Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Electrode Kinetics and Polarization Phenomenon
Caricato da
bhanuTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electrode Kinetics and Polarization Phenomenon
Caricato da
bhanuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1
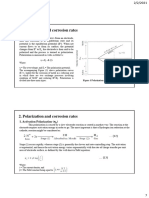
Electrode kinetics and Polarization phenomena
P. Bhanu Prakash, 16005A0805, IV B.Tech Chemical Engineering, JNTUA CEA
The electrochemical reaction differs from a chemical
Abstract-- An electrode is an ideal catalyst in reaction in that at least one of the partial reactions of
that the potential difference at electrode solution the overall electrode reaction must be a charge
interface controls both the thermodynamics and the transfer reaction which involves the transfer of
kinetics of electro chemical reactions. The electrode charge across the double layer. The rate of electrode
kinetics play an important role to understand the reaction is proportional to the current density which
corrosion behavior of the metals in different in turn depends on the electrode potential,
environment. Here the possible to transfer of concentration of the reactants and temperature. As in
electrons between the electrode and electrolyte. This the case of chemical reaction kinetics, the slowest
process is results in a reactant undergoing an reaction in the overall reaction is the rate determining
oxidation and reduction reaction. The electrolysis step in electrode kinetics also. Since the electrode
results in flow of current around the electrical circuit. process is heterogenous in nature, its reaction rate is
The rate of current can be controlled between the
considerably influenced by the double layer
metal and species of solution. Polarization is
structure, adsorption of reactants, products,
collective term for certain mechanical side effects (of
a electrochemical process) by which isolating barrier supporting electrolyte and other addition agents.
developing the interface between the electrode and
electrolyte. This polarization influence the reaction
mechanism chemical kinetics of electrode which 2. Polarization:
leads to corrosion. It is decreases the potential of Polarization is a mechanism that typically results
electrode. in a change in the potential of an electrode during
. electrolysis, when the anode’s potential becomes
nobler than that of the cathode. It has the effect
I. INTRODUCTION (based on conditions) of decreasing the output
1.Electrode kinetics: voltage of batteries, and increasing the voltage
Electrode reactions are heterogeneous processes required for electrolysis cells or lowering currents.
involving a number of steps whose kinetics depend Polarization can also be described as a kinetic
on the rate of charge transfer and mass transfer and deviation from equilibrium due to an electric current
the rate of chemical reactions coupled with charge passing through a galvanic cell. Polarization may
transfer. The reaction kinetics of an electrochemical occur at the cathode (cathodic polarization) or at the
reaction depend not only on the concentration of the anode (anodic polarization). Cathodic polarization is
reactants, the temperature and the material of the more common.
catalyst but also on the electrode potential. Since the
electrode potential depends on the concentration of
the reactants, temperature etc., it is possible to II. EXPLANATION
calculate the various thermodynamic parameters Electrode kinetics:
from the study of electrode potential as a function of In this section we will develop a quantitative current
temperature or concentration. flowing in either the reductive or oxidative steps can
be predicted using the following expressions for the
influence of the electrode voltage on the rate of
2
electron transfer. For simplicity we will consider a
single electron transfer reaction between two species where the term in the exponential is the free energy
(O) and (R) change in taking the reactant from its initial value to
the transition state divided by the temperature and
The current flowing in either the reductive or gas constant. This free energy plot is also
oxidative steps can be predicted using the following qualitatively valid for electrode reactions
expressions
ic = -FAKred(O)
ia = FAKox(R)
For the reduction reaction the current (ic) is related to
the electrode area (A), the surface concentration of
the reactant [O]o, the rate constant for the electron
transfer (kRed or kOx) and Faraday's constant (F). A
similar expression is valid for the oxidation, now the
current is labelled (ia), with the surface concentration
that of the species Similarly the rate constant for
electron transfer corresponds to that of the oxidation
process. Note that by definition the reductive current
is negative and the oxidative positive, the difference
in sign simply tells us that current flows in opposite
directions across the interface depending upon
whether we are studying an oxidation or reduction.
To establish how the rate constants kox and kred are
Polarization:
influenced by the applied voltage we will use
Polarization as an electrochemical phenomenon is
transition state theory from chemical kinetics. You
will recall that in this theory the reaction is of importance in the corrosion process. For all
considered to proceed via an energy barrier. The metals and alloys in any aqueous environment,
summit of this barrier is referred to as the transition cathodic polarization always reduces the corrosion
state. rate. Cathodic protection refers to the application of
a cathodic polarization to a corroding system.
