Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Isca CHP 8 Summary
Caricato da
Sai KrishnaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Isca CHP 8 Summary
Caricato da
Sai KrishnaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PREPARED AND COMPILED BY ASHIK BABU
CHAPTER 8: EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
GRID COMPUTING CLOUD VS GRID CLOUD VS GRID
>It is a network of computing or processor machines managed with a kind of software such
as middleware, in order to access and use the resources remotely. Similarities Differences Basis On-Premise Private cloud Outsourced Private Cloud
>It is a cost effective solution 1) Both grid & cloud 1) Grid computing is not
>Enables heterogeneous resources of computers to work cooperatively and collaboratively computing are scalable economically suited for Location Usually store in same Located off site and when there is a
to solve a scientific problem. storing small objects geographical location of change of location the data is
>Grid computing requires the use of software that can divide and carve out pieces of a Load balancing of such as 1 byte to whereas users, else accessed through transmitted through long distances.
program as one large system image to several thousand computers. applications running Cloud computing can internet
separately on variety of store from 1byte to Management Managed by Org. itself Managed by 3rd party & cloud itself
OS & connected through several terabytes
CLOUD COMPUTING
1) It is the use of computing resources as a service web service. 2) Grid computing Network Network management and The cloud is fully deployed at 3rd
2) The internet is visualized as cloud, hence it is called computation done through internet 2) Both computing focuses on network issue resolving are party site & organizations connect
3) Users can access database resources from anywhere anytime involves multi-tenancy & computationally easier and networks have high either through dedicated connection
4) It is a combination of hardware & software muti-tasking intensive operations bandwidth and low latency. or Internet.
5) Location of physical resources & device access are not known to end user 3) Both provide service whereas
6) Companies can scale up to massive capacities without having to invest in new level agreements Cloud computing focuses Performance Depends on the network & Depends on the 3rd party
infrastructure or license new software & pay only for what they on standard & high CPU resources
7) Customers use what they need on internet & pay only for what they use use SLA Defined b/w org & its users Strictly as per 3rd part organization
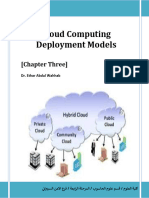
CLOUD COMPUTING ENVIRONMENT
COMMUNITY CLOUD
PUBLIC CLOUD PRIVATE CLOUD HYBRID CLOUD
A Private cloud shared b/w several organizations
It is used by general public. This includes individuals, corporations & It resides within the boundaries of an organization - It is a combination of at least one private & one public cloud
other types of organizations. Public clouds are administered by 3rd & is used exclusively for the organizations - It has private initially & for additional resources public
CHARACTERISTICS
parties or vendors over the internet & the services are offered on pay benefits. cloud is used
1. Collaborative and Distributive Maintenance: Being
per use basis. - It is a private cloud extended to the public cloud and aims
distributive, better cooperation provides better
CHARACTERISTICS at utilizing the power of the public cloud by retaining the
results.
CHARACTERISTICS 1. Secure: Since managed by origination, least properties of the private cloud.
2. Cost effective: The cloud is being shared, so it’s
1. Highly scalable: The resources being large service providers make chance of data being leaked out
cost effective too.
sure that all request are granted 2. Central Control: No need for organization to rely CHARACTERISTICS
3. Partially secure: Since cloud is shared by
2. Highly available: Anybody from anywhere can access on anybody & is controlled by organization itself 1. Scalable: The hybrid cloud with the help of its public
organization, there is possibility of leakage of data
3. Affordable: User has to pay only for what they are using 3. Affordable: User has to pay only for what they counterpart is also scalable.
from one organization to another, though safe
4. Less Secure: since offered & controlled by 3rd party, it is less secure are using 2. Stringent SLAs: Overall the SLAs are more stringent
from external world.
5. Stringent SLA’s: SLA’s are strict & violation are avoided 4. Weak SLA: SLA are agreement b/w user & 3. Partially Secure: Private cloud is secured but public cloud
service provider. Formal SLA’s do not exist/ are has high risk of security breach, so partially secure.
ADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES weak in private cloud 4. Complex Cloud Management: Because it involves more
1. Low cost private cloud
1. No limit on no of users than one type of deployment models & high users
2. Allows collaborative work on the cloud.
2. Strict SLA’s are followed ADVANTAGES
3. Allows sharing of responsibilities among the
3. No infrastructure required for maintaining the cloud 1. High level of security & privacy ADVANTAGES
organizations.
