Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
Caricato da
विशाल पुडासैनीTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
Caricato da
विशाल पुडासैनीCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Lesson Plan: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
By: Dr. Lila Raj Koirala
Number of
Week No. Chapter Assignment
Period
1. Introduction
Definition and Scope of Engineering Thermodynamics,
Microscopic Versus Macroscopic Viewpoint,Concepts
and Definitions - System, Boundary, Surrounding,
1 Thermodynamic Properties, Thermodynamic 2
Equilibrium, Assignment 1: Numericals
Regarding Chapter 1
State, Path, Process and Cycle, Quasi-Equilibrium
Processes, Common Properties - Pressure, Specific
2 Volume, Temperature, Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 2
and Equality of Temperature
2. Energy and Energy Transfer
Types of Energy - Stored Energy, Transient Energy, Total
Energy, Energy Transfer - Heat Transfer, Work Transfer,
Similarities and Differences between Heat Transfer and Assignment 2: Numericals
3 Work Transfer, Expressions for Displacement Work 2 Regarding Chapter 2
Transfer: Isobaric, isochoric,
Isothermal, Adiabatic and Polytropic Processes, Power
3. Properties of Pure Substances
Pure Substance and State Postulate, Ideal Gas and
Ideal Gas Relations, Two phase (Liquid and Vapour)
Systems: Change of Phase, Subcooled Liquid, Saturated
Liquid, Wet Mixture, Critical Point
4 2
Change of Phase, Subcooled Liquid, Saturated Liquid, Assignment 3: Numericals
Wet Mixture, Critical Point, Quality, Moisture Content, Regarding Chapter 3
Saturated Vapour and Superheated Vapour
Properties of Two Phase Mixture, Other Thermo-
dynamic Properties - Internal Energy, Enthalpy, Specific
5 Heats, Development of Property Data: Graphical Data 2
Presentation and Tabular Data Presentation
4. First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics for Control Mass (Closed
6 System/Non Flow Process), First Law of Thermo- 2
dynamics for Control Mass Undergoing Cyclic Process
First Law of Thermodynamics for Control Volume (Open
System/Flow Process), Analysis of Control Assignment 4: Numericals
7 2 Regarding Chapter 4
Volume at Steady State and at Unsteady State
Control Volume Application: Steady and Unsteady Work
Applications and Steady and Unsteady Flow
8 Applications, Other Statements of the first Law 2
5. Second Law of Thermodynamics
Necessity of Formulation of Second Law, Entropy and
Second Law of Thermodynamics for an Isolated System,
Reversible and Irreversible Processes, Entropy and
9 Process Relations for an Ideal Gases and Incompressible 2
Substances
Assignment 5: Numericals
Regarding Chapter 5
Control Mass Formulation of Second Law, Control
10 Volume Formulation of Second Law, Isentropic Process 2
for an Ideal Gas and for an Incompressible Substances
Carnot Cycle, Heat Engine, Heat Pump, Refrigerator,
11 Kelvin- Planck and Clausius Statements of the Second 2
Law of Thermodynamics and their Equivalence
6. Thermodynamic Cycles
Classification of Thermodynamic Cycles, Air Standard
12 Brayton Cycle, Rankine Cycle, Internal Combustion 2
Cycles (Operation of Two and Four Sroke Engines) Assignment 6: Numericals
Regarding Chapter 6
Air Standard Analysis, Air Standard Otto Cycle,
13 Air Standard Diesel Cycle, Vapour Compression 2
Refrigeration Cycle
7. Introduction to Heat Transfer
Basic Concepts and Modes of Heat Transfer, One
Dimensional Steady State Heat Conduction through a
Plane Wall, Radial Steady State Heat Conduction
14 through a Hollow Cylinder , Heat Flow through 2
Composite Structures, Coposite Plane Wall, Multilayer
Tubes
Assignment 7: Numericals
Regarding Chapter 7
Electrical Analogy for Thermal Resistance,
Combined Heat Transfer and Overall Heat Transfer
Coefficient for Plane Wall and Tube, Nature of
15 Convection: Free and Forced Convection, Heat 2
Radiation, Stefan's Law, Absorptivity, Reflectivity, and
Transmissivity; Black Body, White Body, and Gray Body
Remarks
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Basic Thermodynamics IISCDocumento284 pagineBasic Thermodynamics IISCTS RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ThermodynamicsDocumento284 pagineBasic Thermodynamicsikneo100% (10)
- Basic Thermodynamics SyllabusDocumento284 pagineBasic Thermodynamics SyllabusSecretNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Thermodynamics SyllabusDocumento4 pagineBasic Thermodynamics SyllabusKrish RobertsNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocumento2 pagineFundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat TransferAnil MarsaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sessional - 100 100 Final - Total - 100 100Documento3 pagineSessional - 100 100 Final - Total - 100 100Sagar AcharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal SyllabusDocumento3 pagineThermal Syllabusbrajeshger.Nessuna valutazione finora
