Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CHEM Reviewer Grade 12
Caricato da
Raphael0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
1K visualizzazioni3 pagineThis document provides an overview of key concepts in chemistry. It discusses the classification of matter into pure substances and mixtures. It also describes common units of measurement in chemistry and different types of chemical reactions. The periodic table is introduced along with atomic structure and different classes of elements. Common techniques for separating mixtures like distillation and filtration are also outlined.
Descrizione originale:
A helpful Chemistry Reviewer for Grade 12 students
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document provides an overview of key concepts in chemistry. It discusses the classification of matter into pure substances and mixtures. It also describes common units of measurement in chemistry and different types of chemical reactions. The periodic table is introduced along with atomic structure and different classes of elements. Common techniques for separating mixtures like distillation and filtration are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
1K visualizzazioni3 pagineCHEM Reviewer Grade 12
Caricato da
RaphaelThis document provides an overview of key concepts in chemistry. It discusses the classification of matter into pure substances and mixtures. It also describes common units of measurement in chemistry and different types of chemical reactions. The periodic table is introduced along with atomic structure and different classes of elements. Common techniques for separating mixtures like distillation and filtration are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Dispersed phase
I. UNIT OF MEASUREMENT Dispersing medium
Qualitative observations
Quantitative measurements Properties of colloidal system:
Le Systeme International d’ unites 1. Tyndall effect- scattering of light
- The International system for units(SI) 2. Brownian movement- change speed and
Temperature direction erratically
Celsius temperature scale 3. Electrical properties-uniform electrical
Kelvin temperature scale charges
- William Thompson (Lord Kelvin) 4. Stability and Unstability- remain a true
- Absolute zero solution and coagulated by heating
- 273.15K 5. Adsoptive Property- large surface area
Length
Volume Elements
Mass Compounds
Dietary calorie(C) Ions- electrically charged atoms
Calorie(cal)
3 types:
II. MAKING MEASUREMENTS 1. Monoatomic Cations-loses electron
Precision 2. Monoatomic Anions-gains electron
Accuracy 3. Polyatomic Ions-electric charge
- Standard Deviation
- Percent Error Molecules- smallest discrete units
Physical Properties:
III. MATHEMATICS OF CHEMISTRY 1. Color
Dimensional Analysis 2. State of Matter
3. Boiling point
4. Melting point
BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
5. Density
6. Solubility
I. CLASSIFYING MATTER
7. Electric Conductivity
State
8. Ductility-drawn into wire
Kinetic-Molecular Theory
9. Viscosity-flow
3 levels of matter:
Extensive Properties
1. Particulate- imagination
Intensive Properties
2. Macroscopic- unaided human senses
Physical Changes
3. Symbolic- symbols-represent
Chemical Changes
Energy-capacity to do work
Pure substances
Kinetic Energy-associated with motion
Purified
Potential Energy-energy stored
2 types of mixture: Law of Conservation of Energy- created nor
1. Heterogeneous-uneven texture destroyed & total energy of the universe is
2. Homogeneous-“solutions” constant
Colloid- homogeneous appearance II. METHODS OF SEPERATING
MIXTURES
2 separate phases: Decantation
- Residue & Supernatant Liquid Non Metals
Filtration Metalloids- physical properties of metal but
- Residue & Filtrate chemical properties of non metals
Evaporation Allotropes-nonmetals distinct forms
- Residue & Evaporate
Distillation Formulas
- Residue & Distillate Molecular Formula
Absorption Condensed Formula
- Absorbate & Absorbent Structural Formula
Sublimation- solid->gas Molecular Models
Ball-and-Stick model
ATOMS, MOLECULES AND IONS Space-Filling model
Dalton’s atomic theory- elements Ionic Compounds
composed of tiny particles (Atoms) - Crystal Lattice- 3d network
1. Law of Multiple Proportions Properties of Ionic Compounds:
2. Law of Conservation of Mass 1. Force of attraction-electrostatic force
3. Law of Definite Proportions 2. Force of Repulsion-electrostatic force
John Joseph Thompson 3. Coulomb’s Law-force of attraction or
- Electron, Cathode Ray Experiment repulsion between ions
Ernest Rutherford Binary Compounds-molecules from two
- Proton & Nucleus, Gold-Foil Experiment nonmetals
James Chadwick NAMING CATIONS
- Neutron, bombarding a beryllium atom Monoatomic Cation
