Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Exampleproblemsandsolutionsogata Root Locus
Caricato da
Aamir MansoorCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Exampleproblemsandsolutionsogata Root Locus
Caricato da
Aamir MansoorCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TYPES OF ENTERPRISES
Professor Laura Huang
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
The Enterprise
• Types of enterprises
• Implications for your business and your lifestyle
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
The Enterprise
Value Crea3on Value Distribu3on Reach
• Create value through • Allow various par3es • Reach “everyone” –
it’s opera3ons to capture value how to reach as many
(founders, investors, people as possible
partners, etc.)
Note:
don’t
confuse
‘type
of
enterprise’
with
‘legal
structure’;
legal
structures
are
a
different
topic
to
be
discussed
in
another
module
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Six types of enterprises are the most common
• High growth (aka ‘venture-backed’)
• Lifestyle
All have implica,ons on
• Small business
1) Business Expecta,ons
• By acquisition
• Social focused 2) Lifestyle
• Large Corporate-based
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
The Venture-backed Startup
A high growth enterprise that delivers large returns to founders and investors
Business Implica3ons Lifestyle Implica3ons
• Getting Started: Firms are often small at “birth”, • Personal life comes second
but designed to become very large, very quickly
• “Must grow” mentality overshadows other
– “scalable startups” concerns
– Typical Silicon Valley startup model
– Can put pressure on personal situation
• Financial: usually depends on several rounds of – Lifestyle may suffer, or may need to “go
Angel and/or Venture Capital investment on pause”
• Growth Expectation: rapid growth – Need to be ready to ‘give it all’ for
business growth
• Exit: usually these firms start out with an “exit
strategy”, as investors want a plan to get their
money back
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Lifestyle Business
Your desired lifestyle drives your business ambitions
Business Implica3ons Lifestyle Implica3ons
• Getting Started: Founders have clear view of ‘end • Usually has a healthy life / work balance as
game’ in terms of desired size (revenue or profit) the founders trade off ‘higher growth’
potential for lifestyle
• Financial: usually funded by the founders
themselves, friends and family, or possibly a bank • May involve personal tradeoffs at
loan; probably does not involve formal private moments, or in beginning, but usually
investors (such as venture capitalists) nothing unsustainable
• Growth Expectation:
– grow to cover equity / debt costs
– stops when founders achieve lifestyle desired
• Exit: usually no formal exit; rather, founders run
business to allow desired lifestyle
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Organic Growth Business
Running a stable and manageable operation
Business Implica3ons Lifestyle Implica3ons
• Getting started: Founders usually focused on • Usually has a healthy life / work balance,
starting one shop and not focused on high growth although running a small business can also
be highly stressful depending on the
• Financial: usually funded by the founders,
business and the needs of the founder
friends and family or possibly a bank loan; does
not usually involve formal private investors • May involve long hours as the company is
usually only a handful of employees
• Growth Expectation:
– grow to cover equity / debt costs
– Typically focused on “providing” not on
“wealth”
• Exit: no formal exit envisioned, founders run
business to support family, lifestyle
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship by Acquisition
Buying an existing business
Business Implica3ons Lifestyle Implica3ons
• Getting started: Founders look for an attractive • Highly dependent on exit – whether run for
business (possibly underperforming) to buy and cash or run for sale
run (possibly to grow or improve)
• If run for cash can mean that a founder
• Financial: skips over initial (and possibly stressful)
– usually founders, friends & family, bank loan startup phase
– larger acquisition may have larger private • Due diligence is key - like with a house or
funding (Private equity) car, there are always things you don’t know
• Growth Expectation: when you buy; big question is what
– Growth linked with founders ambitions and “skeletons” are in the closet?
