Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Maths Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2018
Caricato da
buban8888Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Maths Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2018
Caricato da
buban8888Copyright:
Formati disponibili
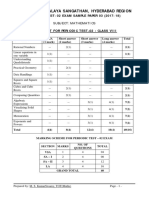
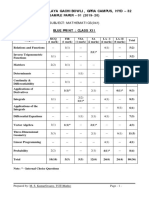
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 04 (2017-18)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041)
BLUE PRINT : CLASS X
VSA SA – I SA – II LA Unit
Unit Chapter Total
(1 mark) (2 marks) (3 marks) (4 marks) Total
Number
system
Real Numbers 1(1) 2(1) 3(1) -- 6(3) 6(3)
Polynomials -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1)
Pair of Linear Equations
Algebra
-- 2(1) 3(1) -- 5(2)
in two variables
20(8)
Quadratic Equations 1(1) -- -- 4(1)* 5(2)
Arithmetic progression 1(1) 2(1) -- 4(1) 7(3)
Coordinate
Geometry
Coordinate Geometry 1(1) 2(1) 3(1)* -- 6(3) 6(3)
Trigonometry
Introduction to
1(1) -- 3(1)* 4(1) 8(3)
Trigonometry
12(4)
Some Applications of
-- -- -- 4(1) 4(1)
Trigonometry
Triangles 1(1) 3(1)* 4(1)* 8(3)
Geometry
Circles -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1) 15(5)
Constructions -- -- -- 4(1) 4(1)
Mensuration
Areas Related to Circles -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1)
10(3)
Surface Areas and
-- -- 3(1)* 4(1) 7(2)
Volumes
Statistics &
probability
Statistics -- -- 3(1) 4(1)* 7(2)
11(4)
Probability -- 4(2) -- -- 4(2)
Total 6(6) 12(6) 30(10) 32(8) 80(30) 80(30)
Note: * - Internal Choice Questions
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 04 (2017-18)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : X DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instruction:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) This question paper contains 30 questions divided into four Sections A, B, C and D.
(iii) Section A comprises of 6 questions of 1 mark each. Section B comprises of 6 questions of 2
marks each. Section C comprises of 10 questions of 3 marks each and Section D comprises of 8
questions of 4 marks each.
(iv) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in four questions of 3
marks each and three questions of 4 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all
such questions.
(v) Use of Calculators is not permitted
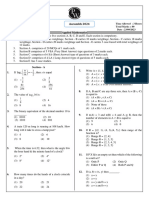
SECTION – A
Questions 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
1 1 p 1 2 p
1. Find the common difference of the AP: , , ,.......
p p p
2. Show that 12n cannot end with the digit 0 or 5 for any natural number n.
3. Find the value of k for which the quadratic equation 4x2 – 3kx + 1 = 0 has two real equal roots.
4. If A(6, –1), B(1, 3) and C(k, 8) are three points such that AB= BC, find the value of k.
1 1
5. If cos , sin then find the value of .
2 2
AD 3
6. In triangle ABC, DE || BC and .If AC = 4.8 cm, find AE.
DB 5
SECTION – B
Questions 6 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
7. Prove that the points (7, 10), (−2, 5) and (3, −4) are the vertices of an isosceles right triangle.
8. Find the least number which when divided by 6, 15 and 18 leave remainder 5 in each case.
9. A card is drawn at random from a well shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability
that the drawn card is (i) neither a king nor a queen (ii) red queen card.
10. A box contains 90 discs, numbered from 1 to 90. If one disc is drawn at random from the box,
find the probability that it bears (i) a prime-number less than 23 (ii) a perfect square number.
11. Find the value of k, so that the following system of equations has no solution:
3 x y 1; (2k 1) x (k 1) y (2k 1).
12. How many three digit natural numbers are divisible by 7?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
SECTION – C
Questions 13 to 22 carry 3 marks each.