with alpha particles producing Metal name + “cation”
electrically neutral particle with mass Transition Series
slightly greater than proton Metal name(charge) + “cation”
Robert Andres Millikan NAMING ANIONS
- Charge of electron (-1.60x10^-19), Oil- Monoatomic Anion
Drop Experiment Nonmetal stem name+ ide +”ion”
Mass Number Polyatomic Ions
A= no. of protons + no. of neutrons - containing oxygen
Isotopes- different neutron - Oxinanions
Isotope Abundance - “ate” largest, “ite”smallest
Percent Abundance= (no. of given atoms/
total no. of atoms) x 100% LESSON 2:
Mass Spectrometry-determines the masses Hydrate
of isotopes and its abundances (atomic Law of Conservation of mass
weight) Lavoiser,1788
Atomic Weight
Types of chemical reactions:
THE PERIODIC TABLE 1. Combination/ synthesis reaction
Groups/Families- vertical 2. Decomposition Reaction
1A- Alkali Metals 3. Single Replacement- activity series of
2A- Alkaline Earth Metals metals
7A- Halogens 4. Double Replacement- solubility rules
8A- Noble gases (most stable) 5. Acid-Base Reaction- “neutralization
Periods reaction” , H2O
Metals 6. Combustion Reaction
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Periodical Exam in Biology IIDocumento8 paginePeriodical Exam in Biology IINovochino CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Quarterly Exam in General BioDocumento6 pagine1st Quarterly Exam in General BioVinlax ArguillesNessuna valutazione finora
- Motorcycle Troubleshooting ManualDocumento15 pagineMotorcycle Troubleshooting ManualJan Warmerdam100% (1)
- Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals GasDocumento2 pagineCompare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals GasJohn Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology II Final ExamDocumento5 pagineGeneral Biology II Final ExamMayar Hasan100% (1)
- CSEC Chemistry June 2018 P2 AnswersDocumento7 pagineCSEC Chemistry June 2018 P2 AnswerscxcchemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Science Reviewer Quarter 2Documento6 pagineEarth Science Reviewer Quarter 2Windy Kyle LimNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry 2Documento11 pagineGeneral Chemistry 2Fayza Jalil BaladingNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Physics 1 2nd Quarter ExamDocumento5 pagineGen Physics 1 2nd Quarter ExamArvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Feedback Control With MATLAB - Boris J. Lurie and Paul J. EnrightDocumento477 pagineClassical Feedback Control With MATLAB - Boris J. Lurie and Paul J. Enrightffranquiz100% (2)
- Chemistry Reviewer 1Documento13 pagineChemistry Reviewer 1John Van Dave TaturoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 7 LAS Quarter 3Documento97 pagineMathematics 7 LAS Quarter 3Villamor Baculi82% (17)
- General and Inorganic Chemistry For Pharmacy PDFDocumento91 pagineGeneral and Inorganic Chemistry For Pharmacy PDFthucinorNessuna valutazione finora
- STEM General Chemistry 1 Q1 M2Documento19 pagineSTEM General Chemistry 1 Q1 M2GINA BAYTA100% (1)
- Earth & Life Science Summative TestDocumento2 pagineEarth & Life Science Summative TestAriane Ignao Lagatic50% (2)
- Gen Physics 1 M.examDocumento2 pagineGen Physics 1 M.examCamille ManlongatNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Exam For General Physics 1 - Quarter 2Documento13 pagineSummative Exam For General Physics 1 - Quarter 2Ma. Tina Valiere Dejaño100% (2)
- Els Midterm Exam 2018Documento6 pagineEls Midterm Exam 2018MarvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Test in Earth and Life Science (Answer Key)Documento2 paginePre-Test in Earth and Life Science (Answer Key)Pocholo GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021-2022 Final Exam General Biology 2Documento6 pagine2021-2022 Final Exam General Biology 2Mark De VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry 1 Reviewer Cpe4Documento13 pagineGeneral Chemistry 1 Reviewer Cpe4Fiona MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocumento4 pagineGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth and Life ScienceDocumento41 pagineEarth and Life ScienceMelanie perez cortez100% (2)
- DRRR 2nd Quarter Periodical Test (Reviewer)Documento36 pagineDRRR 2nd Quarter Periodical Test (Reviewer)Patty KrabbyNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry Module 2 PDFDocumento17 pagineGeneral Chemistry Module 2 PDFwelp100% (1)
- Term Exam in Gen Chem 2018Documento6 pagineTerm Exam in Gen Chem 2018seph bronNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: General Biology 2Documento25 paginePlant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: General Biology 2Ica A TorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 1 Finals 11 STEMDocumento3 pagineBio 1 Finals 11 STEMRosana De AsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Tos-General Chemistry Summative TosDocumento2 pagineTos-General Chemistry Summative TosChona Calvelo100% (1)
