Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs
Caricato da
William Orlando GamboaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs
Caricato da
William Orlando GamboaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
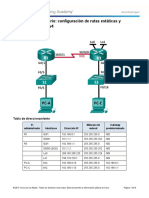
Packet Tracer – Configuring VLANs
Addressing Table
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask VLAN
PC1 NIC 172.17.10.21 255.255.255.0 10
PC2 NIC 172.17.20.22 255.255.255.0 20
PC3 NIC 172.17.30.23 255.255.255.0 30
PC4 NIC 172.17.10.24 255.255.255.0 10
PC5 NIC 172.17.20.25 255.255.255.0 20
PC6 NIC 172.17.30.26 255.255.255.0 30
Objectives
Part 1: Verify the Default VLAN Configuration
Part 2: Configure VLANs
Part 3: Assign VLANs to Ports
Background
VLANs are helpful in the administration of logical groups, allowing members of a group to be
easily moved, changed, or added. This activity focuses on creating and naming VLANs, and
assigning access ports to specific VLANs.
Part 1: View the Default VLAN Configuration
Step 1: Display the current VLANs.
On S1, issue the command that displays all VLANs configured. By default, all interfaces are
assigned to VLAN 1.
Step 2: Verify connectivity between PCs on the same network.
Notice that each PC can ping the other PC that shares the same network.
PC1 can ping PC4
PC2 can ping PC5
PC3 can ping PC6
Pings to PCs in other networks fail.
What benefit will configuring VLANs provide to the current configuration?
Rsta:
Seguridad a los grupos que tienen datos sensibles, se les separa del
resto de la red, disminuyendo las posibilidades de que ocurran
violaciones de información confidencial.
Reducción de costos, el ahorro en el costo resulta de la poca necesidad
de actualizaciones de red caras y usos más eficientes de enlaces y
ancho de banda existente.
Mejor rendimiento, la división de las redes planas de Capa 2 en
múltiples grupos lógicos de trabajo (dominios de broadcast) reduce el
tráfico innecesario en la red y potencia el rendimiento.
Mitigación de la tormenta de broadcast, la división de una red en las
VLAN reduce el número de dispositivos que pueden participar en una
tormenta de broadcast.
Mayor eficiencia del personal de TI: las VLAN facilitan el manejo de la
red debido a que los usuarios con requerimientos similares de red
comparten la misma VLAN.
Part 2: Configure VLANs
Step 1: Create and name VLANs on S1.
Create the following VLANs. Names are case-sensitive:
VLAN 10: Faculty/Staff
VLAN 20: Students
VLAN 30: Guest(Default)
VLAN 99: Management&Native
Step 2: Verify the VLAN configuration.
Which command will only display the VLAN name, status, and associated ports on a switch?
Rsta: Comando Show vlan bref, Se crearon las VLAN pero no hay puertos
asociados
Step 3: Create the VLANs on S2 and S3.
Using the same commands from Step 1, create and name the same VLANs on S2 and S3.
Step 4: Verify the VLAN configuration.
Part 3: Assign VLANs to Ports
Step 1: Assign VLANs to the active ports on S2.
Assign the VLANs to the following ports:
VLAN 10: Fast Ethernet 0/11
VLAN 20: Fast Ethernet 0/18
VLAN 30: Fast Ethernet 0/6
Step 2: Assign VLANs to the active ports on S3.
S3 uses the same VLAN access port assignments as S2.
Step 3: Verify loss of connectivity.
Previously, PCs that shared the same network could ping each other successfully. Try pinging
between PC1 and PC4. Although the access ports are assigned to the appropriate VLANs,
were the pings successful? Why?
Rsta: No tuvo éxito.
What could be done to resolve this issue?
