Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Transmission Line Loss Calculation TL
Caricato da
Manohar Das0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
89 visualizzazioni1 paginaThe document is prepared for loss calculation of transmission , running on panther ACSR
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document is prepared for loss calculation of transmission , running on panther ACSR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
89 visualizzazioni1 paginaTransmission Line Loss Calculation TL
Caricato da
Manohar DasThe document is prepared for loss calculation of transmission , running on panther ACSR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
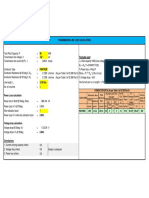
TRANSMISSION LINE LOSS CALCULATION
Total Plant Capacity, P = 80 MW
Transmission line voltage, V = 132 kV Formulae used
Transmission line current @ FL, I = 349.91 Amps I = Plant capacity*1000/(Line voltage*√3))
RT = R20*(1+0.00403*(T-20))
Conductor Type = PANTHER % Power loss = Ploss/P
Conductor Resistance @ 20 deg C, R20 = 0.1390 ohm/km (As per Table 3 of IS 398 Part II) Ploss = 3* I2* R20* L/(No of runs)
Conductor Resistance @ 50 deg C, RT = 0.1558 ohm/km (As per Table 3 of IS 398 Part II) % Voltage drop = Vd/V
Line length, L = 12.00 km Vd=Current per run x Length x 1.732x R20
No. of runs/ckts. = 1
CONDUCTOR DATA (As per Table 3 of IS 398 Part II)
Stranding and Wire Overal DC
Power Loss calculation Aluminium Area Total Current
Diameter l Dia. Approx Resistan Breakin
CODE NAME Sectional rating @
Nomina Conductor Conductor (appro Mass ce @ g Load
Power loss in Watt @ 50deg, Ploss = 686,744 W l
Sectional Area
(AL) (ST) x) 20deg
75deg C
DIA DIA ohm/km
Power Loss in % @ 50deg = 0.86% sq.mm sq.mm sq.mm NO.
(mm)
NO
(mm
(mm) kg/km
(max)
kN A
Wire utilisation factor = 1 PANTHER 200 212.1 261.5 30 3 7 3 21 974 0.139 89.67 487
Power Loss in % with wire utilisation factor = 0.86%
Voltage drop calculation
Voltage drop @ 50deg, Vd = 1,133.09 V
Voltage drop in % @ 50deg = 0.86%
Conclusions:
1. Current carrying capacity criteria OK
2. Voltage drop criteria OK Design is adequate
3. Power loss criteria OK
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Art of War Day TradingDocumento17 pagineArt of War Day TradingChrispen MoyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Calculations For 66KV Switchyard - 32mm Dia Rod-7!3!12Documento8 pagineEarthing Calculations For 66KV Switchyard - 32mm Dia Rod-7!3!12M.K.RameshNessuna valutazione finora
- CBIP Publication 223 PDFDocumento32 pagineCBIP Publication 223 PDFEric Taylor100% (4)
- Designing and Drawing PropellerDocumento4 pagineDesigning and Drawing Propellercumpio425428100% (1)
- 220 V DC Battery Sizing 220 KV Main Station 1Documento25 pagine220 V DC Battery Sizing 220 KV Main Station 1Madhu BTNessuna valutazione finora
- CGL - Instruction & Maintenance Manual Current Transformer Live TankDocumento21 pagineCGL - Instruction & Maintenance Manual Current Transformer Live TankHari Krishna.MNessuna valutazione finora
- Lok - TRAFO BCT Size R0Documento9 pagineLok - TRAFO BCT Size R0Nageswar MakalaNessuna valutazione finora
- EWT Earthing TransformersDocumento4 pagineEWT Earthing TransformersSibolis NaburjuNessuna valutazione finora
- Generator Protection - CalculationDocumento4 pagineGenerator Protection - CalculationBalu MNessuna valutazione finora
- GTP For TransformerDocumento5 pagineGTP For TransformerSatheesh Kumar NatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- 500MW ApgencoDocumento17 pagine500MW ApgencoHari Krishna.MNessuna valutazione finora
- 400KV Substion AP TranscoDocumento256 pagine400KV Substion AP TranscoRaj Kumar PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Abb Rel561 Setting CalculationDocumento28 pagineAbb Rel561 Setting CalculationAbhishek Rajput100% (1)
- IPBD MANUAL-Info Catagory PDFDocumento26 pagineIPBD MANUAL-Info Catagory PDFTirthankar DattaNessuna valutazione finora