The rate of reaction for a chemical process(eg)
Polarization can occur in three ways:
Concentration polarization
Resistance polarization
Activation polarization
Concentration polarization of an electrode is the
result of the formation of a diffusion layer adjacent
to the surface of the electrode where there is a
gradient of ion concentration. Diffusion of the ions
through the layers controls the electrochemical
reaction and is important for processes such as
electroplating and corrosion. Concentration
polarization may be reduced by increasing agitation
or raising the temperature of the electrolyte.
3
Resistance polarization describes the potential drop the electrolysis of the raw material brine. Brine is a
due to the high resistivity of the electrolyte
saturated solution of sodium chloride (Nacl) that is
surrounding the electrode. It may also be a result of
the insulation effect of the film on the electrode obtained from natural salt deposits.
surface formed by the reaction products. Resistance
polarization is expressed by the Ohm's law. 7.Polarization has the capacity to inhibitcertain und
Activation polarization occurs when the esirable corrosive processes.
electrochemical reaction proceeds through several
successive steps. The speed of the overall reaction Conclusion:
is determined by the slowest step (known as the Based on these electrode kinetics can determine the
rate-determining step) of the process. For example, corrosion kinetics and it would be understand about
in a hydrogen reduction reaction, the reaction may the current density it is how depend upon the
proceed as follows electrode area and surface of concentration.
Polarization is resistance to corrosion. Concentration
1. Hydrogen ions are absorbed from the polarization is common in all.
solution onto the anode surface.
2. Electron transfer occurs from the anode to REFERENCE:
the hydrogen ions to form hydrogen.
1.M G. Fontana, corrosion engineering (third
3. The hydrogen atoms form hydrogen gas edition) McGrow Hill company.
molecules. 2.BY W. J. Albery, department of chemistry,
4. Hydrogen gas bubbles are formed imperical college, London.
3.J.OM.Bockris and S.Srinivasarao, fuel cells:
Applications: electrochemistery,New York (1970).
1.It has a number of different uses, particularly in
industry. The principles of cells are used to
make electrical batteries. In science and technology,
a battery is a device that stores chemical energy and
makes it available in an electrical form
2.It can be used for electroplating. Electroplating
occurs when an electrically conductive object is
coated with a layer of metal using electrical current.
Sometimes, electroplating is used to give a metal
particular properties or for aesthetic reasons.
3.Corrosion protection
4.Abrasion and wear resistance
5.The production of jewellery
6.The chlorine-alkali (chloralkali) industry is an
important part of the chemical industry, which
produces chlorine and sodium hydroxide through
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Modern Theory of Corrosion-Principles - Unit 1 Lecture - ABDocumento36 pagineModern Theory of Corrosion-Principles - Unit 1 Lecture - ABVeviet pomataNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Engineering Notes (P.E-409)Documento45 pagineCorrosion Engineering Notes (P.E-409)Mubin Ashraf Sheikh100% (1)
- CH 6 (Corrosion & Degradation of Materials)Documento51 pagineCH 6 (Corrosion & Degradation of Materials)Ermyas DejeneNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento51 pagine1Moh Makhbub AlyNessuna valutazione finora
- E.P Report FinalDocumento44 pagineE.P Report FinalMahesh BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started With Electrochemical Corrosion Measurement3Documento16 pagineGetting Started With Electrochemical Corrosion Measurement3jeronimo fernandez andujarNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of ElectrodepositionDocumento32 pagineTheory of ElectrodepositionrthrbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Polarography Chapter PDFDocumento55 paginePolarography Chapter PDFSagar Kumar100% (1)
- Electrochemistry Lecture NotesDocumento75 pagineElectrochemistry Lecture NotesShashwat KhuranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Double LayerDocumento3 pagineElectrical Double LayerDhanvin PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction KineticsDocumento15 pagineReaction KineticsApp. QuizNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Chemistry I: Electrochemical Methods I For Pharmacy Students 2020-2021Documento62 pagineAnalytical Chemistry I: Electrochemical Methods I For Pharmacy Students 2020-2021SİNEM GÜVENNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Lecture KineticsDocumento43 pagineCorrosion Lecture KineticsBaso Rahmat TarmiziNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumental AnalysisDocumento7 pagineInstrumental AnalysisGabriel EngongaNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started With Electrochemical TestingDocumento7 pagineGetting Started With Electrochemical TestingnaderbahramiNessuna valutazione finora
- Polarography: by Dr. Irfan PervaizDocumento41 paginePolarography: by Dr. Irfan PervaizAyesha LiaqatNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemistry: Dr. G. Purna Chandra RaoDocumento29 pagineElectrochemistry: Dr. G. Purna Chandra RaosreekanthsharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Block 2Documento130 pagineBlock 2Shivam KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento24 pagineUnit 5lgguillen20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eizreen Binti Eizuddin (D20182085830) ElectrochemistryDocumento7 pagineEizreen Binti Eizuddin (D20182085830) ElectrochemistryEizreenNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrochemistryDocumento30 pagineElectrochemistryPankaj Jindam100% (1)
- Ionization: Ionization or Ionisation Is The Process by Which AnDocumento12 pagineIonization: Ionization or Ionisation Is The Process by Which AnIon ArtinNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrode PolarizationDocumento27 pagineElectrode PolarizationMahesh BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IADocumento13 pagineChemistry IAabdulrahmanyoussef9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Rate MeasurementsDocumento30 pagineCorrosion Rate MeasurementsNada MeselhyNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 - Corrosion Kinetics PDFDocumento40 pagine11 - Corrosion Kinetics PDFAnnisah MardiyyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 3Documento7 pagineChemistry 3syed waseemNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolytic ProcessesDocumento9 pagineElectrolytic ProcessesIshitha ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- UEE & T Notes (1) (6th Semester Electrical) - MergedDocumento199 pagineUEE & T Notes (1) (6th Semester Electrical) - MergedAmit HansdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started With Electrochemical Corrosion MeasurementDocumento9 pagineGetting Started With Electrochemical Corrosion Measurementa_attarchiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of The Theory of Osmotic Damp Proofing - PDF 20042010-1543-41Documento15 pagineA Review of The Theory of Osmotic Damp Proofing - PDF 20042010-1543-41kalpna_n3Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Basic of The BasicDocumento23 pagineThe Basic of The BasicAliNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - SCH 401 - Basic Electrochemistry (Compatibility Mode) - 4Documento42 pagine1 - SCH 401 - Basic Electrochemistry (Compatibility Mode) - 4FELIX ORATINessuna valutazione finora
- Polarography PDFDocumento37 paginePolarography PDFTejwant Singh KangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyclic VoltammetryDocumento32 pagineCyclic VoltammetryAneeqa YounasNessuna valutazione finora
- DielectricDocumento53 pagineDielectricPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemical Kinetics of Corrosion-Unit-4: CHE-545-172 DR Ime B.ObotDocumento21 pagineElectrochemical Kinetics of Corrosion-Unit-4: CHE-545-172 DR Ime B.ObotAnonymous NxpnI6jCNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Redox Reactions?Documento18 pagineWhat Are Redox Reactions?Mr. Zee KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Electrochemistry Revision Notes QuizrrDocumento75 pagine17 Electrochemistry Revision Notes QuizrrMONEY ALLNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrolyte SolutionDocumento16 pagineELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrolyte SolutionManthelle MpoNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltametry Usim 15Documento24 pagineVoltametry Usim 15alfin asiatul hurriyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics of Aqueous CorrosionDocumento10 pagineKinetics of Aqueous CorrosionDhiren DarjiNessuna valutazione finora
- MUCLecture 2022 42033403Documento9 pagineMUCLecture 2022 42033403ReedhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gamry The Basics of EIS Part 2Documento13 pagineGamry The Basics of EIS Part 2Mobasher KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Electrochemistry & Equivalent Circuit Elements: Corrosion Battery TestingDocumento13 paginePhysical Electrochemistry & Equivalent Circuit Elements: Corrosion Battery TestingBernabeoNessuna valutazione finora
- IM PresentationDocumento40 pagineIM PresentationMobashir AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal: Origin of The Potential Drop Over The Deposit During Electrophoretic DepositionDocumento6 pagineJournal: Origin of The Potential Drop Over The Deposit During Electrophoretic DepositionMario Misael Machado LòpezNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis: Cations: Etc. AnionsDocumento2 pagineElectrolysis: Cations: Etc. AnionsVIKRAM KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- VoltammetryDocumento37 pagineVoltammetrypramod_arya_htd100% (1)
- Grey Cells 18Documento7 pagineGrey Cells 18Priyanshu BhadanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltametrija I PolarografijaDocumento37 pagineVoltametrija I PolarografijaBranislavaTenjovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolytic ProcessesDocumento9 pagineElectrolytic ProcessesT BhaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Utilisation of Electrical Energy 5th Sem Elect Study Material WebDocumento85 pagineUtilisation of Electrical Energy 5th Sem Elect Study Material WebRobertNessuna valutazione finora