13. Prove that 2 3 is an irrational number.
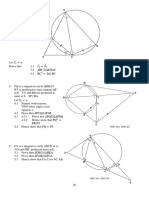
14. In the below figure, the line segment XY is parallel to side AC of ABC and it divides the
AX
triangle into two equal parts of equal areas. Find the ratio .
AB
OR
Sides AB and AC and median AD of a triangle ABC are respectively proportional to sides PQ
and PR and median PM of another triangle PQR. Show that ABC ~ PQR.
15. The three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A(3, −4), B(−1, −3) and C(−6, 2). Find the
coordinates of vertex D.
OR
In the below figure, find the area of triangle ABC (in sq. units).
16. In the above right sided figure, a circle inscribed in triangle ABC touches its sides AB, BC and
AC at points D, E and F respectively. If AB = 12 cm, BC = 8 cm and AC = 10 cm, then find the
lengths of AD, BE and CF.
17. The sum of a two-digit number and the number formed by interchanging its digit is 110. If 10 is
subtracted from the original number, the new number is 4 more than 5 times the sum of the
digits of the original number. Find the original number.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
18. In the below figure, AB and CD are two diameters of a circle with centre O, which are
perpendicular to each other. OB is the diameter of the smaller circle. If OA = 7 cm, find the area
of the shaded region. (use = 22/7)
19. If and are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = 3x2 – 4x + 1, then find a quadratic
2 2
polynomial whose zeroes are and .
20. A vessel is in the form of hemispherical bowl surmounted by a hollow cylinder of same
diameter. The diameter of the hemispherical bowl is 14 cm and the total height of the vessel is
13 cm. Find the total surface area of the vessel. (use = 22/7)
OR
A wooden toy was made by scooping out a hemisphere of same radius from each end of a solid
cylinder. If the height of the cylinder is 10 cm, and its base is of radius 3.5 cm, find the volume
of wood in the toy. (use = 22/7)
3cos 550 4(cos 700 cos ec 200 )
21. Evaluate:
7sin 350 7(tan 50 tan 250 tan 450 tan 650 tan 850 )
OR
If x = a sin b cos and y = a cos b sin , prove that x 2 y 2 a 2 b 2 .
22. An aircraft has 120 passenger seats. The number of seats occupied during 100 flights is given
below:
No. of seats 100-104 104-108 108-112 112-116 116-120
Frequency 15 20 32 18 15
Determine the mean number of seats occupied over the flights
SECTION – D
Questions 23 to 30 carry 4 marks each.
23. A fire in a building B is reported on telephone to two fire stations P and Q, 20 km apart from
each other on a straight road. P observes that the fire is at an angle of 60° to the road and Q
observes that it is at an angle of 45° to the road.
(a) Which station should send its team and how much will this team have to travel?
(b) What according to you, are the values displayed by the teams at fire stations P and Q.
24. Construct a triangle with sides 5 cm, 4 cm and 6 cm. Then construct another triangle whose
2
sides are times the corresponding sides of first triangle.
3
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
1 1
25. Find the number of terms of the AP 18,15 ,13,........., 49 and find the sum of all its terms.
2 2
26. A peacock is sitting on the top of a pillar, which is 9m high. From a point 27 m away from the
bottom of the pillar, a snake is coming to its hole at the base of the pillar. Seeing the snake the
peacock pounches on it. If their speeds are equal at what distance from the whole is the snake
caught?
OR
In a class test, the sum of the marks obtained by P in mathematics and science is 28. Had he got
3 more marks in mathematics and 4 marks less in science, the product of marks obtained in the
two subjects would have been 180. Find the marks obtained by him in the two subjects
separately.
