Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
BE8256 r17 Basic Mechanical Engg PDF
Caricato da
karthik kumarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BE8256 r17 Basic Mechanical Engg PDF
Caricato da
karthik kumarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
For audio explanation and easy learning visit www.padeepz.
com
BE8256 BASIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LTPC
400 4
OBJECTIVE
To impart knowledge on thermodynamics and thermal engineering power generating
units such as engines and theory of machines
UNIT I LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 12
Basic concepts and hints; Zeroth law; First Law of Thermodynamics - Statement and
application; Steady flow energy equation-problems- Second law of Thermodynamics – Kelvin -
Plank statement and Clausius statement- problems; Limitations; Heat Engine, Refrigerator and
Heat Pump, Available energy, Third law of Thermodynamics - Statement.
UNIT II HEATING AND EXPANSION OF GASES 12
Expressions for work done, Internal energy and heat transfer for Constant Pressure, Constant
Volume, Isothermal, Adiabatic and Polytropic processes-Derivations and problems; Free
expansion and Throttling process.
UNIT III AIR STANDARD CYCLES 12
Carnot cycle; Stirlings cycle; Joule cycle; Otto cycle; Diesel cycle; Dual combustion Cycle-
Derivations and problems.
UNIT IV I.C. ENGINES, STEAM AND ITS PROPERTIES AND TEAM 12
Engine nomenclature and classification; SI Engine; CI Engine; Four Stroke cycle, Two stroke
cycle; Performance of I.C.Engine; Brake thermal efficiency; Indicated Thermal Efficiency,
Specific fuel consumption.
Steam - Properties of steam; Dryness fraction; latent heat; Total heat of wet steam; Dry steam;
Superheated steam. Use of steam tables; volume of wet steam, volume of superheated steam;
External work of evaporation; Internal energy; Entropy of vapour, Expansion of vapour, Rankine
cycle. Steam turbines – Impulse and Reaction types - Principles of operation.
UNIT V SIMPLE MECHANISM, FLY WHEEL, DRIVES AND BALNCING 12
Definition of Kinematic Links, Pairs and Kinematic Chains; Flywheel-Turning moment Diagram;
Fluctuation of Energy. Belt and rope drives; Velocity ratio; slip; Creep; Ratio of tensions; Length
of belt; Power Transmitted; gear trains-types. Balancing of rotating masses in same plane;
Balancing of masses rotating in different planes.
OUTCOME
• Students should learn thermodynamics and thermal engineering to understand the
principles behind the operation of thermal equipments like IC engines and turbines etc.,
Students should be able to appreciate the theory behind operation of machinery and be
able to design simple mechanisms
TOTAL : 60 PERIODS
TEXT BOOKS
1. Nag, P.K., “Engineering Thermodynamics “, IInd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co.,
Ltd., 1995
2. Rajput, R .K, “Thermal Engineering”, Laxmi publications (P) Ltd, 2001.
For audio explanation and easy learning visit www.padeepz.com
For audio explanation and easy learning visit www.padeepz.com
3. Khurmi R.S., and Gupta J.K, “Theory of Machines”, Eurasia Publishing House (P) Ltd.,
2004.
REFERENCES
1. Bhaskaran, K.A., and Venkatesh, A., “Engineering Thermodynamics “,Tata McGraw Hill,
1973.
2. Khurmi R.S., and Gupta J.K, “Thermal Engineering”, S.Chand & Company (P) Ltd.,2001.
3. Kothandaraman and Dhomkundwar,”: A course in Thermal Engineering (SI Units)”, Dhanpat
Rai and Sons, Delhi (2001)
