Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Guided Notes - Cycles in Ecosystems 1
Caricato da
Yassine KootCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Guided Notes - Cycles in Ecosystems 1
Caricato da
Yassine KootCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cycles in Ecosystems
Glossary
TERM DEFINITION
hydrosphere
atmosphere
Weather describes the atmospheric conditions over a short period of time at one
weather location (e.g. rain, snow, thunderstorms). Climate describes the weather patterns in a
particular location over a long period of time.
A greenhouse gas is a compound that helps keep Earth warm by trapping heat from the
Sun. Greenhouse gases, which include carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane,
greenhouse gas
allow sunlight to freely pass through the atmosphere, but then absorb some of that
energy as it is radiated back from the Earth, making the atmosphere and Earth warmer.
the process by which plants and select other organisms transform radiant energy from
photosynthesis
the Sun into usable chemical energy
cellular respiration a metabolic process within cells that converts nutrients into ATP
ATP adenosine triphosphate, an energy biomolecule found in cells
geosphere
biosphere
water cycle
nitrogen cycle
carbon cycle
Fossil fuels are natural, organic fuels that form over millions of years from dead,
fossil fuels
decayed, and buried plants and animals. e.g. coal, petroleum, and natural gas
a change in global or regional climate patterns, most commonly referring to the current
climate change rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels due to fossil fuel use and other human
activities
Copyright © 2018 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Objective
In this lesson, you will _______________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________.
The Four Main Spheres
All life on Earth is connected, but life is also connected to the ________________ parts of the environment.
The four spheres of Earth interact to perform all of Earth’s ____________________. Any change to one sphere
will likely ____________ the other spheres.
The Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere includes all __________ that’s present on and near the surface of Earth. Of all the
water on Earth, about 97% is ________ __________ found in the ____________.
Only 3% is ____________________ that can humans can use. More than ______-____________ of the
freshwater available exists in solid form as ____________ ______, including ____________________.
Permafrost is ________ or ________ that is usually bound by ______ and remains
____________________ ____________ for at least two years.
The Atmosphere
The atmosphere is made up of a ____________ of
__________ which surround Earth. Based on
____________________, the atmosphere is divided into ________
layers. The ____________________ lies just above Earth’s surface
and is where most of Earth’s ____________ occurs.
Atmospheric Gases
▪ Nitrogen (N2) is the ________ ________________ gas, making
up about ______% of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is a major
component of all ________________ and of ____________
________________ (DNA).
▪ Argon is the most abundant of the __________ gases, which
together make up about 1% of the atmosphere.
Copyright © 2018 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
▪ Carbon dioxide (CO2) is another important __________ ______.
It is also a ____________________ gas, which helps keep the Earth warm and habitable. Plants require
carbon dioxide for ____________________________.
▪ Water vapor is also both a __________ gas and a ____________________ gas.
▪ Oxygen (O2) occupies ______% of the air, making it the second most abundant gas in the atmosphere.
Most eukaryotes and certain prokaryotes are ____________, which means they need ____________ for
cellular respiration. ________________ aerobes need oxygen for survival and growth.
On the other hand, some organisms die in the presence of oxygen. These are called ________________
________________. Organisms that can perform both aerobic and anaerobic respiration are called
____________________ anaerobes.
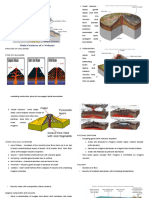
The Geosphere
The geosphere consists of __________, ________, and natural landforms such as ________________
and ________________. The geosphere is crucial to Earth’s ________________ and is part of
Earth’s ____________________.
Many organisms have evolved special ____________________ that allow them to live in and around certain
landforms. For example, mountain goats have thick, woolly fur and large lungs that allow them to live at high
altitudes. Bacteria that live in a volcano have mutations that allow them to survive in the extreme heat.
The Biosphere
The biosphere encompasses all ____________ ________________ on Earth, as well as their body
processes, such as ____________________________, cellular respiration, and the
________________ of waste.
Copyright © 2018 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Water, Nitrogen, and Carbon Cycles
The Water Cycle
The water cycle describes the ____________________ ________________ of water on and around Earth. The
________ of water on Earth is almost always ________________.
The ________ drives the water cycle. The Sun’s ________ influences processes such as
____________________, ____________, and storms.
Some water ____________________ from plant leaves. This process is called __________________________.