27. A bucket open at the top, and made up of a metal sheet is in the form of a frustum of a cone.
The depth of the bucket is 24 cm and the diameters of its upper and lower circular ends are 30
cm and 10 cm respectively. Find the cost of metal sheet used in it at the rate of Rs 10 per 100
cm2. [Use π = 3.14]
1 1
28. If sec = x + , Prove that sec + tan = 2x or .
4x 2x
29. Prove that “In a triangle, if the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other
two sides, then the angle opposite to the first side is a right angle.
OR
Prove that “If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in
distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio”.
30. From the following data, draw the two types of cumulative frequency curves and determine the
median from the graph.
Height(in cm) Frequency
140-144 3
144-148 9
148-152 24
152-156 31
156-160 42
160-164 64
164-168 75
168-172 82
172-176 86
176-180 34
OR
Compare the modal ages of two groups of students appearing for an entrance examination:
Age(in years) 16-18 18-20 20-22 22-24 24-26
Group A 50 78 46 28 23
Group B 54 89 40 25 17
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chemistry ProjectDocumento51 pagineChemistry ProjectSiddhanth AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2018Documento6 pagineMaths Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2018jay danenjeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Documento5 pagineMaths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Írfäñ MøhdNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018 3Documento5 pagineMaths Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018 3Írfäñ MøhdNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2018 2Documento5 pagineMaths Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2018 2Írfäñ MøhdNessuna valutazione finora
- 1279188485maths Class X Sample Paper 02 For Board Exam 2019Documento5 pagine1279188485maths Class X Sample Paper 02 For Board Exam 2019Kamal govadaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1333912206maths Class X Sample Paper 10 For Board Exam 2019Documento5 pagine1333912206maths Class X Sample Paper 10 For Board Exam 2019CYBER DUDE PLAYSNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Documento5 pagineMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Icse 2011 Maths Solution 1aDocumento5 pagineIcse 2011 Maths Solution 1aSanjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Documento5 pagineMaths Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01veeNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Sample Paper 01 For Sessing Ending Exam (2017-18)Documento5 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Sample Paper 01 For Sessing Ending Exam (2017-18)SanjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Documento5 pagineMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Documento5 pagineMaths Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Mathematics (041) (Standard)Documento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Mathematics (041) (Standard)ShrikantNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Documento5 pagineMaths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Areeb GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Documento5 pagineMaths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Anonymous TvppppNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Basic Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Documento6 pagineMaths Basic Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Sahu Sahuji AyushNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Basic Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Documento6 pagineMaths Basic Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Dharmendra SankhlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Periodic Test-03 Exam Sample Paper 01 (2018-19)Documento5 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Periodic Test-03 Exam Sample Paper 01 (2018-19)AdtNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Xi See Sample Paper 05 For 2016 17Documento4 pagineMaths Class Xi See Sample Paper 05 For 2016 17hydrogenproton1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03 2020 21Documento8 pagineMaths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03 2020 21Psy KoTeaYenNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Practice QuestionsDocumento5 pagineMaths Practice QuestionsKiyotakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Documento3 pagineMaths Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Xi Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 For 2020 21Documento6 pagineMaths Class Xi Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 For 2020 21Srijita SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 (2017-18)Documento4 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 (2017-18)Jayashree Krishnakumar PillaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02Documento6 pagineMaths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 02Sonali SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01 2020 21Documento8 pagineMaths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01 2020 21Psy KoTeaYenNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02 2020 21Documento9 pagineMaths Class Ix Session Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02 2020 21Psy KoTeaYenNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Documento3 