Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
PPP Notes
Caricato da
needthisforepiCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PPP Notes
Caricato da
needthisforepiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Biochemistry Notes (Quiz #3)
--
Harper’s: Pentose Phosphate Pathway & Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (summary)
Alternative route for glucose metabolism
Leads to:
o formation of NADPH (for fatty acid and steroid synthesis)
o maintaining reduced glutathione (antioxidant activity)
o ribose synthesis (for nucleotide and nucleic acid formation)
Biomedical importance
Genetic deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) dehydrogenase acute hemolysis of RBC
hemolytic anemia
Glucuronic acid synthesized via uronic acid pathway glucuronides (significant for conjugation
and excretion of metabolites and foreign chemicals)
o Deficiency in pathway essential pentosuria
o Lack of gulonolactone oxidase in pathway explains why ascorbic acid is a dietary
requirement
Deficiency of enzymes for fructose and galactose metabolism essential fructosuria, hereditary
fructose intolerance, galactosemia
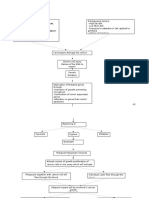
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
aka hexose monophosphate shunt (HMP shunt)
G6P IS BOTH THE SUBSTRATE AND END PRODUCT
3 G6P molecules 3 CO2 + 3 5-carbon sugars (pentoses) regeneration of 2 GP molecules + 1
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P/GADP)
o 3 G6P 3 CO2 + 3 pentoses 2 G6P + 1 GADP
Pentoses in pathway:
o Ribulose-5-phosphate
o Xylulose-5-phosphate
o Ribose-5-phosphate
2 GADP can regenerate 1 G6P
Reactions catalyzed by fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase are not freely reversible
PPP occurs in cytosol
NADP+ as hydrogen acceptor
Two phases
o IRREVERSIBLE oxidative phase
G6P dehydrogenation and decarboxylation ribulose-5-phosphate
o REVERSIBLE nonoxidative phase
Ribulose-5-phosphate G6P
Enzymes involved: transketolase, transaldolase
Oxidative Phase of PPP
Generates NADPH
STEP 1: G6P dehydrogenation 6-phosphogluconate
o ENZYME: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
NADP-dependent
o Occurs via the formation of 6-phosphogluconolactate
6-phosphogluconolactate hydrolysis by gluconolactone hydrolase
STEP 2: 6-phosphogluconate decarboxylation ribulose-5-phosphate
o ENZYME: 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
NADP+ as hydrogen acceptor
Hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
o Isoenzyme of G6P dehydrogenase
o Provides NADPH for hydroxylation and for 11-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1
o Catalyzes reduction of inactive cortisone to active cortisol in the liver, nervous system,
adipose tissue
o MAJOR SOURCE OF INTRACELLULAR CORTISOL
May be important in obesity and metabolic syndrome
Nonoxidative Phase of PPP
Ribulose-5-phosphate is a substrate of TWO enzymes:
o Ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase
Alters configuration of ribulose’s C3 yields epimer Xylulose 5-phosphate
o Ribulose-5-phosphate ketoisomerase
Converts to aldopentose Ribose-5-phosphate (used for nucleotide and nucleic
acid synthesis)
Transketolase
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Pengaturan Sistem RespirasiDocumento18 paginePengaturan Sistem RespirasiMaulidya MagfirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change Vulnerability Assessment of The Verde Island Passage, PhilippinesDocumento100 pagineClimate Change Vulnerability Assessment of The Verde Island Passage, PhilippinesGodofredo SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA ExtractionDocumento56 pagineDNA ExtractionZain YaqoobNessuna valutazione finora
- Geology and The Age of Earth - A. SnellingDocumento213 pagineGeology and The Age of Earth - A. Snelling7ett_40% (5)
- Listado de Especies Maldi Biotyper - Enero 2014Documento52 pagineListado de Especies Maldi Biotyper - Enero 2014Elias ENessuna valutazione finora