investors needs (e.g. return requirements)
• Exit: usually run for existing cash-flow or to
improve profitability; may sell at higher price later
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Social Ventures
Focused on social impact; but may also have a profit mission
Business Implica3ons Lifestyle Implica3ons
• Getting started: Founders pursue growth and • Lifestyle implications depend heavily on
profits in support of a broader social mission type of venture envisioned, it’s reach, the
funding (friends & family vs. formal
• Financial: usually via the founders, friends,
investors)
family, bank loan, and in some cases Angel and/
or Venture Capital investment (if the investors
sense growth potential)
• Growth Expectation: depends on founders and
investors
• Exit: usually focused on achieving social mission,
rarely a formal exit envisioned unless combining
with larger socially oriented firm
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Corporate Intrapreneurship
Jump starting new growth from within a large enterprise
Business Implica3ons Lifestyle Implica3ons
• Getting started: usually started at highest levels • Would be directly linked with internal
of a corporation or in a ‘skunkworks’ manner (i.e. corporate and business unit objectives,
secret project of an executive) goals, needs, and pressures
• Financial: largely funded by either the
corporation or a business unit
• Growth Expectation:
– Usually aimed at jumpstarting growth, entering
a new or fast-paced market that the parent can
not enter easily
• Exit: purpose is to establish new growth engines
or assets for the parent company
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Types of Enterprises
Type Examples
Venture Uber
Lifestyle Custom pool tables
Small Local town boot shop
Acquisi3on Manufacturing plant
Social Cotopaxi
Corporate Classic skunkworks – Boeing
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Types of Enterprises
Key points:
• Be aware of how the type of enterprise you pursue,
the requirements to get started, and your desired
lifestyle all mesh together
• Ultimately you will need to decide what is right you
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE
KNOWLEDGE FOR ACTION Entrepreneurship
WHARTON ONLINE Entrepreneurship
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bootstrap Brilliance: Mastering Self-Funding for a Start=up BusinessDa EverandBootstrap Brilliance: Mastering Self-Funding for a Start=up BusinessNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of EnterprisesDocumento21 pagineTypes of EnterprisesViviana IftimieNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of EntrepreneurshipDocumento31 pagineTypes of EntrepreneurshipJemina Andrea TungculNessuna valutazione finora
- CIE Unit 2 MBA FTDocumento67 pagineCIE Unit 2 MBA FTNaman LadhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Initiative: Readiness and Ability in Initiating Action. Risk: The Hazard or Chance of LossDocumento5 pagineInitiative: Readiness and Ability in Initiating Action. Risk: The Hazard or Chance of LossButterflyNessuna valutazione finora
- Start Up Law: Lums Fall 2021 Maria KhanDocumento19 pagineStart Up Law: Lums Fall 2021 Maria Khansaman salamNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 2.A - Entrepreneurship & Small BusinessDocumento27 paginePart 2.A - Entrepreneurship & Small BusinesszhengcunzhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EntreprenuershipDocumento30 pagineIntroduction To EntreprenuershipJoshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 6Documento23 pagineClass 6Riya GuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Introduction Dr. M Arsalan Nazir: 1. Educational BackgroundDocumento23 pagineSelf-Introduction Dr. M Arsalan Nazir: 1. Educational BackgroundMahrukh ChohanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 EntrepreneurDocumento16 pagineCH 2 EntrepreneurAmanuel TekalignNessuna valutazione finora
- The Foundations of EntrepreneurshipDocumento52 pagineThe Foundations of EntrepreneurshipNazmus SakibNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 - Week 3 Lecture 2 - Topic 2 - Business Size and GrowthDocumento33 pagineWeek 2 - Week 3 Lecture 2 - Topic 2 - Business Size and GrowthCareerPlan FiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrep Consolidated LecturesDocumento15 pagineEntrep Consolidated LecturesEarl Josh ManansalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento27 pagineChapter 1Faiza KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1) ED The Foundation of ED Week 1Documento26 pagine1) ED The Foundation of ED Week 1Homayra Anjum AuhonaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Entrepreneurial MindDocumento30 pagineThe Entrepreneurial MindHitesh Joshi67% (3)
- Module 1 EntrepreneurshipDocumento24 pagineModule 1 Entrepreneurshipheart.sopeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship: I Keep Revising My Vision. Only When You Can Dream It, You Can Do ItDocumento15 pagineEntrepreneurship: I Keep Revising My Vision. Only When You Can Dream It, You Can Do Itjignesh parmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Small Business Start Up: Unit 7Documento54 pagineManaging Small Business Start Up: Unit 7Lutfi Dwi ArtoNessuna valutazione finora
- III - Entrepreneurial ProcessDocumento34 pagineIII - Entrepreneurial Processandhi06wijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise EconomicDocumento7 pagineEnterprise Economicywv22gg89jNessuna valutazione finora
