Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Job Safety Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTD
Caricato da
Tigor GurningTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Job Safety Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTD
Caricato da
Tigor GurningCopyright:
Formati disponibili
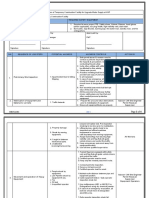
ROHAN BUILDERS (I) PVT LTD
Job Safety Analysis
DSM Engineering - MIDC Ranjangaon
PROJECT / TASK : Backfilling, levelling and Compaction for making Road CONTRACTOR: Rohan Builders JOB No.:
SUPERVISOR : Jaffer LOCATION : All over the site. DATE:
JOB STEP HAZARDS Control Measure ACTION
Break the job into steps. List the hazard or type of harm List the necessary control measures to be followed to Person who will ensure
Listing work which may be hazardous. identified with each step eliminate the identified hazards this happens
Backfilling, levelling & Compaction Vehicle Movement (Hit Hazard) Documents of mobile plants/vehicle to be cleared
before entering the site. Mr. Prakash Shinde
Check for Horn, Lights, brakes, rear view glass and
reverse horn to be done.
Valid licence to be checked for the Driver/Operator.
Access to be cleared from all unwanted materials
or traffic to enter the work area.
Helper to be provided for controlling the traffic by
signal & swing area of the equipment using for
levelling.
Area will be isolated with the help of barricading or
providing supervision for compaction equipment.
Continues supervision to be provided.
PPE’s to be provided (Safety Shoes, Helmet, Hand
gloves, goggles if required dust mask also be
provided.
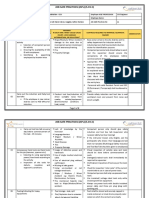
ROHAN BUILDERS (I) PVT LTD
Job Safety Analysis
Material Fall Hazard Do not overload the vehicle carrying the soil for
backfilling.
Barricading have to be done wherever there is an
Fall hazard area lower than the road after backfilling and
proper signage to be displayed if there is any deep.
Daily tool box to be given to all.
Continuous supervision to be provided.
Safety goggle to be provided.
Eye hazard
Nose mask to be provided.
Dust Hazard
Proper Area lighting to be provided other than
Working at night equipment or Vehicle light.
Job Hazard Analysis Attendees:
Name Signature Date
Written by:
Reviewed by:
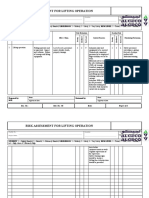
ROHAN BUILDERS (I) PVT LTD
Job Safety Analysis
Score TABLE OF CONSEQUENCE Score LIKELIHOOD
People Plant Environment
5 – Very High/ Multiple Fatalities Greater than Catastrophe, destruction of sensitive environment, worldwide 5 – Almost The event is expected to occur in most
Catastrophic $10Million Loss attention. Likely EPA prosecution. More than 30 days delay. certain circumstances. Likely to occur frequently-
More than 1 per year
4 – High/ Major Fatality or Permanent Disabilities $1Million to Disaster, high levels of media attention, high cost of clean 4 – likely/ The event will probably occur in most
$10Million Loss up. Offsite environmental harm, more than 10 days delay. probable circumstances. Likely to occur several tines. 1
per year
3 – Moderate Major Injuries - Incapacitations or $100Thousand to Major spills, onsite release, substantial environmental 3– The event should occur at some time. Likely to
requiring time of work $1Million Loss nuisance, more than 1day delay. (Leads to an additional moderate/ occur some time. 1 per 5 years
resources call out i.e. SES) occasional
2 – Low/ Minor Significant Injuries – Medical $10Thousand to Significant spills (leads to a call out of Site Emergency 2 – remote/ The event could occur at some time. Unlikely
Treatments, non-permanent injury $100Thousand Loss Response Group) unlikely but possible. 1 per 10 years
1 – Very Low/ Minor Injuries – First Aid Treatments Less than Low environmental impact. Minor Spills less than 80 Litres. 1 – rare/ The event may occur only in exceptional
Insignificant (cuts/bruises) $10Thousand Loss very circumstances. Assumed it may not be
unlikely experienced. 1 per 100 years
Action Required
Intolerable Task not to start till the risk is eliminated or reduced. Bring to the immediate attention of
5 6 7 8 9 10 8 - 10
management. Formal assessment required. MUST reduce the risk as a matter of priority.
High Bring to the immediate attention of management. Task not to start till the risk is eliminated or
4 5 6 7 8 9 7
reduced. Further Assessment required. MUST reduce the risk as a matter of priority.
Significant Risk Bring to the attention of supervision. Review risks and ensure that they are reduced to as low as
3 4 5 6 7 8 6 reasonably practicable. To be dealt with as soon as possible, preferably before the task
commences. Introduce some form of hardware to control risk.
Moderate Risk Needs to be controlled but not necessarily immediately, an action plan to control the risk should be
2 3 4 5 6 7 5 drawn up. Review effectiveness of controls. Ensure responsibilities for control are specified.
Low Risk If practical reduce the risk. Ensure personnel are competent to do the task. Manage by routing
1 2 3 4 5 6 2-4
procedure. Monitor for change
1 2 3 4 5 A JHA considers a variety of activities/tasks involved in a job scope and analyses the key hazards (sources of harm) and their
consequences (types of harm) eg. Sources of harm – lifting a heavy pipe, which is manual handling. Types of harm – Back strain.
Main Points – On how to write a JHA. Hierarchy of Hazard Management – Control Measures
1. Define the task – what is to be done. These steps outline what should be planned for when deciding what control measures are to be put in
2. Review previous JHA if any – have we done it before? place. Whenever possible the highest step should be used first and then progress down the list.
3. Identify the steps – what is to be done. 1. Eliminate the hazard.
4. Identify the hazards of each step. 2. Substitution.
5. Identify who or what could be harmed. 3. Reducing the frequency of a hazardous task.
6. Give the task a risk rating – Consequence + Frequency 4. Enclosing the hazard.
7. Develop solutions to eliminate or control hazards in each step. 5. Additional procedures.
8. Review the risk rating after the control system has been implemented. 6. Additional supervision.
9. If risk rating unacceptable review the solutions till risk rating acceptable. 7. Additional training.
10. Agree who will implement the control system. 8. Instructions / information.
11. Document the JHA and discuss with the relevant personnel. 9. Some personal protective equipment.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Job Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDDocumento5 pagineJob Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDsoubhagyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDDocumento4 pagineJob Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDsoubhagyaNessuna valutazione finora
- JSA For Demolation Work at Exiting OfficeDocumento3 pagineJSA For Demolation Work at Exiting OfficeMohammed MinhajNessuna valutazione finora
- RA - For Precast ChambersDocumento5 pagineRA - For Precast ChambersKallem RajashekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Jsa For Civil Confined Space EntryDocumento11 pagineJsa For Civil Confined Space EntryAmit SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Exacavation Job Safety AnalysisDocumento1 paginaExacavation Job Safety AnalysisNeelakantamNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Hazard Analysis: Task Excavation and Laying of Cable From A8 To A9Documento4 pagineJob Hazard Analysis: Task Excavation and Laying of Cable From A8 To A9OGBONNAYA MARTINSNessuna valutazione finora
- FO-JSA-08 - Lifting, Lowering, Laying and Backfilling of 6'' PipelineDocumento4 pagineFO-JSA-08 - Lifting, Lowering, Laying and Backfilling of 6'' PipelineRidha Bennasr100% (1)
- RA For Site Office Construction - ZeDocumento9 pagineRA For Site Office Construction - ZeimranNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) WorksheetDocumento4 pagineJob Hazard Analysis (Jha) WorksheetSamer AlsumaryNessuna valutazione finora
- JsaDocumento7 pagineJsaAnees TNessuna valutazione finora
- JSA-002 JSA For TCFDocumento4 pagineJSA-002 JSA For TCFRafeeq Ur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- JSA 02-03 Vertical Borehole and Anode Bed InstallationDocumento5 pagineJSA 02-03 Vertical Borehole and Anode Bed InstallationHaleemUrRashidBangash50% (2)
- Ref: Section / Dept: Civil Activity: Risk Assessment For False CeilingDocumento1 paginaRef: Section / Dept: Civil Activity: Risk Assessment For False CeilingJack P100% (2)
- Best Hse FileDocumento5 pagineBest Hse FileGilbert GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessment: Method Statement Painting ActivitiesDocumento11 pagineRisk Assessment: Method Statement Painting ActivitiesWalid Amdouni100% (1)
- Precast Erection JSWDocumento6 paginePrecast Erection JSWPrabhakaran GurunathanNessuna valutazione finora
- JSA For Diesel Filling at Del CampDocumento6 pagineJSA For Diesel Filling at Del CampMohammed Ali QaziNessuna valutazione finora
- SRB-JSA-41-Thrust Boring - 01 Febr 2010 - 56PL - KM 1+578Documento9 pagineSRB-JSA-41-Thrust Boring - 01 Febr 2010 - 56PL - KM 1+578kkalvi100% (1)
- Safe Work Method Statement: Excavation, Trenching and Underground ServicesDocumento5 pagineSafe Work Method Statement: Excavation, Trenching and Underground ServicesMorhne RufinNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Safety Analysis (Jsa) FormDocumento4 pagineJob Safety Analysis (Jsa) FormNaukhez A. KashifNessuna valutazione finora
- JSP For AsphaltDocumento8 pagineJSP For Asphaltmohammed tofiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessment - Portable Ladders - 2021Documento3 pagineRisk Assessment - Portable Ladders - 2021Asakundwi MukhwaNessuna valutazione finora
- ARK JSA Manual Excavation A 3Documento9 pagineARK JSA Manual Excavation A 3REMYANessuna valutazione finora
- RA - Plumbing Works Rev. BDocumento8 pagineRA - Plumbing Works Rev. BResearcherNessuna valutazione finora
- Cleaning Chlorination Water Tank Risk AnalysisDocumento2 pagineCleaning Chlorination Water Tank Risk AnalysisRamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazard IdentificationDocumento13 pagineHazard Identificationdiviyanraj95Nessuna valutazione finora
- Excavation of RoadDocumento7 pagineExcavation of RoadCharles LambNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk AssessmentDocumento5 pagineRisk AssessmentIshan DankharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily JSA - Fence Post InstallationDocumento5 pagineDaily JSA - Fence Post Installationshoaib akhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- RS Concrete Pumping Risk AssessmentDocumento8 pagineRS Concrete Pumping Risk AssessmentLito PanchoNessuna valutazione finora
- JSA For Road BarrierDocumento3 pagineJSA For Road BarrierMohammed MinhajNessuna valutazione finora
- F5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionDocumento13 pagineF5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionTaiwo Oshin100% (1)
- Risk AssessmentDocumento3 pagineRisk AssessmentAkinbami Olorunnifemi100% (1)
- 08n Safety Action PlanDocumento103 pagine08n Safety Action PlanMohammed MinhajNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessment For Stone WorkDocumento17 pagineRisk Assessment For Stone WorkKhuda BukshNessuna valutazione finora
- Sealcoating /crack Repair Parking Lots: Job Safety AnalysisDocumento3 pagineSealcoating /crack Repair Parking Lots: Job Safety AnalysisRetselisitsoe0% (1)
- Risk Assessment For Lifting OperationDocumento2 pagineRisk Assessment For Lifting OperationdsadasNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement For ExcavationDocumento2 pagineMethod Statement For ExcavationGkou Dojku100% (1)
- HSE-RA-019 Steel Fixing - Rev 0Documento15 pagineHSE-RA-019 Steel Fixing - Rev 0عمروNessuna valutazione finora
- JSP For Over Head Crane (JSP-HHI-Comm-07)Documento4 pagineJSP For Over Head Crane (JSP-HHI-Comm-07)Farooq MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- JSA 01 (Mechanical Excavation and Soil Loading Unloading, Night Shift)Documento1 paginaJSA 01 (Mechanical Excavation and Soil Loading Unloading, Night Shift)abdulthahseen007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ra 02 - Anti-Termite TreatmentDocumento4 pagineRa 02 - Anti-Termite TreatmentHafiz M WaqasNessuna valutazione finora
- JSA Backfilling, Leveling, (Night Shift)Documento14 pagineJSA Backfilling, Leveling, (Night Shift)Mohammad Al Masa'dehNessuna valutazione finora
- Excavations JSA Final 2015Documento5 pagineExcavations JSA Final 2015jithin shankarNessuna valutazione finora
- INSTALLATION OF Toilet Cubicle PartitionDocumento4 pagineINSTALLATION OF Toilet Cubicle PartitionLeo Pascual100% (1)
- Risk Assessmen For-Excavation-And-BackfillingDocumento4 pagineRisk Assessmen For-Excavation-And-BackfillingEngrHazrat Maaz100% (1)
- JSA-010 Excavation Sampling PDFDocumento5 pagineJSA-010 Excavation Sampling PDFArgaYurIstiawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Idoc - Pub - Task Risk Assessment For RadiographyDocumento5 pagineIdoc - Pub - Task Risk Assessment For RadiographySasi YNessuna valutazione finora
- F5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionDocumento11 pagineF5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionTaiwo OshinNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - Risk Assessment - PlumpingDocumento7 pagine10 - Risk Assessment - Plumpingmahmoud nada0% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis WorksheetDocumento4 pagineJob Safety Analysis WorksheetSAHIL SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Tower CarneDocumento2 pagineTower CarnenabeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Brick Masonry - EHS Risk AssessmentDocumento2 pagineBrick Masonry - EHS Risk Assessmentnagarjuna100% (3)
- RA For Cable Pulling and WiringDocumento11 pagineRA For Cable Pulling and Wiringnikhilsingh1087Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jsa006-Construction of Retaining WallDocumento5 pagineJsa006-Construction of Retaining WallWan Muhammad Faiz100% (1)
- JSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware HouseDocumento9 pagineJSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware Houseradeep100% (1)
- JSA - Backfilling, Levelling Metteling & CompactionDocumento2 pagineJSA - Backfilling, Levelling Metteling & CompactionRaju KhalifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDDocumento4 pagineJob Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDDocumento6 pagineJob Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDsoubhagya100% (1)
- 00 CM-HSE-SWP-01 Safety InductionDocumento3 pagine00 CM-HSE-SWP-01 Safety InductionTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidance Note For Drop Zone Management Within The VESI - February 2016Documento7 pagineGuidance Note For Drop Zone Management Within The VESI - February 2016Tigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- 00 CM-HSE-SWP-02 Incident ReportingDocumento5 pagine00 CM-HSE-SWP-02 Incident ReportingTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- OCP For Security ActivitiesDocumento2 pagineOCP For Security ActivitiesTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- LSR Rule5 BookletDocumento38 pagineLSR Rule5 BookletTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- Ocp For CanteenDocumento4 pagineOcp For CanteenTigor Gurning0% (2)
- Procedure For Communication, Participation and ConsultantationDocumento5 pagineProcedure For Communication, Participation and ConsultantationTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- OCP For Monitoring and Control of Dust FumesDocumento1 paginaOCP For Monitoring and Control of Dust FumesTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- OCP For Sanitary MaintenanceDocumento1 paginaOCP For Sanitary MaintenanceTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- OCP For Mock Drill of Onsite Emergency PlanDocumento3 pagineOCP For Mock Drill of Onsite Emergency PlanTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- ISMS Access ControlDocumento29 pagineISMS Access ControlTigor Gurning100% (1)
- OCP For Machine SafetyDocumento1 paginaOCP For Machine SafetyTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- JHA For Painting WorkDocumento2 pagineJHA For Painting WorkTigor Gurning100% (1)
- JHA For Shuttring and DeshuttringDocumento2 pagineJHA For Shuttring and DeshuttringTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- OCP For Handling of MaterialsDocumento3 pagineOCP For Handling of MaterialsTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- OCP For Housekeeping and Air Quality MonitoringDocumento3 pagineOCP For Housekeeping and Air Quality MonitoringTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- QMS - Risk Register - Risk Identification: Related Internal/ External Issues or RequirementsDocumento26 pagineQMS - Risk Register - Risk Identification: Related Internal/ External Issues or RequirementsTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- JHA For Concreting WorkDocumento2 pagineJHA For Concreting WorkTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagram of ISO 45001 Implementation Process: To Learn More About The ISO 45001, Click HereDocumento1 paginaDiagram of ISO 45001 Implementation Process: To Learn More About The ISO 45001, Click HereTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDDocumento4 pagineJob Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Aid Training Siemens ContractorDocumento11 pagine1st Aid Training Siemens ContractorTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- Db Shr 010 전사 안전보건방침Documento2 pagineDb Shr 010 전사 안전보건방침Tigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- Free 3x3 Risk-MatrixDocumento1 paginaFree 3x3 Risk-MatrixTigor Gurning100% (3)
- AUDIT OF: ISO 45001:2016 Occupational Health & SafetyDocumento15 pagineAUDIT OF: ISO 45001:2016 Occupational Health & SafetyTigor GurningNessuna valutazione finora
- tdr100 - DeviceDocumento4 paginetdr100 - DeviceSrđan PavićNessuna valutazione finora
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocumento66 pagineIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofcicil josyNessuna valutazione finora
- TOEFLDocumento6 pagineTOEFLSekar InnayahNessuna valutazione finora
- TP1743 - Kertas 1 Dan 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Sains 2023-20243Documento12 pagineTP1743 - Kertas 1 Dan 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Sains 2023-20243Felix ChewNessuna valutazione finora
- Donation Drive List of Donations and BlocksDocumento3 pagineDonation Drive List of Donations and BlocksElijah PunzalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Creative Thinking (2) : Dr. Sarah Elsayed ElshazlyDocumento38 pagineCreative Thinking (2) : Dr. Sarah Elsayed ElshazlyNehal AbdellatifNessuna valutazione finora
- Is.14785.2000 - Coast Down Test PDFDocumento12 pagineIs.14785.2000 - Coast Down Test PDFVenkata NarayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- PHP IntroductionDocumento113 paginePHP Introductionds0909@gmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Sangeetahealingtemples Com Tarot Card Reading Course in UsaDocumento3 pagineSangeetahealingtemples Com Tarot Card Reading Course in UsaSangeetahealing templesNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Resource Management by John Ivancevich PDFDocumento656 pagineHuman Resource Management by John Ivancevich PDFHaroldM.MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- QG To AIS 2017 PDFDocumento135 pagineQG To AIS 2017 PDFMangoStarr Aibelle VegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantity DiscountDocumento22 pagineQuantity Discountkevin royNessuna valutazione finora
- Intelligent Smoke & Heat Detectors: Open, Digital Protocol Addressed by The Patented XPERT Card Electronics Free BaseDocumento4 pagineIntelligent Smoke & Heat Detectors: Open, Digital Protocol Addressed by The Patented XPERT Card Electronics Free BaseBabali MedNessuna valutazione finora
- ML7999A Universal Parallel-Positioning Actuator: FeaturesDocumento8 pagineML7999A Universal Parallel-Positioning Actuator: Featuresfrank torresNessuna valutazione finora
- Amazon Case StudyDocumento22 pagineAmazon Case StudySaad Memon50% (6)
- Possession: I. A. Definition and Concept Civil Code Art. 523-530 CasesDocumento7 paginePossession: I. A. Definition and Concept Civil Code Art. 523-530 CasesPierrePrincipeNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface CareDocumento18 pagineSurface CareChristi ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Guaranty Corp. v. Manlapaz - PunzalanDocumento3 pagineHome Guaranty Corp. v. Manlapaz - PunzalanPrincess Aliyah Punzalan100% (1)
- A Survey On Multicarrier Communications Prototype PDFDocumento28 pagineA Survey On Multicarrier Communications Prototype PDFDrAbdallah NasserNessuna valutazione finora
- Sacmi Vol 2 Inglese - II EdizioneDocumento416 pagineSacmi Vol 2 Inglese - II Edizionecuibaprau100% (21)
- BACE Marketing Presentation FINALDocumento14 pagineBACE Marketing Presentation FINALcarlosfelix810% (1)
- 87 - Case Study On Multicomponent Distillation and Distillation Column SequencingDocumento15 pagine87 - Case Study On Multicomponent Distillation and Distillation Column SequencingFranklin Santiago Suclla Podesta50% (2)
- KV Tripple Eccentric Butterfly Valve-LinDocumento12 pagineKV Tripple Eccentric Butterfly Valve-LinWelma JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- In Comparison With Oracle 8i, 9i Is Have Lot Many New Features. Important IsDocumento241 pagineIn Comparison With Oracle 8i, 9i Is Have Lot Many New Features. Important IsBalaji ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminium Extrusion Industry in IndiaDocumento3 pagineAluminium Extrusion Industry in Indiakalan45Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vice President Enrollment Management in Oklahoma City OK Resume David CurranDocumento2 pagineVice President Enrollment Management in Oklahoma City OK Resume David CurranDavidCurranNessuna valutazione finora
- Projects: Term ProjectDocumento2 pagineProjects: Term ProjectCoursePinNessuna valutazione finora
- BreezeAIR 8000 Data SheetDocumento2 pagineBreezeAIR 8000 Data Sheetalfasukarno100% (1)
- 7Documento101 pagine7Navindra JaggernauthNessuna valutazione finora
- List of People in Playboy 1953Documento57 pagineList of People in Playboy 1953Paulo Prado De Medeiros100% (1)