Water __________ rises up in the air,
where __________ temperatures
As water vapor _________________, the
________________ the vapor into tiny water droplets in the air grow heavier.
water droplets, forming ___________. Water falls from clouds in the form of
________, __________, ________, or hail.
The Sun _________ up the water,
causing it to change into water Melting snow and rain seep into
Water __________ ________
the soil. This process is called
vapor, or __________________, mountains and hills to form or
The Nitrogen Cycle ________________________.
into the ____________________. join streams and ___________.
The infiltrated water either joins
This process is known as
a ____________ or __________
____________ ____________.
deeper into the ________ to
form ______________________.
Copyright © 2018 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen is an important component of all ________________, ________, and chlorophyll. Living organisms
________ use the nitrogen in the air (N2) directly for body processes. Nitrogen is fixed into biologically useable
forms through the ________________ __________.
Atmospheric N2
Denitrification Nitrogen Fixation
Denitrifying bacteria break down Nitrogen-fixing _______________
________________ to form convert ____________________
nitrogen ______, which returns nitrogen (N2) into ____________.
to the ____________________.
Ammonification
Assimilation Bacteria called
Plants absorb nitrogen ____________________ break
Nitrification
____________________ from down __________ products and
Nitrifying bacteria convert
the ________, and animals return nitrogen to the ________.
____________ into oxygen-
______________ these plants.
containing compounds
( ________________ and
________________ ).
Copyright © 2018 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Carbon Cycle
Interaction Between Atmosphere Interaction Between Atmosphere
and Biosphere and Hydrosphere
Plants use ____________ ____________ ____________ and other bodies of
in the atmosphere for atmospheric CO2 water take in ____________
__________________________. ____________ from the
photosynthesi
Animals acquire ____________ ____________________.
s
by consuming ____________. combustion
They release ____________ respiration
___________ back into Interaction Between
the atmosphere during Geosphere and
__________________. Atmosphere
When people burn
Interaction Between Biosphere decay __________ _______,
decomposers
and Geosphere they release
When organisms die, they __________, ____________ ___________
fossil fuels
and ____________ enters the ________. back into the
After millions of years, their remains may ____________________.
turn into ____________ __________.
Burning ____________ __________ releases ____________ ____________ in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide
is a ____________________ ______. Human activities that release carbon dioxide have ____________ and, as
a result, more ________ is being trapped in the ____________________, causing Earth to be ____________
than usual. This warming is a phenomenon of ____________ ____________.
Summary
How do human activities contribute to the water, nitrogen, and carbon cycles?
Copyright © 2018 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Ecosystem in A JarDocumento2 pagineEcosystem in A Jarmilenerato2240Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Atmosphere and Living Things Worksheet AnswersDocumento18 pagineThe Atmosphere and Living Things Worksheet Answers2E (9) HON MARITA JANENessuna valutazione finora
- Biome Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineBiome Lesson Planapi-252165886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biophysical Environments: The AtmosphereDocumento5 pagineBiophysical Environments: The AtmosphereAnanya UppalNessuna valutazione finora
- Guided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Documento6 pagineGuided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Yassine KootNessuna valutazione finora
- Rock Cycle Worksheet 2Documento5 pagineRock Cycle Worksheet 2Louis Fetilo FabunanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomes and EcosystemsDocumento31 pagineBiomes and EcosystemsFrance KennethNessuna valutazione finora
- Glacial LandformsDocumento5 pagineGlacial LandformsqBataye NhiBatayengeNessuna valutazione finora
- Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Part 1Documento5 pagineContinental Drift and Plate Tectonics Part 1Jakie UbinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluids In The Earth's Crust: Their Significance In Metamorphic, Tectonic And Chemical Transport ProcessDa EverandFluids In The Earth's Crust: Their Significance In Metamorphic, Tectonic And Chemical Transport ProcessNessuna valutazione finora
- Silo - Tips - Student Exploration Plate Tectonics PDFDocumento5 pagineSilo - Tips - Student Exploration Plate Tectonics PDFFlvcko SlimNessuna valutazione finora
- Ni2 G 8 Underground Water Powerpoint - Ver - 3Documento8 pagineNi2 G 8 Underground Water Powerpoint - Ver - 3Logadarshini Chandra100% (1)
- Earthquake & SeismologyDocumento43 pagineEarthquake & Seismologymuktha mukuNessuna valutazione finora