- NU LFA W1 GEENT01X The Entrepreneurial Mind (Autosaved)Documento45 pagineNU LFA W1 GEENT01X The Entrepreneurial Mind (Autosaved)UnknownymousNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Entrepreneurial MindsetDocumento34 pagine2 - Entrepreneurial Mindsetalien_on_earthNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6Documento31 pagineLecture 6Trí NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrep Meaning &caracteristics - StudentsDocumento44 pagineEntrep Meaning &caracteristics - Studentsamitroy2866Nessuna valutazione finora
- EP Lecture 04 & 05Documento35 pagineEP Lecture 04 & 05Afsana Mimi (211011065)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Entrepreneurship: Chapter #1Documento22 pagineIntroduction To Entrepreneurship: Chapter #1Forever KingNessuna valutazione finora
- TO Entrepreneurship: by Abhishek DuttaguptaDocumento40 pagineTO Entrepreneurship: by Abhishek DuttaguptaGean Rose Canceran100% (1)
- Overview of Entrepreneurship: The Entrepreneurial PerspectiveDocumento69 pagineOverview of Entrepreneurship: The Entrepreneurial PerspectivevikramNessuna valutazione finora
- Entre Mba CH 7 & 8Documento53 pagineEntre Mba CH 7 & 8Hussen MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Raising Capital For The Entrepreneurial Path: Prepared By: Cheryl Y. DulayDocumento35 pagineRaising Capital For The Entrepreneurial Path: Prepared By: Cheryl Y. DulayPRINCESS LYKA MAE PALOMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Entrepreneurship: Beenish QureshiDocumento18 pagineIntroduction To Entrepreneurship: Beenish QureshiHermain Fayyaz KarimNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To EntrepreneurshipSumalinog Gonzaga GelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDocumento13 pagineIntroduction To EntrepreneurshipAhmed Aman100% (1)
- Unit IV & V - Entrepreneurship 20.12.2018Documento60 pagineUnit IV & V - Entrepreneurship 20.12.2018Berihu GirmayNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship FinalDocumento12 pagineEntrepreneurship FinalBashar S. Al-MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro EntrepreneurshipDocumento53 pagineIntro EntrepreneurshipHabib NuredinNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurial DecisonDocumento13 pagineEntrepreneurial DecisonAmanuel TekalignNessuna valutazione finora
- Startup Funding: Entrepreneurship and StartupsDocumento95 pagineStartup Funding: Entrepreneurship and StartupsAhmed Hadad0% (1)
- Techno Lesson 1Documento15 pagineTechno Lesson 1Earl EsparesNessuna valutazione finora
- (Lecture 2) - (Entrepreneurs and Characteristics of Entrepreneurial Ventures)Documento37 pagine(Lecture 2) - (Entrepreneurs and Characteristics of Entrepreneurial Ventures)Tran Thi Ngoc Anh (BTEC HN)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento31 pagineLecture 2Trí NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDocumento13 pagineIntroduction To EntrepreneurshipKadir Say'sNessuna valutazione finora
- Raising CapitalDocumento29 pagineRaising CapitalJheam Reinz MontesNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship PeriodicDocumento2 pagineEntrepreneurship PeriodicMildred Peña TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- L1 Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDocumento35 pagineL1 Introduction To EntrepreneurshipMâyNessuna valutazione finora
- BAM 074 ReviewerDocumento13 pagineBAM 074 ReviewerFatima Alexa MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Warner Spencer 3Documento36 pagineWarner Spencer 3Carl YapNessuna valutazione finora
- Startupfinancing 101Documento16 pagineStartupfinancing 101юрий локтионовNessuna valutazione finora
- S28 29 PDFDocumento41 pagineS28 29 PDFcalvin gastaudNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento56 pagineLecture 2Cao ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Entrepreneurial Perspective: Chapter #1Documento37 pagineThe Entrepreneurial Perspective: Chapter #1AamaajiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship 1Documento40 pagineEntrepreneurship 1Nishtha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship OverviewDocumento30 pagineEntrepreneurship OverviewLerench james CamposNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDocumento19 pagineIntroduction To EntrepreneurshipAnna MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship and SMEDocumento24 pagineEntrepreneurship and SMEMohsin KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Built To LastDocumento7 pagineBuilt To LastMarlon Amiel SungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship 2Documento37 pagineEntrepreneurship 2Uzair TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 1-2 - Foundations of EntrepreneurshipDocumento38 pagineWEEK 1-2 - Foundations of EntrepreneurshipHannah Shiela MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahria University (Karachi Campus) : Task 1Documento2 pagineBahria University (Karachi Campus) : Task 1Aamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 4 - Linear Variable Differential Transformer - LVDT PDFDocumento5 pagineLAB - 4 - Linear Variable Differential Transformer - LVDT PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 8 - Sequencing and Cascading Circuits Using FluidSIM PDFDocumento4 pagineLAB - 8 - Sequencing and Cascading Circuits Using FluidSIM PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 5 - Electric Actuators and Mechanisms PDFDocumento6 pagineLAB - 5 - Electric Actuators and Mechanisms PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 5 - Electric Actuators and Mechanisms PDFDocumento6 pagineLAB - 5 - Electric