4. Widely used in development, deployment & management of 2. Small in size, controlled & maintained by 1. Highly scalable
4. Better security than the public cloud.
enterprise applications at affordable costs organization 2. Better security than public cloud
3. Improves average server utilization
LIMITATIONS
LIMITATIONS LIMITATIONS
1. Autonomy of the organization is lost and security
1. Security assistance is low LIMITATIONS 1. Security features are not as good as public cloud
features are not as good as the private cloud.
2. Privacy & organizational autonomy are not possible Budget is constraint & they also have loose SLA’s 2. It is complex to manage
2. Not suitable where there is no collaboration.
CLOUD COMPUTING SERVICE MODELS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Different instances of IaaS Platform as a Service (PaaS) Software as a Service (SaaS)
It is a hardware-level service, provides computing resources PaaS provides the users the ability to develop and deploy an It provides ability to the end users to access an application
such as processing power, memory, storage, and networks for Database as a Service (DBaaS): application on the development platform over the Internet that is hosted and managed by the
cloud users to run their application on-demand. This allows - Provides seamless mechanisms to create, store, and access Examples: service provider.
users to maximize the utilization of computing capacities. databases at a host site on demand Google AppEngine, Windows Azure Compute Examples:
Examples: - It can be accessed through any Application Programming Own word document in google doc, edit photo online in
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Compute Engine, Interfaces (APIs) or Web User Interfaces Characteristics of IaaS pixlr
OpenStack and Eucalyptus. 1. All in One: Develop, test, deploy, host and maintain
applications in the same Integrated Development Characteristics of IaaS
Desktop as a Service (DTaaS):
Characteristics of IaaS Environment. 1. One to Many: a single instance of the application can
It is a pay per use cloud service delivery model that enables
1. Web access to the resources: No physical access to server & 2. Built-in Scalability: Capable of handling varying loads be shared by multiple customers.
users to use desktop virtualization without buying or
access made over internet efficiently. 2. Web Access: Allows to access the from any location
managing their own infrastructure.
2. Centralized management: Ensures effective resource 3. Collaborative Platform: Enables collaboration among when device is connected to the Internet.
management & utilization developers, most for project planning and communication 3. Centralized Management: Since hosted and managed
Backend as a Service (BaaS):
3. Shared infrastructure: one-to-many delivery model and Provides developers to connect their application to back end 4. Diverse Client Tools: Offers a wide variety of client tools from the central location, it provides automatic
allows multiple IT users to share cloud storage with new added services. like Web User Interface (UI), Application Programming updates to ensure that each customer is accessing the
4. Elasticity and Dynamic Scaling: provide the resources & Interface (API) etc. & allow developers to choose the tool most recent version
elastic services where the usage of resources can be Network as a Service (NaaS): of their choice. 4. Multi-device Support: Can be accessed from any end
increased or decreased as per requirements. - Provides needed data communication capacity to 5. Offline Access: Sync data with local IDE & develop locally user devices such as desktops, laptops, tablets,
5. Metered Services: Allows IT users to rent the computing accommodate bursts in data traffic during data-intensive the app & deploy it online when connected to internet smartphones etc.
resources instead of buying it & charges is based on amount activities 5. Better Scalability: It ensures better scalability than
of usage - Operate using three common service models: Virtual Services offered by IaaS traditional software by deployment of PaaS & IaaS
Private Network (VPN), Bandwidth on Demand (BoD) and 1. Programming Languages: wide variety of programming 6. API Integration: Capable of integrating with other
Services offered by IaaS Mobile Virtual Network (MVN). languages like Java, PHP, Python, Ruby etc. for the software/services through standard API
1. Compute: Virtual CPU & virtual memory for the virtual developers to develop applications. 7. High availability:
machines Storage as a Service (STaaS): 2. Application Frameworks: Joomla, WordPress, Sinatra etc.
2. Storage: Provides: Backend storage for virtual machine Provides storage infrastructure on a subscription basis at for application development. Different instances of SaaS
images & storing files low-cost and convenient way to store data, synchronize data, 3. Database: Provide databases like ClearDB, Cloudant,
3. Network: Provides virtual networking such as virtual manage off-site backups, mitigate risks, and preserve Redis etc. to communicate with database. 1. Testing as a Service (TaaS.
router, switch, and bridge records 4. Other Tools: Provides all tools that are required to 2. API as a Service (APIaaS)
4. Load Balancers: Provide load balancing capability at develop, test, and deploy an application. 3. Email as a Service (EaaS)
infrastructure layer
GOALS OF CLOUD ADVANTAGES OF CLOUD COMPUTING SECURITY ISSUES/CHALLENGES TO CLOUD COMPUTING
OTHER CLOUD SERVICE MODELS COMPUTING 1. Almost Unlimited Storage: Gives almost unlimited storage 1. Confidentiality: Prevention of the unauthorized disclosure of the data
1) To create a highly efficient IT capacity. So no need to worry about running out of storage & it can be attained by use of TC3 (Total Claim Capture & Control)
Communication as a Service (CaaS): ecosystem space or increasing the current capacity. 2. Integrity: Prevention of unauthorized modification of data and it
It is an outsourced enterprise communication solution that can 2) To scale the IT ecosystem 2. Automatic Software Integration: Software integration occurs ensures that data is of high quality, correct, consistent and accessible
be leased from a single vender. quickly, easily and cost-effectively automatically & no additional efforts to customize and 3. Availability: Prevention of unauthorized withholding of data and it
Examples are: Voice over IP (VolP), Instant Messaging (IM), based on the evolving business integrate the applications. ensures the data backup through BCP & DRP.
Collaboration and Videoconferencing needs 3. Backup and Recovery: Since all the data is stored in the 4. Architecture: Its reliable and scalable infrastructure is dependent on
3) To reduce costs related to IT cloud, backing it up and restoring the same is relatively much the design and implementation to support the overall framework. It can
Data as a Service (DaaS): energy/power consumption easier. significantly lower the company’s IT expenses
It provides data on demand to a diverse set of users, systems or 4) To enable or improve 4. Cost Efficiency: It is the most cost efficient method to use, 5. Audit: Auditing is type of checking that ‘what is happening in the
application. The data may include text, images, sounds, and "Anywhere Access “for ever maintain and upgrade. It can significantly lower the Cloud environment.
videos. Data encryption and operating system authentication are increasing users company’s IT expenses 6. Data Stealing: Some Cloud providers do not use their own server,
commonly provided for security.It is highly used in geography 5) To enable rapidly provision 5. Easy Access to Information: One can access the information instead use from other service providers & risk of data stealing occurs.
data services and financial data services. resources as needed from anywhere, where there is an Internet connection. 7. Privacy: Most important issue & is embedded in each phase & risk of
6) To access services and data from 6. Quick Deployment: The entire system can be fully privacy must be decreased
Security as a Service (SECaaS): anywhere at any time functional in a matter of few minutes in case of quick 8. Software Isolation: To understand virtualization and other logical
It is a new approach to security in which cloud security is moved 7) To consolidate IT infrastructure deployment isolation techniques
into the cloud itself whereby cloud service users will be
protected from within the cloud using a unified approach to
threats. Four mechanisms are Email filtering, Web content CHARACTERISCTICS OF CLOUD COMPUTING IMPLEMENTATION / ADAPTATION ISSUES OF CLOUD COMPUTING
filtering, Vulnerability management and Identity management. 1. High Scalability: Enable servicing for larger audiences through high scalability. 1. Threshold Policy: In order to test if the program works, develops, or improves and
2. High Availability and Reliability: Availability of servers is supposed to be high and implements; a threshold policy is of immense importance in a pilot study before moving
Identity as a Service (IDaaS): more reliable as the chances of infrastructure failure are minimal the program to the production environment
It enables users to access the authentication infrastructure that is 3. Agility: It works in distributed mode & shares resources among users and tasks, 2. Interoperability: If a company outsources or creates applications with one cloud
built, hosted, managed and provided by the third party service improves efficiency computing vendor, it creates problems of achieving interoperability of applications
provider. It includes directory services, authentication services, 4. Multi-sharing: Multiple user & applications can work more efficiently with cost between two cloud computing vendors
risk and event monitoring, single sign-on services, and identity reductions by sharing common infrastructure 3. Unexpected Behavior: It is important to test the application in the cloud with a pilot
and profile management. 5. Virtualization: Allows server & storage device to increasingly share & utilize study to check for unexpected behavior.
apps by easy migrate 4. Hidden Costs: The service providers do not reveal ‘what hidden costs are’.
6. Performance: Monitored & consistent & loosely coupled architecture are 5. Software Development in Cloud: To develop software using high-end databases, the
constructed using web services most likely choice is to use cloud server pools at the internal data corporate centre and
7. Maintenance: They are easier because they are not to be installed on each user extend resources temporarily for testing purposes.
system & can be accessed from different places 6. Environment Friendly Cloud Computing : Cloud computing is more environment
8. Services in Pay-Per-Use Mode: SLA’s b/w the provider & user must be defined friendly as it reduces the number of hardware components needed to run the application
when complexity of services is offered in pay per use mode
PREPARED AND COMPILED BY ASHIK BABU
CHAPTER 8: EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
MOBILE COMPUTING COMPONENTS OF MOBILE COMPUTING TANGIBLE BENEFITS OF MOBILE LIMITATIONS OF MOBILE COMPUTING
Mobile Communication COMPUTING 1. Insufficient Bandwidth:
It refers to the technology that
Infrastructure put in place to ensure that seamless and Mobile Internet access is generally slower than direct cable connections
allows transmission of data via a
reliable communication goes on. 1. It provides mobile workforce with remote 2. Security Standards
computer without having to be
access to work order details Security is major concern, since one can easily attack the VPN through a huge number of
connected to a fixed physical link.
Mobile Hardware 2. Enables mobile sales personnel to update networks interconnected through the line.
Mobile voice communication is
This includes mobile devices or device components that work order status in real-time 3. Power consumption
widely established throughout the
receive or access the service of mobility. The 3. Facilitates access to corporate services Mobile computer rely on expensive batteries when power outlet / portable generator not available
world and has had a very rapid
characteristics of mobile computing hardware are defined and information 4. Transmission interferences
increase in the number of
by the size and form factor, weight, microprocessor, 4. Provides remote access to the corporate Weather, terrain, and the range from the nearest signal point can all interfere with signal
subscribers to the various cellular
primary storage, secondary storage etc. Knowledgebase reception
networks over the last few years.
5. Enables to improve management 5. Potential health hazards
An extension of this technology is
Mobile Software effectiveness by enhancing information People who use mobile devices while driving are often distracted from driving are thus assumed
the ability to send and receive data
It is the actual programme that runs on the mobile quality, information flow, and ability to be more likely involved in traffic accidents.
across these cellular networks.
hardware and deals with the characteristics and 6. Human interface with device:
requirements of mobile applications Screens and keyboards tend to be small, which may make them hard to use
HOW MOBILE COMPUTING WORKS? GREEN COMPUTING BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE (BYOD)
It is the study and practice of establishing / using computers and IT It refers to business policy that allows employees to use their preferred
1. The user enters or access data using the application on handheld computing device. resources in a more efficient and environmentally friendly and responsible computing devices, like smart phones and laptops for business purposes. It
2. The new data are transmitted from handheld to site’s information system where way. Green computing is the environmentally responsible use of means employees are welcome to use personal devices to connect to the
files are updated and the new data are accessible to others computers & related resources. corporate network to access information and application.
3. Now both systems (handheld and site’s computer) have the same information and
are in sync GREEN COMPUTING / GREEN IT BEST PRACTICES ADVANTAGES OF BYOD
4. The process work the same way starting from the other direction. 1. Happy Employees: Employees love to use their own devices when at work
Develop a sustainable Green Computing plan 2. Lower IT Budgets: There would be financial savings to the organization
ISSUES IN MOBILE COMPUTING 1. Involve stakeholders to include checklists, recycling policies, since employees would be using the devices they already possess
recommendations for purchase & disposal of green computer 3. IT reduces support requirement: IT department does not have to provide
2. Encourage IT community to use best practices. end user support and maintenance for all these devices resulting in cost
SECURITY ISSUES
1. Confidentiality: Preventing unauthorized users from gaining access to critical
3. Ongoing communication & campus recruitment to produce notable savings.
information. results 4. Easy Adoption of new technologies: Employees are generally proactive in
2. Integrity: Prevention of unauthorized modification, destruction, creation of adoption of new technologies that result in enhanced productivity of employees
information. Recycle leading to overall growth of business.
3. Availability: Ensuring authorized users getting the access they require 1. Dispose e-waste per law 5. Increased employee efficiency: The efficiency of employees is more when
4. Legitimate: Ensuring that only authorized users have access to services. 2. Dispose in an environmental friendly manner the employee works on his/her own device
5. Accountability: Ensuring that the users are held responsible for their security 3. Recycle computers through manufacturers recycling services
related activities EMERGING BYOD THREATS
Make environmentally sound purchase decisions Network Risks
LOCATION INTELLIGENCE 1. Purchase of desktop computers, notebooks and monitors based on In case of company owned device, it has complete visibility of devices
As the mobile computers move, they encounter networks with different features. It environmental attributes connected to the network which helps to analyze traffic & data exchanged over
must be able to switch from infrared mode to radio mode & operation to satellite 2. Use server & storage virtualization internet
mode when moving from indoor to outdoor & urban to rural. 3. Eliminate environmental sensitive materials
4. Provide a clear, consistent set of performance criteria for the design of Device Risks
products A lost or stolen device can result in an enormous financial & reputational
REVISING THE TECHNICAL ARCHITECTURE
Mobile users are demanding and are important to the business world. The application embarrassment to an organization as the device may hold sensitive corporate
and data architectures must also be revised to support the demands put upon them by Reduce Paper Consumption information
the mobile connectivity. 1. Use e-mail and electronic archiving
2. Print both sides of paper Application Risks
3. Use online marketing rather than paper based marketing A majority of employees phones & smart devices that are connected to
POWER CONSUMPTION
Mobile computers rely on battery and battery must be capable of longer operation corporate network aren’t protected by security software & organization not as
times. Power consumption to be minimized to increase battery life. Conserve Energy “who is responsible for device security”
1. Use LCD rather than CRT monitors
BANDWIDTH 2. Use notebooks rather than desktop computers Implementation Risks
Bandwidth utilization can be improved by logging (bulk operations against short 3. Use the power-management features to turn off hard drives and displays It must mandate development of a robust implementation policy, as the absence
requests) and compression of data before transmission. when no activity done of BYOD policy would fail to communicate employee expectations & increase
4. Power-down the CPU and all peripherals during inactivity the chances of device misuse
RELIABILITY, COVERAGE, CAPACITY & COST 5. Employ alternative energy sources
Wireless network is less reliable, have less geographic coverage and reduced 6. Adapt more of web conferencing offers instead of travelling
bandwidth, are slower, and cost more than the wired-line network services
WEB 2.0
The two major contributors of web 2.0 are
- Technological advances by AJAX WEB 3.0 /SEMANTIC WEB
- Other application – RSS, Eclipse - It describes sites wherein the computers will be generated raw data on their own
One of the most significant differences between Web 2.0 and the traditional World without direct user interaction.
Wide is that Web 2.0 facilitates greater collaboration and information sharing among - Web 3.0 is logical step-in evolution of internet & web technologies
Internet users, content providers and enterprises. -It uses “Data web” technology & described as “Machine to User” standard in
Thus migration from the “read-only web” to “read-write web”. internet
APPICATIONS OF WEB 2.0 COMPONENTS OF WEB 3.0
1. Social Media: It is an important application of web 2.0 as it provides a fundamental 1. Semantic Web: provides the web user a common framework that could be used to
shift in the way people communicate and share information. share and reuse the data across various applications, enterprises, and community
2. Marketing: Engages customers in various stages of the product development cycle boundaries.
& allows the marketers to collaborate with consumers on various aspects 2. Web Services: It is a software system that supports computer-to-computer
3. Education: Helps students & faculty with more opportunities to interact & interaction over the Internet.
collaborate with their peers in an educations cenario
COMPONENTS OF WEB 2.0
1. Usage of Ajax and other new technologies:
Ajax is a way of developing web applications that combines XHTML and CSS
standards-based presentation that allows the interaction with the web page and data
interchange with and XSLT
2. Blogging: Blog is a journal, diary, or a personal website that is maintained on the
internet, and it is updated frequently by the user
3. Communities: These are an online space formed by a group of individuals to share
their thoughts, ideas and have a variety of tools to promote Social Networking
4. Wiki: A Wiki is a set of co-related pages on a particular subject and allow users
to share content.
5. Folksonomy: It allows free classification of information available on web using
tagging approach
6. File Sharing/Podcasting: This is the facility, which helps users to send their media
files and related content online for other people of the network to see and contribute
7. Mashups: People on internet can congregate services from multiple vendors to
create a completely new service
8. RSS-generated Syndication: RSS is a format for syndicating web content that
allows feed the freshly published web content to the users through the RSS reader
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingDa EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review On Cloud Computing: SSRN Electronic Journal February 2020Documento6 pagineA Review On Cloud Computing: SSRN Electronic Journal February 2020Maryam AldossaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDDa EverandCloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing: Architecture and Services: Ms. Shubham DadheechDocumento4 pagineCloud Computing: Architecture and Services: Ms. Shubham Dadheechshubham dadheechNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt1:Introduction To Cloud Computing: Types of Cloud Computing: 1-Public Cloud 2-Private Cloud 3-Hybrid CloudDocumento158 pagineChapt1:Introduction To Cloud Computing: Types of Cloud Computing: 1-Public Cloud 2-Private Cloud 3-Hybrid CloudUmair DawreNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Modern Monthly Updates School Newspaper Classroom News A4 Email NewsletterDocumento2 pagineGreen Modern Monthly Updates School Newspaper Classroom News A4 Email NewsletteryuktaNessuna valutazione finora
- Information Security in Cloud Computing: August 2014Documento6 pagineInformation Security in Cloud Computing: August 2014Aseer Istiaq Azad 1813654630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud ComputingDocumento38 pagineCloud ComputingjivasaNessuna valutazione finora
- 225 W0004 PDFDocumento5 pagine225 W0004 PDFAkash MaldiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing Environment Through Encryption Algorithms - A Review PaperDocumento6 pagineCloud Computing Environment Through Encryption Algorithms - A Review Paper9797047233Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing: January 2020Documento89 pagineCloud Computing: January 2020shNessuna valutazione finora
- Usability of Wireless Sensor Network Data in A Cloud EnvironmentDocumento6 pagineUsability of Wireless Sensor Network Data in A Cloud EnvironmenterpublicationNessuna valutazione finora
- Efficient Attribute-Based Encryption Outsourcing S 221130 143512Documento12 pagineEfficient Attribute-Based Encryption Outsourcing S 221130 143512Gattem Raghu RamNessuna valutazione finora
- Topics:: Isca By: Saurabh Vig (Mca) +91-9897095049Documento25 pagineTopics:: Isca By: Saurabh Vig (Mca) +91-9897095049Sunkara Rajesh ChowdaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Cloud Computing EnvironmentDocumento6 pagineReview of Cloud Computing EnvironmentInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Cloud ComputingDocumento26 pagine1.1 Cloud ComputingnareshNessuna valutazione finora
- CS8791 Cloud Two MarksDocumento32 pagineCS8791 Cloud Two MarksMahi MahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Triumph in The sky-WPS OfficeDocumento24 pagineTriumph in The sky-WPS OfficeDharmrajNessuna valutazione finora
- Clearing The Clouds On Cloud Computing S-51490823 PDFDocumento6 pagineClearing The Clouds On Cloud Computing S-51490823 PDFFisehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap3-Modèles de Dep-1617Documento22 pagineChap3-Modèles de Dep-1617MANAÏ BelighNessuna valutazione finora
- Security in IoTDocumento26 pagineSecurity in IoTashuNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject IndexDocumento28 pagineSubject Indexaksahy varmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Cloud Deployment Model and Security Issues of Software As A Service SaaS For Cloud ComputingDocumento4 pagineImportance of Cloud Deployment Model and Security Issues of Software As A Service SaaS For Cloud Computingmohamed faisalNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic PPT On Cloud ComputingDocumento32 pagineBasic PPT On Cloud ComputingSavyasachi Vats54% (13)
- Unit 3 NewDocumento24 pagineUnit 3 Newakramshaik2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Head CloudDocumento2 pagineHead Cloudapi-25997182Nessuna valutazione finora
- FOG COMPUTING AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUD COMPUTING Research Paper - NewDocumento16 pagineFOG COMPUTING AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUD COMPUTING Research Paper - NewMinahil Ahmad100% (1)
- Introduction To CCDocumento27 pagineIntroduction To CCHobikNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Cloud ComputingDocumento24 pagineFundamentals of Cloud ComputingRahul BorateNessuna valutazione finora
- Security Challenges in Cloud ComputingDocumento8 pagineSecurity Challenges in Cloud ComputingAb IrNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Cloud Deployment Model and Security Issues of Software As A Service SaaS For Cloud ComputingDocumento4 pagineImportance of Cloud Deployment Model and Security Issues of Software As A Service SaaS For Cloud ComputingABCNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing (CSE8146) : Prepared byDocumento35 pagineCloud Computing (CSE8146) : Prepared bynitin goswamiNessuna valutazione finora
- SSRN Id3649074Documento3 pagineSSRN Id3649074Riva MakNessuna valutazione finora
- Implication of Virtualization and Cloud Computing in Technical EducationDocumento4 pagineImplication of Virtualization and Cloud Computing in Technical EducationInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNessuna valutazione finora
- QuestionsDocumento9 pagineQuestionsIsrat Jahan Rain BorshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Secure Cloud Computing Using Aes and Rsa Algorithms: K.R.MonishaDocumento6 pagineSecure Cloud Computing Using Aes and Rsa Algorithms: K.R.Monishajayashree dNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijet V4i3p33 PDFDocumento10 pagineIjet V4i3p33 PDFInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Data MangementDocumento4 pagineData Mangementessid sabraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter1 - Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocumento11 pagineChapter1 - Introduction To Cloud Computinghaithamokour11Nessuna valutazione finora
- SITA1503 - Fog and Cloud Computing - Course MaterialDocumento160 pagineSITA1503 - Fog and Cloud Computing - Course MaterialVigneshwar SNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Billing Model: A Review: AbstractDocumento4 pagineCloud Billing Model: A Review: AbstractManzoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Security Ch3Documento13 pagineCloud Security Ch3hmsa7863Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Cloud Computing: Prepared By: Sushil SahDocumento71 pagineIntroduction To Cloud Computing: Prepared By: Sushil Sahsushil@irdNessuna valutazione finora
- Private Vs Public Cloud: August 2013Documento6 paginePrivate Vs Public Cloud: August 2013Abhishek RaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of Computing Mainframe To Cloud A Systematic StudyDocumento6 pagineEvolution of Computing Mainframe To Cloud A Systematic StudyanuragNessuna valutazione finora
- Gacc - Bca507 - Unit 4 NotesDocumento20 pagineGacc - Bca507 - Unit 4 NotesAkashNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Cloud Computing?: Luit Infotech Private LimitedDocumento6 pagineWhat Is Cloud Computing?: Luit Infotech Private LimitedKaleab FekaduNessuna valutazione finora
- Grid Computing: 3 Semester, CSE, NCETDocumento7 pagineGrid Computing: 3 Semester, CSE, NCETVaishnav DesaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud McqsDocumento4 pagineCloud McqseliyazNessuna valutazione finora
- Fog Computing - PresentationDocumento15 pagineFog Computing - PresentationHNessuna valutazione finora
- THummar Sir Research Paper 2021Documento3 pagineTHummar Sir Research Paper 2021zinga007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anish Paper FinalDocumento16 pagineAnish Paper FinalVASANTHI.V Dept Of MCANessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud ComputingDocumento57 pagineCloud ComputingnahrraineNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing - Unit 1Documento61 pagineCloud Computing - Unit 1bpavithra26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Implementation of Virtualization in Cloud ComputingDocumento3 pagineAnalysis and Implementation of Virtualization in Cloud ComputingmahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Facets of Security in The CloudDocumento7 pagineDifferent Facets of Security in The CloudPrerna AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- CC 1Documento31 pagineCC 1Just Another humanNessuna valutazione finora
- AAQUIB, R. CHATURVEDI, A. Cloud Computing - Characteristics and Services A Brief Review PDFDocumento6 pagineAAQUIB, R. CHATURVEDI, A. Cloud Computing - Characteristics and Services A Brief Review PDFGabriel AzevedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nisha Report3.....Documento19 pagineNisha Report3.....abdulqaiyum710636Nessuna valutazione finora
- Az 900Documento95 pagineAz 900Ion ArseneNessuna valutazione finora
- MasterDocumento65 pagineMasterJenniferP.Barroso0% (1)
- Internship PPT On SAP-ABAPDocumento22 pagineInternship PPT On SAP-ABAPAnushka Choudhary0% (1)
- 21 H 2 Z 32 B 4Documento12 pagine21 H 2 Z 32 B 4jaimedejNessuna valutazione finora
- Massive Open On-Line and Formats of MediaDocumento8 pagineMassive Open On-Line and Formats of MediaPatricia CondeNessuna valutazione finora
- GT-POWER Engine Simulation Software: HighlightsDocumento2 pagineGT-POWER Engine Simulation Software: HighlightsIrfan ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Im 966-1Documento15 pagineIm 966-1angelica.alarcon.santosNessuna valutazione finora
- Hum102 Report of ProjectDocumento19 pagineHum102 Report of ProjectSamiullah MalhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro CH 03ADocumento18 pagineIntro CH 03Aapi-3831049100% (7)
- HSM USB Serial Driver Release Notes PDFDocumento32 pagineHSM USB Serial Driver Release Notes PDFVeimar CelisNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Clean ExceptionDocumento4 pagineLast Clean ExceptionHavanna G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 8.1. Conditional AlgorithmsDocumento10 pagineWorksheet 8.1. Conditional AlgorithmsYiineth DaniielaNessuna valutazione finora
- Conclusions and RecommendationsDocumento49 pagineConclusions and RecommendationsGil TeodosipNessuna valutazione finora
- TLE 7 Lesson 1Documento69 pagineTLE 7 Lesson 1Mary Jane Blanco FioNessuna valutazione finora
- CXCI Cordex 2v0 Quick RefDocumento2 pagineCXCI Cordex 2v0 Quick RefGuillermo OvelarNessuna valutazione finora
- ES074Documento158 pagineES074jeddijNessuna valutazione finora
- ADFDocumento54 pagineADFSagar GaikwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Midshire Business Systems - Ricoh MP CW2200SP - A0 Wide Format Colour BrochureDocumento8 pagineMidshire Business Systems - Ricoh MP CW2200SP - A0 Wide Format Colour BrochureadietoppingNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelo Ecm370Documento420 pagineModelo Ecm370RENO100% (2)
- QA QC Digital Radiography PDFDocumento20 pagineQA QC Digital Radiography PDFEsa AldiNessuna valutazione finora
- Arml 2009 2014 PDFDocumento530 pagineArml 2009 2014 PDFjordanrmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Na Dell 24 Monitor P2417H Product Spec Sheet US EnglishDocumento2 pagineNa Dell 24 Monitor P2417H Product Spec Sheet US Englishمحمد كريشةNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 Connectors: 1. Connector DestinationDocumento17 pagineGroup 5 Connectors: 1. Connector DestinationREMZONANessuna valutazione finora
- Applies To:: EBS Data Model Comparison Report Overview (VIDEO) (Doc ID 1290886.1)Documento10 pagineApplies To:: EBS Data Model Comparison Report Overview (VIDEO) (Doc ID 1290886.1)herculean2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- 844E Gigacenter Quick Start Guide: Package ContentsDocumento12 pagine844E Gigacenter Quick Start Guide: Package ContentsNini KitsNessuna valutazione finora
- PLC-Driver (V5) Siemens LOGO! - Ethernet TCP-IP - Programming InterfaceDocumento7 paginePLC-Driver (V5) Siemens LOGO! - Ethernet TCP-IP - Programming InterfaceAdelmoKarigNessuna valutazione finora
- Javascript Multiple Choice Questions and Answers-Sheet 1Documento276 pagineJavascript Multiple Choice Questions and Answers-Sheet 1mamidi sudeepNessuna valutazione finora
- BLDC 2Documento6 pagineBLDC 2Pravat SatpathyNessuna valutazione finora
- GoldLine RTA30Documento4 pagineGoldLine RTA30SantiagoMangudoEscaladaNessuna valutazione finora
- COBIT-2019-Design-Toolkit TKT Eng 1218Documento60 pagineCOBIT-2019-Design-Toolkit TKT Eng 1218Kanza BellaNessuna valutazione finora