Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Assigned Experiment Report (2015-ME-76)
Caricato da
muhammad aliDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Assigned Experiment Report (2015-ME-76)
Caricato da
muhammad aliCopyright:
Formati disponibili
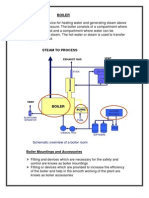
BOILER: Types, Function, Design Parameters & Applications
Definition:
A necessary component (closed vessel) of thermal power plant which is used to;
“Heat water or any liquid, generate steam or vapor, superheat the steam or any combination
of the aforementioned processes, under pressure for external use, by supplying energy either
from the combustion of fuel, from electricity or by nuclear energy”.
Fig 1: Sectioned view of Boiler with various components
Types:
There are various types of boiler based upon the axis of shell, fuel used, pressure etc.
1. Position of water and hot gases
Fire Tube
Water Tube
2. Pressure generated by Boiler
High pressure boiler
Low pressure boiler
3. Orientation of Boiler
Horizontal axis boiler
Vertical axis boiler
4. Position of Boiler
Externally fired boiler
Internally fired boiler
5. Fuel used
Solid fuel fired boiler
Liquid fuel fired boiler
Gaseous fuel fired boiler
Function:
As there are many types of boiler so we’ll explain only most widely used boiler’s function
here and that is the water tube boiler.
Fig 2: Water Tube Boiler along with various parts
Water tube boiler is that kind of boiler in which water flows inside the pipes while steam
surrounds these pipes and flows inside the shell. It has been developed owing to higher
steam generation rate, greater steam pressures and superheated steam. They can quickly
respond to variations in load requirements.
There are two main drums in this boiler. One is
called the ‘upper’ drum which is connected to
the feed water inlet, down-comer and riser
tubes for the flow of colder water and steam
generated respectively. Other is the ‘lower’
drum which accompanies the relatively hot
water due to which natural convection of water
takes place (colder water has higher density
than hot water and steam) as water is being
heated in the riser tube by the direct flow of hot
gases. Steam finally gathers above the surface
of colder water and leaves the upper drum via
steam outlet attached to this drum.
Fig 3: Simplified view of WTB
Components of Boiler:
1. Boiler Feed Water System
Water which is being converted to steam is ‘Feed water’ while the system that regulates it is
called ‘Feed water system’.
Feed water system has two types:
Open feed System
Closed feed system
There are two main sources of feed water:
Condensed steam returned from the processes
Raw water arranged from outside the boiler’s plant processes (Makeup Water)
2. Boiler Steam System
The peculiar system that controls the boiler’s processes is boiler steam system. They perform
the function of collecting and controlling all the generated steam during the process. They
send this generated steam to the point of use via pipes. Pressure gauges and valves among
other things are used to control and regulate the steam pressure throughout the process.
3. Boilers Fuel System
Boiler requires fuel to generate steam and fuel system comprises all the parts required to
generate the steam and what type of components are required, it depends upon the type of
fuel used.
ASME Design Rules for WTB:
ASME design rules for WTB are represented as PWT rules which are applied specifically to
design following parts of water tube boilers.
Tubes and Pipes:
Tubes of Economizer, Boiler generator and super-
heater must be in conformance with the specifications
mentioned in the PG requirements of which a little
portion is shown below.
Similarly, there are some rules for seamless steel pipes
and about the thickness of the tube in which a fusible
plug is to be installed.
Fig 4: Some specifications for
designing tubes & pipes
Tube wall thickness:
The minimum tube wall thickness made up of carbon or alloy steel working under maximum
allowable pressure shall be determined according to the following rules.
