Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Eng Blood Supply and Innervation o
Caricato da
Or0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni41 pagineanatomy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoanatomy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni41 pagineEng Blood Supply and Innervation o
Caricato da
Oranatomy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 41
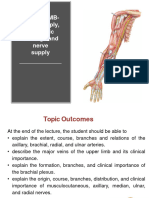
Innervation and blood supply of
the upper limb. Carpal tunnel.
Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D.
Spinal nerves
Brachial plexus
Brachial plexus
Brachial plexus
Lateral cord
• Musculocutaneous nerve:
• perforates the coracobrachialis muscle
• runs between the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles
• its sensory end-branch is the lateral antebrachial
cutaneous nerve
• Motor innervation: flexors of the arm
• Skin innervation: (lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve)
lateral part of the forearm
Lateral cord
• Median nerve (lateral part):
• runs in the medial bicipital groove lateral to the brachial
artery
• passes between the two heads of the pronator teres
• in the forearm it runs between the flexor digitorum
superficialis and profundus
• goes through the carpal tunnel
• Motor innervation: majority of forearm’s flexors
• Skin innervation: radial part of the palm
Medial cord
• Median nerve (medial part)
• Ulnar nerve:
• in the middle part of the arm it pierces the medial intermuscular
septum and enters into the „extensor muscle compartment”
• in the elbow region it goes around the medial epicondyle
(groove for ulnar nerve)
• passes between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris
• with ulnar vessels run through the Guyon’s canal above the
flexor retinaculum
• Motor innervation: minority of forearm’s flexors and majority
of hand’s muscles
• Skin innervation: ulnar side of the hand
Medial cord
• Medial brachial cutaneous nerve:
• only sensory innervation
• medial surface of the arm
• Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve:
• only sensory innervation
• medial surface of the forearm
Posterior cord
• Axillary nerve:
• passes through the quadrangular space surrounds the
surgical neck of the humerus
• its sensory branch the superior lateral brachial cutaneous
nerve
• Motor innervation: deltoid and teres minor
• Skin innervation: (superior lateral brachial cutaneous
nerve) superior lateral part of the arm
Posterior cord
• Radial nerve:
• locates behind the axillary and brachial arteries
• with the profunda brachii artery enter to the groove for
radial nerve of humerus
• brachial branches:
posterior brachial cutaneous nerve
inferior lateral brachial cutaneous nerve
posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve
Posterior cord
• Radial nerve:
• runs between the brachioradialis and brachialis muscles at the
lateral part of the cubital (elbow) region and here it divides two
main branches:
Deep branch: among the extensors of the forearm
Superficial branch: only sensory innervation
• Motor innervation: extensors of the arm and forearm
• Skin innervation: posterior surfaces of the arm and forearm,
lower lateral surface of the arm, dorsal radial side of the hand
Summary of the skin innervation of
the hand
Summary of the skin innervation of
the hand
Vasculature of the upper limb
Superficial palmar arch
Deep palmar and dorsal arches
Deep veins of the upper limb
• the deep veins run accompanying the
arteries (their names are the same)
• two veins are accompanying the small and
middle arteries below the superior third of
the upper limb
Superficial veins of the upper limb
• the superficial or subcutaneous veins are
independent from the arteries
• two main subcutaneous veins and one
important anastomosis are on the upper
limb
Triangular, Quadrangular spaces
(and Triangular interval)
Triangular, Quadrangular spaces
(and Triangular interval)
Carpal tunnel
Carpal tunnel
Carpal tunnel syndrome
• Caused by pressure on the median nerve within the carpal
tunnel.
• The etiology of this condition is often obscure, though in some
instances the nerve injury may be a direct effect of increased
pressure on the median nerve caused by overuse, swelling of the
tendons and tendon sheaths (e.g.: rheumatoid arthritis) and
cysts arising from the carpal joints.
• Increased pressure can cause venous congestion that produces
nerve edema and anoxic damage of the median nerve itself.
• Patients typically report pain and pins and needles in the
distribution of the median nerve. Weakness and loss of muscle
bulk of the thenar muscles may also occure.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Thank you for your attention.