- Rock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsDocumento4 pagineRock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsJuno PajelNessuna valutazione finora
- Littoral Cells and Sediment BudgetDocumento18 pagineLittoral Cells and Sediment Budgetmrceejay100% (1)
- ECOLOGY-1 (Compatibility Mode)Documento6 pagineECOLOGY-1 (Compatibility Mode)Tony Sdj100% (1)
- The Planet EarthDocumento62 pagineThe Planet EarthJohn OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch01 Earth in ContextDocumento33 pagineCh01 Earth in ContextmimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 6 KISS QuestionsDocumento13 pagineModule 6 KISS QuestionsHewadNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 AssessmentDocumento3 pagineWeek 2 Assessmentjanice alquizarNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 Weathering and SoilsDocumento21 pagine3.1 Weathering and SoilsjjjNessuna valutazione finora
- Coasts Key Word Glossary (1) MDocumento5 pagineCoasts Key Word Glossary (1) MRia PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Weathering & SoilDocumento59 pagineChapter 6 Weathering & SoilCristina RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainable EcosystemsDocumento5 pagineSustainable EcosystemsbobNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Forming FactorsDocumento3 pagineSoil Forming FactorsDylanOSullivanNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Formation WorksheetDocumento4 pagineSoil Formation WorksheetNina AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- The Restless EarthDocumento164 pagineThe Restless Earthb_osborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather and Climate - WorksheetDocumento4 pagineWeather and Climate - Worksheetlavender2x2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Sedimentary RocksDocumento64 pagineChapter 5 Sedimentary RocksJabir JammyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 WeatheringDocumento25 pagine3.1 WeatheringSipu GiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Cycle Y5Documento28 pagineWater Cycle Y5Menaga Ilangkovan100% (1)
- Rock Cycle Comic StripDocumento4 pagineRock Cycle Comic Stripapi-297070185100% (1)
- Layers of The EarthDocumento66 pagineLayers of The EarthIreneo Villanueva BatagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Structure..Documento10 pagineEarth Structure..Maitum Gemark BalazonNessuna valutazione finora
- Karnataka StratigraphyDocumento32 pagineKarnataka StratigraphyJaminiBoruahNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth's Energy BudgetDocumento4 pagineEarth's Energy BudgetSunay MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomes Kinds of EcosystemDocumento4 pagineBiomes Kinds of EcosystemDesiree G. SacasanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Water Cycle WorksheetDocumento2 pagineThe Water Cycle WorksheetFe Pakias GullodNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution-History and EvidenceDocumento19 pagineEvolution-History and Evidencekatexxx100% (1)
- 7th Grade BiomesDocumento19 pagine7th Grade BiomesCristianNoriegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Around Us Book 5Documento252 pagineScience Around Us Book 5Geofrey100% (1)
- Global Warming Is The Most Important Issue of The 21 CenturyDocumento2 pagineGlobal Warming Is The Most Important Issue of The 21 CenturyVarmenUchihaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomes ActivityDocumento3 pagineBiomes ActivitybabyduckiezNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Cycle WebquestDocumento6 pagineWater Cycle Webquestapi-330037580100% (1)
- Predicting Natural Hazards PowerPointDocumento29 paginePredicting Natural Hazards PowerPointZarlene SierraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsDocumento4 pagineRock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsJACKSON SANDERS-PUGHNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsDocumento42 pagineIGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsxerxesNessuna valutazione finora
- Water AssignmentDocumento3 pagineWater Assignmentapi-239344986100% (1)
- Plate Tectonics SEDocumento6 paginePlate Tectonics SEFlvcko SlimNessuna valutazione finora
- Jubail International School Trimester# 2Documento3 pagineJubail International School Trimester# 2Umama MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand Out EcosystemDocumento6 pagineHand Out EcosystemEvan GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- First Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Documento3 pagineFirst Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Ederzon IlustricimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy and EquilibriaDocumento24 pagineEnergy and EquilibriaRAGINI RAMACHANDRANNessuna valutazione finora
- Geology QuestionsDocumento14 pagineGeology Questionsanon_2257765420% (1)