- TD SylabusDocumento5 pagineTD SylabusNenu Na RakshasiNessuna valutazione finora
- TD Course FileDocumento18 pagineTD Course FileBadari Narayan P100% (1)
- Thermal Science 2ndDocumento2 pagineThermal Science 2ndSyh TfkNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Thermodynamics Key ConceptsDocumento57 pagineEngineering Thermodynamics Key ConceptsBasu SbNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics and Combustion: Fundamental Concepts of ThermodynamicsDocumento3 pagineThermodynamics and Combustion: Fundamental Concepts of ThermodynamicsVineeth SivarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical and Geometrical Theory of Chemical and Phase ThermodynamicsDa EverandClassical and Geometrical Theory of Chemical and Phase ThermodynamicsNessuna valutazione finora
- VTU ThermodynamicsDocumento2 pagineVTU ThermodynamicsVinay KorekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch6402 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics-I L T P C3 0 0 3 ObjectiveDocumento1 paginaCh6402 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics-I L T P C3 0 0 3 ObjectiveRajesh KtrNessuna valutazione finora
- TD Lesson Plan and SyllabusDocumento7 pagineTD Lesson Plan and Syllabuschandrasekhar reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics Digital MaterialDocumento356 pagineThermodynamics Digital MaterialEdith LapetajeNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics ManualDocumento99 pagineThermodynamics ManualBISHAL AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
- TD Lecture Plan 2022Documento2 pagineTD Lecture Plan 2022Abdul Majid KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics Course HandoutDocumento6 pagineThermodynamics Course HandoutAmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical MeasurementsMechanical MeasurementsDocumento2 pagineMechanical MeasurementsMechanical MeasurementsNenu Na RakshasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics SyllabusDocumento4 pagineThermodynamics Syllabusramian10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Engineering SyllabusDocumento2 pagineThermal Engineering SyllabusMithilesh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- BTD Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineBTD Lesson Planpratik039Nessuna valutazione finora
- BNMIT Thermodynamics Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineBNMIT Thermodynamics Lesson PlanHemanth KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- KIIT Aerospace Thermodynamics Course OverviewDocumento5 pagineKIIT Aerospace Thermodynamics Course Overviewmaaz ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- BITS F111 1004 UpdatedDocumento6 pagineBITS F111 1004 UpdatedSUGEET SOODNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Objectives:: Course Title: Course No.: InstructorDocumento2 pagineCourse Objectives:: Course Title: Course No.: InstructorDicky KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Me8391Documento56 pagine03 Me8391BALAKRISHNANNessuna valutazione finora
- BE Syllabus of Mumbai Uni2Documento9 pagineBE Syllabus of Mumbai Uni2Rajendra B PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- THERMODocumento1 paginaTHERMOamireddysugunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Get Syllabus PDFDocumento1 paginaGet Syllabus PDFraju kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bits F111 1004 20230811181755Documento6 pagineBits F111 1004 20230811181755Sourabh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MEC 189.2 Thermal ScienceDocumento4 pagineMEC 189.2 Thermal ScienceSyh TfkNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsDocumento3 pagineSyllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsGautam GunjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Documento36 pagineChapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Ng Kee NainNessuna valutazione finora
- St. MICHEAL Engineering BasicsDocumento41 pagineSt. MICHEAL Engineering Basicsnagarajan224Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics CH 102Documento15 pagineThermodynamics CH 102Rana MaazNessuna valutazione finora
- Mehran University Thermal Sciences Course OutlineDocumento2 pagineMehran University Thermal Sciences Course OutlineAnonymous mqIqN5zNessuna valutazione finora
- BTD SyllabusDocumento3 pagineBTD SyllabusSubuddhi DamodarNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Tech (Mechanical Engineering) III Semester (Common With PCC-AE-201, PCC-MAE-201)Documento2 pagineB. Tech (Mechanical Engineering) III Semester (Common With PCC-AE-201, PCC-MAE-201)vikaskumar1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Weather and Life: An Introduction to BiometeorologyDa EverandWeather and Life: An Introduction to BiometeorologyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4Da Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Thermodynamics of Non-Electrolyte SolutionsDa EverandClassical Thermodynamics of Non-Electrolyte SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics and Introductory Statistical MechanicsDa EverandThermodynamics and Introductory Statistical MechanicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionDa EverandIntroduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionValutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Thermodynamics of Point Defects and Their Relation with Bulk PropertiesDa EverandThermodynamics of Point Defects and Their Relation with Bulk PropertiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Classical Physics: Optics, Fluids, Plasmas, Elasticity, Relativity, and Statistical PhysicsDa EverandModern Classical Physics: Optics, Fluids, Plasmas, Elasticity, Relativity, and Statistical PhysicsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesDa EverandAdvanced Engineering Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Experimental Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 1993Da EverandExperimental Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 1993M.D. KelleherNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringDa EverandPhysics for Students of Science and EngineeringValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Career Objective: Er. Bishal Pudasaini AddressDocumento4 pagineCareer Objective: Er. Bishal Pudasaini Addressविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Career Objective: Er. Bishal Pudasaini AddressDocumento4 pagineCareer Objective: Er. Bishal Pudasaini Addressविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocumento4 pagineFundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transferविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Question 1Documento1 paginaQuestion 1विशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Development Old Question1Documento1 paginaDevelopment Old Question1विशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Question 1Documento1 paginaQuestion 1विशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 18Documento1 paginaLecture 18विशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
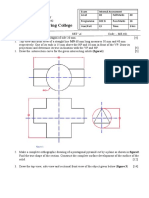
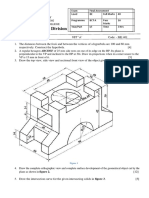
- Engineering Drawing - Question BankDocumento32 pagineEngineering Drawing - Question Bankविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 11Documento1 paginaLecture 11विशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- KEC Final Assessment Workshop Technology ExamDocumento2 pagineKEC Final Assessment Workshop Technology Examविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Examination Control DivisionDocumento1 paginaExamination Control Divisionविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Assessment Level Full Marks Program BCT A Pass Marks Year/Part I/II TimeDocumento4 pagineExam Assessment Level Full Marks Program BCT A Pass Marks Year/Part I/II Timeविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Set A WorkshopDocumento2 pagineSet A Workshopविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop - Objective - QuestionsDocumento2 pagineWorkshop - Objective - Questionsविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- BCE B KecDocumento2 pagineBCE B Kecविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Drawing Exam QuestionsDocumento2 pagineEngineering Drawing Exam Questionsविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Tribhuwan University Institute of Engineering Thapathali CampusDocumento42 pagineTribhuwan University Institute of Engineering Thapathali Campusविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Drawing I Final Assessment QuestionDocumento3 pagineEngineering Drawing I Final Assessment Questionविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Tribhuwan University Institute of Engineering Thapathali CampusDocumento42 pagineTribhuwan University Institute of Engineering Thapathali Campusविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop - Objective - QuestionsDocumento2 pagineWorkshop - Objective - Questionsविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Namelist 2075 Batch FinalDocumento8 pagineNamelist 2075 Batch Finalविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Set A WorkshopDocumento2 pagineSet A Workshopविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Kathmandu Engineering College Kalimati 2075 FalgunDocumento2 pagineKathmandu Engineering College Kalimati 2075 Falgunविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- ADT3 ResultsDocumento5 pagineADT3 Resultsविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Final MarksDocumento4 pagineFinal Marksविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- Examination Control DivisionDocumento2 pagineExamination Control Divisionविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- AL ApplicantsDocumento3 pagineAL Applicantsविशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- BCT A 2Documento2 pagineBCT A 2विशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- BCT A 2Documento2 pagineBCT A 2विशाल पुडासैनीNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ 140Documento14 pagineMCQ 140Aawez AkhterNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical OperationDocumento14 pagineMechanical OperationThiyaga RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- ECU MS 3 Sport GT3 Cup Manual Setup GuideDocumento26 pagineECU MS 3 Sport GT3 Cup Manual Setup GuideAngel LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey of Tea Vendors 01Documento2 pagineSurvey of Tea Vendors 01Sandeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 3512TA - 1000kVA - LV - Spec Sheet PDFDocumento5 pagine3512TA - 1000kVA - LV - Spec Sheet PDFavinash_1229Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kaplan Turbine Working As A Propeller CFD InvestigDocumento11 pagineKaplan Turbine Working As A Propeller CFD InvestigclaudehackerNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Sizes and Flow Rates for Air Flush DrillingDocumento14 paginePipe Sizes and Flow Rates for Air Flush DrillingzapspazNessuna valutazione finora
- Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocumento6 pagineMultidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesWiz Calvin ManutdNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - ch01 - SQ - E: Solutions MarksDocumento37 pagine4 - ch01 - SQ - E: Solutions Marks5A35 YIP HOI PAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus of Diploma in Electrical EngineeringDocumento17 pagineSyllabus of Diploma in Electrical EngineeringJoson Chan100% (1)
- GH G ConversionDocumento146 pagineGH G ConversionjorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamix Brochure EN WebDocumento9 pagineFundamix Brochure EN Webjgjb4csrj7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Line Sizing GuidelinesDocumento31 pagineLine Sizing Guidelinesc_nghia100% (3)
- Two-Phase Flow (Gas-Flow) Line SizingDocumento24 pagineTwo-Phase Flow (Gas-Flow) Line SizingvictorvikramNessuna valutazione finora
- Zseise 40 ADocumento23 pagineZseise 40 ANini FarribasNessuna valutazione finora
- Volkswagen 2.0L TDI Common Rail Engine Service TrainingDocumento90 pagineVolkswagen 2.0L TDI Common Rail Engine Service TrainingАлла Харютина100% (1)
- Ceiling Mounted Chilled Water UnitDocumento2 pagineCeiling Mounted Chilled Water UnitPrinces Katherine VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment & Dimensions: EH4500: Standard Equipment Optional Equipment Eh4500 Ac Wheel MotorDocumento2 pagineEquipment & Dimensions: EH4500: Standard Equipment Optional Equipment Eh4500 Ac Wheel MotorAndi Wardiman AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sub Sea Hot Stab (Sub Sea High Pressure Quick Disconnect)Documento2 pagineSub Sea Hot Stab (Sub Sea High Pressure Quick Disconnect)estelauNessuna valutazione finora
- Delta Ia-Mds Vfd-Ed Um en 20150910-1Documento280 pagineDelta Ia-Mds Vfd-Ed Um en 20150910-1FahadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cylinder Cutout Cylinder CutoutDocumento12 pagineCylinder Cutout Cylinder CutoutIsrael Miranda ZamarcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Projects Oil and Gas BrochureDocumento20 pagineProjects Oil and Gas BrochureRussel John RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- IFFCO Urea ProcesspdfDocumento3 pagineIFFCO Urea ProcesspdfBalas43Nessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial ReactorsDocumento10 pagineIndustrial ReactorssarahNessuna valutazione finora
- ME6502 Heat and Mass Transfer SyllabusDocumento26 pagineME6502 Heat and Mass Transfer Syllabusamdeva0% (1)
- FMC Smith Meter 01 - Mesurement Product & SystemDocumento70 pagineFMC Smith Meter 01 - Mesurement Product & SystemDucVikingNessuna valutazione finora
- Ufc 3 430 09Documento106 pagineUfc 3 430 09carlcrowNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Conservation Oppurtunities in Boiler SystemDocumento34 pagineEnergy Conservation Oppurtunities in Boiler SystemSiddharth Jain67% (3)
- 3/27/2016 Portable AC On Rent Pune - Portable AC Rentals Pune - AC Rentals Pune On SulekhaDocumento3 pagine3/27/2016 Portable AC On Rent Pune - Portable AC Rentals Pune - AC Rentals Pune On SulekhadcoolsamNessuna valutazione finora