- Chemistry Before Modern HistoryDocumento26 pagineChemistry Before Modern Historypepito protacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Tos-Pretest-Posttest - Earth and Life ScienceDocumento5 pagineTos-Pretest-Posttest - Earth and Life ScienceRudula AmperNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Quarterly Examination in General Biology 1 SY 2022-2023Documento10 pagineSecond Quarterly Examination in General Biology 1 SY 2022-2023Ruby Uriarte100% (1)
- 3rd Summative Test in General Chemistry 2Documento1 pagina3rd Summative Test in General Chemistry 2christian baltao100% (1)
- Physics Reviewer Stem 12Documento6 paginePhysics Reviewer Stem 12Josue NaldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test No. 2 in Chemistry 2 (Q3)Documento2 pagineSummative Test No. 2 in Chemistry 2 (Q3)Franzhean Balais CuachonNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento63 pagineIntroductionJoyce Estrevencion100% (1)
- Gmail FWD - 1ST QUARTER GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 SUMMATIVE TESTDocumento6 pagineGmail FWD - 1ST QUARTER GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 SUMMATIVE TESTGaby DuranNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry Grade 12 ModuleDocumento90 pagineGeneral Chemistry Grade 12 ModuleJELANY AQUINONessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Quarter Exam FinalDocumento8 pagine4th Quarter Exam FinalMaria Fe VibarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 1: Physical PropertiesDocumento3 pagineChemistry 1: Physical Propertieskeith herreraNessuna valutazione finora
- GenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocumento8 pagineGenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter Reviewerjoshua tejadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2 - L4 - Chemical Equilibrium and Reaction StateDocumento34 pagineQ2 - L4 - Chemical Equilibrium and Reaction State4th AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 Summative Test 1Documento3 pagineGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 Summative Test 1MA. HAZEL TEOLOGO100% (1)
- DRRR Midterms ReviewerDocumento16 pagineDRRR Midterms ReviewerHans Matthew AntiojoNessuna valutazione finora
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Parallel Assessment 3&4Documento2 pagineGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Parallel Assessment 3&4rhaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Activities: How Humans Harness Earth's Energy in Producing Electricity?Documento3 pagineAdditional Activities: How Humans Harness Earth's Energy in Producing Electricity?Kristine NombrefiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 - General Chemistry 1 - LAS 1DDocumento8 pagineWeek 2 - General Chemistry 1 - LAS 1Ddo san namNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer For PhysicsDocumento3 pagineReviewer For PhysicsRegina Victoria Ortega100% (1)
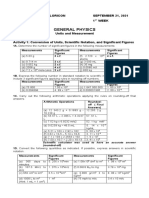
- General Physics: Andrie Jacob G. Doloricon SEPTEMBER 21, 2021 Grade Xii - Stem D 1 WeekDocumento6 pagineGeneral Physics: Andrie Jacob G. Doloricon SEPTEMBER 21, 2021 Grade Xii - Stem D 1 WeekReynaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Pretest in General Chemistry 2 MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read and Analyze The Statements and Questions Carefully. Identify The Best OptionDocumento2 paginePretest in General Chemistry 2 MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read and Analyze The Statements and Questions Carefully. Identify The Best OptionSalinas SalinasNessuna valutazione finora
- PW-23-Theoretical Yield and Percent Yield CalcsDocumento4 paginePW-23-Theoretical Yield and Percent Yield CalcsYna ForondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shs Gen - Chem 1-q1 Mel-4 Week-1Documento9 pagineShs Gen - Chem 1-q1 Mel-4 Week-1Kian Junsay Tan100% (1)
- Gr. 12 Chemistry Module 1 NotesDocumento24 pagineGr. 12 Chemistry Module 1 NotesAndrea EdwardsNessuna valutazione finora
- Long Quiz Earth and Life ScienceDocumento2 pagineLong Quiz Earth and Life SciencePocholo GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics 1 W 3-4Documento12 pagineGeneral Physics 1 W 3-4Emily Munsad AntolijaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Science (Second Quarter)Documento3 pagineEarth Science (Second Quarter)Christine Mananghaya100% (2)
