Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nonchromosomal Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria: Genetic Transformation of Escherichia Coli by R-Factor DNA
Caricato da
MicroposterDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nonchromosomal Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria: Genetic Transformation of Escherichia Coli by R-Factor DNA
Caricato da
MicroposterCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nonchromosomal Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria: Genetic Transformation
Of Escherichia coli by R-Factor DNA.
Sidra Zafar
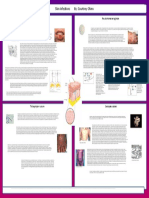
Introduction Methods Results 1 Results Conclusion
Bacterial Strains and R Factors: Expression of Antibiotic Resistance by Competent • This experiment shows that purified R-factor DNA can
The rapid spread of antibiotic resistance in microbes is
Cells transform Escherichia coli treated with CaCl2 to
a growing biological concern around the world. David • I-like - R factor( R64-11) which specifies resistant to
and Barry Zimmerman, in their book, the Killer Germs, • The kinetics of transformation of drug-sensitive multiple antibiotic resistance.
tetracycline ( Tc) and Streptomycin ( Sm) were used and
state that microbes are finding ways to counteract or F-like R factor that carries resistance to kanamycin Escherichia coli to kanamycin resistance by closed R6 • Closed and open circular forms of R-factor DNA are
neutralize the effects of antibiotics, making them ( Km), neomycin ( Nm), Choloramphenical ( Cm) and DNA is shown in Fig 1. Resistance to Kanamycin was both capable of transforming cells into antibiotic
useless. This led to the question: Can bacteria be Sulphonomide ( Su) was used. seen immediately by a small fraction of cells treated resistant but open cells may denaturize.
genetically transformed to become antibiotic resistant with Calcium chloride after uptake of R-factor DNA.
in the laboratory? if yes, how can this help us in the DNA prep: • Escherichia coli cells that have been transformed by
Effect of DNA Concentration R-factor contain an independently replicating closed
future? Cohen, Chang and Hsu answered this • Covalently closed R factor DNA was isolated and
question in their experiment on Non- chromosomal • Transformation ability of several different circular DNA species identical to R-factor parent and
purified from Escherichia Coli.
antibiotic resistance in bacteria: the Genetic concentrations of closed circular R6 DNA is shown in can also transfer this by conjugation.
transformation of Escherichia coli by R- Factor DNA. Transformation Reaction mixture: fig 2. A linear relationship of transformation frequency • This shows that DNA from both F-like and I-like R
The experiment shows the transformation of • Escherichia coli was grown at 37° with OD of 0.85 at to DNA concentration was seen, meaning higher factor is capable of transforming Escherichia coli into
Escherichia coli cells treated with Calcium chloride to 590 nm. Cells, chilled and centrifuged. After concentration of DNA platted equals higher antibiotic resistant cells.
multiple antibiotic resistance by purified R-factor*. The centrifugation, bacteria were re-suspended in 1/2 original transformation to resistant cells. About 105 transformed
scientists report that treatment of Escherichia coli cells bacteria were obtained per micro gram of R-factor • The observation that DNA obtained from non-
volume of calcium chloride and kept at 0° for 20 mins. Fig 1. Kinetics of expression of Kanamycin resistance in transformed
with calcium chloride makes the Escherichia coli Escherichia coli . After incubation of CaCl2 treated cells with R6 DNA, DNA. transmissible plasmid is able to transform Escherichia
capable of taking up molecules of R-factor (drug • 0.2 ml of cells treated with Calcium were added to 0.1 bacteria diluted 10 –folds into antibiotic free broth. At times shown, coli indicates the important use of this method for future
ml of DNA solution and incubated for 60 mins at 0°. samples of bacteria spread onto agar plates containing kanamycin: Requirements for Transformation by R-Factor DNA investigation of non transferable independently
resistant) DNA. Drug resistance is seen in a small
incubated over night 37° for determination of number of transformants. An replicating species of plasmid DNA.
fraction of the bacterial population immediately after • Bacteria then heat pulsed for 2 mins allowing uptake of identical sample was plated on antibiotic-free nutrient agar to determine • The experiment also showed that closed circular R6
uptake of DNA. They also find that the introduced R- R factor DNA, chilled and platted onto agar containing total viable cells. Transformation frequency is expressed in terms of the DNA have the best transformation ability. Although • Further investigation and knowledge about the
factor DNA can persist in these cells as an appropriate antibiotics or diluted 10 times in L broth. number of kanamycin resistant bacteria relative to total number of viable circular open DNA have the ability to transform, the transformational capabilities of other bacterial
independently replicating plasmid, and has the same cells. denaturing abolish the transforming ability of open organisms using these methods can possibly help
reproduction and antibiotic resistance functions as that • Cell survival was greater then 50% after CaCl2 treatment circular R-factor DNA. diminish bacterial resistance of antibiotics.
of the parent R-factor. and heat pulse.