Rsta: Asignando puertos troncales a los Switches
CONCLUSION
Las VLANs son un medio muy poderoso a la hora de gestionar redes de área
local de mediano y gran tamaño. Ampliamente utilizadas hoy en día, el
conocimiento y comprensión de las mismas es fundamental para cualquier
administrador de redes.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 17.5.9 Packet Tracer - Interpret Show Command OutputDocumento8 pagine17.5.9 Packet Tracer - Interpret Show Command OutputliliosorioNessuna valutazione finora
- !!!prueba de Habilidades CCNA VINYDocumento32 pagine!!!prueba de Habilidades CCNA VINYViny Alexander MendietaNessuna valutazione finora
- CS 1.2.1.1 Inicialización y Recarga de Un Router y Un SwitchDocumento9 pagineCS 1.2.1.1 Inicialización y Recarga de Un Router y Un SwitchDiego Lopez67% (3)
- 4.6.5 Packet Tracer - Connect A Wired and Wireless LANDocumento9 pagine4.6.5 Packet Tracer - Connect A Wired and Wireless LANedgar armando marin50% (2)
- 9.1.3-Packet-Tracer - Identify-Mac-And-Ip-Addresses - es-XLDocumento5 pagine9.1.3-Packet-Tracer - Identify-Mac-And-Ip-Addresses - es-XLfabiola fernanda100% (1)
- Packet Tracer Skills Integration ChallengeDocumento5 paginePacket Tracer Skills Integration Challengejefersson velasquez mendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios CCNADocumento12 pagineEjercicios CCNAJose Arturo Perpiñan RuedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea 2 2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic ConnectivityDocumento16 pagineTarea 2 2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic ConnectivityCristian RicauteNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocumento13 pagine2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settingsedgar armando marin100% (1)
- 3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Who Hears The Broadcast - ILMDocumento5 pagine3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Who Hears The Broadcast - ILMAnfred Angelis Cuenca leivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Desarrollo - Practica 3 - IDLTDocumento11 pagineDesarrollo - Practica 3 - IDLTJhonNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge InstructionsDocumento4 pagine9.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge InstructionsYopNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 2 1 4Documento4 pagine8 2 1 4Luis CarrilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Grupo21 Tarea5Documento65 pagineGrupo21 Tarea5gustavohenaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings - ILM-yerly - ChiquilloDocumento17 pagine6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings - ILM-yerly - ChiquillojerryNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocumento6 pagine2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsJari Vega0% (1)
- 1078776901Documento77 pagine1078776901laura0% (1)
- Trabajo Colaborativo 1 - CiscoDocumento52 pagineTrabajo Colaborativo 1 - CiscoGloria Elena Cardenas TamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unad PDFDocumento376 pagineUnad PDFFelipe MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.2.3 Packet Tracer Troubleshooting Static Routes InstructionsDocumento2 pagine2.3.2.3 Packet Tracer Troubleshooting Static Routes InstructionsIsabel HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.1 Packet Tracer - Implement EtherchannelDocumento3 pagine6.4.1 Packet Tracer - Implement Etherchannelwilly perezNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteDocumento7 pagine11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteEdwin ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1.4.6 Lab - SmartlabDocumento24 pagine4.1.4.6 Lab - SmartlabBayron Andres Ruiz AguileraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.9.1 Packet Tracer - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - FerDocumento4 pagine2.9.1 Packet Tracer - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - Feredgar armando marinNessuna valutazione finora
- Unidad 1: Paso 1 - Actividad Colaborativa 1Documento18 pagineUnidad 1: Paso 1 - Actividad Colaborativa 1Edward Mauricio Cárdenas BravoNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - Physical ModeDocumento11 pagine10.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - Physical ModeHidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer: Configuración de Los Parámetros Iniciales Del SwitchDocumento6 paginePacket Tracer: Configuración de Los Parámetros Iniciales Del SwitchAndreaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings Instructions IGDocumento25 pagine2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings Instructions IGhectorNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Comandos Ccna2 v5.0Documento5 pagineManual de Comandos Ccna2 v5.0henrychavezcondeNessuna valutazione finora