- A) Purpose of The Examination:: Sop No. Imm /Qm/12 Issue No.: 04 ISSUE DATE: 15april 2015 REV. NO.: 00 Rev. Date: 00Documento7 pagineA) Purpose of The Examination:: Sop No. Imm /Qm/12 Issue No.: 04 ISSUE DATE: 15april 2015 REV. NO.: 00 Rev. Date: 00prityNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Cultivation and Yield Performance of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus Ostreatus) On Wheat Straw Mixed With Horticultural Waste (Apple Pomace) in Different Ratio and Their Nutritional EvaluationDocumento14 pagineA Study On Cultivation and Yield Performance of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus Ostreatus) On Wheat Straw Mixed With Horticultural Waste (Apple Pomace) in Different Ratio and Their Nutritional EvaluationPheap ChanPisethNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Upload 2019 PDFDocumento55 pagineSyllabus Upload 2019 PDFMhohammad RifatNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbal Mini-CourseDocumento92 pagineHerbal Mini-CourselauraritonNessuna valutazione finora
- Contents of All Volumes: Natural Products Structural Diversity-I Secondary Metabolites: Organization and BiosynthesisDocumento763 pagineContents of All Volumes: Natural Products Structural Diversity-I Secondary Metabolites: Organization and BiosynthesisMarcio BragaNessuna valutazione finora
- 48 - Lecture - Presentation - 0 2Documento56 pagine48 - Lecture - Presentation - 0 2shea studiesNessuna valutazione finora
- General System TheoryDocumento307 pagineGeneral System TheoryCarlos Luiz100% (3)
- Biodanza by Rolando Toro in EnglishDocumento90 pagineBiodanza by Rolando Toro in EnglishJohn Jamieson100% (3)
- BeckyOrtiz ResumeDocumento2 pagineBeckyOrtiz ResumeBecky OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary Motor Cortex Changes After Amputation Correlate With Phantom Limb Pain and The Ability To Move The Phantom Limb 2016 NeuroImageDocumento11 paginePrimary Motor Cortex Changes After Amputation Correlate With Phantom Limb Pain and The Ability To Move The Phantom Limb 2016 NeuroImageLuís EduardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Malignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)Documento4 pagineMalignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)nursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Haploid CultureDocumento35 pagineHaploid CultureSpark is within me89% (18)
- WMG Giswnh 1.0Documento48 pagineWMG Giswnh 1.0Faisal ArdhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- "Phytochemical and Biological Studies On Leaves of Acalypha Indica Linn" byDocumento31 pagine"Phytochemical and Biological Studies On Leaves of Acalypha Indica Linn" bySridhar YadlapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- NutriophysiologyDocumento26 pagineNutriophysiologyAmal ShajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Free RadicalsDocumento18 pagineFree Radicalsswetha ramNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromosomal AbberationsDocumento33 pagineChromosomal AbberationsMubeena MoossaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Blood 1Documento11 pagineThe Blood 1Justine AlvaradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Home PDFDocumento38 pagineHome PDFJeimy MaciasNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 31A Exercise 4Documento6 pagineBIO 31A Exercise 4Genevieve Gayoso50% (2)
- Allergic Rhinitis & Vasomotor Rhinitis: Dr. Ritesh Mahajan ENT Consultant GMC, KathuaDocumento70 pagineAllergic Rhinitis & Vasomotor Rhinitis: Dr. Ritesh Mahajan ENT Consultant GMC, Kathuamanoj kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Miranda Et Al 2018 What Are Jaguars Eating in A Half-Empty ForestDocumento8 pagineMiranda Et Al 2018 What Are Jaguars Eating in A Half-Empty ForestEverton MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Armando Alducin - Creacion o EvolucionDocumento111 pagineArmando Alducin - Creacion o EvolucionmarianNessuna valutazione finora
- IliopsoasDocumento6 pagineIliopsoasSandro PinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Foundations of Ekistics PDFDocumento15 pagineThe Foundations of Ekistics PDFMd Shahroz AlamNessuna valutazione finora