Actuators and Mechanisms PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 3 - Limit Switches Interfacing Using PLC PDFDocumento5 pagineLAB - 3 - Limit Switches Interfacing Using PLC PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 4 - Linear Variable Differential Transformer - LVDT PDFDocumento5 pagineLAB - 4 - Linear Variable Differential Transformer - LVDT PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 3 - Limit Switches Interfacing Using PLC PDFDocumento5 pagineLAB - 3 - Limit Switches Interfacing Using PLC PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 5 - Electric Actuators and Mechanisms PDFDocumento6 pagineLAB - 5 - Electric Actuators and Mechanisms PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Engineering Task 1 PDFDocumento3 pagineComplex Engineering Task 1 PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB - 4 - Linear Variable Differential Transformer - LVDT PDFDocumento5 pagineLAB - 4 - Linear Variable Differential Transformer - LVDT PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Engineering Task 2 PDFDocumento3 pagineComplex Engineering Task 2 PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Engineering Task 1 PDFDocumento3 pagineComplex Engineering Task 1 PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Engineering Task 2 PDFDocumento3 pagineComplex Engineering Task 2 PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Python Packages 17052020 104702am PDFDocumento5 paginePython Packages 17052020 104702am PDFAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahria University: Introduction To MechatronicsDocumento4 pagineBahria University: Introduction To MechatronicsAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- EEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressDocumento16 pagineEEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- EEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressDocumento29 pagineEEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- EEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressDocumento18 pagineEEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahria University: Introduction To MechatronicsDocumento4 pagineBahria University: Introduction To MechatronicsAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 19 - 20 10062020 025505pmDocumento22 pagineLecture 19 - 20 10062020 025505pmAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Resident: ApplicantDocumento3 pagineLocal Resident: ApplicantAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch16 Lecture NotesDocumento40 pagineCh16 Lecture NotesAhmed TahmidNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz # 1: Bahria University (Karachi Campus)Documento1 paginaQuiz # 1: Bahria University (Karachi Campus)Aamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
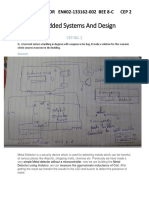
- Aamir Cep2 EsdDocumento4 pagineAamir Cep2 EsdAamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Instructions (Read Carefully Before Creating Project Report)Documento6 pagineImportant Instructions (Read Carefully Before Creating Project Report)Aamir MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Ogata Root LocusDocumento32 pagineOgata Root Locusvignesh0617100% (1)
- Quiz ProblemsDocumento23 pagineQuiz ProblemsNhel AlvaroNessuna valutazione finora
- IAS 16 - Property, Plant & EquipmentDocumento34 pagineIAS 16 - Property, Plant & EquipmentBill YuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Millionaire in You PDFDocumento9 pagineThe Millionaire in You PDFPomija0% (1)
- Gilead Sciences Inc (Gild-O) : Average ScoreDocumento12 pagineGilead Sciences Inc (Gild-O) : Average ScoreInvest StockNessuna valutazione finora
- The Relationship of Financial Literacy, Investment Experience, and Personal Goals On The Investment and Loan Decisions of Philippine Navy OfficersDocumento11 pagineThe Relationship of Financial Literacy, Investment Experience, and Personal Goals On The Investment and Loan Decisions of Philippine Navy OfficersIjahss JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- 1) Assess The Current Financial Health and Recent Financial Performance of The Firm. Identify Any Strengths or WeaknessesDocumento2 pagine1) Assess The Current Financial Health and Recent Financial Performance of The Firm. Identify Any Strengths or WeaknessesJane SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse of Fintech 2018: Blockchain Investment Exceeds 2017 Annual TotalDocumento2 paginePulse of Fintech 2018: Blockchain Investment Exceeds 2017 Annual TotalSergio VinsennauNessuna valutazione finora
- Ciby HDFC PDFDocumento3 pagineCiby HDFC PDFTina PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- NTPC Ratio Analysis FinalDocumento45 pagineNTPC Ratio Analysis FinalDaman Deep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- ValueInvesting - Io - Financials & Models TemplateDocumento60 pagineValueInvesting - Io - Financials & Models TemplateTan TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Project-Investocks Publication 2020Documento4 pagineProject-Investocks Publication 2020Rainier Ibañez ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Hutchison Whampoa Case ReportDocumento6 pagineHutchison Whampoa Case ReporttsjakabNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Bsma 1a March 6Documento9 pagineAssignment Bsma 1a March 6Maeca Angela SerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ju Iba - 202203091Documento26 pagineJu Iba - 202203091MF IQBALNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13Documento11 pagineChapter 13MekeniMekeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivatives FT YtDocumento28 pagineDerivatives FT YtSuchit Backup1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bucket ListDocumento92 pagineBucket ListTomas Kas100% (2)