- Actividad 1Documento8 pagineActividad 1VALERY ANDREA TIBAQUIRA MORENONessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo Fase2 GrupoxxDocumento13 pagineTrabajo Fase2 GrupoxxDerwin Martinez RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configure DHCPv4 - ILMDocumento4 pagine7.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configure DHCPv4 - ILMjuan guaNessuna valutazione finora
- Actividad Semana 2 Construccion de Actividades de Aprendizaje Integrando TicDocumento8 pagineActividad Semana 2 Construccion de Actividades de Aprendizaje Integrando TicJORGE NIEBLESNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocumento10 pagine6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesAndrés MeloNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.10.2 Practica 7Documento9 pagine11.10.2 Practica 7davidNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.6.1 Packet Tracer - Switch Security Configuration - ILMDocumento3 pagine11.6.1 Packet Tracer - Switch Security Configuration - ILMjuan guaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enrutamiento Por Llamada Telefónica Bajo Demanda (DDR)Documento2 pagineEnrutamiento Por Llamada Telefónica Bajo Demanda (DDR)Miguel Angel Sanz ProvencioNessuna valutazione finora
- Diplomado CiscoDocumento51 pagineDiplomado CiscobussinessNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.6.6 Lab - Calculate IPv4 Subnets RealizadoDocumento4 pagine11.6.6 Lab - Calculate IPv4 Subnets Realizado- OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Avance Documento Final-16-02 CCNPDocumento7 pagineAvance Documento Final-16-02 CCNPluis vladimir cubillos sanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.6.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine TCP and UDP CapturesDocumento28 pagine4.6.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine TCP and UDP CapturesDICO ANessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluacion N°2 - Unidad-2Documento6 pagineEvaluacion N°2 - Unidad-2Victor Rojas0% (1)
- Prueba de Habilidades CcnaDocumento4 paginePrueba de Habilidades CcnaCasildaGoyenecheNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.2.3.4 Lab - Exploring FTPDocumento10 pagine10.2.3.4 Lab - Exploring FTPAnonymous BAkKFO87Dp0% (1)
- Practica 2Documento9 paginePractica 2Juan Miguel MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- Administración Remota y Conectividad Entre Linux y WindowsDocumento8 pagineAdministración Remota y Conectividad Entre Linux y WindowsJuan Miguel MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Resuelto)Documento8 pagine2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Resuelto)Miguel MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Actividad 5.2.2.2: Dominios de Broadcast de Segmentos de Routers.Documento4 pagineActividad 5.2.2.2: Dominios de Broadcast de Segmentos de Routers.Paul Vintimilla TapiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.5.1 Packet Tracer - WLAN Configuration - ILMDocumento4 pagine13.5.1 Packet Tracer - WLAN Configuration - ILMFernando FallaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.3.7 Solución de Problemas de Implementación de VLAN 1Documento15 pagine6.2.3.7 Solución de Problemas de Implementación de VLAN 1ANDRES FELIPE TOLOZA RESTREPONessuna valutazione finora
- Proceso Instalación Servicio IMSDocumento15 pagineProceso Instalación Servicio IMSdraga dragonNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNASv1.1 Chp08 Lab-A-Site2Site-VPN Student - En.es PDFDocumento27 pagineCCNASv1.1 Chp08 Lab-A-Site2Site-VPN Student - En.es PDFJUAN CARLOS BEDOYA MALAMBONessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMDocumento8 pagine4.4.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMEdwin Fabian LievanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuracion de Redes VlanDocumento3 pagineConfiguracion de Redes VlanAndrew Acosta SornozaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3TSM1 - Enciso Montoya Kenia Michelle - P01aDocumento3 pagine3TSM1 - Enciso Montoya Kenia Michelle - P01ak e n i a ;;Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsDocumento3 pagine6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsSaylin NicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.-Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGDocumento3 pagine1.-Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGcyber el parqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Emmanuel Aguirre Pineda - 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions - Documentos de GoogleDocumento3 pagineEmmanuel Aguirre Pineda - 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions - Documentos de GoogleEmmanuel AguirreNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions - ILMDocumento14 pagine6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions - ILMLaura AyalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer: Configuración de Redes VLAN: TopologíaDocumento4 paginePacket Tracer: Configuración de Redes VLAN: TopologíaMarcos Antonio De LeónNessuna valutazione finora
- Enlace de Personal Mes de MayoDocumento6 pagineEnlace de Personal Mes de MayoWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Verificacion SemaforosDocumento1 paginaVerificacion SemaforosWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ensayo Proyecto de GradoDocumento3 pagineEnsayo Proyecto de GradoWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Avance Lab - Remoto - 10.2.3.5 Lab - Configuring Stateless and Stateful DHCPv6Documento23 pagineAvance Lab - Remoto - 10.2.3.5 Lab - Configuring Stateless and Stateful DHCPv6William Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- EXPOCICION 10 BelcyDocumento8 pagineEXPOCICION 10 BelcyWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Matriz de Control de Documentos de VehículosDocumento1 paginaMatriz de Control de Documentos de VehículosWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.2.3.5 Lab - Configuring Stateless and Stateful DHCPv6Documento28 pagine10.2.3.5 Lab - Configuring Stateless and Stateful DHCPv6William Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.3.1.1 IoE and DHCP InstructionsDocumento5 pagine10.3.1.1 IoE and DHCP InstructionsAlex Huertas Urrego0% (1)
- 2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features LABORATORIO REMOTODocumento17 pagine2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features LABORATORIO REMOTOWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fase 1 Fase Inicial de ConocimientoDocumento5 pagineFase 1 Fase Inicial de ConocimientoWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.3.1.1 IoE and DHCP InstructionsDocumento5 pagine10.3.1.1 IoE and DHCP InstructionsAlex Huertas Urrego0% (1)
- Grupo - 203092 - 5 Tarea 3Documento3 pagineGrupo - 203092 - 5 Tarea 3William Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.3.1.1 IoE and DHCP InstructionsDocumento5 pagine10.3.1.1 IoE and DHCP InstructionsAlex Huertas Urrego0% (1)
- FASE Final DO PreguntasDocumento4 pagineFASE Final DO PreguntasWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introcuccion y FundamentosDocumento2 pagineIntrocuccion y FundamentosWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unidad 2 Fase 3 - Identificar Un Problema EpistemológicoDocumento5 pagineUnidad 2 Fase 3 - Identificar Un Problema EpistemológicoWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ip Jesus PulidoDocumento2 pagineIp Jesus PulidoWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Humedales Estrategicos en ColombiaDocumento4 pagineHumedales Estrategicos en ColombiaWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo Colaborativo Actividades A DesarrollarDocumento3 pagineTrabajo Colaborativo Actividades A DesarrollarWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- FASE Final DO PreguntasDocumento4 pagineFASE Final DO PreguntasWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- ACTA de REUNION Proyecto Gas Domiciliario Queja - 2019Documento3 pagineACTA de REUNION Proyecto Gas Domiciliario Queja - 2019William Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unidad 2 Fase 3 - Identificar Un Problema EpistemológicoDocumento5 pagineUnidad 2 Fase 3 - Identificar Un Problema EpistemológicoWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.2.3.2 Packet Tracer - FTP Instructions IGDocumento3 pagine10.2.3.2 Packet Tracer - FTP Instructions IGAnonymous MIt76IXuxNessuna valutazione finora
- Cuadro Problemas EpistemologicosDocumento2 pagineCuadro Problemas EpistemologicosWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutela YurianaDocumento2 pagineTutela YurianaWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Historia de ColombiaDocumento3 pagineHistoria de ColombiaWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Proyecto de GulupaDocumento7 pagineProyecto de GulupaWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Proyecto de GulupaDocumento8 pagineProyecto de GulupaWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Historia de ColombiaDocumento2 pagineHistoria de ColombiaWilliam Orlando GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajpo Del ChirinosDocumento8 pagineTrabajpo Del Chirinosleo100% (1)