Fig 5: Some specifications for tube wall thickness
Tube connections:
Tubes, pipes and nipples can be attached to the shells, heads and headings by:
1-Expanding & Flaring
Fig 6: Tube connections by expanding & Flaring
2-Expanding & Beading
Fig 7: Tube connections by expanding & Beading
3-Expanded, flared, seal welded, and re-expanded after welding
Fig 8: Tube connections by expanded, flared, seal
welded, and re-expanded after welding
4- Expanded, seal welded, and re-expanded after welding or seal welded and expanded
after welding
Fig 9: Tube connections by expanded, seal welded,
and re-expanded after welding or seal welded and
expanded after welding
Similarly, there are other rules for stay bolting box-type headers, staying segment of heads,
firing doors and access and firing doors. But owing to the brevity of report, only some of the
rules for designing water tube boiler have been discussed. All these rules are followed by all
the manufacturers worldwide to ensure the safety and performance of boilers. Here rules for
only water tube boiler have been presented but each type of boiler has its own rules as
developed by ASME.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1.1 Background of The Project 1.2 Problem Statement 1.3 Objectives of The Project 1.4 Project ScopeDocumento21 pagine1.1 Background of The Project 1.2 Problem Statement 1.3 Objectives of The Project 1.4 Project ScopeAbdi samad MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal LabDocumento38 pagineThermal LabKRRISH MAHESHWARINessuna valutazione finora
- Boilers PrintDocumento66 pagineBoilers PrintsuswagatNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Mountings and Accessories PDFDocumento4 pagineBoiler Mountings and Accessories PDFShankar JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Boe Notes by RameshDocumento22 pagineBoe Notes by RameshVelpuri RameshBabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Water and Fire Tube BoilersDocumento13 pagineStudy of Water and Fire Tube BoilersPriyanshu NandanNessuna valutazione finora
- BoilerDocumento7 pagineBoilerKunal SupekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Manual Applied Thermodynamics (ME-210)Documento35 pagineLaboratory Manual Applied Thermodynamics (ME-210)sachinmagrawal2484Nessuna valutazione finora
- Boiller Types Sabic PDFDocumento40 pagineBoiller Types Sabic PDFMuhammad Hamza NaveedNessuna valutazione finora
- BoilerDocumento17 pagineBoilerVictoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout FinalDocumento254 pagineHandout FinalMalik ForbesNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 1-Steam Generating Unit and Its AuxiliariesDocumento23 pagineMODULE 1-Steam Generating Unit and Its Auxiliarieskoko blueNessuna valutazione finora
- 12-Design Fundamentals of BoilerDocumento12 pagine12-Design Fundamentals of BoilerVishalVaishNessuna valutazione finora
- COE Phase 2 Partial Requirement: Operation and Maintenance of BoilersDocumento11 pagineCOE Phase 2 Partial Requirement: Operation and Maintenance of BoilersMico CampoNessuna valutazione finora
- CH-14 Design Fundamentals of BoilerDocumento15 pagineCH-14 Design Fundamentals of BoilerRavi ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- ATD LabDocumento32 pagineATD Labneeraj sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketel Uap (Boiler)Documento38 pagineKetel Uap (Boiler)ua3172923Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Lecture 4 Steam Generator and ConditionarDocumento19 pagine3 Lecture 4 Steam Generator and ConditionarHasib RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Wiki MenuDocumento9 pagineWiki MenuThokozaniMpofuNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Water Tube BoilerDocumento12 pagineFire Water Tube BoilerFatma HelalNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Construction Part-1Documento130 pagineBoiler Construction Part-1tareas1978100% (2)
- Unit 5 Steam GeneratorsDocumento75 pagineUnit 5 Steam GeneratorsNishad BhavsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerDocumento22 pagineBoiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerZeshan AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenance and Operation of BoilersDocumento40 pagineMaintenance and Operation of BoilersMico CampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation and Process: Starting A BoilerDocumento3 pagineOperation and Process: Starting A BoilerJoanna MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 Steam GenerationDocumento30 pagineUnit 3 Steam GenerationkhalimnNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 2: Page 1 of 7Documento7 pagineExperiment No. 2: Page 1 of 7Kunal SupekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand Out-Boiler CompleteDocumento40 pagineHand Out-Boiler Completemuhammad umarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Study of A Steam Generating UnitDocumento13 paginePhysical Study of A Steam Generating Unitashier dave calulot80% (5)
- Lancashire BoilerDocumento6 pagineLancashire BoilerNikhilesh BhargavaNessuna valutazione finora
- In Simple A Boiler May Be Defined As A Closed Vessel in Which Steam Is Produced From Water by Combustion of FuelDocumento9 pagineIn Simple A Boiler May Be Defined As A Closed Vessel in Which Steam Is Produced From Water by Combustion of FuelJomari Tobes SatorreNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Three: Steam Generators 3.1 DefinitionDocumento43 pagineChapter Three: Steam Generators 3.1 DefinitionHeber Farid Fabrica Quispe100% (1)
