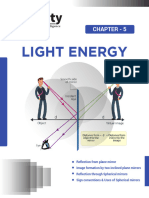
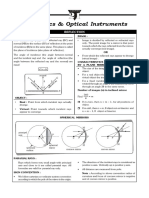
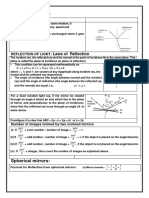
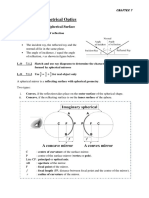
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
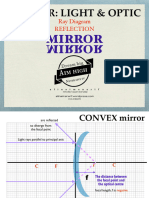
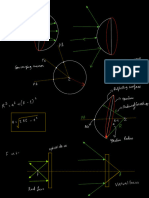
Real Object: Use "Real-Is-Positive" For Signs
Caricato da
kcTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Real Object: Use "Real-Is-Positive" For Signs
Caricato da
kcCopyright:
Formati disponibili
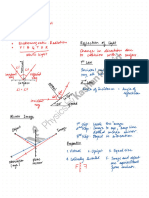
Concave (converging) mirror Equation to find focal length for a thin lense Use “real-is-positive” for
signs
1
n 1 1
1
Front of
mirror Back of
mirror
f R1 R2
principal C f Real
axis object
Center of focal
curvature point (-)R₁ (+)R₂
Virtual (-) q
image
Double-concave
lense
Convex (diverging) mirror
f, the focal length is negative also.
Front of Back of
mirror mirror q, when object is far, is found from q=f, so it is
negative also.
principal f C
axis
focal Center of
point curvature
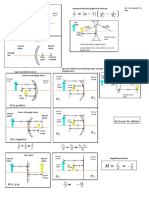
Sign convention for one refracting surface (example,
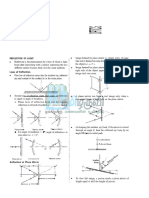
Sign convention for mirrors fish glass bowl)
Concave (converging) mirror Real
Front of Back of object
Front of
mirror Back of
surface
(+) p
surface
(+) R 1 Real
mirror
(+) p real virtual
R₂ image
(-) q
object image
(+) R
(+) q
(-) R Double-convex
real (+) q
image
n1 n2 lense
M is positive
back of front of
Convex (diverging) mirror
Front of surface surface
mirror Back of (-) p
mirror
virtual real (+) q
(+) p (-) R object image By Nasser M. Abbasi
(+) R
(-) q virtual
image n1 n2
M is negative
1
p 1q 1f n1
n2
n 2 n 1
p q R
Flat mirror
back of front of
Front of Back of surface surface Magnification formula
mirror mirror (-) p
q
(+) p
virtual
object
real
image
(+) q
M h
h
p
(-) q
virtual
image n1 n2
n1
M=1, p=q
p n2
q
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- All in One SCIENCE 10 - Mid Map - CH 9Documento2 pagineAll in One SCIENCE 10 - Mid Map - CH 9narasakuru79Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection: Convex Mirror Nature of Image and Its FormationDocumento2 pagineReflection: Convex Mirror Nature of Image and Its FormationNimendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Documento4 pagineRay Optics and Optical Instruments - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024bhaveshkumarbijaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Reflection and Refraction (@StudyManiaStore)Documento18 pagineLight Reflection and Refraction (@StudyManiaStore)GIRIDHARAN MURUGANNessuna valutazione finora
- Light EnergyDocumento55 pagineLight EnergygpfphysicsNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-Ray Optics-IDocumento3 pagine01-Ray Optics-IAnurag AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Optics Optical InstrumentsDocumento9 pagineRay Optics Optical InstrumentsEternalChronosNessuna valutazione finora
- RAY ConceptDocumento19 pagineRAY ConceptMAHESWARA RAO ThotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ometrical Optics TheoryDocumento55 pagineOmetrical Optics TheorylouisafesuhacNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Experiment 6Documento4 paginePhysics Experiment 6ramkewat744Nessuna valutazione finora
- 25 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - KeynotesDocumento28 pagine25 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - KeynotesthorNessuna valutazione finora
- Mirror Related QueDocumento13 pagineMirror Related Quelodhishivansh2567Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proyecciones en Dibujo Tecnico MecánicoDocumento4 pagineProyecciones en Dibujo Tecnico MecánicoOscarArteagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 筆記 2022年6月19日Documento6 pagine筆記 2022年6月19日小貓Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geometrical OpticsDocumento20 pagineGeometrical OpticsPRIYAA A/P JAYASANKAR / UPMNessuna valutazione finora