- PigmentDocumento11 paginePigmentJai Balaji BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Isotope BrochureDocumento1 paginaIsotope BrochureFaith A. Dorado100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocumento4 pagineEarth and Life Science ReviewerKris Lea Delos Santos100% (1)
- Class - Xi - Biology: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Module - 1Documento20 pagineClass - Xi - Biology: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Module - 1priyam dasNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer Before The NumberDocumento2 pagineMultiple Choice: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer Before The NumberJojo JoestarNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 4 Know Me Better: Jed Enjelo C. Pabe STEM 12 ADocumento6 pagineActivity 4 Know Me Better: Jed Enjelo C. Pabe STEM 12 AJanine NicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Science ReviewerDocumento8 pagineScience ReviewerIT'S JAY STEPHEN0% (1)
- General Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Documento11 pagineGeneral Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNessuna valutazione finora
- Kulkarni Shilpa A.Documento148 pagineKulkarni Shilpa A.MSKCNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Vino Gano Ginger and Herbal Liquor On The Heamatological Parameters of The Wistar RatsDocumento5 pagineEffect of Vino Gano Ginger and Herbal Liquor On The Heamatological Parameters of The Wistar RatsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS PaintingDocumento81 pagineMSDS PaintingPaulina PaskahriaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidDocumento7 pagine2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidGustavo ResendeNessuna valutazione finora
- Campa Cola - WikipediaDocumento10 pagineCampa Cola - WikipediaPradeep KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid Lesson 1 Ethics & Moral PhiloDocumento13 pagineMid Lesson 1 Ethics & Moral PhiloKate EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inspirational Quotes General and ExamsDocumento6 pagineInspirational Quotes General and Examsasha jalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Muharem Bazdulj - The Second Book (Writings From An Unbound Europe) - Northwestern University Press (2005) PDFDocumento154 pagineMuharem Bazdulj - The Second Book (Writings From An Unbound Europe) - Northwestern University Press (2005) PDFjeff tehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - Reinforced Concrete - IntroductionDocumento62 pagineLecture 1 - Reinforced Concrete - IntroductionChristopher PaladioNessuna valutazione finora
- Fo Transfer ProcedureDocumento8 pagineFo Transfer ProcedureadityasahayNessuna valutazione finora
- Rezhna Hassan FarajDocumento2 pagineRezhna Hassan FarajchristoptNessuna valutazione finora
- Habitat Preference of Great Argus Pheasant ArgusiaDocumento11 pagineHabitat Preference of Great Argus Pheasant ArgusiaFaradlina MuftiNessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentDocumento13 pagineAssignmentSwakshar DebNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelton2014 Para-Equilibrium Phase DiagramsDocumento7 paginePelton2014 Para-Equilibrium Phase DiagramsAbraham Becerra AranedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignDocumento1 paginaLoad Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignBunkun15Nessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento413 pagineUntitledjgj38j90Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1704 Broschuere Metal-Coating en EinzelseitenDocumento8 pagine1704 Broschuere Metal-Coating en EinzelseiteninterponNessuna valutazione finora
- Tyba S4 Syntax PDFDocumento107 pagineTyba S4 Syntax PDFIndahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Documento503 pagineCho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Claudemiro costaNessuna valutazione finora
- مشخصات فنی بیل بکهو فیات کوبلکو b200Documento12 pagineمشخصات فنی بیل بکهو فیات کوبلکو b200Maryam0% (1)
- Hazel Rhs Horticulture Level 2 Essay 1Documento24 pagineHazel Rhs Horticulture Level 2 Essay 1hazeldwyerNessuna valutazione finora
- ZW250-7 BROCHURE LowresDocumento12 pagineZW250-7 BROCHURE Lowresbjrock123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Veg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenDocumento2 pagineVeg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenmusicalcarpetNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1Documento7 paginePresentation 1Abdillah StrhanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnDocumento14 pagineA Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnPaul SchumannNessuna valutazione finora
- DUPIXENT Doctor Discussion GuideDocumento4 pagineDUPIXENT Doctor Discussion GuideTAP THANH CHAUNessuna valutazione finora