pagineMaths Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Documento3 pagineMaths Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Viii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Documento3 pagineMaths Class Viii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Ravi KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Viii Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Documento6 pagineMaths Class Viii Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Volety Sai SudheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 03Documento4 pagineMaths Class X Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 03saikeerthanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Vii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 01Documento3 pagineMaths Class Vii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 01SreeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020 PDFDocumento5 pagineMaths Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020 PDFRajasri RsNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Documento4 pagineMaths Class X Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Sai dineshNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class VII Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Documento3 pagineMaths Class VII Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Shib Shankar PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class 9 Sample Paper FinalDocumento32 pagineMaths Class 9 Sample Paper FinalManuvendra Kumar GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Ix Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 03Documento4 pagineMaths Class Ix Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 03Harsh kanyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Documento4 pagineMaths Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Nooman ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 02 1Documento5 pagineMaths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 02 1ahmedmansurr98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Half Yearly Test Paper - Applied MathematicsDocumento4 pagineHalf Yearly Test Paper - Applied Mathematicslohiyadhrumil2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1745806749maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 02Documento5 pagine1745806749maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 02AdtNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabi and Zainab International School Panshekara, Kano.: End of First Term ExaminationDocumento2 pagineRabi and Zainab International School Panshekara, Kano.: End of First Term ExaminationRabiu KabirNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 01Documento6 pagineMaths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Revised Sample Paper 01Bhavya JangidNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Documento5 pagineMaths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Nashra KhanamNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03 1Documento5 pagineMaths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03 1ahmedmansurr98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Documento6 pagineMaths Class VIII Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01Latha RajaiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Algone12023 ExamDocumento28 pagineAlgone12023 Exammitboyusa17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manoj Chauhan Sir: Mathematics byDocumento30 pagineManoj Chauhan Sir: Mathematics byRaval sagarNessuna valutazione finora
- 10-Math PB-2-set-2Documento6 pagine10-Math PB-2-set-2priya chandanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths-BP (241) - SET-BDocumento1 paginaMaths-BP (241) - SET-Bamankumar193023Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Xi Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01 2019Documento5 pagineMaths Class Xi Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01 2019neomatrix70Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1Documento5 pagineMaths Class VII Session Ending Exam 2020 Sample Paper 01 1ahmedmansurr98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dpp-2 English PC BwyryeuDocumento7 pagineDpp-2 English PC Bwyryeum2595jn9d9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class Xii Mock Test Paper 05 For 2017 18Documento4 pagineMaths Class Xii Mock Test Paper 05 For 2017 18aaryangargNessuna valutazione finora
- Arihant CAT Practice Set 1 With Solutions PDFDocumento23 pagineArihant CAT Practice Set 1 With Solutions PDFSubhajit SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Set Theory NDocumento6 pagineSet Theory Nkaeshav manivannanNessuna valutazione finora
- SQP-3 Maths Basic Class 10Documento13 pagineSQP-3 Maths Basic Class 10NiPPUN BHARDWAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Staff Selection CommissionDocumento1 paginaStaff Selection Commissionbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- www.crackingpatching.com.txtDocumento1 paginawww.crackingpatching.com.txtbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Annexure-I Candidate'S Statement and DeclarationDocumento5 pagineAnnexure-I Candidate'S Statement and Declarationbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- MSRNDocumento1 paginaMSRNbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transcoder FunctionsDocumento1 paginaTranscoder Functionsbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technologies Used in Telecommunication NetworksDocumento18 pagineTechnologies Used in Telecommunication Networksbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- In SignallingInAP CAP Operation ListDocumento4 pagineIn SignallingInAP CAP Operation Listbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- An RaxDocumento42 pagineAn Raxbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- in SignallingInAP CAP Operation List PDFDocumento3 paginein SignallingInAP CAP Operation List PDFbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- C-Dot 256p An-Rax (Isdn) User ManualDocumento50 pagineC-Dot 256p An-Rax (Isdn) User Manualbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
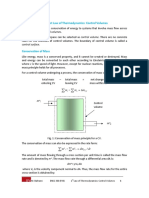
- First Law of Thermodynamics - Control VolumesDocumento11 pagineFirst Law of Thermodynamics - Control Volumesbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- CBT PDFDocumento1 paginaCBT PDFbuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Essay On Digital India About 400-500 Words - BrainlyDocumento1 paginaEssay On Digital India About 400-500 Words - Brainlybuban8888100% (1)
- Essay On Digital India About 400-500 Words - BrainlyDocumento1 paginaEssay On Digital India About 400-500 Words - Brainlybuban8888100% (1)
- For VodafoneDocumento1 paginaFor Vodafonebuban8888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cert-Ece Mathematics: Final CoachingDocumento7 pagineCert-Ece Mathematics: Final CoachingHary KrizNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 22Documento6 pagineProblem Set 22Reynaldo Martin Coloma Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting: Week Three SolutionsDocumento10 pagineCombinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting: Week Three SolutionsSandeep SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Secant and Tangent LinesDocumento6 pagineSecant and Tangent LinesHammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Teachers Name: Mr. Vanbogaert Name of Unit: Congruency Proofs and Everything in BetweenDocumento23 pagineTeachers Name: Mr. Vanbogaert Name of Unit: Congruency Proofs and Everything in BetweenRyan VanBogaertNessuna valutazione finora
- Koleksi Soalan Matematik Tambahan SPM 2004-2009-DifferentiationDocumento10 pagineKoleksi Soalan Matematik Tambahan SPM 2004-2009-DifferentiationSforazzura Suhaimi50% (6)
- JIT TERM 1 Geometry Document For Collation - RemovedDocumento4 pagineJIT TERM 1 Geometry Document For Collation - RemovedafikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphing Rational FunctionDocumento33 pagineGraphing Rational FunctionLavigne EmphasisNessuna valutazione finora
- Triangle CongruenceDocumento7 pagineTriangle CongruenceJay UsNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: NAME - SCOREDocumento5 pagineDepartment of Education: NAME - SCOREMarites James - LomibaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre - Calculus: Conics: CirclesDocumento18 paginePre - Calculus: Conics: CirclesPororoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trignometry DDocumento12 pagineTrignometry DAvianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tmta Precalculus Exam 2011Documento13 pagineTmta Precalculus Exam 2011iitforumNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Science Project Work Session Ending Exam 2013-14Documento39 pagineComputer Science Project Work Session Ending Exam 2013-14Rahul SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pert Mathematics Formula SheetDocumento16 paginePert Mathematics Formula SheetNathan HurwitzNessuna valutazione finora
- First Periodic Test: RD RDDocumento13 pagineFirst Periodic Test: RD RDJUVELYN BELLITANessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 22Documento10 pagineLesson 22Jeany Pearl EltagondeNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1W1 DIVISIBILITY RULES 2510 and 369Documento63 pagineQ1W1 DIVISIBILITY RULES 2510 and 369MaicaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Quarter EXAM FinalDocumento7 pagine3rd Quarter EXAM FinalJudelyn ParungaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pseudo PrimesDocumento10 paginePseudo PrimesyeshaNessuna valutazione finora
- ASMO 2019 Maths Grade 7Documento10 pagineASMO 2019 Maths Grade 7anthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12 Mathematics Exam Question PapersDocumento14 pagineGrade 12 Mathematics Exam Question PapersMaggie kaimbaNessuna valutazione finora
- 30 C 1 Mathematics StandardDocumento23 pagine30 C 1 Mathematics Standard131079kunjanNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs Short Questions Math FSC Part1Documento62 pagineMCQs Short Questions Math FSC Part1yumnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11: National Senior CertificateDocumento16 pagineGrade 11: National Senior Certificaterowan chibiNessuna valutazione finora
- Number System and Counting Atreya RoyDocumento26 pagineNumber System and Counting Atreya RoyPramod BeriNessuna valutazione finora
- SolidDocumento23 pagineSolidhkpatel9Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3D Analytical GeometryDocumento3 pagine3D Analytical GeometryMadhurya ManiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ched Precalculus Part5Documento50 pagineChed Precalculus Part5Rashid IgnacioNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 Inverse Trigo Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)Documento4 pagineCH 2 Inverse Trigo Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)CRPF School67% (3)