References: Gray’s Anatomy for Students
Hand out of Dr. Katalin Kocsis
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis: Peripheral
nerve surgery: A Resource for Surgeons
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Siatic NerveDocumento33 pagineSiatic Nervenithin nairNessuna valutazione finora
- Hockey Slap ShotDocumento14 pagineHockey Slap Shotapi-557422190Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hamstring StretchDocumento14 pagineHamstring StretchRatnaPrasadNalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Topographic Anatomy Superior LimbsDocumento59 pagineTopographic Anatomy Superior Limbsstefiromsev6826Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics BookDocumento78 paginePhysics BookOrNessuna valutazione finora
- Brachial PlexusDocumento98 pagineBrachial PlexussandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Vessels of Upper LimbDocumento23 pagineBlood Vessels of Upper Limbkhalid_shinasNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy - Pectoral Region and Axilla PDFDocumento4 pagineAnatomy - Pectoral Region and Axilla PDFAngel KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Axillary ArteryDocumento16 pagineAxillary ArteryHarsha MudigoudaNessuna valutazione finora
- ANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmDocumento88 pagineANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmNur Liyana MohamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology Final Exam QuestionsDocumento5 paginePsychology Final Exam QuestionsOr100% (1)
- Anatomy of The ARMDocumento17 pagineAnatomy of The ARMJacob MasikaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Neck PDFDocumento67 pagineThe Neck PDFAhmad Akram NatshehNessuna valutazione finora
- Brachial PlexusDocumento30 pagineBrachial Plexusapi-199163990% (1)
- Anatomy of ArmDocumento22 pagineAnatomy of Armromaisa akhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Working With Appendicular Sciatica, Part III (Myofascial Techniques)Documento5 pagineWorking With Appendicular Sciatica, Part III (Myofascial Techniques)Advanced-Trainings.com100% (3)
- Nerves of Upper LimbDocumento24 pagineNerves of Upper LimbShimmering MoonNessuna valutazione finora
- I.9. Classical Genetics FinalDocumento50 pagineI.9. Classical Genetics FinalOrNessuna valutazione finora
- The Axilla: Shah Hussain LECTURER (Surgical)Documento81 pagineThe Axilla: Shah Hussain LECTURER (Surgical)Ibrar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Summary From MooreDocumento131 pagineAnatomy Summary From MooreNishma Malde100% (2)
- Throwers Ten Exercise ProgramDocumento5 pagineThrowers Ten Exercise ProgramAdmirNessuna valutazione finora
- Triangels of NeckDocumento86 pagineTriangels of NeckNayela AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.blood Supply of Upper LimbDocumento52 pagine6.blood Supply of Upper LimbBlessed LoveNessuna valutazione finora
- Membrul Superior MGDocumento118 pagineMembrul Superior MGMihai OpreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brachial Plexus ExaminationDocumento7 pagineBrachial Plexus ExaminationMalvinder Singh DhillonNessuna valutazione finora
- Katya 30-Day-Challenge-Bikini-Body-Week-1 PDFDocumento8 pagineKatya 30-Day-Challenge-Bikini-Body-Week-1 PDFGeraldyneNessuna valutazione finora
- Posterior Compartment of ArmDocumento18 paginePosterior Compartment of Armshakur /Nessuna valutazione finora
- Session 4, L3 ARMDocumento16 pagineSession 4, L3 ARMFirst LuckNessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior Compartment of The ArmDocumento46 pagineAnterior Compartment of The ArmAuza Moses IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- The ForearmDocumento26 pagineThe Forearmapi-249972919Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arm and Cubital FossaDocumento40 pagineArm and Cubital FossaAbdelrhman AbubakrNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lecture 5 Brachial PlexusDocumento66 pagineAnatomy Lecture 5 Brachial PlexusSathvika ChallarapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve and Blood Supply of Upper ExtremitiesDocumento12 pagineNerve and Blood Supply of Upper ExtremitiesBenjamin PrabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Supply of Upper Limb: Axilla & ArmDocumento35 pagineBlood Supply of Upper Limb: Axilla & ArmfdjkvfjvNessuna valutazione finora
- Cervical, Brachial PlexusDocumento31 pagineCervical, Brachial PlexusSophy AhdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood & Nerve Supply of Forearm.Documento30 pagineBlood & Nerve Supply of Forearm.Shimmering MoonNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.axilla 2Documento37 pagine5.axilla 2Pradip ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- UL4-armDocumento26 pagineUL4-armfaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 14802upper Limb Blood Vessels and LymphaticsDocumento21 pagine14802upper Limb Blood Vessels and LymphaticsZiad AlaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 11 - The NeckDocumento19 pagineLec 11 - The Neckbf28215Nessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionDocumento13 pagineUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- Cubital FossaDocumento19 pagineCubital FossaAhmed SharafNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles of The Thoracic Wall, Pectoral Region - 2023 - 1Documento28 pagineMuscles of The Thoracic Wall, Pectoral Region - 2023 - 1202112360Nessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion Topics IA1 AnatDocumento9 pagineDiscussion Topics IA1 AnatPhysics TutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Adductor CanalDocumento10 pagineAdductor CanalLakshu DevNessuna valutazione finora
- UL Radial NerveDocumento22 pagineUL Radial NerveandreNessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior Compartment of The ForearmDocumento55 pagineAnterior Compartment of The ForearmAuza Moses IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Kovacs Files AnatomyDocumento124 pagineKovacs Files Anatomyshmirtb100% (2)
- Biceps Brachii OriginDocumento40 pagineBiceps Brachii OriginDanish GujjarNessuna valutazione finora
- ElbowDocumento35 pagineElbowSanmukhiya Darshit ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture FiveDocumento35 pagineLecture FivePiniel MatewosNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Supply and Nerve Supply of Upper LimbDocumento94 pagineBlood Supply and Nerve Supply of Upper LimbthrrishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Documento23 pagineAnatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Handount Limbs CompleteDocumento67 pagineHandount Limbs CompletebigprogrammeramNessuna valutazione finora
- The Spinal CordDocumento22 pagineThe Spinal Cordcy lifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The ArmDocumento38 pagineAnatomy of The ArmAkomolede AbosedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Anatomy NotesDocumento5 pagineClinical Anatomy NotesYehansa WijethungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brachial Plexus InjuriesDocumento11 pagineBrachial Plexus InjuriesLorenzo AmpilNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Vessels: Artery Capillary VeinDocumento27 pagineBlood Vessels: Artery Capillary Veinapi-19641337Nessuna valutazione finora
- Axilla Presentation by IfunayaDocumento36 pagineAxilla Presentation by IfunayaogbokobolaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Nerves and Nerve Injuries of The Upper LimbsDocumento72 pagine8 Nerves and Nerve Injuries of The Upper LimbsAbdelrhman AbubakrNessuna valutazione finora
- Front of Thigh, Femoral Triangle and Femoral VesselsDocumento35 pagineFront of Thigh, Femoral Triangle and Femoral Vesselsgospel munkondya100% (1)
- Venous Drainage of Upper LMBDocumento49 pagineVenous Drainage of Upper LMBidrimuha333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Larynx and TracheaDocumento23 pagineLarynx and Tracheaoreoluwa emmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior Compartment of ForearmDocumento25 pagineAnterior Compartment of Forearmromaisa akhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- SGDDocumento7 pagineSGDJanine Vega Calayo100% (1)
- Anatomy: Veins of The Forearm and Arteries of The Arm.Documento36 pagineAnatomy: Veins of The Forearm and Arteries of The Arm.Mercy AdeolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bambang WDocumento25 pagineBambang Woges paikiNessuna valutazione finora
- I.8. The Cell Cycle QandADocumento45 pagineI.8. The Cell Cycle QandAOrNessuna valutazione finora
- II.2 Cytogenetics, Teratology, MutationsDocumento48 pagineII.2 Cytogenetics, Teratology, MutationsOrNessuna valutazione finora
- I.6. Nucleus, Replication, Transcription, Translation UrbánVDocumento21 pagineI.6. Nucleus, Replication, Transcription, Translation UrbánVOrNessuna valutazione finora
- I.4. Peptides, Nucleic AcidsUrbánV ValidDocumento39 pagineI.4. Peptides, Nucleic AcidsUrbánV ValidOrNessuna valutazione finora
- I.7. Further ORGANELLES: Endoplazmic Reticulum, Golgi-Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, MitochondriaDocumento23 pagineI.7. Further ORGANELLES: Endoplazmic Reticulum, Golgi-Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, MitochondriaOrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 9Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 9OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 1Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 1OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics-Motion Analysis: Lecture Notes PhysiotherapistDocumento79 pagineBiomechanics-Motion Analysis: Lecture Notes PhysiotherapistOrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 11Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 11OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 10Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 10OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Center of GravityDocumento4 pagineCenter of GravityOrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 9Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 9OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 6Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 6OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 7Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 7OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 3Documento4 pagineBasics of Psychology 3OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 5Documento3 pagineBasics of Psychology 5OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Skull: Anna L. Kiss Department of Human Morphology and Developmental Biology Semmelweis University 2015Documento19 pagineSkull: Anna L. Kiss Department of Human Morphology and Developmental Biology Semmelweis University 2015OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 2Documento6 pagineBasics of Psychology 2OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Psychology 4Documento4 pagineBasics of Psychology 4OrNessuna valutazione finora
- 0900 - L Kiss Anna - Eng - Skull IIDocumento29 pagine0900 - L Kiss Anna - Eng - Skull IIOrNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood: Anna L. Kiss Department of Human Morphology and Developmental Biology Semmelweis University Budapest 2014Documento28 pagineBlood: Anna L. Kiss Department of Human Morphology and Developmental Biology Semmelweis University Budapest 2014OrNessuna valutazione finora
- General Osteology Ahtrology ADocumento28 pagineGeneral Osteology Ahtrology AOrNessuna valutazione finora
- 0900 Katz Sandor Eng Pelvis Gross Anatomy of The LDocumento60 pagine0900 Katz Sandor Eng Pelvis Gross Anatomy of The LOrNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest Cavity, Vertebral Column and Back Muscles. Respiratory MusclesDocumento35 pagineChest Cavity, Vertebral Column and Back Muscles. Respiratory MusclesOr100% (2)
- 0800 Katz Sandor Eng Vertebral Column Muscles of TDocumento33 pagine0800 Katz Sandor Eng Vertebral Column Muscles of TOrNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles Tendon Phy I So TherapistDocumento31 pagineMuscles Tendon Phy I So TherapistOrNessuna valutazione finora
- 1pages From The Anatomy of Sports Injuries - Brad WalkerDocumento6 pagine1pages From The Anatomy of Sports Injuries - Brad WalkerFatimah SalsabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Di̇z Eklemi̇ni̇n Anatomi̇si̇ Ve Bi̇yomekani̇ği̇ - Bau (1) - 2Documento67 pagineDi̇z Eklemi̇ni̇n Anatomi̇si̇ Ve Bi̇yomekani̇ği̇ - Bau (1) - 2erfan mohammadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Bramantya SP Ot - Diagnosis and Management in Upper Extremity ProblemDocumento3 pagineDr. Bramantya SP Ot - Diagnosis and Management in Upper Extremity ProblemChristian HarnatNessuna valutazione finora
- Ankleandfoot 2Documento10 pagineAnkleandfoot 2Jamilah FlorendoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jakarta School of Prosthetics & Orthotics: Upper Limb Prosthetics Course Work Manual 2010Documento84 pagineJakarta School of Prosthetics & Orthotics: Upper Limb Prosthetics Course Work Manual 2010Adinda Dinda100% (1)
- Asian Yoga Sports Championship SyllabusDocumento9 pagineAsian Yoga Sports Championship SyllabusGaurav guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Ex OINADocumento15 pagineUpper Ex OINAChristi EspinosaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide To Examination of Joints-ModifiedDocumento26 pagineA Guide To Examination of Joints-ModifiedKishanti BalachandranNessuna valutazione finora
- V-Y FlapDocumento14 pagineV-Y FlapTrần Nhật QuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Positioning and Moving of Hemiplegic Pt. Bed Mobility ExercisesDocumento133 paginePositioning and Moving of Hemiplegic Pt. Bed Mobility Exercisesktin17100% (1)
- System Exams - Promotion Exam MusculoskeletalDocumento4 pagineSystem Exams - Promotion Exam Musculoskeletalespo176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics of Patellofemoral Joint': Ronald P. Grelsamer, MD" John R. Klein, MDDocumento13 pagineBiomechanics of Patellofemoral Joint': Ronald P. Grelsamer, MD" John R. Klein, MDBrunoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ankle Foot OrthosisDocumento23 pagineAnkle Foot OrthosisEma ListiyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- U10-Distal Radius FracturesDocumento121 pagineU10-Distal Radius Fracturesrajasekhar ANessuna valutazione finora
- 2002, Vol. 7, Issues 2, Techniques in Carpal Tunnel SurgeryDocumento136 pagine2002, Vol. 7, Issues 2, Techniques in Carpal Tunnel Surgerymontserrat santiago sanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ortho MCQDocumento6 pagineOrtho MCQLaw YouNessuna valutazione finora
- Pune Trauma Course Brochure 29-03-2024Documento29 paginePune Trauma Course Brochure 29-03-2024sriharshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Body VocabularyDocumento1 paginaAdvanced Body Vocabularycandespi75Nessuna valutazione finora
- Locate The Apex Beat in The Given Subject by Palpation and Report Your FindingsDocumento8 pagineLocate The Apex Beat in The Given Subject by Palpation and Report Your Findingsrov3r 2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shoulder 2020 RohofDocumento36 pagineShoulder 2020 Rohofpocadew100% (1)
- Humeral Shaft Fractures: Supervisior: Dr. Dewi Kurniati P, SP - OT Teguh Triananda PutraDocumento20 pagineHumeral Shaft Fractures: Supervisior: Dr. Dewi Kurniati P, SP - OT Teguh Triananda Putrateguh triananda putraNessuna valutazione finora
- Docc Hilford - Dance of ShivaDocumento21 pagineDocc Hilford - Dance of ShivaboboNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Overhaul Slider Project Manual v1.8Documento34 pagineBody Overhaul Slider Project Manual v1.8Jose Luis LeguiaNessuna valutazione finora