding Chris - PDFJm Tolentino100% (1)
- SOAPIEDocumento4 pagineSOAPIEdhianne_garcia2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento12 pagineHealth Teaching PlanFrancis SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- BSN 2 4 GRP II Ndtlec WRDocumento22 pagineBSN 2 4 GRP II Ndtlec WRChristine AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento7 pagineHealth Detailed Lesson PlanBREVISH DAME FRANCO100% (4)
- Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Fundamentals in Nursing Practice (Lecture) Course Output (Final Term)Documento3 pagineWestern Mindanao State University College of Nursing Fundamentals in Nursing Practice (Lecture) Course Output (Final Term)Reann LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento2 pagineHealth Teaching Plancary248975% (20)
- Team Rounds With One-Minute Care PlanDocumento4 pagineTeam Rounds With One-Minute Care Planapi-367705934100% (2)
- Id Brief For Interactive Elearning #1Documento5 pagineId Brief For Interactive Elearning #1api-339005618Nessuna valutazione finora
- Invitation, R&RDocumento7 pagineInvitation, R&RAli Murad MirjatNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 Quantitative ResearchDocumento69 pagineGroup 1 Quantitative ResearchJohn Billy EscardaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthropology Blue BookDocumento127 pagineAnthropology Blue BookValentina Rivas GodoyNessuna valutazione finora
- PSY 101L - Summer - 2021Documento5 paginePSY 101L - Summer - 2021teyllerNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management & Six SigmaDocumento10 pagineTotal Quality Management & Six SigmaJohn SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- The Ngee Ann Kongsi Gold Medal: Annex 2: Profiles of Top Award RecipientsDocumento10 pagineThe Ngee Ann Kongsi Gold Medal: Annex 2: Profiles of Top Award RecipientsweiweiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Micah White's ResumeDocumento2 pagineMicah White's ResumemicahjwhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- College ProposalDocumento165 pagineCollege ProposalAvipsa Acharya0% (1)
- Indiana Secondary Transition Resource CenterDocumento1 paginaIndiana Secondary Transition Resource CenterIndiana Family to FamilyNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Questions and AnswersDocumento45 pagineInterview Questions and AnswersVignesh GoldNessuna valutazione finora
- Social & Cre STD 6 Corona Series ExamDocumento7 pagineSocial & Cre STD 6 Corona Series Examfrank kipkoechNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Indian EducationDocumento10 pagineHistory of Indian EducationSayali HaladeNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Sequence Teacher As Planner Assessor and ReporterDocumento2 pagineLearning Sequence Teacher As Planner Assessor and Reporterapi-297768775Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pop Culture ModuleDocumento108 paginePop Culture ModuleJas Paras100% (1)
- BCA - 4 Sem - Ranklist - May - June 2011Documento30 pagineBCA - 4 Sem - Ranklist - May - June 2011Pulkit GosainNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Information Technology ProjectDocumento38 pagineIntroduction To The Information Technology ProjectRajee ThangenthiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Aromatherapy HandbookDocumento62 pagineAromatherapy HandbookEsther Davids96% (24)
- Ed 124 Unit 2 Part 3Documento8 pagineEd 124 Unit 2 Part 3Elsa Jane VillacortaNessuna valutazione finora
- Suhaila Ob 3Documento2 pagineSuhaila Ob 3api-356351085Nessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Development Non TeachingDocumento1 paginaProfessional Development Non TeachingRoylan RosalNessuna valutazione finora
- B2 CB Audioscript For MELDocumento23 pagineB2 CB Audioscript For MELpnnlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Program JenDocumento1 paginaClassroom Program JenjenilynNessuna valutazione finora
- Sankalp SPL Practice Test Result For Batch Sankalp820lotheld On 07 June 2019 PDFDocumento7 pagineSankalp SPL Practice Test Result For Batch Sankalp820lotheld On 07 June 2019 PDFLakshay GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 EDUC8 MODULE 1 IntroductionDocumento14 pagine2022 EDUC8 MODULE 1 IntroductionAmelia Bragais RemallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter of Approval To Conduct ResearchDocumento3 pagineLetter of Approval To Conduct ResearchANGEL ALMOGUERRANessuna valutazione finora
- Navodaya Vidyalaya SamitiDocumento3 pagineNavodaya Vidyalaya SamitihareshtankNessuna valutazione finora
- Kea NB191 2019 07 19 10 58 15Documento4 pagineKea NB191 2019 07 19 10 58 15Rakesh S DNessuna valutazione finora
- A.J. Ayer - The Concept of A Person 1963Documento288 pagineA.J. Ayer - The Concept of A Person 1963JYDeGroot100% (4)
- DLLDocumento3 pagineDLLMarvin ClutarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of ChangeDocumento6 pagineTheories of ChangeADB Knowledge SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora