Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chemical Bonds and Reactions
Caricato da
Brigitte0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
29 visualizzazioni3 pagineAnatomy and Philosophy
Titolo originale
Anaphy Chapter 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoAnatomy and Philosophy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
29 visualizzazioni3 pagineChemical Bonds and Reactions
Caricato da
BrigitteAnatomy and Philosophy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
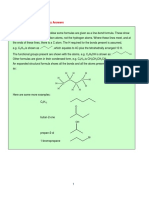
Chemical bonds – occur when outermost
electrons (valence shell electrons) are
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY transferred or shared between atoms.
REVIEWER
(CABUG, RICARDO JR. A. BSMT 133) Three types of chemical bonds:
1. Ionic bond – occurs when electrons are
CHAPTER 2: The Chemical Basis of Life transferred between atoms, creating
2.1 BASIC CHEMISTRY oppositely charge ions. (Example: NaCl)
1. Chemistry – is the scientific discipline - Ion – a charged atom formed because of a
concerned with the atomic composition and donation or gain of an electron(s).
structure of substances and the reactions they Electron shells - is the outside part of
undergo. an atom around the atomic nucleus. It is a group
of atomic orbitals with the same value of the
Matter, Mass, and Weight: principal quantum number n.
1. Matter – is anything that occupies space and Valence shells – it is the outermost shell
has mass. that can hold up to 8 electrons.
2. Mass – is the amount of matter in an object. Octet rule – is a chemical rule of thumb that
3. Weight – is the gravitational force acting on an reflects observation that atoms of main-group
object of a given mass. elements tend to combine in such a way that
4. Kilogram (kg) – the international unit for each atom has eight electrons in its valence
mass. shell, giving it the same electron configuration
as a noble gas.
Elements and Atoms: Electronegativity – is the ability of the atoms
1. Element – is the simplest type of matter nucleus to pull electrons towards it.
having unique chemical properties. It also
composed of atoms of only one kind. Covalent Bonding:
Example: Carbon – Carbon atoms 2. Covalent bond – forms when atoms share one
Oxygen – oxygen atoms or more pairs of electrons. (Example:
Hydrogen molecule)
(Note: About 96% of the body’s weight results Molecule – 2 or more atoms chemically combine
from the elements oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, or the resulting combination of atoms.
and nitrogen.)
Single covalent bond – is when only one pair of
electrons is shared between atoms.
2. Atom – is the smallest particle of an element
Double covalent bond – is where two pairs of
that has the chemical characteristics of that
electrons are shared between the atoms rather
element. It also contains protons, electrons,
than just one pair. Some simple molecules
and neutrons.
containing double bonds.
(The nucleus accounts for 99.97% of an atom’s
Polar covalent bond – form when there is an
mass, but only 1-tentrillionth of its volume.)
unequal sharing of electrons. (Example: Water
3. Proton – positively charged particle located
H2O)
inside the nucleus.
Polar molecules – have an asymmetrical
4. Neutron - neutral charged particle located in
electrical charge.
the nucleus.
Has a positive “end” and a negative “end.”
5. Electron – negative charged particle located
Nonpolar covalent bond - are a type of
outside the nucleus.
chemical bond where two atoms share a pair of
6. Electron cloud – is an informal term in
electrons with each other.
physics. It is used to describe where electrons
Nonpolar molecules – have a symmetrical
are when they go around the nucleus of an
electrical charge.
atom.
3. Hydrogen bond - is a partially electrostatic
7. Atomic number – is the unique number of
attraction between a hydrogen which is
protons in each atom of an element.
bound to a more electronegative atom such
8. Mass number – is the number of protons and
as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine, and another
neutrons.
adjacent atom bearing a lone pair of
electrons.
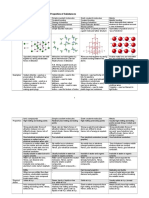
Electrons and Chemical Bonding:
Molecules and Compounds: elements or new compounds. (Represented
1. Molecule – is formed when two or more symbolically as: AB A+B.)
atoms chemically combined to form a Catabolism - is the set of metabolic pathways
structure that behaves as an independent that breaks down molecules into smaller units
unit. that are either oxidized to release energy or
2. Compound – is a substance resulting from used in other anabolic reactions. Catabolism
the chemical combination of two or more breaks down large molecules into smaller
different types of atoms. units.
Hydrolysis - is a chemical process in which a
Dissociation: molecule of water is added to a substance.
1. Dissociate – Sometimes this addition causes both
(with reference to a molecule) to split into substance and water molecule to split into two
separate smaller atoms, ions, or molecules, parts.
especially reversibly. Metabolism – the chemical processes that
2. Electrolytes – is a substance that produces occur within a living organism in order to
an electrically conducting solution when maintain life. all of the anabolic and catabolic
dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. reactions in the body.
The dissolved electrolyte separates into
cations and anions, which disperse 3. Exchange reaction – is a combination of a
uniformly through the solvent. decomposition reaction and a synthesis
reaction. It occurs between compounds that,
2.2 CHEMICAL REACTIONS when written as a molecular equation, appear
1. Chemical reaction – is the formation or to involve the exchange of parts between the
breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, two reactants. (Represented symbolically as:
ions, molecule, or compounds. AB + CD AC + BD.)
2. Reactants – the substances that enter into a
chemical reaction. Energy and Chemical Reactions:
3. Products – the substances that result from 1. Reversible reaction - are reactions in which
the chemical reaction. reactants form products and the products can
also react with each other to re-form the
A+B C+D reactants.
Reactants Product Equilibrium – when the ate of product
formation equals the rate of reactant
Classification of Chemical Reactions: formation.
1. Synthesis reaction – when two or more 2. Energy – is the capacity to do work.
reactants combine to form a larger, more 3. Work – is the moving of matter.
complex product. (Build a new molecule) 4. Kinetic energy – is energy caused by the
(Represented symbolically as: A + B AB.) movement of an object and is the form of
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – is a energy that actually does work.
complex organic chemical that provides 5. Potential energy – is stored energy.
energy to drive many processes in living 6. Chemical energy – is a form of potential energy
cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve that are stored in chemical bonds. (Example:
impulse propagation, chemical synthesis. ATP ADP + P.)
Anabolism - the synthesis of complex 7. Mechanical energy – is energy resulting from
molecules in living organisms from simpler the position or movement of an object.
ones together with the storage of energy;
constructive metabolism. Rate of Chemical Reactions:
Dehydration reaction - also known as 1. Rate – at which a chemical reaction proceeds is
Zimmer's hydrogenesis, is a chemical influenced by several factors:
reaction that involves the loss of a water Concentration of the reactants
molecule from the reacting molecule. Reactants - differ from one another in their
ability to undergo chemical reactions.
2. Decomposition Reaction - is a type of Concentration - Within limits, the greater
chemical reaction in which a single the concentration of the reactants, the
compound breaks down into two or more greater the rate at which a chemical
Thank you for using www.freepdfconvert.com service!
Only two pages are converted. Please Sign Up to convert all pages.
https://www.freepdfconvert.com/membership
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Documento5 pagineAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Chris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNessuna valutazione finora
- C2-Chemical Basis of LifeDocumento2 pagineC2-Chemical Basis of LifeLorrine MagramoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Documento17 pagineChapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Kayte Middleton100% (1)
- Anatomy of an atom and basic chemistryDocumento5 pagineAnatomy of an atom and basic chemistryKat OrcinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 2 - Elements Atoms Carbon - OwlDocumento22 pagineClass 2 - Elements Atoms Carbon - OwlLinda WuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture NotesDocumento3 pagineLecture NotesIdk UlitNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDocumento4 pagine01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDaniel Angelo MiradorNessuna valutazione finora
- Rebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamDocumento5 pagineRebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamjoshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioDocumento7 pagine2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioRayumaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Chemistry of LifeDocumento55 pagine1 - Chemistry of LifeDaniel KipnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Prelim Org Chem Lecture Notes Chap 1 Intro To Organic ChemistryDocumento5 paginePrelim Org Chem Lecture Notes Chap 1 Intro To Organic ChemistryKaye Selene Raphaelle SyNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio IN Science: Submitted To: Mrs. Remelyn P. Guilaran Submitted By: Shiaira Mae M. Eduarte: Andrea Kate M. AbagaDocumento11 paginePortfolio IN Science: Submitted To: Mrs. Remelyn P. Guilaran Submitted By: Shiaira Mae M. Eduarte: Andrea Kate M. AbagaShaii EduarteNessuna valutazione finora
- The Chemical BasisDocumento6 pagineThe Chemical BasisGel Austin PascuaNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento4 pagineChemistryKent RosimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: You Must Understand Chemistry To Understand Life (And To Pass This Course) !Documento5 pagineChapter 2: You Must Understand Chemistry To Understand Life (And To Pass This Course) !jwinters20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microparasitology IntroDocumento36 pagineMicroparasitology IntroLady DanielleNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemlec Mod 1 6Documento50 pagineBiochemlec Mod 1 6Sean Michael ComprendioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeDocumento35 pagineChapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeJustin RobenyNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology Chapter 2 Chemical Foundations For CellDocumento2 pagineAP Biology Chapter 2 Chemical Foundations For Cellwrenet1231503Nessuna valutazione finora
- AtomDocumento4 pagineAtomanjaliNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Chemical LifeDocumento5 pagine2 Chemical LifeEly FructuosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading-The Different Types of BondsDocumento2 pagineReading-The Different Types of BondsSeu WorkNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ChemistryDocumento14 pagineBasic ChemistryPitherNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology: 2.1 Atoms: Fundamental Building Blocks of All Matter in The UniverseDocumento50 pagineChapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology: 2.1 Atoms: Fundamental Building Blocks of All Matter in The UniverseShemmy Delotina DadulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Documento3 pagineEastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Isaac PiaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Chemistry VocabDocumento2 pagineChapter 2 Chemistry VocababNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Atoms and MoleculesDocumento5 pagineLaws of Atoms and MoleculesPranav ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Notes For Form 2Documento70 pagineChemistry Notes For Form 2Charles OtienoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Components of CellDocumento77 pagineChemical Components of Cellrollen grace fabulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure: Electron Proton NeutronDocumento4 pagineAtomic Structure: Electron Proton NeutronTalao, Angelie Rei S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 Outline AP BioDocumento4 pagineCH 2 Outline AP BioSabaAskariNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2, Chemistry, PDFDocumento11 pagineModule 2, Chemistry, PDFMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENessuna valutazione finora
- Unit II - Lecture NotesDocumento5 pagineUnit II - Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (1)
- Chemistry of Life: Unit 2Documento12 pagineChemistry of Life: Unit 2Divine Josol CamposanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ChemistryDocumento14 pagineBasic ChemistryAtul DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- NAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimDocumento22 pagineNAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimAnila AftabNessuna valutazione finora
- Early Chemistry: Early Chemists Only Believed in 1 Element: Dirt Later Chemists Believed in 4 ElementsDocumento14 pagineEarly Chemistry: Early Chemists Only Believed in 1 Element: Dirt Later Chemists Believed in 4 ElementsDili Apriana AksariNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chem 2 ReviewerDocumento5 pagineGeneral Chem 2 ReviewerBeverly A PanganibanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Introductory Chemistry & Biochemistry: Phosphate Head (Polar)Documento12 pagineChapter 2 - Introductory Chemistry & Biochemistry: Phosphate Head (Polar)Rajarathinam1235463Nessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceDocumento2 pagineMODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceEmma Cristie BalahadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Chapter 6 ReviewDocumento3 pagineChemistry Chapter 6 Reviewjuan carlos quispe mamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Llogers - General Chemistry m1-m6Documento18 pagineLlogers - General Chemistry m1-m6api-639087356Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1Q - Week 2 Physical ScienceDocumento19 pagine1Q - Week 2 Physical ScienceJEBONIE TUBICENessuna valutazione finora
- All Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsDocumento11 pagineAll Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsmNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemi Try Review: A. Elements (Chapter 2)Documento7 pagineChemi Try Review: A. Elements (Chapter 2)Valentina RumhizhaNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemDocumento2 pagineBiochempc llonosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Definitions PDFDocumento9 pagineDefinitions PDFAlexia LudlowNessuna valutazione finora
- ميد Fire behaviourDocumento117 pagineميد Fire behaviourOmar NaimatNessuna valutazione finora
- EnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 03 - 2 Characterizing Air Pollution Oct 2015Documento115 pagineEnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 03 - 2 Characterizing Air Pollution Oct 2015Alexis Bryan RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding Types Explained in 40 CharactersDocumento14 pagineChemical Bonding Types Explained in 40 CharacterselisaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 2.4 Chemistry GZDocumento187 pagine2020 2.4 Chemistry GZgeetub1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondingDocumento5 pagineChemical BondingStellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeDocumento40 pagineChapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeDannyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023Documento48 pagineLecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023PPNessuna valutazione finora
- REVIEWERDocumento7 pagineREVIEWERrhymeNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 6 Chemical BondingDocumento14 pagineCH 6 Chemical Bondingapi-240972605Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms and MoleculesDocumento4 pagineAtoms and MoleculesHitesh kalraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life TAYAMDocumento19 pagineChapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life TAYAMMaria Divina SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Globalization 1Documento1 paginaGlobalization 1BrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial ContraceptivesDocumento1 paginaArtificial ContraceptivesBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- HEARTDocumento1 paginaHEARTBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- LayersDocumento1 paginaLayersBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- ArtificialDocumento1 paginaArtificialBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Contraceptives pt.2Documento1 paginaArtificial Contraceptives pt.2BrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Methods of ContraceptionDocumento1 paginaNatural Methods of ContraceptionBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial ContraceptivesDocumento1 paginaArtificial ContraceptivesBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- EntDocumento1 paginaEntBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 "Discuss The Characteristics of Entrepreneurs"Documento1 paginaAssignment 1 "Discuss The Characteristics of Entrepreneurs"BrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- EntDocumento1 paginaEntBrigitteNessuna valutazione finora
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Chem 2nd Quarter w4 w5Documento28 pagineLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Chem 2nd Quarter w4 w5ilostmyselfintothewoodsNessuna valutazione finora
- As A Level GCE Chemistry Salters Mark Scheme June 2006Documento43 pagineAs A Level GCE Chemistry Salters Mark Scheme June 2006ExamStuffNessuna valutazione finora
- Nanotechnology - Gunter Schmid (Wiley-VCH, 2008) PDFDocumento2.664 pagineNanotechnology - Gunter Schmid (Wiley-VCH, 2008) PDFMokeng Mokoma100% (5)
- 11 - Topic 20 Organic Chemistry AnswersDocumento60 pagine11 - Topic 20 Organic Chemistry AnswersNeen NaazNessuna valutazione finora
- LessonPPT1 KMTDocumento64 pagineLessonPPT1 KMTRaiv LondresNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercury FulminateDocumento11 pagineMercury FulminateAnoshän IndreswaränNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Test BankDocumento30 pagineChemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Test Bankwadeperlid9d98k100% (31)
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocumento3 pagineSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- ELC 2019 Curriculum and Syllabus (2020!10!26 20-35-03 UTC)Documento202 pagineELC 2019 Curriculum and Syllabus (2020!10!26 20-35-03 UTC)Sri Charan VukkumNessuna valutazione finora
- EP 99-5266 Removal of Heavy Metals From WastewaterDocumento58 pagineEP 99-5266 Removal of Heavy Metals From WastewaterYoga Pratama100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 06-Mar-2022 PDFDocumento18 pagineAdobe Scan 06-Mar-2022 PDFCerena SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 13H ConjugatedDocumento41 pagine13H ConjugatedSandipNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 EdittedDocumento15 pagineModule 3 EdittedMARIE ANN DIAMANessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry S4 SB PDFDocumento480 pagineChemistry S4 SB PDFRoykin Mugisha82% (11)
- Unit 3.2 - Covalent BondingDocumento11 pagineUnit 3.2 - Covalent BondingAylin KasaNessuna valutazione finora
- 0620+IGCSE+Chemistry+Scheme+of+Work (From+2023)Documento22 pagine0620+IGCSE+Chemistry+Scheme+of+Work (From+2023)Alexander Stip Martínez50% (2)
- GhghhiyuyyDocumento4 pagineGhghhiyuyyDurgesh TrivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To ExercisesDocumento13 pagineAnswers To Exercisesar_gon214Nessuna valutazione finora
- Corma 1985Documento124 pagineCorma 1985Leonan Dos Santos RodriguesNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Configuration Chem 101Documento11 pagineElectron Configuration Chem 101Nathan TienamenNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Plasma Treatment On The Dyeability of Silk Fabric by UsingDocumento8 pagineThe Effect of Plasma Treatment On The Dyeability of Silk Fabric by UsingLatifNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Tunneling DNA IntegrityDocumento8 pagineQuantum Tunneling DNA IntegrityAvigyanSinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 4 2011Documento12 pagineCH 4 2011Sendu RasaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Fundamental Approach To Ordinary Chemistry PDFDocumento745 pagineA Fundamental Approach To Ordinary Chemistry PDFivan kahwaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008 Kedah SPM Chemistry AnsDocumento18 pagine2008 Kedah SPM Chemistry Ansjee2kkNessuna valutazione finora
- Benzene (Arene) Notes On Chemical ReactionsDocumento33 pagineBenzene (Arene) Notes On Chemical ReactionsdanielmahsaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 025 1st Periodic Exam ReviewDocumento4 pagineCHE 025 1st Periodic Exam ReviewCelina PilloraNessuna valutazione finora
- 0654 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2019)Documento159 pagine0654 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2019)Vibhor Pandey67% (3)
- Atomic BasicsDocumento4 pagineAtomic Basicsapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- LG 1.2 Properties of Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupsDocumento10 pagineLG 1.2 Properties of Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupswangmorisNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeDa EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDa EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsDa EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationDa EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (18)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationDa EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNessuna valutazione finora
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDa EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDa EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDa EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Advanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlDa EverandAdvanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementDa EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilDa EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryDa EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (25)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesDa EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (14)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentDa EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Introduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisDa EverandIntroduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableDa EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNessuna valutazione finora