Expression of Different Drug Resistance Markers in
• Drug resistance was assayed on nutrient agar plates Transformed Bacteria
with the antibiotics indicated.
*Genetic component of bacteria that provides • Table 2 shows transformation of Escherichia coli for
resistance to antibiotics and can be transferred from various antibiotic resistance markers carried by R6
one bacterium to another by conjugation. Results 2 DNA. Escherichia coli transformed and became
resistant to all antibiotics except Streptomycin. It is
TABLE 2. Expression of different drug resistance markers in possible that expression of Sn marker in transformed
transformed bacteria. bacteria may require more incubation in antibiotic free
Number resistance to medium then used in this experiment.
References
Fig 2. Effect of concentration of R-factor DNA on transformation frequency. Stanley N. Cohen, Annie C.Y Chang,Leslie Hsu, Nonchromosomal Antibiotic
Various concentrations of covalently-closed R6 DNA were assayed for their ability to Resistance in Bacteria: Genetic Transformation of Escherichia coli by R-Factor
transform calcium chloride treated Escherichia coli cells to kanamycin resistance. DNA, Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA Vol.69, No.8,pp.2110-2114, August 1972
Transformation frequency was determined after 120-min incubation in antibiotic-free Barry E. Zimmerman, David J. Zimmerman, The Killer Germs, USA, McGraw-hill
Table 2: After transformation of calcium chloride- treated
medium to allow complete expression of Km resistance. Companies, september 2002.
Escherichia coli by R6, samples of bacterial cultures were
spread onto plates containing the antibiotics indicated.
Separate bacterial clones isolated from each antibiotic
plate were examined for the presence of other antibiotic
resistance determinants by stabbing colony samples onto
appropriate drug-containing plates.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocumento1 paginaPathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens of The Vagina-CitationsDocumento1 paginaPathogens of The Vagina-CitationsMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Infections of The Liver Revised - Nick GriffinDocumento1 paginaInfections of The Liver Revised - Nick GriffinMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive Site, Erika HuertaDocumento1 paginaPathogens of The Female Reproductive Site, Erika HuertaMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens in The Lungs-Jeffrey DelgadilloDocumento1 paginaPathogens in The Lungs-Jeffrey DelgadilloMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Jesse Wackerbarth - CNS Pathogens RevisedDocumento1 paginaJesse Wackerbarth - CNS Pathogens RevisedMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Infections by Allison BakerDocumento1 paginaEye Infections by Allison BakerMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Wylie, ClareDocumento1 paginaWylie, ClareMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Savannah Whitington: Your Brain On DrugsDocumento1 paginaSavannah Whitington: Your Brain On DrugsMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaDocumento1 paginaPathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver PathogensDocumento1 paginaLiver PathogensMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urogenital Tract-Maija SwansonDocumento1 paginaThe Urogenital Tract-Maija Swansonmswanson5975Nessuna valutazione finora
- Emily Scroggs Microorganisms Affecting The KidneyDocumento1 paginaEmily Scroggs Microorganisms Affecting The KidneyMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowDocumento1 paginaPathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinDocumento1 paginaPathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Lung Infections - Jessica de AndaDocumento1 paginaLung Infections - Jessica de AndaMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- EarInfections FatimaKhalidDocumento1 paginaEarInfections FatimaKhalidMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS Pathogens-Jesse WackerbarthDocumento1 paginaCNS Pathogens-Jesse WackerbarthMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogen (Poster Med Micro)Documento1 paginaPathogen (Poster Med Micro)joejackson6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gaby Saenz - The MeningesDocumento1 paginaGaby Saenz - The MeningesMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Zach Lee - Mouth MicrobesDocumento1 paginaZach Lee - Mouth MicrobesMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie EspinosaDocumento1 paginaPathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosaannie_espinosa_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- BlaC