- Chapter Two Steam Power PlantDocumento42 pagineChapter Two Steam Power PlantPercy Aduviri FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual 2022Documento42 pagineLab Manual 2022Hardik PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fossil Fuel Steam GeneratorDocumento33 pagineFossil Fuel Steam Generatorchaiya sonwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Babcock and Wilcox BoilerDocumento6 pagineBabcock and Wilcox BoilerGautam GunjanNessuna valutazione finora
- BoilerDocumento14 pagineBoileravv456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2 Steam BoilersDocumento131 pagineUnit-2 Steam Boilersvaidehi6326Nessuna valutazione finora
- Boilers Mountings 1Documento3 pagineBoilers Mountings 1Jacob ChezzNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Lecture - Boiler Parts & Accessories, and Heat Loss Reduction in BoilerDocumento35 pagine2nd Lecture - Boiler Parts & Accessories, and Heat Loss Reduction in BoilerHaseeb RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Boiler Instrument and Control: 1. Horizontal, Vertical or InclinedDocumento20 pagineSteam Boiler Instrument and Control: 1. Horizontal, Vertical or InclinedmorolosusNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Types and ClassificationsDocumento26 pagineBoiler Types and ClassificationshardikNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics Engine TwoDocumento34 pagineThermodynamics Engine TwoUsamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diploma 4 THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL (Copy)Documento19 pagineDiploma 4 THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL (Copy)AjitKumarPandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler and Boiler PerformanceDocumento64 pagineBoiler and Boiler PerformanceDipti PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam & Power Generation Lab (ME-218-F)Documento27 pagineSteam & Power Generation Lab (ME-218-F)Abdalla ElemamNessuna valutazione finora
- A Preface On The BoilersDocumento46 pagineA Preface On The Boilerslaloo01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 1Documento16 pagineAssignment No 1AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewDa EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewNessuna valutazione finora
- The Weir Direct-Acting Feed Pump - Working InstructionsDa EverandThe Weir Direct-Acting Feed Pump - Working InstructionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersDa EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNessuna valutazione finora
- Heating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsDa EverandHeating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Geothermal Energy: Sustainable Heating and Cooling Using the GroundDa EverandGeothermal Energy: Sustainable Heating and Cooling Using the GroundNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingDa EverandEngineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesDa EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Locomotive Construction and MaintenanceDa EverandSteam Locomotive Construction and MaintenanceNessuna valutazione finora
- Pakistan Affairs 2016Documento15 paginePakistan Affairs 2016Syeda Fariya Nisar AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental GovernanceDocumento1 paginaEnvironmental Governancemuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Information TechnologyDocumento2 pagineInformation Technologymuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental ScienceDocumento1 paginaEnvironmental Sciencemuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Interdisciplinary Nature of Environmental ScienceDocumento1 paginaInterdisciplinary Nature of Environmental Sciencemuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Cho9781139626859 026Documento24 pagineCho9781139626859 026muhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- FPSC Fee Challan Css 2019Documento1 paginaFPSC Fee Challan Css 2019Muhammad AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Assessment and ManagementDocumento3 pagineEnvironmental Assessment and Managementmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of Wind TurbinesDocumento9 pagineAn Overview of Wind Turbinesmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector DiagramsDocumento7 pagineVector Diagramsmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- All Data LinksDocumento1 paginaAll Data Linksmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- QuotesDocumento1 paginaQuotesmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- PicturesDocumento1 paginaPicturesmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- IR TemplateDocumento2 pagineIR Templatemuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Which System Suits Pakistan The BestDocumento3 pagineWhich System Suits Pakistan The Bestmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- The Naion-State SystemDocumento1 paginaThe Naion-State Systemmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Black Holes GoDocumento1 paginaBlack Holes Gomuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Data VAWTsDocumento13 pagineTechnical Data VAWTsmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- FypDocumento11 pagineFypmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- KashmirUpdateReport 8july2019Documento43 pagineKashmirUpdateReport 8july2019muhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Pak Affairs - How To PrepareDocumento2 paginePak Affairs - How To Preparemuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Maths-2017 UpdatedDocumento2 pagineApplied Maths-2017 UpdatedMuhammad Ishtiaq100% (1)
