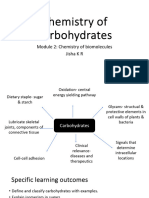
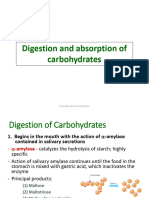
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Scan Jun 15, 2019
Caricato da
RajeshTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Scan Jun 15, 2019
Caricato da
RajeshCopyright:
Formati disponibili
-...
----------------
176 Objective Food Sc ience and Safety Standards
TABL E I :
C lass ification of carboh ydrat es based on molecular size
.
Sugar 1111/t/.J; Source
Carb11hyilN1te!i Exllmple
- Fruits, starch
Monos::iccharid e Glucose Glucose
(singh~ sugar uni t) Ga l:1rtost.> Gulactose M ilk ( as lactose)
Fructose Fru ctose Fru it
Oligosac:c haridc
Uisu,:c:lwr1de Sucrose Glucose -1 Fructose Sugar cane, beet
Lactose Glucose + Ga lal: lose M ilk
(] sugar u111rs)
Tr1sacc/10ridt 1 lsnmalt otriose Glu cose + Glucose + Glucose Degradation prod uct
of starch
(3 sugar units) Gent ia nosc Glucose + Glucose + fr uctose Gentia n rh izome
Pol) saccharide Starch Glucose Cereal s, tubers
(more than I0 Cellulose Gluc ose Plant stem
sugar units) Pectin Galacturoni c aci d Fru its
Algi ni c acids Monou ronic acid + guluron ic acid Brown seaweeds
Carrageenans Ga lactose Red seaweed
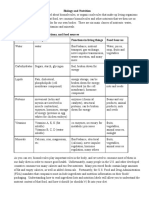
TABLE 2:
Dietary fiber functions and benefits
Type of fiber Fu11ctio11s Benefits
- -
Soluble • It adds bulk to ou r diet, • Lowers b load sugar levels
• It has high satiety value • Reduce risk o f colorectal cancer
• II attracts water and gets
converted to gel during digestion.
The gel traps carbohydrates thus
slowi ng absorption of glucose
• It balan ces intestinal pH and
sti mulates intesti nal ferme ntation
-- -- production of short-chai n fatty acids
Inso lu ble fi ber • It adds bul k to our diet' • It reduces ri sk of heart di sease
• It has high sati ety value • It may redu ce onset ris k or symptoms
• It lowers total and LDL cholesterol of metabo li c syndrome and dia betes
• It regul ates blood sugar • It fac ilitates regularity
• It increases the passage of foods • It allev iates constipation
thro ugh th e digestive system
• It add s bulk to the stool
~
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2Da Everand2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate 1Documento60 pagineCarbohydrate 1jahahn.t.sullivanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition-3: Dietary Carbohydrates or Nutritional Importance of CarbohydratesDocumento4 pagineNutrition-3: Dietary Carbohydrates or Nutritional Importance of CarbohydratesammuNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate (STM)Documento42 pagineCarbohydrate (STM)Jessica chiNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocumento32 pagineDigestion and AbsorptionFiqri NovianNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - CarbohydratesDocumento25 pagine2 - CarbohydratesEDISON DE LOS SANTOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 - Blood SugarDocumento11 pagineLecture 2 - Blood SugartagmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Food and Human NotesDocumento7 pagineChapter 5 Food and Human Notes4107 曾凱謙 Tsang Hoi Him HymnNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 105 - Lab Activity # 3 - Macronutrients: CarbohydrateDocumento10 pagineNCM 105 - Lab Activity # 3 - Macronutrients: CarbohydrateclrssNessuna valutazione finora
- Charbohydrate: Unit - IiDocumento8 pagineCharbohydrate: Unit - IiHemant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- LECT 1&2 - CHO & Energy BalanceDocumento22 pagineLECT 1&2 - CHO & Energy BalancenorshaheeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Avdhesh CarbohydratesDocumento28 pagineAvdhesh CarbohydratesClassic AddaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4-Biochemistry Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento15 pagineUnit 4-Biochemistry Carbohydrate MetabolismÂmoOł ÀhmdNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry and Biology of FoodDocumento48 pagineChemistry and Biology of FoodjaedenNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion of CarbohydratesDocumento30 pagineDigestion of CarbohydratesRona May EsperanzateNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrates and AbsorptionDocumento33 pagineCarbohydrates and AbsorptionSammi TovarNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Mechanism of Disease Nutritonal PersepectivesDocumento50 pagineBasic Mechanism of Disease Nutritonal PersepectivesQuswah MaharaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of CarbohydratesDocumento1 paginaTypes of CarbohydratesNisha LazarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR WaseemDocumento33 pagineDigestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR WaseemIMDCBiochem100% (2)
- Nutrition Department Medical School University of Sumatera UtaraDocumento39 pagineNutrition Department Medical School University of Sumatera UtaraShanaz AlvikhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates 2023Documento37 pagineChemistry of Carbohydrates 2023andrade.sanchithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Curs 1 2015 DZDocumento44 pagineCurs 1 2015 DZIoana DiaconuNessuna valutazione finora
- Glucan and Vital Gluten - Isolation, Properties and ApplicationsDocumento28 pagineGlucan and Vital Gluten - Isolation, Properties and ApplicationsJyoti Jha100% (1)