- Práctica N ° 04 - Cata de CaféDocumento31 paginePráctica N ° 04 - Cata de CaféLIZ MILAGROS BURGA CARONessuna valutazione finora
- Ses-Mart-Tut-La Importancia de La Autonomía para La Toma DecisionesDocumento5 pagineSes-Mart-Tut-La Importancia de La Autonomía para La Toma DecisionesOscar ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.anexo Certificado Marcado CEDocumento1 pagina2.anexo Certificado Marcado CElydiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inf. Fuente Señalizacion VialDocumento4 pagineInf. Fuente Señalizacion VialZ�SIMO VARGAS TORRENessuna valutazione finora
- Microempresa PDFDocumento10 pagineMicroempresa PDFWilly GalvezNessuna valutazione finora
- Camino Del IncaDocumento1 paginaCamino Del Incacaminoinca1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 The Cell Cycle and Its Regulation ADocumento26 pagine2020 The Cell Cycle and Its Regulation ATOMAS DAVID CHICA LLAMASNessuna valutazione finora
- Tratados Internacionales Del Medio AmbienteDocumento23 pagineTratados Internacionales Del Medio AmbienteCompu InteligenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cien Años de Soledad y La ArquitecturaDocumento4 pagineCien Años de Soledad y La ArquitecturaLina Fernanda Gomez ErazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medición de Los CristalesDocumento25 pagineMedición de Los CristalesRonald Richard Quiliche GalvezNessuna valutazione finora
- Practica 15Documento6 paginePractica 15MARIA LOURDES SILVA GARCIANessuna valutazione finora
- Farmacologia Aplicada A La EnfermeríaDocumento16 pagineFarmacologia Aplicada A La EnfermeríaNikol Oroz riveraNessuna valutazione finora
- EXAMEN FINAL AG 2021 J. Vasquez.Documento5 pagineEXAMEN FINAL AG 2021 J. Vasquez.Juan Eduardo Vasquez CarrisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Act. 2. - Cuadro de Concentración Principios Pedagógicos.-1Documento9 pagineAct. 2. - Cuadro de Concentración Principios Pedagógicos.-1Margarita Del Rocio Cano MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ensayo Propiedad Intelectual y Su Importancia en La Sociedad GuatemaltecaDocumento9 pagineEnsayo Propiedad Intelectual y Su Importancia en La Sociedad GuatemaltecaKrls Prz100% (1)
- Ensayo Sobre Las Propiedades de Los Signos.Documento6 pagineEnsayo Sobre Las Propiedades de Los Signos.Oscar AritaNessuna valutazione finora
- SSE 7 SECUNDARIA - Educación FísicaDocumento8 pagineSSE 7 SECUNDARIA - Educación FísicasebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- Tecnicas Predictivas TermografiaDocumento6 pagineTecnicas Predictivas TermografiaAleymar Arturo Travi JojoaNessuna valutazione finora
- RelevadoresDocumento56 pagineRelevadoresVania YerenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseño de Vestuario ColonialDocumento7 pagineDiseño de Vestuario Colonialdiego sanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- DPC For 001 Transmittal BravanteDocumento17 pagineDPC For 001 Transmittal BravanteLUISA RICONessuna valutazione finora
- Provisión de Acompañamiento A Mujeres Víctimas de Violencia Por Mujeres de La Comunidad Capacitadas y ArticuladasDocumento1 paginaProvisión de Acompañamiento A Mujeres Víctimas de Violencia Por Mujeres de La Comunidad Capacitadas y ArticuladasBaneza Puma MamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Me 2023 112201499 Apn Dpo%pfaDocumento2 pagineMe 2023 112201499 Apn Dpo%pfaEmiliano GranjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organiza Tu TiempoDocumento21 pagineOrganiza Tu TiempomelissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electiva 1 Fundamentos Instr. Ind.Documento7 pagineElectiva 1 Fundamentos Instr. Ind.Henry Eliecer Vega LobatonNessuna valutazione finora
- Actividades de TrigonometrÍaDocumento1 paginaActividades de TrigonometrÍasalonsosanz100% (1)
- 1.0. Memoria Descriptiva AcobambaDocumento34 pagine1.0. Memoria Descriptiva AcobambaEvelyn Jesus RiosNessuna valutazione finora
- PCR-Tiempo Real (PCR-RT) Hisopado Nasofaringeo 10/03/2021 Positivo 10/03/2021 Interpretación de ResultadosDocumento1 paginaPCR-Tiempo Real (PCR-RT) Hisopado Nasofaringeo 10/03/2021 Positivo 10/03/2021 Interpretación de ResultadosTORTA ReposteríaNessuna valutazione finora
- Contrato de Prestación de Servicios Personales IndependientesDocumento6 pagineContrato de Prestación de Servicios Personales IndependientesDelia GalvánNessuna valutazione finora