- 33 KV Line Boq and Price - ComparativeDocumento1 pagina33 KV Line Boq and Price - ComparativeManohar Das100% (1)
- Transmission Line Loss Calculation TL PDFDocumento1 paginaTransmission Line Loss Calculation TL PDFManohar Das100% (1)
- Relay Setting Calculation-NPC-Yas152Documento15 pagineRelay Setting Calculation-NPC-Yas152মোঃ মহসিনNessuna valutazione finora
- TKIS Relay Setting NewDocumento34 pagineTKIS Relay Setting NewsalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Specification Compliance HT - 1 Panel - 24072020 - Smart Electric (ABB)Documento48 pagineTechnical Specification Compliance HT - 1 Panel - 24072020 - Smart Electric (ABB)Muthu KumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- DBAD118077 A REND CT - Sizing CalculationDocumento10 pagineDBAD118077 A REND CT - Sizing CalculationBravery DamanikNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Micro and Macro EnvironmentDocumento8 pagineMarketing Micro and Macro EnvironmentSumit Acharya100% (1)
- IS8084 BusductDocumento29 pagineIS8084 BusductKrishnendu BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 132kV Substation SettingsDocumento77 pagine132kV Substation Settingsmv_mallik100% (3)
- CC-SC Current Calculation Moose-ZebraDocumento4 pagineCC-SC Current Calculation Moose-ZebraSomen SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Transformer PDFDocumento13 pagineEarthing Transformer PDFNelson SarriasNessuna valutazione finora
- 400kV Circuit Breaker - O&MDocumento109 pagine400kV Circuit Breaker - O&Msantoshkumar67% (3)
- Drawings of Switchyard Bay Marshalling KioskDocumento74 pagineDrawings of Switchyard Bay Marshalling KioskNihar SenapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- GRP Relay Setting CalcDocumento15 pagineGRP Relay Setting Calcamulya1981100% (1)
- GTP Inverter Transformer Rev 02Documento5 pagineGTP Inverter Transformer Rev 02Jaks JaksNessuna valutazione finora
- 415V PDB CUM MCC DH - I (Revised)Documento29 pagine415V PDB CUM MCC DH - I (Revised)susovan bIswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Vendor List For PV Solar ProjectDocumento2 pagineVendor List For PV Solar ProjectManohar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Distance Protection CalculationDocumento2 pagineDistance Protection CalculationDileep ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP Calculation by LMDocumento8 pagineDSLP Calculation by LMPrasad YeluripatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Circuit Force Calculation For 132 KV Substation at Noida-Sector 62Documento7 pagineShort Circuit Force Calculation For 132 KV Substation at Noida-Sector 62raghvendraNessuna valutazione finora
- 50/75/100 MVA, 220/132 KV & 50/75/100 MVA, 22/33 KV Outdoor SubstationDocumento16 pagine50/75/100 MVA, 220/132 KV & 50/75/100 MVA, 22/33 KV Outdoor Substationdeepthik27Nessuna valutazione finora
- LineDocumento63 pagineLinesvanand880% (1)
- Fault Level CalculationDocumento3 pagineFault Level CalculationVERMAZ ENGG. DESIGNNessuna valutazione finora
- DrawingDocumento6 pagineDrawingAssistant executive engineerNessuna valutazione finora
- 220kV PGCIL BUSBARDocumento24 pagine220kV PGCIL BUSBARJayam Harinatha Guptha100% (1)
- 4-D03108-0 - Conductor Sizing & BPI Cantilever Strength CalculationDocumento13 pagine4-D03108-0 - Conductor Sizing & BPI Cantilever Strength CalculationunnvishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.6kV VCU GTPDocumento3 pagine6.6kV VCU GTPArunava Basak100% (1)
- Direct Stroke Lightning Protection Calculation For 110Kv Switchyard by Lighting Mast ReferenceDocumento11 pagineDirect Stroke Lightning Protection Calculation For 110Kv Switchyard by Lighting Mast ReferenceneerajNessuna valutazione finora
- 33kv CT Calculations PDFDocumento31 pagine33kv CT Calculations PDFAmit NagNessuna valutazione finora
- CT Knee Point Voltage Calclution For Siemens RelayDocumento21 pagineCT Knee Point Voltage Calclution For Siemens Relayvishnu kumar VyasNessuna valutazione finora
- NS222 Major Substation Earthing Layout DesignDocumento37 pagineNS222 Major Substation Earthing Layout DesignJose ValdiviesoNessuna valutazione finora
- 220kV Busbar & Bus Coupler Control & Relay Panel - 07.09.18Documento49 pagine220kV Busbar & Bus Coupler Control & Relay Panel - 07.09.18Guru Mishra100% (1)
- Capacitive Voltage Transformer - SpecificationDocumento6 pagineCapacitive Voltage Transformer - Specificationbalaeee123Nessuna valutazione finora
- 220kV and 33kV Circuit Breakers BHEL PDFDocumento77 pagine220kV and 33kV Circuit Breakers BHEL PDFSellappan Muthusamy75% (4)
- Transformer OverFluxDocumento3 pagineTransformer OverFluxNeelakandan MasilamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing of Gis Type ElkDocumento21 pagineEarthing of Gis Type ElkJairo Morales100% (1)
- 400KV & 220KV DR PanelDocumento53 pagine400KV & 220KV DR PanelBijaya Kumar MohantyNessuna valutazione finora
- 400KV SwitchYard DocumentationDocumento52 pagine400KV SwitchYard Documentation20-269 vinayNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Trends and Issues in Nursing ManagementDocumento8 pagineCurrent Trends and Issues in Nursing ManagementMadhu Bala81% (21)
- Single Line Diagram of 132kv LILO SubstationDocumento2 pagineSingle Line Diagram of 132kv LILO SubstationEr. Ajit Solanke100% (1)
- 27 - 400 - 220 - 132kV - DB - Tandem Isolator R3 Jan 12 PDFDocumento30 pagine27 - 400 - 220 - 132kV - DB - Tandem Isolator R3 Jan 12 PDFAshok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- AAAC Panther (Up)Documento1 paginaAAAC Panther (Up)sougata mukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil Soak Pit CalculationDocumento2 pagineOil Soak Pit CalculationROHIT MCNessuna valutazione finora
- 132kV TBC CRPDocumento46 pagine132kV TBC CRPMeera DeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Aegis Multifunction RelayDocumento4 pagineAegis Multifunction RelaySuranjana DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaj CortecDocumento6 pagineVaj CortecvenkateshbitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminium Pipe Bus PDFDocumento6 pagineAluminium Pipe Bus PDFaviral mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- 8BK80 ModifiedDocumento57 pagine8BK80 Modifiedrohitvdave5250% (2)
- Earthing Calculation For Ac: PDF Created With Pdffactory Trial VersionDocumento2 pagineEarthing Calculation For Ac: PDF Created With Pdffactory Trial VersionSAEL SOLARNessuna valutazione finora
- Cathodic Calculation (ICCP) Single ShalloWellDocumento11 pagineCathodic Calculation (ICCP) Single ShalloWellArif RusyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aoi-01-Eng-2024Documento81 pagineAoi-01-Eng-2024Kuldeep ShekhawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech - Spec.ACSR 95.15Documento1 paginaTech - Spec.ACSR 95.15Ilir DalipiNessuna valutazione finora
- ZW49740TCDocumento1 paginaZW49740TCSathish Kumar YallampalliNessuna valutazione finora
- PV Solar Project - 1100 KWP Block Size: Cable Calculation For Cable From Inverter To LT BreakerDocumento2 paginePV Solar Project - 1100 KWP Block Size: Cable Calculation For Cable From Inverter To LT BreakerManohar Das100% (1)
- Document Checklist 060912Documento12 pagineDocument Checklist 060912Manohar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Location:PV Solar Plant - 30MW SR No. Description Specification UOM TotalDocumento2 pagineProject Location:PV Solar Plant - 30MW SR No. Description Specification UOM TotalManohar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Coming Power Hub: RajasthanDocumento8 pagineComing Power Hub: RajasthanManohar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Asia Energy Outlook To 2030Documento20 pagineAsia Energy Outlook To 2030Manohar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Body Shop Case Analysis. The Challenges of Managing Business As Holistic ConfigurationDocumento28 pagineThe Body Shop Case Analysis. The Challenges of Managing Business As Holistic ConfigurationHanna AbejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Article Information: Keywords: Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, Cribriform Pattern, Parotid GlandDocumento7 pagineAdditional Article Information: Keywords: Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, Cribriform Pattern, Parotid GlandRizal TabootiNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Group 3 11abmb1Documento32 pagineResearch Group 3 11abmb1arianeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Q3 Figure Life DrawingDocumento10 pagineLesson 1 Q3 Figure Life DrawingCAHAPNessuna valutazione finora
- Paul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryDocumento162 paginePaul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryTista ArumNessuna valutazione finora
- Survivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanDocumento4 pagineSurvivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanGinnie Faustino-GalganaNessuna valutazione finora
- A 138Documento1 paginaA 138pooja g pNessuna valutazione finora
- DS Important QuestionsDocumento15 pagineDS Important QuestionsLavanya JNessuna valutazione finora
- An Eastern Orthodox Understanding of The Dangers of Modernity and TechnologyDocumento10 pagineAn Eastern Orthodox Understanding of The Dangers of Modernity and TechnologyTimothy ZelinskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Advertisement: National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli - 620 015 TEL: 0431 - 2503365, FAX: 0431 - 2500133Documento4 pagineAdvertisement: National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli - 620 015 TEL: 0431 - 2503365, FAX: 0431 - 2500133dineshNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Science 13th Edition Miller Test BankDocumento18 pagineEnvironmental Science 13th Edition Miller Test Bankmarykirbyifsartwckp100% (14)
- Hw10 SolutionsDocumento4 pagineHw10 Solutionsbernandaz123Nessuna valutazione finora
- PGCRSM-01-BLOCK-03 Research Design ExperimentalDocumento29 paginePGCRSM-01-BLOCK-03 Research Design ExperimentalVijilan Parayil VijayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Existentialism in LiteratureDocumento2 pagineExistentialism in LiteratureGirlhappy Romy100% (1)
- Paper 1 AnalysisDocumento2 paginePaper 1 AnalysisNamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Health ChecklistDocumento4 pagineAnimal Health ChecklistcapsfastNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition 2022 PIRDocumento22 pagineNutrition 2022 PIRAlmira LacasaNessuna valutazione finora
- RPH Week 31Documento8 pagineRPH Week 31bbwowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Web-Based Attendance Management System Using Bimodal Authentication TechniquesDocumento61 pagineWeb-Based Attendance Management System Using Bimodal Authentication TechniquesajextopeNessuna valutazione finora
- CUBE Dealer Book 2009Documento280 pagineCUBE Dealer Book 2009maikruetzNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To HDLDocumento28 pagineIntroduction To HDLBack UpNessuna valutazione finora
- Ti05001 PDFDocumento1 paginaTi05001 PDFanggieNessuna valutazione finora
- Transparency and Digitalization in The Public Administration of RomaniaDocumento8 pagineTransparency and Digitalization in The Public Administration of RomaniaMădălina MarincaşNessuna valutazione finora
- Notice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsDocumento5 pagineNotice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsJustia.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Bgrim 1q2022Documento56 pagineBgrim 1q2022Dianne SabadoNessuna valutazione finora
- DAA UNIT 1 - FinalDocumento38 pagineDAA UNIT 1 - FinalkarthickamsecNessuna valutazione finora