- Human PhysiologyDocumento257 pagineHuman PhysiologyAyushNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Copy CARBSDocumento46 pagineStudent Copy CARBSRomeo DiestaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrates LabDocumento5 pagineCarbohydrates LabFrance LataoanNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 08-02-24Documento113 pagineCarbohydrate Metabolism 08-02-24Saloni SaloniNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbs (1) (4 Files Merged)Documento315 pagineCarbs (1) (4 Files Merged)omaryadak0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Random Blood Sugar Measurement: Lab Class 4Documento11 pagineRandom Blood Sugar Measurement: Lab Class 4sontori miliNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundament of Nut Lecture 3 CarDocumento50 pagineFundament of Nut Lecture 3 Carmahnoor ashiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry of BileDocumento47 pagineBiochemistry of BileBiomedical Science MyanmarNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbohydratesDocumento20 pagineCarbohydratesSadaf JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 MacronutrientsDocumento3 pagineChapter 3 MacronutrientsMaxdjye EyjdxamNessuna valutazione finora
- FODMAPS Everywhere and Not A Thing To Eat!:, SERIES #188 Nutrition Issues in Gastroenterology, Series #188Documento9 pagineFODMAPS Everywhere and Not A Thing To Eat!:, SERIES #188 Nutrition Issues in Gastroenterology, Series #188Amiee WilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Macronutrients & Exercise: 2.1 Carbohydrates For Health & ExerciseDocumento31 pagineMacronutrients & Exercise: 2.1 Carbohydrates For Health & ExerciseNurul AinNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemical Digestive and Absorption Process of Dietary-Sunarti-Biochemistry (2015)Documento36 pagineBiochemical Digestive and Absorption Process of Dietary-Sunarti-Biochemistry (2015)nayanikatesalonikaNessuna valutazione finora
- PS106 Biochemistry ReviewerDocumento7 paginePS106 Biochemistry ReviewerMishelle DayagNessuna valutazione finora
- Serat PanganDocumento29 pagineSerat PanganAmalia Noviyanti AmelNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Carbohydrate in Health and DiseasesDocumento41 pagineRole of Carbohydrate in Health and Diseasesuttarasingh100% (2)
- Chapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESDocumento47 pagineChapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESKinjal100% (1)
- 4.digestion of CarbohydratesDocumento45 pagine4.digestion of CarbohydratesEkber IsmayilovNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbsDocumento40 pagineCarbsAnonymous eDD0YqzPMNessuna valutazione finora
- 526 3 CarbohydratesDocumento21 pagine526 3 CarbohydratesKIKI AULIANessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrient I - 2324S1Documento43 pagineNutrient I - 2324S1makinico321Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESDocumento47 pagineChapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESGlenn ClementeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Carbohydrates (Part 2)Documento25 pagine2 - Carbohydrates (Part 2)Sean Polo MallariNessuna valutazione finora
- CC ChekDocumento105 pagineCC ChekMarie LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Glucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsDocumento31 pagineGlucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsnikenNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Lesson 1Documento38 pagineMidterm Lesson 1Alexa QuizomNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion of Food (PS)Documento12 pagineDigestion of Food (PS)Pragya SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Santiago Achuri Anngy Marcela Bohórquez Sandra Milena Bustos Adriana Martínez Introduction To Food Engineering Group 2Documento15 pagineSantiago Achuri Anngy Marcela Bohórquez Sandra Milena Bustos Adriana Martínez Introduction To Food Engineering Group 2Santiago AchuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Kriyasharir: Mahatma Gandhi Ayurved College Hospital & Research Centre Salod (H), WardhaDocumento39 pagineDepartment of Kriyasharir: Mahatma Gandhi Ayurved College Hospital & Research Centre Salod (H), WardhaAvanti ShendurjaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology and NutritionDocumento7 pagineBiology and NutritionMargaret McDonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 23 Metabolism and Energy ProductionDocumento68 pagineChapter 23 Metabolism and Energy ProductionZahid HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Documento41 pagineDigestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Divya AgarawalNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento51 pagineGlycolysisKazar ProbusNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbohydratesDocumento33 pagineCarbohydratesDeboo X Xavier100% (1)
- Triose-Lipid Synthesis Tetrose - Glucose OxidationDocumento4 pagineTriose-Lipid Synthesis Tetrose - Glucose OxidationCosmic PhilippinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Metab - Lectures 3,4 Slides, 2020-21Documento15 pagineCarbohydrate Metab - Lectures 3,4 Slides, 2020-21W BNessuna valutazione finora
- Lipid Metabolism NewDocumento147 pagineLipid Metabolism NewMelissa SalayogNessuna valutazione finora
