Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Proof Elasticity Linear Demand PDF
Caricato da
Julio HernandezDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Proof Elasticity Linear Demand PDF
Caricato da
Julio HernandezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
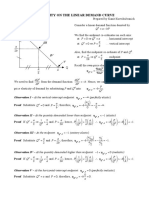
ELASTICITY ON THE LINEAR DEMAND CURVE
Prepared by Kanit Kuevibulvanich
P
I Consider a linear demand function denoted by
a Qd = a − bP
b
II We find the endpoint co-ordinates on each axis:
at P = 0 ⇒ Qd = a … horizontal intercept
€ a
III at Qd = 0 ⇒ P = … vertical intercept
€ b
a
2b € Also, find the midpoint co-ordinate of P and Qd:
IV a a
€ at P = ⇒ Qd = … midpoint
2b 2
€ V
Recall the own-price elasticity of demand:
a Q %ΔQd dQd P
a € ηQ d ,P = =
2 %ΔP dP Qd
dQd d
€ the demand function: dQ = −b . Hence, we can simply find the own-
We need to find from
€ dP €dP
P
price elasticity of demand by substituting P and Qd into: ηQ d ,P = −b d .
Q
€ €
Observation I – At the vertical-intercept endpoint: ηQ d ,P = −∞ (perfectly elastic)
Proof Substitute Qd = 0 and P =
a € a ( ) a
; therefore, ηQ d ,P = −b b = − = −∞ .
b 0 0
€
Observation II – At the quantity demanded lower than midpoint: ηQ d ,P < −1 (elastic)
€
a €1 2 €a " 1 % 2" a % "P% "1%
Proof If Qd < ⇒ d > and P > ; hence, P$ d ' > $ ' ∴ ηQ d ,P = −b$ d ' < −b$ ' < −1.
2 Q a 2b # Q & a # 2b & #Q & #b&
€
Observation III – At the midpoint: ηQ d ,P = −1 (unitary elastic)
€ € €
a a
a a ( )
Proof Substitute Q = and P = ; therefore, ηQ d ,P = −b 2b = − 2 = −1.
d
2 2b a a
2 2
€
Observation IV – At the quantity demanded higher than midpoint: −1 < ηQ d ,P < 0 (inelastic)
€ €
a 1 2 a€ " 1 % 2" a % "P% "1%
Proof If Q > ⇒ d < and P < ; hence, P$ d ' < $ ' ∴ ηQ d ,P = −b$ d ' > −b$ ' > −1.
d
2 Q a 2b # Q & a # 2b & #Q & #b&
€
Observation V – At the horizontal-intercept endpoint: ηQ d ,P = 0 (perfectly inelastic)
€ € € 0
Proof Substitute Q = a and P = 0; therefore, ηQ d ,P = −b = 0 .
d
a
€
€ €
€
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Elasticity & SurplusDocumento6 pagineElasticity & SurplusakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions Goldstein Chapter 9 1Documento19 pagineSolutions Goldstein Chapter 9 1Anonymous rn2qoBPjKy67% (3)
- Proof Elasticity Linear DemandDocumento1 paginaProof Elasticity Linear DemandTanim BegNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuis Mikro1 2 SolDocumento2 pagineKuis Mikro1 2 Solkhansaaa.mitriwpNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Formulas and ExpressionsDocumento5 pagineMicroeconomics Formulas and ExpressionsSteveNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Effect of Current MagnetismDocumento5 pagineMagnetic Effect of Current MagnetismEternalChronos100% (1)
- DocDocumento2 pagineDocfatemanipu1997Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 FTP - 2-WT PDFDocumento34 pagine3 FTP - 2-WT PDFMohama KarimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocumento40 pagineMechanical Properties of FluidsEx0ticNessuna valutazione finora
- Cour Not ExampleDocumento4 pagineCour Not ExampleMelik GüngörNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics 2 and General Chemistry 2 Term 1 Formula ReviewerDocumento2 pagineGeneral Physics 2 and General Chemistry 2 Term 1 Formula ReviewerKarl LampaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Paper - 02: 199 200 Cos 2 Cos CosDocumento7 pagineSolution Paper - 02: 199 200 Cos 2 Cos CosLokesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 7B Final Equation SheetDocumento3 pagine7B Final Equation SheetFangZiWenNessuna valutazione finora
- ch8 - 2 BasicSystemModelingfHaudraulicSystem PDFDocumento31 paginech8 - 2 BasicSystemModelingfHaudraulicSystem PDFVignesh GNessuna valutazione finora
- 1468564124EText (CH 9, M 4Documento9 pagine1468564124EText (CH 9, M 4varshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecuaciones Fisica 3Documento2 pagineEcuaciones Fisica 3Ana Virginia MontoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecuaciones Fisica 3Documento2 pagineEcuaciones Fisica 3Marcel Gabriel Morett OsorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Prob 2 5Documento2 pagineProb 2 5Morteza YounesiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathimatical Ch2Documento39 pagineMathimatical Ch2Ermiyas DebelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout 8: Cournot CompetitionDocumento5 pagineHandout 8: Cournot CompetitionRaulNessuna valutazione finora
- R R Q KQ F: Formula Sheet. Electricity and Magnetism, Coulomb's Law and Electric FieldsDocumento3 pagineR R Q KQ F: Formula Sheet. Electricity and Magnetism, Coulomb's Law and Electric Fieldskishore_sailuxNessuna valutazione finora
- Coupling of Elasticity, Flow and Material BalanceDocumento29 pagineCoupling of Elasticity, Flow and Material BalanceDicky AlviansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula / Mathematical MethodDocumento7 pagineFormula / Mathematical MethodRabiaSaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium Analysis in EconomicsDocumento24 pagineEquilibrium Analysis in EconomicsHara Tiara PakpahanNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT - Analog Circuit - PN Junction Diode - L16Documento12 pagineMIT - Analog Circuit - PN Junction Diode - L16Fen XiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics II: Electromagnetism and OpticsDocumento41 paginePhysics II: Electromagnetism and Opticsabha singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 AKDocumento14 pagineChapter 2 AKSan jayNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 13: Outline: Hour 1Documento33 pagineClass 13: Outline: Hour 1akirank1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Eq SheetDocumento2 pagineFinal Eq SheetMariana AngelesNessuna valutazione finora
- Decision TheoryDocumento9 pagineDecision TheorytommasobocconimailNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamic Lesson 3Documento5 pagineThermodynamic Lesson 3kelebekkNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Physics Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineQuantum Physics Cheat SheetRobin PoincareNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec3 MktEquil UncertainDocumento42 pagineLec3 MktEquil UncertainebbamorkNessuna valutazione finora
- PN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimDocumento42 paginePN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimasadNessuna valutazione finora
- PYQs 2020Documento21 paginePYQs 2020Kumar RathodNessuna valutazione finora
- MarginalnotesDocumento6 pagineMarginalnoteshoussamNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 112 Formulae IIIDocumento3 paginePhysics 112 Formulae IIISaied RajehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Caltech Ee 151 Lecture2Documento6 pagineCaltech Ee 151 Lecture2mdasifhassanapspdclNessuna valutazione finora
- Isothermal Gas Expansion: P V T P V TDocumento4 pagineIsothermal Gas Expansion: P V T P V Twolfofphysics08IPMP01Nessuna valutazione finora
- AdvancedPhysics 5 Problems bc930101Documento13 pagineAdvancedPhysics 5 Problems bc930101Bogar CCNessuna valutazione finora
- Exams 2015,2005-2007 With Solutions PDFDocumento46 pagineExams 2015,2005-2007 With Solutions PDFAhmed KhairiNessuna valutazione finora
- Price & Quantity DynaDocumento38 paginePrice & Quantity DynadrjoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Session2 SolutionsDocumento9 pagineSession2 SolutionsLuca CastellaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes 08 Solving For PotentialsDocumento20 pagineNotes 08 Solving For PotentialsSofía Rodas VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- MA8353 PEC - by EasyEngineering - Net 02Documento183 pagineMA8353 PEC - by EasyEngineering - Net 02SumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetika Reaksi Kimia & KatalisisDocumento6 pagineKinetika Reaksi Kimia & KatalisisFatmawati PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- A V P A V P: PressureDocumento2 pagineA V P A V P: PressurePearl Alexandra FabitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternating Current - 3Documento5 pagineAlternating Current - 3noi KlNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulae Chp1 7Documento1 paginaFormulae Chp1 7puso sediaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHP 2 PhysicsDocumento17 pagineCHP 2 Physicscse.220840131017Nessuna valutazione finora
- BSP1703 NotesDocumento33 pagineBSP1703 NotesChloe TewNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Fluid & Thermal SystemsDocumento26 pagineUnit 2 Fluid & Thermal Systemscaca0% (1)
- Lecture7 EngDocumento20 pagineLecture7 EngjoseNessuna valutazione finora
- PLUS Two Physics 18.08.2023Documento55 paginePLUS Two Physics 18.08.2023mohammednasal6667Nessuna valutazione finora
- Course4 Termo2020Documento16 pagineCourse4 Termo2020adrian2r04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adv Foundation FormulaDocumento2 pagineAdv Foundation FormulaKAI CHUAN CHUNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocumento14 pagineElectric Potential and CapacitanceCHINMAY UPADHYAYA X-DNessuna valutazione finora
- Exerciselist5 Eja2022 Physics SolutionsDocumento4 pagineExerciselist5 Eja2022 Physics SolutionsfelicioNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY303 Assignment 2 Solutions PDFDocumento5 paginePHY303 Assignment 2 Solutions PDFJohn McLovenNessuna valutazione finora
- Economic ActivityDocumento6 pagineEconomic ActivityDharam JagroopNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Affecting Balance of PaymentsDocumento3 pagineFactors Affecting Balance of Paymentsashu khetan100% (5)
- Structure of The Airline IndustryDocumento14 pagineStructure of The Airline IndustryShuvendraNessuna valutazione finora
- (Christopher Dougherty) Introduction To EconometriDocumento389 pagine(Christopher Dougherty) Introduction To EconometriSoohak LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Valuing Business EDP SDMDocumento104 pagineValuing Business EDP SDMsamrulezzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Economics For LASUDocumento277 pagineMicro Economics For LASUhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial EconomicDocumento4 pagineFinancial EconomicJacob MullerNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 11 Dividend PolicyDocumento56 pagineCHAPTER 11 Dividend PolicyMatessa AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercury QuestionsDocumento6 pagineMercury Questionsapi-239586293Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes XII Principles of TaxationDocumento6 pagineLecture Notes XII Principles of TaxationNgamije Jackson67% (3)
- LA Economic Systems Worksheets EditedDocumento9 pagineLA Economic Systems Worksheets EditedOthelia HanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture16 PDFDocumento30 pagineLecture16 PDFkate ngNessuna valutazione finora
- Globalization and Its Impact On IndiaDocumento3 pagineGlobalization and Its Impact On IndiaJananee Rajagopalan100% (1)
- Marketing Management - Lecture Notes Lecture 1 - Thursday August 9, 2018Documento2 pagineMarketing Management - Lecture Notes Lecture 1 - Thursday August 9, 2018Abbas WazeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Economics BBA MCQDocumento17 pagineManagerial Economics BBA MCQPrayag rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Institutionl EconomicsDocumento31 pagineInstitutionl EconomicsC M ChaurasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Sem-Week 1Documento11 pagineSecond Sem-Week 1Caren mae LatoneroNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Micro Review NoteDocumento73 pagineIntermediate Micro Review NoteKaiyuan HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- MB0042 Managerial Economics Assignment - Semester 1Documento32 pagineMB0042 Managerial Economics Assignment - Semester 1Shravanti Bhowmik SenNessuna valutazione finora
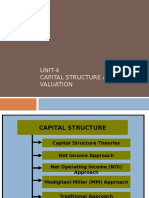
- Unit 4Documento14 pagineUnit 4hitekshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coca Cola Company Is A Global Soft Drink Beverage Company TickeDocumento3 pagineCoca Cola Company Is A Global Soft Drink Beverage Company TickeAmit PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 - The City As A Growth MachineDocumento15 pagineGroup 4 - The City As A Growth MachineDaffa AlweeNessuna valutazione finora
- Yield Curve and TheoriesDocumento9 pagineYield Curve and TheorieskalukollasjpNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Policy and Economic Reforms Papers 2Documento59 pagineIndustrial Policy and Economic Reforms Papers 2Alberto LucioNessuna valutazione finora
- Robert W Kolb Series Energy Finance and Economics Analysis and Valuation Risk Management and The Future of Energy 1Documento12 pagineRobert W Kolb Series Energy Finance and Economics Analysis and Valuation Risk Management and The Future of Energy 1Jerry ChiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Euro Currency MarketDocumento33 pagineEuro Currency Marketsfkokane83% (6)
- Economics P1 May-June 2021 MG EngDocumento19 pagineEconomics P1 May-June 2021 MG EngTshegofatso JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ExamDocumento12 pagineFinal ExamKang JoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Competitiveness Report 2004/2005 Executive SummaryDocumento13 pagineGlobal Competitiveness Report 2004/2005 Executive SummaryWorld Economic Forum100% (4)
- Globalization and EducationDocumento36 pagineGlobalization and EducationJhez de la PeñaNessuna valutazione finora