- Corporate Financing Decision (MFIN 641) Mba V Term Kathmandu University School of ManagementDocumento39 pagineCorporate Financing Decision (MFIN 641) Mba V Term Kathmandu University School of ManagementSichen UpretyNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis of The ProjectDocumento14 pagineSynopsis of The Projectmrcopy xeroxNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Trade A News BreakoutDocumento4 pagineHow To Trade A News BreakoutJason2Kool100% (2)
- David Hillier (2019)Documento12 pagineDavid Hillier (2019)eriwirandanaNessuna valutazione finora
- EEFCDocumento2 pagineEEFCmithilesh tabhaneNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 TABLE - Kode Etik Manajer Investasi - Updated 20170324 Bilingual - FINALDocumento6 pagine4 TABLE - Kode Etik Manajer Investasi - Updated 20170324 Bilingual - FINALSheila AriskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kurkure ProjectDocumento21 pagineKurkure Projectdhanbad3Nessuna valutazione finora
- ING Group 2Documento4 pagineING Group 2Puneet JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto Insurance AffordabilityDocumento32 pagineAuto Insurance AffordabilityArmaghanAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- AdidasDocumento6 pagineAdidasLorenz BaguioNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 09Documento53 pagineModule 09samaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Financial Statements and Ratio Analysis: Principles of Managerial Finance, Brief, 7e (Gitman)Documento75 pagineChapter 3 Financial Statements and Ratio Analysis: Principles of Managerial Finance, Brief, 7e (Gitman)El jokerNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 DTE MEIC - January 16, 2023 by Tammy ChamblessDocumento19 pagine0 DTE MEIC - January 16, 2023 by Tammy Chamblessben44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldDa EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (55)
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootDa EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootNessuna valutazione finora
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDa EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderDa EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (398)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyDa EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- 100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziDa Everand100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziNessuna valutazione finora
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyDa EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldDa EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (107)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumDa EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (12)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andDa EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (709)
- YouTube Secrets: The Ultimate Guide on How to Start and Grow Your Own YouTube Channel, Learn the Tricks To Make a Successful and Profitable YouTube ChannelDa EverandYouTube Secrets: The Ultimate Guide on How to Start and Grow Your Own YouTube Channel, Learn the Tricks To Make a Successful and Profitable YouTube ChannelValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (48)
- The AI Advantage: How to Put the Artificial Intelligence Revolution to WorkDa EverandThe AI Advantage: How to Put the Artificial Intelligence Revolution to WorkValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (7)
- An Ugly Truth: Inside Facebook's Battle for DominationDa EverandAn Ugly Truth: Inside Facebook's Battle for DominationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDa EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (104)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceDa EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Who's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesDa EverandWho's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- The Bitcoin Standard: The Decentralized Alternative to Central BankingDa EverandThe Bitcoin Standard: The Decentralized Alternative to Central BankingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (41)
- Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI for Beginners: The Complete GuideDa EverandArtificial Intelligence & Generative AI for Beginners: The Complete GuideValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyDa EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (421)
- Invent and Wander: The Collected Writings of Jeff Bezos, With an Introduction by Walter IsaacsonDa EverandInvent and Wander: The Collected Writings of Jeff Bezos, With an Introduction by Walter IsaacsonValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (123)
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseDa EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (12)
- The $100 Startup by Chris Guillebeau: Summary and AnalysisDa EverandThe $100 Startup by Chris Guillebeau: Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (8)
- Your AI Survival Guide: Scraped Knees, Bruised Elbows, and Lessons Learned from Real-World AI DeploymentsDa EverandYour AI Survival Guide: Scraped Knees, Bruised Elbows, and Lessons Learned from Real-World AI DeploymentsNessuna valutazione finora