- Advt No 03 2024 WebsiteDocumento9 pagineAdvt No 03 2024 WebsiteRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Mar2021 ExamCentre RJDocumento10 pagineMar2021 ExamCentre RJRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- NOtifcationof REWARDDocumento3 pagineNOtifcationof REWARDRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Vacancy Circular AAO NSRTC Dated 08012024 0Documento6 pagineVacancy Circular AAO NSRTC Dated 08012024 0RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- advtSAG JRF16022024Documento4 pagineadvtSAG JRF16022024RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- IIAC Vacancy CircularDocumento5 pagineIIAC Vacancy CircularRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 Executive Assistant Field Officer Posts Advt Details Application Form KOF RaichurDocumento21 pagine16 Executive Assistant Field Officer Posts Advt Details Application Form KOF RaichurRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayushman PDFDocumento8 pagineAyushman PDFRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Edoc - Pub Mcqs in Food Science and TechnologyDocumento7 pagineEdoc - Pub Mcqs in Food Science and TechnologyRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- S.No Port of Origin of Journey House No Date of Arrival Date Until Quarantined Port of Final DestinationDocumento3 pagineS.No Port of Origin of Journey House No Date of Arrival Date Until Quarantined Port of Final DestinationRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Walk-In-Interview: Sl. No. Venue Date and Reporting TimeDocumento7 pagineWalk-In-Interview: Sl. No. Venue Date and Reporting TimeRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- JCI RecruitmentDocumento7 pagineJCI RecruitmentRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- S.No Date of Arrival Date Until Quarantine D Port of Origin of Journey Port of Final DestinationDocumento3 pagineS.No Date of Arrival Date Until Quarantine D Port of Origin of Journey Port of Final DestinationRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayushman PDFDocumento8 pagineAyushman PDFRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled PresentationDocumento1 paginaUntitled PresentationRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Jun 29, 2019Documento1 paginaScan Jun 29, 2019RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Anticovity Toothpaste: DentalDocumento1 paginaAnticovity Toothpaste: DentalRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Jun 29, 2019Documento1 paginaScan Jun 29, 2019RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Jun 29, 2019 PDFDocumento1 paginaScan Jun 29, 2019 PDFRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Jun 15, 2019Documento2 pagineScan Jun 15, 2019RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Jun 15, 2019Documento1 paginaScan Jun 15, 2019RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 2 Food ScienceDocumento7 pagineExam 2 Food ScienceRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Jun 15, 2019Documento2 pagineScan Jun 15, 2019RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Notification Employees Provident Fund Organisation Assistant Posts PDFDocumento40 pagineNotification Employees Provident Fund Organisation Assistant Posts PDFMahesh PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Quicker Basic CalculationDocumento42 pagineQuicker Basic CalculationSukant MakhijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan May 21, 2019Documento4 pagineScan May 21, 2019RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- APEDA in Export of Agricultural Processed Food ProductsDocumento37 pagineAPEDA in Export of Agricultural Processed Food Productsprathamesh kaduNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Green Yellow Modern English Intrapersonal Communication Educational Presentation - 20231109 - FixDocumento12 pagineBlue Green Yellow Modern English Intrapersonal Communication Educational Presentation - 20231109 - FixmhailvandalzNessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Point of ViewDocumento2 pagineScientific Point of Viewpavans EnglishNessuna valutazione finora
- Sinetch Itey Icebreaker 1Documento17 pagineSinetch Itey Icebreaker 1JewelNessuna valutazione finora
- Rewirement With Notes The Science of Well-BeingDocumento33 pagineRewirement With Notes The Science of Well-Beingswikar AcharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Giant Cell Tumor of Bone - An Overview: Current Concepts ReviewDocumento8 pagineGiant Cell Tumor of Bone - An Overview: Current Concepts ReviewDwi fitria nivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To World of Dream Team For Your SuccessDocumento49 pagineWelcome To World of Dream Team For Your SuccessUNKNOWN DREAMERNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Annual Report (Final)Documento38 pagine2019 Annual Report (Final)gjsdizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan IKM KSM PK FEBRUARI 2022Documento28 pagineLaporan IKM KSM PK FEBRUARI 2022Nur iffahNessuna valutazione finora
- K4health-The Mhealth Planning Guide Key Considerations For Integrating Mobile Technology Into Health Programs-2015!04!06Documento49 pagineK4health-The Mhealth Planning Guide Key Considerations For Integrating Mobile Technology Into Health Programs-2015!04!06DitaMaryaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Situation Analysis: Children in Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim MindanaoDocumento335 pagineSituation Analysis: Children in Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim MindanaoTerence YuNessuna valutazione finora
- Peavey XR 1220 Manual (ENG) PDFDocumento120 paginePeavey XR 1220 Manual (ENG) PDFRuben David Hurtado RoblesNessuna valutazione finora
- Canadas Physician ShortageDocumento11 pagineCanadas Physician ShortageFion LamNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Condition Before Common EraDocumento2 pagineHuman Condition Before Common EraACM23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Research Vegetable SiomaiDocumento23 pagineResearch Vegetable SiomaiPas Pas93% (14)
- Cell Damage and DeathDocumento1 paginaCell Damage and DeathfgdhgfrhNessuna valutazione finora
- Pe-501003-009 STPDocumento9 paginePe-501003-009 STPJeyakumar ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood ConversationDocumento300 pagineBlood ConversationMohsin NabeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pilferage Control in HospitalsDocumento4 paginePilferage Control in HospitalsDr. Rakshit Solanki100% (3)
- Iman Tavassoly CVDocumento6 pagineIman Tavassoly CVGladis HutahaeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bethesda Thyroid 2017Documento6 pagineBethesda Thyroid 2017Ladipo Temitope AyodejiNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Monitor PC-5000 User Manual PDFDocumento85 paginePatient Monitor PC-5000 User Manual PDFdanniel9090100% (1)
- Ogl 322 FinalDocumento2 pagineOgl 322 Finalapi-538747121100% (1)
- Cancer - 2011 - Hajdu - A Note From History Landmarks in History of Cancer Part 2Documento10 pagineCancer - 2011 - Hajdu - A Note From History Landmarks in History of Cancer Part 2Pilar AufrastoNessuna valutazione finora
- Closure MineDocumento14 pagineClosure MineAmilton filhoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Secret of LaughterDocumento5 pagineThe Secret of LaughterlastrindsNessuna valutazione finora
- Sandy Hill CHC SIS Letter WatsonDocumento3 pagineSandy Hill CHC SIS Letter WatsonJon WillingNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet Addiction - ResearchDocumento13 pagineInternet Addiction - ResearchpipedsNessuna valutazione finora
- Birthday Party - Character SketchesDocumento2 pagineBirthday Party - Character SketchesDhivyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 74 - SHE Specification Matla Reheat Attemperator Scope (Boiler) - 25102012 Rev0 PDFDocumento85 pagine74 - SHE Specification Matla Reheat Attemperator Scope (Boiler) - 25102012 Rev0 PDFvenkatrangan2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- EMResource - NEDOCS Definitions and Tracking LogDocumento2 pagineEMResource - NEDOCS Definitions and Tracking LogkingdonNessuna valutazione finora
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyDa EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Da EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (40)
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietDa EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellDa EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNessuna valutazione finora
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookDa EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellDa EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (81)
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonDa EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (33)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarDa EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (351)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyDa EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Eat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessDa EverandEat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessNessuna valutazione finora
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthDa EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeDa EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (411)
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeDa EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Eat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthDa EverandEat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouDa EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNessuna valutazione finora
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainDa EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (38)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsDa EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (49)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomDa EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthDa EverandThe Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthNessuna valutazione finora
- Hungry for Change: Ditch the Diets, Conquer the Cravings, and Eat Your Way to Lifelong HealthDa EverandHungry for Change: Ditch the Diets, Conquer the Cravings, and Eat Your Way to Lifelong HealthValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (7)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeDa EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingDa EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Molecules of Emotion: Why You Feel the Way You FeelDa EverandMolecules of Emotion: Why You Feel the Way You FeelValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (128)
- How to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeDa EverandHow to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Stark Naked 21-Day Metabolic Reset: Effortless Weight Loss, Rejuvenating Sleep, Limitless Energy, More MojoDa EverandThe Stark Naked 21-Day Metabolic Reset: Effortless Weight Loss, Rejuvenating Sleep, Limitless Energy, More MojoNessuna valutazione finora