- Applied Maths-2017 UpdatedDocumento2 pagineApplied Maths-2017 UpdatedMuhammad Ishtiaq100% (1)
- DAWN Editorials March 2017Documento1 paginaDAWN Editorials March 2017Cʜocoɭʌtƴ ƁoƴNessuna valutazione finora
- HistoryDocumento1 paginaHistorymuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Morris JGHdefDocumento7 pagineMorris JGHdefmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- PerseveranceDocumento1 paginaPerseverancemuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Cutting Fluids On The Life of Cutting ToolDocumento3 pagineEffect of Cutting Fluids On The Life of Cutting Toolmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- White StarDocumento1 paginaWhite Starmuhammad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Hear and SpellDocumento3 pagineHear and Spellcarlo lastimosaNessuna valutazione finora
- T8 B20 NEADS Trip 2 of 3 FDR - Transcript - NEADS Rome NY - DRM 2 - Dat 2 - PG 1-83 - Color-CodedDocumento83 pagineT8 B20 NEADS Trip 2 of 3 FDR - Transcript - NEADS Rome NY - DRM 2 - Dat 2 - PG 1-83 - Color-Coded9/11 Document ArchiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Pmwasabi EB3Documento4 paginePmwasabi EB3AlleleBiotechNessuna valutazione finora
- Ruling The CountrysideDocumento9 pagineRuling The Countrysiderajesh duaNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of IndexDocumento4 pagineTypes of IndexKantha EnduriNessuna valutazione finora
- Ats1811 MLDocumento16 pagineAts1811 MLWathNessuna valutazione finora
- IBEC BPL System ArchitectureDocumento2 pagineIBEC BPL System ArchitectureAleksandar ConevNessuna valutazione finora
- Encryption LessonDocumento2 pagineEncryption LessonKelly LougheedNessuna valutazione finora
- BS en Iso 11114-4-2005 (2007)Documento30 pagineBS en Iso 11114-4-2005 (2007)DanielVegaNeira100% (1)
- Beer Distribution Game - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento3 pagineBeer Distribution Game - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSana BhittaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Thousands of Relocation Jobs Await You Anytime, Anywhere!: About UsDocumento3 pagineThousands of Relocation Jobs Await You Anytime, Anywhere!: About UsWeackson Guerrier100% (1)
- 213-Article Text-620-1-10-20201118Documento6 pagine213-Article Text-620-1-10-20201118Arlin FebriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm D7830 - D7830M-2013 - 8750Documento3 pagineAstm D7830 - D7830M-2013 - 8750Wael SeoulNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Post Bail For Your Temporary Liberty?Documento5 pagineHow To Post Bail For Your Temporary Liberty?Ruel Benjamin Bernaldez100% (1)
- Micro Link Information Technology Business College: Department of Software EngineeringDocumento34 pagineMicro Link Information Technology Business College: Department of Software Engineeringbeki4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Algebra Functions and Authentic Applications 5th Edition Jay Lehmann Solutions ManualDocumento31 pagineIntermediate Algebra Functions and Authentic Applications 5th Edition Jay Lehmann Solutions Manualchiliasmevenhandtzjz8j100% (32)
- GM1. Intro To FunctionsDocumento5 pagineGM1. Intro To FunctionsGabriel Benedict DacanayNessuna valutazione finora
- Why CPVC Pipes FailDocumento12 pagineWhy CPVC Pipes FailNikita Kadam100% (1)
- QuaverEd Lesson Plan 6-7Documento10 pagineQuaverEd Lesson Plan 6-7zgyleopardNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Calculation Sheet: Project No: Date: Sheet No.:1 1 Computed By: SubjectDocumento1 paginaDesign Calculation Sheet: Project No: Date: Sheet No.:1 1 Computed By: SubjectAbdelfatah NewishyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch10ex10-3 Cost AccountingDocumento2 pagineCh10ex10-3 Cost AccountingRichKingNessuna valutazione finora
- Product DetailsDocumento215 pagineProduct DetailsEric MagnayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Submission Form Register - STR (20210929)Documento1 paginaMaterial Submission Form Register - STR (20210929)HoWang LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tia-Eia-Is 801-1 - 2001Documento148 pagineTia-Eia-Is 801-1 - 2001John UrdanetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maneesh Misra CV - 1Documento3 pagineManeesh Misra CV - 1Rohit KarhadeNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP QBDocumento8 pagineDSP QBNithya VijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Psar Techspec Autologicsoftwaretechspecfor Psarvehicles en PF v2.0Documento183 paginePsar Techspec Autologicsoftwaretechspecfor Psarvehicles en PF v2.0PhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Relative Clauses (Who, Which, That) For B LevelDocumento16 pagineRelative Clauses (Who, Which, That) For B LevelOğuzhan KarabayNessuna valutazione finora
- Color Management Handbook Vol2Documento28 pagineColor Management Handbook Vol2ianjpr100% (2)