- Projections L1Documento61 pagineProjections L1subhasree.ghosh.cse21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ometrical Optics Formulae SheetDocumento5 pagineOmetrical Optics Formulae SheetMUKUL sainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Arihant Physics Revision Map For OctoberDocumento3 pagineArihant Physics Revision Map For Octobermohit parbatNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy 214 - Optics and Acoustics: Jumarie E. Coreses, Rche, RCHT MST - ChemistryDocumento60 paginePhy 214 - Optics and Acoustics: Jumarie E. Coreses, Rche, RCHT MST - ChemistryjumarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Reflection Detail NotesDocumento6 pagineLight Reflection Detail NotesNitesh KumawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Focal Lenght of Convex Mirror Using Convex LensDocumento2 pagineFocal Lenght of Convex Mirror Using Convex LensAmit Sutar100% (2)
- Jjeb Mock Examinations 2022 Physics Marking Guide A LevelDocumento22 pagineJjeb Mock Examinations 2022 Physics Marking Guide A Levelwalubi SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Diagram (MIRROR)Documento11 pagineRay Diagram (MIRROR)Haziq AimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Reflection and Refraction: Shobhit Nirwan'SDocumento18 pagineLight Reflection and Refraction: Shobhit Nirwan'S2erwrNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Optics FormulasDocumento8 pagineRay Optics Formulassamueljoshuah2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- ProjectionsDocumento48 pagineProjectionsYtyt GffgNessuna valutazione finora
- A Wavefront Is The Locus of Points (Wavelets) Having The Same Phase of Oscillations. WavefrontDocumento22 pagineA Wavefront Is The Locus of Points (Wavelets) Having The Same Phase of Oscillations. WavefrontJinshy VinodNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Diagramming and Mirror EquationDocumento54 pagineRay Diagramming and Mirror Equationnathanielstanaj.mNessuna valutazione finora
- LightDocumento3 pagineLightgm6mry8mrgNessuna valutazione finora
- 34b Reflection and Mirrors II AnalyticalDocumento27 pagine34b Reflection and Mirrors II AnalyticalseijikellsNessuna valutazione finora
- Light - Shobhit NirwanDocumento22 pagineLight - Shobhit NirwanAakash KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PDT UNIT9 (Students)Documento51 paginePDT UNIT9 (Students)fariq100% (3)
- Pantulan Cahaya Pada Cermin SatahDocumento4 paginePantulan Cahaya Pada Cermin SatahHEHENessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Documento28 pagineChapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Heindrich Lloyd Mendoza BasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 24 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocumento37 pagineChapter - 24 Ray Optics and Optical Instrumentsagoel0844Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ray OpticsDocumento62 pagineRay OpticsmrdaddydaddaNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Ray Theory Part2Documento24 pagine02 Ray Theory Part2Saurabh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE-Physics: 1 V 1 R 1 V V R 1 2R M 1Documento12 pagineJEE-Physics: 1 V 1 R 1 V V R 1 2R M 1sagar panchalNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 OpticsDocumento33 pagine16 OpticsDebayanbasu.juNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics For WorksheetDocumento25 pagineOptics For WorksheetAUDREYNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Lenses EM SpectrumDocumento25 pagineLight Lenses EM SpectrumSYED MUHAMMAD UZAIRNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics NEET Study Materials Download PDFDocumento21 pagineOptics NEET Study Materials Download PDFbrovinsbrovinNessuna valutazione finora