- Biomes AssignmentDocumento3 pagineBiomes AssignmentLady Ann Enanoria MurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocumento11 pagineProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Sandstone and Carbonates, Dolomite and Dolomitization)Documento7 pagineClassification of Sandstone and Carbonates, Dolomite and Dolomitization)Tushar NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand-Out For VolcanoesDocumento4 pagineHand-Out For VolcanoesalyssaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 WeatheringDocumento21 pagine8 Weatheringnayvalente11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Guided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Documento6 pagineGuided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Yassine KootNessuna valutazione finora
- Guided Notes - The Carrying Capacity of Ecosystems 1Documento6 pagineGuided Notes - The Carrying Capacity of Ecosystems 1Yassine KootNessuna valutazione finora
- PAUT Course Material PDFDocumento189 paginePAUT Course Material PDFYassine Koot100% (3)
- Boiler & Pressure Vessel Inspection Report PDFDocumento1 paginaBoiler & Pressure Vessel Inspection Report PDFEslam KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Inspection Procedure 0222 160 P PT PTJ 0008Documento7 pagineVisual Inspection Procedure 0222 160 P PT PTJ 0008Yassine Koot100% (1)
- 12 - RadiosensitivityDocumento2 pagine12 - RadiosensitivityYassine KootNessuna valutazione finora
- 18.2 Nutrient CycleDocumento4 pagine18.2 Nutrient Cyclezain ul AbideenNessuna valutazione finora
- The 4 Cycles in The Great Barrier ReefDocumento3 pagineThe 4 Cycles in The Great Barrier Reefapi-339744501100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Earth Systems Part 2Documento18 pagineLesson 3 Earth Systems Part 2huehuehueNessuna valutazione finora
- Unity 4 BiosphereDocumento9 pagineUnity 4 BiosphereFredson kalindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenDocumento10 pagineEcosystem: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenJK JHANessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 SampleDocumento23 pagineModule 3 SampleMa. Florie MozoNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 BiologyDocumento32 pagineClass 9 BiologyAbinaya ParthasarathyNessuna valutazione finora
- Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980Documento5 pagineForest (Conservation) Act, 1980cprcdocumentation01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cycles WorksheetDocumento4 pagineCycles WorksheetRose Belle A. GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- GEE 001 - General Education Elective 1Documento61 pagineGEE 001 - General Education Elective 1Angeline Angeles100% (1)
- Plastic PollutionDocumento10 paginePlastic PollutionJOHN CHINANessuna valutazione finora
- Cycles of Matter VocabularyDocumento4 pagineCycles of Matter Vocabularyapi-454466657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical OceanographyDocumento8 pagineChemical OceanographyHalima akterNessuna valutazione finora
- IPCC AR6 WGI FAQ Chapter 01Documento8 pagineIPCC AR6 WGI FAQ Chapter 01SamNessuna valutazione finora
- Big 3Documento27 pagineBig 3dhe darmawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Book 2Documento424 pagineBook 2Anonymous DPt7hpiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch01 Xviii-045Documento46 pagineCh01 Xviii-045Anonymous 2MMAztJ5tNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change A Silent Threat by Sylvain Richer de ForgesDocumento225 pagineClimate Change A Silent Threat by Sylvain Richer de ForgesSylvain Richer de ForgesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Third Level by Jack FinneyDocumento22 pagineThe Third Level by Jack FinneyDharshan NagendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer in Science With Answer KeyDocumento5 pagineReviewer in Science With Answer KeyMelmar ReverenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cycles WorksheetDocumento4 pagineCycles WorksheetJenniferNessuna valutazione finora
- Sci9 WB IssuuDocumento27 pagineSci9 WB IssuuHansanee ChathurikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Berry 2021 Impact of Human CO2 DOIDocumento37 pagineBerry 2021 Impact of Human CO2 DOIFiachMacNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrogen and Carbon CycleDocumento4 pagineNitrogen and Carbon CycleAnna Marie LaganzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Above Ground Biomass Estimation Using Multispectral Sentinel-2 Msi Data: A Preliminary Experiment in Wangchan Forest Learning Center, ThailandDocumento6 pagineAbove Ground Biomass Estimation Using Multispectral Sentinel-2 Msi Data: A Preliminary Experiment in Wangchan Forest Learning Center, ThailandM'Souk LadsavongsaNessuna valutazione finora
- GH Chakra Environment Purvalokan 2022 (With Watermark)Documento237 pagineGH Chakra Environment Purvalokan 2022 (With Watermark)Aditi JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pollution, Waste and The Throwaway CultureDocumento3 paginePollution, Waste and The Throwaway CultureTootsie de los SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lutz - Et - al-2007-JGR POC Flux PDFDocumento26 pagineLutz - Et - al-2007-JGR POC Flux PDFBella MorteNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Literacy PDFDocumento17 pagineClimate Literacy PDFLeeda849Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Sequestration in SoilsDocumento4 pagineCarbon Sequestration in SoilsDee875Nessuna valutazione finora