- Conventional DC Electrochemical TechniquesDocumento17 pagineConventional DC Electrochemical TechniquesKarla CaicedoNessuna valutazione finora
- IonizationDocumento14 pagineIonizationsvirkomartinkoNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Electrogravimetry and Coulometry AY2223S2Documento41 pagine9 Electrogravimetry and Coulometry AY2223S2Matty JakeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2M - BmiDocumento48 pagine2M - BmiAshok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - Ii Principles of PhotocatalysisDocumento10 pagineChapter - Ii Principles of PhotocatalysisAbbas aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolyzer Modules A) Unipolar and B) Bipolar Cell ConfigurationsDocumento8 pagineElectrolyzer Modules A) Unipolar and B) Bipolar Cell ConfigurationsAnuj ShahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Michigan Clinic 2008 NotesDocumento10 pagineMichigan Clinic 2008 NotesCoach Brown100% (3)
- Thyroid OphthalmopathyDocumento59 pagineThyroid OphthalmopathyLavanya MadabushiNessuna valutazione finora
- Penelitian-Amanda Desviani PDocumento89 paginePenelitian-Amanda Desviani PvantopelNessuna valutazione finora
- V. Aa. Gram A/S: DescriptionDocumento2 pagineV. Aa. Gram A/S: Descriptioncontango O&GNessuna valutazione finora
- Fosroc Conplast SP335: Multi-Range Water Reducing AdmixtureDocumento2 pagineFosroc Conplast SP335: Multi-Range Water Reducing AdmixtureVincent JavateNessuna valutazione finora
- MB Marine Product Guide 2022 RevNDocumento35 pagineMB Marine Product Guide 2022 RevNamir sadighiNessuna valutazione finora
- Leonard Peikoff-Introduction To LogicDocumento20 pagineLeonard Peikoff-Introduction To Logicbursa07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alix Pelletier Luginbühl - Works / PRINT VERSIONDocumento44 pagineAlix Pelletier Luginbühl - Works / PRINT VERSIONJonathan Philippe LEVYNessuna valutazione finora
- Ducted Exhaust Ventilation Fans: Low Noise, High Performance Air and Moisture ExtractionDocumento4 pagineDucted Exhaust Ventilation Fans: Low Noise, High Performance Air and Moisture ExtractionNicolas BaquedanoNessuna valutazione finora
- CD Compre Exam 2 Key AnswerDocumento6 pagineCD Compre Exam 2 Key AnswerGrace LazaroNessuna valutazione finora
- D8045-16 Standard Test Method For Acid Number of Crude Oils and Petroleum Products by CatalyticDocumento6 pagineD8045-16 Standard Test Method For Acid Number of Crude Oils and Petroleum Products by CatalytichishamNessuna valutazione finora
- All Electricity Worksheets For Midterm 22Documento22 pagineAll Electricity Worksheets For Midterm 22Maryam AlkaabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rapid Review Hematology PDFDocumento155 pagineRapid Review Hematology PDFBaguma Michael100% (3)
- World Wide Emission Free E-Motercycle ProjectDocumento20 pagineWorld Wide Emission Free E-Motercycle ProjectAkshay SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- English 10-1 Personal Response EssayDocumento2 pagineEnglish 10-1 Personal Response Essayapi-467840192Nessuna valutazione finora
- MAUS Catalogue PDFDocumento10 pagineMAUS Catalogue PDFCarolina Garcés MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal Uh English XDocumento1 paginaSoal Uh English XhenniherawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- NABARD Grade A 2020 Phase 2 ESI ARDDocumento6 pagineNABARD Grade A 2020 Phase 2 ESI ARDrohit bhosadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3.3 Inside An AtomDocumento42 pagineLesson 3.3 Inside An AtomReign CallosNessuna valutazione finora
- INSTITUTO CAMBRIDGE de Cultura Inglesa - EXÁMENES 2020: Kids 1Documento3 pagineINSTITUTO CAMBRIDGE de Cultura Inglesa - EXÁMENES 2020: Kids 1Mel DeniseNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Summary - I Hear You Summary Michael Sorensen - Read in 7 MinutesDocumento10 pagineBook Summary - I Hear You Summary Michael Sorensen - Read in 7 MinutesNogüey JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- InvoiceDocumento1 paginaInvoicesunil sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplementary Spec To API Specification 17D Subsea Wellhead and Tree Equipment With Justifications S 561Jv2022 11Documento81 pagineSupplementary Spec To API Specification 17D Subsea Wellhead and Tree Equipment With Justifications S 561Jv2022 11maximusala83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Saep 1160Documento12 pagineSaep 1160JithuJohn100% (1)
- ISO 9001 Required DocumentationDocumento3 pagineISO 9001 Required Documentationdnmule100% (1)
- Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocumento19 pagineMechanism of Enzyme ActionRubi AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Distiller - ManualDocumento2 pagineWater Distiller - ManualSanjeevi JagadishNessuna valutazione finora
- Adobeconstruct 19 NeubDocumento34 pagineAdobeconstruct 19 NeublailanuitNessuna valutazione finora
- Lead and Manage People TTLMDocumento41 pagineLead and Manage People TTLMHenok Mehari100% (1)
- Genius 7 On Bill Acceptor ManualDocumento10 pagineGenius 7 On Bill Acceptor ManualJose Maria PerezNessuna valutazione finora