- Academic Unit-1: Bachelor of Engineering (CSE, IT, CSE-IBM)Documento18 pagineAcademic Unit-1: Bachelor of Engineering (CSE, IT, CSE-IBM)PARAS MEHTANessuna valutazione finora
- Optical InstrumentsDocumento23 pagineOptical InstrumentsShivani Ekant YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometrical Optics: Curved MirrorDocumento61 pagineGeometrical Optics: Curved MirrorMr. XNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometrical Optics: Velocity of ImageDocumento47 pagineGeometrical Optics: Velocity of ImageMr. XNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento6 pagineUntitledJishan AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- 20Documento12 pagine20Rajat Verma X D 39Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geomatics EngineeringDocumento9 pagineGeomatics Engineeringnavneet sinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Optics & Optical Instrument Most WantedDocumento17 pagineRay Optics & Optical Instrument Most Wantedramianx01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics MIRRORS ProjectDocumento39 paginePhysics MIRRORS Projectaneesh.ubanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics of The EYE 1Documento10 pagineOptics of The EYE 1Veronica NedelcuNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th-Physics Retro PDFDocumento21 pagine12th-Physics Retro PDFSamarpitMinzNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 9 - Conic SectionsDocumento162 pagineUnit 9 - Conic Sectionsyoussef islam0% (1)
- SQ1 9-1 12Documento2 pagineSQ1 9-1 12ynwwaranNessuna valutazione finora
- 8-OPTICS-01 - TheoryDocumento23 pagine8-OPTICS-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodal SlideDocumento3 pagineNodal SlideNidhi GoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Spherical Mirror InspDocumento11 pagineSpherical Mirror Inspdassoumyadeep447Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formação Da ImagemDocumento59 pagineFormação Da ImagemHugo Leandro PendragonsNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Object: Use "Real-Is-Positive" For SignsDocumento1 paginaReal Object: Use "Real-Is-Positive" For SignskcNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Study Tips and Ideas That Really WorkDocumento2 pagine14 Study Tips and Ideas That Really WorkkcNessuna valutazione finora
- Damien Etienne - Exercices Corrigés D'algèbre Linéaire. 1-De Boeck (2006)Documento278 pagineDamien Etienne - Exercices Corrigés D'algèbre Linéaire. 1-De Boeck (2006)kc100% (2)
- Equations Différentielles Et ExercixesDocumento1 paginaEquations Différentielles Et ExercixeskcNessuna valutazione finora
- François Liret Dominique Martinais - Algèbre 1re Année - Cours Et Exercices Avec Solutions-Dunod (Juin 2003)Documento291 pagineFrançois Liret Dominique Martinais - Algèbre 1re Année - Cours Et Exercices Avec Solutions-Dunod (Juin 2003)kc100% (1)
- Jean-Philippe Ansermet, Sylvain D. Brechet - Principles of Thermodynamics-Cambridge University Press (2019)Documento542 pagineJean-Philippe Ansermet, Sylvain D. Brechet - Principles of Thermodynamics-Cambridge University Press (2019)kc100% (1)
- Ooo OooooooooDocumento11 pagineOoo OooooooookcNessuna valutazione finora
- GFGFHNDocumento5 pagineGFGFHNkcNessuna valutazione finora
- CoooolDocumento1 paginaCoooolkcNessuna valutazione finora
- JHJJJJJJ56786785678GFGH ( ' (GGGGGGGGGGG GG: Jytfi, 10374 56789687Documento4 pagineJHJJJJJJ56786785678GFGH ( ' (GGGGGGGGGGG GG: Jytfi, 10374 56789687kcNessuna valutazione finora
- GFGFHNDocumento5 pagineGFGFHNkcNessuna valutazione finora
- Nouveau Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocumento1 paginaNouveau Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationkcNessuna valutazione finora
- Flash CardsDocumento1 paginaFlash CardskcNessuna valutazione finora