Genes and The Battle Against B-Lactamse in MDA TuberculosisDocumento1 paginaBlaC Genes and The Battle Against B-Lactamse in MDA TuberculosisMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Courtney Chinn - Skin InfectionsDocumento1 paginaCourtney Chinn - Skin InfectionsMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Maladies of The Heart - Milan KantariaDocumento1 paginaMaladies of The Heart - Milan KantariaMicroposterNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Etiology of HIV and AIDSDocumento3 pagineEtiology of HIV and AIDSAnggy PrayudhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Capstone Essay-2Documento10 pagineCapstone Essay-2api-460858215Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kernow LMC Newsletter - August 2019 Edition FINAL USEDocumento15 pagineKernow LMC Newsletter - August 2019 Edition FINAL USECornwall and Isles of Scilly LMCNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Eczema: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocumento19 pagineDermatology Eczema: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAiman Tymer100% (1)
- EssayDocumento61 pagineEssayRevina AmaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Indicators FormulasDocumento2 pagineHealth Indicators Formulaskristinetan21Nessuna valutazione finora
- DR Nur Farhanah SPPD - Penggunaan AB Rasional 1 PDFDocumento16 pagineDR Nur Farhanah SPPD - Penggunaan AB Rasional 1 PDFFlorantia Setya NugrohoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quest A Key To Ug Paediatrics PDFDocumento192 pagineQuest A Key To Ug Paediatrics PDFSpice Reader100% (6)
- Chapter 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology1926Documento33 pagineChapter 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology1926Liezel CauilanNessuna valutazione finora
- VirologyLearnTable 2017-Sketchy PDFDocumento4 pagineVirologyLearnTable 2017-Sketchy PDFdfgbdfgNessuna valutazione finora
- Articulo de Biomedicina 1 de Diciembre 2020Documento5 pagineArticulo de Biomedicina 1 de Diciembre 2020Alejandro SousaNessuna valutazione finora
- Australia Visa PDFDocumento6 pagineAustralia Visa PDFminjiew50% (2)
- Welcome Homeopathy - Dr. S. C. MadanDocumento195 pagineWelcome Homeopathy - Dr. S. C. Madanreza100% (4)
- Slide Pediatric TuberculosisDocumento112 pagineSlide Pediatric TuberculosisFenny RahmadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Health 7 4th Grading DiscussionDocumento14 pagineHealth 7 4th Grading Discussionivy quirogNessuna valutazione finora
- Enfermedades EmergentesDocumento216 pagineEnfermedades EmergentesCaaarolNessuna valutazione finora
- Leishmaniasis KuliahDocumento28 pagineLeishmaniasis KuliahNadiya KusnadiNessuna valutazione finora
- River Valley News Shopper, August 8, 2011Documento36 pagineRiver Valley News Shopper, August 8, 2011Pioneer GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Vac-Status Team Member QA FINAL 1-20-22Documento7 pagineVac-Status Team Member QA FINAL 1-20-22Jim HoftNessuna valutazione finora
- School TB Case Letterhead 12.29.16Documento2 pagineSchool TB Case Letterhead 12.29.16Hank LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 MOH Questions of PROMETRIC Licensing Exam For General PractitionersDocumento3 pagine2016 MOH Questions of PROMETRIC Licensing Exam For General Practitionersibrahim 12Nessuna valutazione finora
- C5. Viral VaccineDocumento16 pagineC5. Viral VaccineBen BuddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pfizer Killed Your Friends Amp Family For Profit 92 of COVID Deaths Were Among The Triple VaccinatedDocumento7 paginePfizer Killed Your Friends Amp Family For Profit 92 of COVID Deaths Were Among The Triple VaccinatedmikeNessuna valutazione finora
- 432 One Great SummerDocumento1 pagina432 One Great SummerElishaDaceyNessuna valutazione finora
- Improved Chicken RearingDocumento4 pagineImproved Chicken RearingAnonymous asCQ7N7GVNessuna valutazione finora
- COVID-19 Quarantine and Isolation - CDCDocumento10 pagineCOVID-19 Quarantine and Isolation - CDCFraulein LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Iap Guide Book On Immunization Iap Immunization Time Table 2011Documento1 paginaIap Guide Book On Immunization Iap Immunization Time Table 2011Gaurav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Layer Chicken FarmingDocumento18 pagineLayer Chicken FarmingKhampa Ngawang Phuntsho100% (4)
- Respiratory VirusesDocumento123 pagineRespiratory VirusesvaidyamNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Plan MrsiaDocumento1 paginaActivity Plan MrsiaChristopher Lirasan Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora