Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Experiment: Comparing How Substances Change State: Apparatus
Caricato da
zainurain zainal abidin0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
24 visualizzazioni3 pagineTitolo originale
Practical_sheet_Changing State.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
24 visualizzazioni3 pagineExperiment: Comparing How Substances Change State: Apparatus
Caricato da
zainurain zainal abidinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Name: _____________________________ Class: _______________
Experiment: Comparing how substances change state
In this practical you will investigate and compare how two different substances change state.
Apparatus
You will need:
beaker (250 cm3)
boiling tube and boiling tube rack
thermometer (0–100 °C)
stopclock
clamp, stand and boss
Bunsen burner, tripod and gauze
heat-resistant mat
stearic acid
crushed ice
eye protection
SAFETY INFORMATION
Wear eye protection at all times.
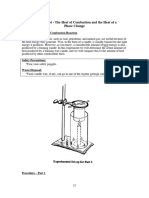
Method for melting stearic acid
1. Fill the beaker with water until it is about three-
quarters full.
2. Place it on a gauze above the Bunsen burner.
3. Wear eye protection, and heat the water with the
Bunsen burner, until it starts to boil.
4. Place 5 g of stearic acid in the boiling tube, and
place this in the beaker of boiling water. Hold a
thermometer, with the bulb in the centre of the
stearic acid, with a clamp, as shown in the diagram.
5. Record the temperature of the stearic acid every
minute until it reaches about 70 °C.
6. Using tongs, carefully lift the boiling tube from the
water and place it in a boiling tube rack. Now
measure and record the temperature every minute
as the stearic acid cools. Record the temperature at
which you see the stearic acid begin to solidify. This
is the melting temperature; it should be near 50 °C.
7. Repeat the investigation with the same stearic acid,
until you have three readings for the melting point.
Omit any anomalies (readings that are very different
from the others) and calculate the mean value.
Results
Note down:
first melting point of stearic acid
second melting point of stearic acid
third melting point of stearic acid
Calculate the mean value for the melting point of stearic acid
Time (min) Temperature (°C)
0
1
Temperature (°C)
First melting point Second melting point Third melting point Average
Method for melting ice and boiling water
1. Put about 3 cm depth of crushed ice into a 250 cm3 beaker.
2. Use the thermometer to record the temperature in the table at time 0 min. In the third column,
write down whether the water is a solid, a liquid or a gas or changing between two of these.
3. Set up the beaker of ice over the Bunsen burner. Light your Bunsen burner and heat the ice over
a blue flame. Start your stopwatch as you start heating.
4. Record the temperature every minute. Do not remove the thermometer from the beaker when you
are reading it.
5. Continue until the water is boiling and then take two more readings.
6. Turn your Bunsen burner off and allow the apparatus to cool before clearing away.
Results
1. Draw up a table like this to record all repeat readings for melting and boiling water. Also record
the temperatures at which ice melts and and which water boils.
Time (min Temperature (°C) State of matter
0
1
Analyse and interpret data
2. Draw two graphs, with lines of best fit and using mean values where apropriate. One graph
should show what happens as stearic acid melts and the other should show the melting of ice and
boiling
of water.
3. Describe what is happening at each stage of when the shape of the graph changes.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Procedure Proposal Experiment 22Documento21 pagineProcedure Proposal Experiment 22Thomas L. Knight80% (5)
- The Properties of Water-Partnered Lab Report 2Documento9 pagineThe Properties of Water-Partnered Lab Report 2api-2423695850% (1)
- 19c Latent Heat of FusionDocumento3 pagine19c Latent Heat of FusionAndrae Tennant100% (1)
- CIVL 5076 Notes Complete 02Documento87 pagineCIVL 5076 Notes Complete 02Ahmad SanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Analysis of Thrust Chambers: RPA: Tool For Rocket Propulsion AnalysisDocumento26 pagineThermal Analysis of Thrust Chambers: RPA: Tool For Rocket Propulsion AnalysisBill M. SpragueNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Experiment For Measuring The Latent Heat of IceDocumento2 pagineHome Experiment For Measuring The Latent Heat of IcechlronaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Ice Water SteamDocumento4 pagineIce Water SteamDustdragonNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrocher Patric Trending DataDocumento4 pagineCorrocher Patric Trending DataJackie McCarthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat of Fusion and IceDocumento3 pagineHeat of Fusion and Iceapi-702229801Nessuna valutazione finora
- Melting and Freezing Stearic AcidDocumento3 pagineMelting and Freezing Stearic AcidJoko SusiloNessuna valutazione finora
- M3 Chem1050 LMDocumento9 pagineM3 Chem1050 LMPPK Cat yanNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 Experiment No 1Documento3 pagineClass 9 Experiment No 1Dreamy YTNessuna valutazione finora
- File 5 27 - 1-23Documento23 pagineFile 5 27 - 1-23Almajd MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Heat of Combust and Phase W PictureDocumento4 pagine6 Heat of Combust and Phase W Pictureaeliaeli29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heating and Cooling Curve of WaterDocumento5 pagineHeating and Cooling Curve of WaterYoung PilotNessuna valutazione finora
- 212 Latent Heat of Water BunsenDocumento1 pagina212 Latent Heat of Water BunsenCostas PaschalidesNessuna valutazione finora
- Dystan Medical Supply Company - Cold Packs and Hot Packs Lab ReportDocumento10 pagineDystan Medical Supply Company - Cold Packs and Hot Packs Lab ReportVivek Patel80% (5)
- Experiment 5 in Chemistry For Engineers - ThermochemistryDocumento2 pagineExperiment 5 in Chemistry For Engineers - Thermochemistrykristine lorenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Freezing and Melting of Water: ExperimentDocumento8 pagineFreezing and Melting of Water: ExperimentagrikarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Phase Change Lab: INTRODUCTION: When Heat Is Added To Ice, It Will Melt and Change To WaterDocumento1 paginaPhase Change Lab: INTRODUCTION: When Heat Is Added To Ice, It Will Melt and Change To WaterOZZIE OTTERBEINNessuna valutazione finora
- OrgChem Prelim ManualDocumento13 pagineOrgChem Prelim ManualCHEA MICH L. ABELLANONessuna valutazione finora
- The Plateau ProblemaDocumento4 pagineThe Plateau ProblemaMuhammad AbidNessuna valutazione finora
- HT Lab Report File 19112043 Jayesh Kumar Verma Group One Exp-4 Newton's Law of CoolingDocumento6 pagineHT Lab Report File 19112043 Jayesh Kumar Verma Group One Exp-4 Newton's Law of CoolingJayesh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- FPDepressionDocumento2 pagineFPDepressionMaryam Adila JusohNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 8 - Calorimetry Edit June'14Documento11 pagineLab 8 - Calorimetry Edit June'14davidrbadkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem PlanningDocumento4 pagineChem PlanningJiadong YeNessuna valutazione finora
- PT2NDQTR ColligativepropertiesDocumento5 paginePT2NDQTR ColligativepropertiesNicolette BingtanNessuna valutazione finora
- Stearic AcidDocumento4 pagineStearic Acidpchenault50% (2)
- Universidad Tecnologica Centroamericana: Cambios de FaseDocumento14 pagineUniversidad Tecnologica Centroamericana: Cambios de FaseAndrea SortoNessuna valutazione finora
- Enthalpy of Solution and ReactionDocumento5 pagineEnthalpy of Solution and ReactionCarmen GoguNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: - Date: - Grade & Section: - Score: - Getting To Know GasesDocumento5 pagineName: - Date: - Grade & Section: - Score: - Getting To Know GasesArniel Catubig0% (1)
- The Hand Warmer Designv2Documento3 pagineThe Hand Warmer Designv2Mohommad YawariNessuna valutazione finora
- Blake EbinerDocumento2 pagineBlake Ebinerapi-245726692Nessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Affecting SolubilityDocumento3 pagineFactors Affecting SolubilityAnna Van GoudoeverNessuna valutazione finora
- Activitity No12 Melting Point and Boiling Point DeterminationDocumento7 pagineActivitity No12 Melting Point and Boiling Point DeterminationVaron Soriano SulitNessuna valutazione finora
- PROCEDUREDocumento17 paginePROCEDUREOliver MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- SpecificheatlabreportDocumento3 pagineSpecificheatlabreportapi-216637770Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1 Measurment in ChemistryDocumento7 pagineLab 1 Measurment in ChemistryAmanda WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem032 - Simple Distillation and Boiling Point DeterminationDocumento3 pagineChem032 - Simple Distillation and Boiling Point DeterminationBryanNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemE WorkbookDocumento35 pagineChemE WorkbookVincent GuiaNessuna valutazione finora
- How The Carbon Dioxide Production Rate Is Affected by Different Conditions of Yeast BioDocumento2 pagineHow The Carbon Dioxide Production Rate Is Affected by Different Conditions of Yeast BioStashNessuna valutazione finora
- Environment MattersDocumento3 pagineEnvironment Matterslamouna.lamittaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activities Term 2Documento6 pagineActivities Term 2studies for sundarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Cve501-Cve526 - Eng15b00342yDocumento17 pagineLab Report Cve501-Cve526 - Eng15b00342yAble ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Charles Law LabDocumento2 pagineCharles Law Labapi-645795047Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics4 01measuringtemperatureDocumento4 paginePhysics4 01measuringtemperatureapi-238185553Nessuna valutazione finora
- PropertiesofWaterLab 1Documento6 paginePropertiesofWaterLab 1Brittany BarnettNessuna valutazione finora
- Episode 608 3 Heating and Cooling CurvesDocumento3 pagineEpisode 608 3 Heating and Cooling CurvesweiliNessuna valutazione finora
- Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation LabDocumento4 pagineFreezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation LabBeatrice Dominique Caragay25% (4)
- Experiment 6 (Calibration of Temperature Measuring Devices - A4)Documento16 pagineExperiment 6 (Calibration of Temperature Measuring Devices - A4)Jamiel CatapangNessuna valutazione finora
- I'm Really SteamedDocumento2 pagineI'm Really SteamedmamazookeeprNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Freeze Melt Water NspireDocumento3 pagine18 Freeze Melt Water NspireTha KantanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationDocumento5 pagineExperiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationMae Joy PalmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheets in SolutionDocumento2 pagineActivity Sheets in SolutionAURORA () CARIAGANessuna valutazione finora
- Investigation The Relationship Between Hydrochloric Acid and Sodium ThiosulphateDocumento9 pagineInvestigation The Relationship Between Hydrochloric Acid and Sodium Thiosulphatelena0% (1)
- Molar Mass by Freezing Point Depression: ExperimentDocumento11 pagineMolar Mass by Freezing Point Depression: ExperimentEmmanuel JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Freezing PT Depr Lab AP StudentDocumento2 pagineFreezing PT Depr Lab AP StudentMinecraft LeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 212 Determination of The Latent Heat of Fusion of IceDocumento4 pagineExperiment 212 Determination of The Latent Heat of Fusion of IceKerim SabicNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 212 Determination of The Latent Heat of Fusion of IceDocumento4 pagineExperiment 212 Determination of The Latent Heat of Fusion of Iceمصطفى العباديNessuna valutazione finora
- SALTISE Chem Protocol Colligative Properties v2Documento9 pagineSALTISE Chem Protocol Colligative Properties v2Khaeru NisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceDa EverandRefrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather Studies: The Commonwealth and International Library: Rural and Environmental Studies DivisionDa EverandWeather Studies: The Commonwealth and International Library: Rural and Environmental Studies DivisionNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: - ClassDocumento6 pagineName: - Classzainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Sheet Changing StateDocumento35 paginePractical Sheet Changing Statezainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissolving and Solutions QuestionsDocumento1 paginaDissolving and Solutions Questionszainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Units and Measurement: Physics Mrs. CoyleDocumento29 pagineUnits and Measurement: Physics Mrs. Coylezainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Explorace 2017Documento2 pagineScience Explorace 2017zainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory SystemDocumento1 paginaRespiratory Systemzainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Celery LabDocumento4 pagineCelery Labzainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Explorace 2017Documento2 pagineScience Explorace 2017zainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Qs On ClassificationDocumento5 pagineMultiple Choice Qs On Classificationzainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Frog Dissection ScriptDocumento3 pagineFrog Dissection Scriptzainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Features of The 5 Classes of VertebratesDocumento1 paginaFeatures of The 5 Classes of Vertebrateszainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysing Muscle StrengthDocumento3 pagineAnalysing Muscle Strengthzainurain zainal abidinNessuna valutazione finora
- THERMODYNAMICSDocumento3 pagineTHERMODYNAMICSAngelene Nova MondaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Uniform FlowDocumento60 pagineNon Uniform Flowhelloyou101100% (1)
- Cartuchos Sandvik PDFDocumento16 pagineCartuchos Sandvik PDFJefatura de Planta Invemet PeruNessuna valutazione finora
- Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.)Documento10 pagineKenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.)valentine mutungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Incropera Ex 2.2 7 Ed.Documento2 pagineIncropera Ex 2.2 7 Ed.luanremNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento46 pagineLecture 2Atalelew ZeruNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM Standards of Prestressing Tendons (Properties and Corresponding Values of Fpy and Fpu)Documento3 pagineASTM Standards of Prestressing Tendons (Properties and Corresponding Values of Fpy and Fpu)AaronNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery 2nd Mid QP BitsDocumento8 pagineFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery 2nd Mid QP BitsBell P PedNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid 30Documento10 pagineFluid 30RafaelTeixeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration Analysis of Rectangular Plates Coupled With Uid: Y. Kerboua, A.A. Lakis, M. Thomas, L. MarcouillerDocumento17 pagineVibration Analysis of Rectangular Plates Coupled With Uid: Y. Kerboua, A.A. Lakis, M. Thomas, L. MarcouilleryohannesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid-Fluid Reaction KineticsDocumento34 pagineFluid-Fluid Reaction KineticsHarsh TekriwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Lectr Online Clases Separation Processes - Prepared By:ms - Ammarah BatoolDocumento161 pagineRevision Lectr Online Clases Separation Processes - Prepared By:ms - Ammarah BatoolHajra AamirNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Foundation Engineering: Shallow Foundations: Allowable Bearing Capacity and SettlementDocumento45 paginePrinciples of Foundation Engineering: Shallow Foundations: Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlementvishal kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction and Classification of Fluid Machines: Hemant KR ChoudharyDocumento8 pagineIntroduction and Classification of Fluid Machines: Hemant KR ChoudharyBalmukund KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Isrm2019 Cosserat Biot Diego e Rodrigo PDFDocumento8 pagineIsrm2019 Cosserat Biot Diego e Rodrigo PDFRodrigo Peluci de FigueiredoNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 6Documento133 pagineSection 6ILAYAPERUMAL K100% (2)
- Stress Strain and The Young ModulusDocumento3 pagineStress Strain and The Young ModulusChi Nguyễn PhươngNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet Metal Forming ProcessesDocumento15 pagineSheet Metal Forming ProcessesasifNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth DamsDocumento51 pagineEarth DamsC_C_8717100% (4)
- Unit - 1: General Features of Reinforced ConcreteDocumento36 pagineUnit - 1: General Features of Reinforced ConcretemdaashuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento1 paginaAssignment 1Pragya YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration CalculationsDocumento24 pagineRefrigeration CalculationsShankarMukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvulas Apollo GLPDocumento4 pagineValvulas Apollo GLPJuan Carlos Pardo RimachiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 17Documento17 pagineChapter 17islamkibaatein316Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coil TubingDocumento15 pagineCoil TubingOgbadiboNessuna valutazione finora
- Losses in Steam TurbineDocumento6 pagineLosses in Steam TurbineMohamed Abashar MusmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 3 ProblemsDocumento2 pagineTutorial 3 ProblemsBhavishya GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 07 MS2220 Basic Fluid Mechanics CH 5 Finite Control Volume Analysis Part 2Documento42 pagineWeek 07 MS2220 Basic Fluid Mechanics CH 5 Finite Control Volume Analysis Part 2Jessy PatriciaNessuna valutazione finora