- Elaborare Modele de Rating in Conformitate Cu IFRS 9Documento8 pagineElaborare Modele de Rating in Conformitate Cu IFRS 9MstefNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To SAP: Venkat Emani FICO Certified Consultant / TrainerDocumento22 pagineIntroduction To SAP: Venkat Emani FICO Certified Consultant / TrainerVenkat EmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Negotiation SimulationDocumento11 pagineNegotiation SimulationJade Arbee BarbosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Processing and Management Information System (AvtoBərpaEdilmiş)Documento6 pagineData Processing and Management Information System (AvtoBərpaEdilmiş)2304 Abhishek vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shaira Narrative Report (Final)Documento7 pagineShaira Narrative Report (Final)Sheryll TamangNessuna valutazione finora
- PQM Quiz FinalDocumento11 paginePQM Quiz FinalSyeda Sadaf ZahraNessuna valutazione finora
- LP Addition of PolynomialsDocumento5 pagineLP Addition of PolynomialsJolina Bagwisa LptNessuna valutazione finora
- GutsDocumento552 pagineGutsroparts cluj100% (1)
- Ayaw at GustoDocumento4 pagineAyaw at GustoJed VillaluzNessuna valutazione finora
- Altium Designer Training For Schematic Capture and PCB EditingDocumento248 pagineAltium Designer Training For Schematic Capture and PCB EditingAntonio Dx80% (5)
- List of ErpDocumento2 pagineList of Erpnavyug vidyapeeth trust mahadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lac MapehDocumento4 pagineLac MapehChristina Yssabelle100% (1)
- Esmeril Makita PDFDocumento16 pagineEsmeril Makita PDFwjzabalaNessuna valutazione finora
- ESUR Guidelines 10.0 Final VersionDocumento46 pagineESUR Guidelines 10.0 Final Versionkon shireNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Exploration: Magnetism (Find Gizmo Icon On Eclass)Documento4 pagineStudent Exploration: Magnetism (Find Gizmo Icon On Eclass)Abdel Majeed Tuffaha0% (1)
- Emc VNX MatrixDocumento8 pagineEmc VNX Matrixpolivni0% (1)
- Arch Plan-Agner Boco (For Blue Print) - p1Documento1 paginaArch Plan-Agner Boco (For Blue Print) - p1Jay CeeNessuna valutazione finora
- B2 UNIT 6 Test StandardDocumento6 pagineB2 UNIT 6 Test StandardКоваленко КатяNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion FundamentalsDocumento30 pagineCombustion FundamentalsPrem SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Models For Seat Allocation On Flights: Moshe Dror,?Documento12 pagineNetwork Models For Seat Allocation On Flights: Moshe Dror,?Isabel VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do I Predict Event Timing Saturn Nakshatra PDFDocumento5 pagineHow Do I Predict Event Timing Saturn Nakshatra PDFpiyushNessuna valutazione finora
- PGT Computer Science Kendriya Vidyalaya Entrance Exam Question PapersDocumento117 paginePGT Computer Science Kendriya Vidyalaya Entrance Exam Question PapersimshwezNessuna valutazione finora
- Heating Curve Lab Report - Ava MonizDocumento7 pagineHeating Curve Lab Report - Ava Monizapi-533828039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hatchery Practice: InternationalDocumento40 pagineHatchery Practice: Internationalabhe prasetyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project Report by Himanshu Yadav Student of Fostiima Business SchoolDocumento55 pagineFinal Project Report by Himanshu Yadav Student of Fostiima Business Schoolak88901Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8 Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry PDFDocumento23 pagineUnit 8 Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry PDFCh AswadNessuna valutazione finora
- MGMT 4Documento26 pagineMGMT 4Said GunayNessuna valutazione finora
- Working With Hierarchies External V08Documento9 pagineWorking With Hierarchies External V08Devesh ChangoiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104Documento57 pagine1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104f.kpobi1473Nessuna valutazione finora
- TSM 101 Course Outline (2022)Documento2 pagineTSM 101 Course Outline (2022)ChryseanjNessuna valutazione finora