4. Pandya A. and Shah, “ Theory of Machines “, Charatakar Publishers, 1975.
5. Smith, “Chemical Thermodynamics “, Reinhold Publishing Co., 1977.
For audio explanation and easy learning visit www.padeepz.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Heat Pumps: Solving Energy and Environmental ChallengesDa EverandHeat Pumps: Solving Energy and Environmental ChallengesTakamoto SaitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Be8256 Basic Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocumento1 paginaBe8256 Basic Mechanical Engineering SyllabusAnonymous dL8dsCncNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow, Mixing and Heat Transfer in Furnaces: The Science & Applications of Heat and Mass Transfer Reports, Reviews & Computer ProgramsDa EverandFlow, Mixing and Heat Transfer in Furnaces: The Science & Applications of Heat and Mass Transfer Reports, Reviews & Computer ProgramsK. H. KhalilNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics SyllabusDocumento1 paginaThermodynamics SyllabusRam KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics SyllabusDocumento1 paginaThermodynamics SyllabusSrinivasan SNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuels, Furnaces and Refractories: International Series on Materials Science and TechnologyDa EverandFuels, Furnaces and Refractories: International Series on Materials Science and TechnologyValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- AE8301 Syllabus Covers Thermodynamics, Cycles, Heat TransferDocumento3 pagineAE8301 Syllabus Covers Thermodynamics, Cycles, Heat TransferAttakaththi DineshNessuna valutazione finora
- AE8301-AERO ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Syllabus 2017 Regulation PDFDocumento3 pagineAE8301-AERO ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Syllabus 2017 Regulation PDFAttakaththi DineshNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Plant Engineering Course OverviewDocumento7 paginePower Plant Engineering Course OverviewsumikannuNessuna valutazione finora
- THERMAL ENGINEERINGDocumento6 pagineTHERMAL ENGINEERINGArunkumar MunimathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - I/II Subject Name: Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineGujarat Technological University: Semester - I/II Subject Name: Basic Mechanical EngineeringNirmal KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME6352 Manufacturing Technology LTPC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivesDocumento14 pagineME6352 Manufacturing Technology LTPC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivespugazhNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Engineering and HMTDocumento2 pagineThermal Engineering and HMTArunkumar MunimathanNessuna valutazione finora
- ATD SyllabusDocumento3 pagineATD Syllabusprashanth prabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- ME6404 Thermal Engineering Gas Power CyclesDocumento1 paginaME6404 Thermal Engineering Gas Power CyclesKani SelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocumento2 pagineBasic Mechanical EngineeringAPOLLO Sem 4 I.T.Nessuna valutazione finora
- St. MICHEAL Engineering BasicsDocumento41 pagineSt. MICHEAL Engineering Basicsnagarajan224Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power PlantDocumento1 paginaPower PlantSahi NagarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Engineering SyllabusDocumento144 pagineThermal Engineering SyllabusVpr NaturalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Engineering (9053)Documento6 pagineThermal Engineering (9053)Sai TharunNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal EnggDocumento2 pagineThermal EnggAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocumento76 pagineRefrigeration and Air Conditioningmat_pran100% (3)
- 3.1 Thermodynamics L T P 4 - 2 RatioanleDocumento21 pagine3.1 Thermodynamics L T P 4 - 2 RatioanleArchNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Tech (ME) Semester VIIDocumento9 pagineB. Tech (ME) Semester VIISanjeev DahiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Thermodynamics (BTME-305-18)Documento14 pagineBasic Thermodynamics (BTME-305-18)Surjit Kumar GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Engineering SyllabusDocumento2 pagineThermal Engineering SyllabusSamuelHericNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Engineering ThermodynamicsDocumento3 pagineBasic Engineering Thermodynamicsapi-296698256Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento3 pagineGujarat Technological UniversityRavi Teja TNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal EngineeringDocumento6 pagineThermal Engineeringmore_sandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- ME6301-SCAD-MSM - by WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFDocumento167 pagineME6301-SCAD-MSM - by WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFMohsin EngrNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Code Subject Name Year/Sem: II / IV Faculty Name: Total HRS: 60 Tutorial: 15Documento3 pagineSubject Code Subject Name Year/Sem: II / IV Faculty Name: Total HRS: 60 Tutorial: 15parassuNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics: Course Code: BTM 302 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineThermodynamics: Course Code: BTM 302 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveAdhwareshBharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal EngineeringDocumento6 pagineThermal Engineeringtarek ali ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ME-351 - Applied Thermodynamics II - Course Plan - Rev - 01 PDFDocumento4 pagineME-351 - Applied Thermodynamics II - Course Plan - Rev - 01 PDFVimleshKumarSharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME1251 SylabusDocumento4 pagineME1251 SylabusazaathmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Moodle Basic ThermodynamicsDocumento14 pagineMoodle Basic ThermodynamicsArpan BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Me 3-1Documento20 pagine18 Me 3-1Ashok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Sem Syllabus EnergyDocumento4 pagine3rd Sem Syllabus EnergyManoj PepiNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus For Bachelor of Technology Mechanical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineSyllabus For Bachelor of Technology Mechanical EngineeringGaurang JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- EMEDocumento3 pagineEMEVirani BharatNessuna valutazione finora
- SyllabusDocumento4 pagineSyllabusArjun SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-1 BBSahoo MB124Documento33 pagineModule-1 BBSahoo MB124AllNessuna valutazione finora
- ME8595 Thermal Engineering II FormulasDocumento11 pagineME8595 Thermal Engineering II Formulasmmk.mech59Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anna University CoimbatoreDocumento28 pagineAnna University CoimbatoreVignesh PvlNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus BME PDFDocumento2 pagineSyllabus BME PDFAbhishek JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Fall 2019, NAME-7 Course Code: NAME 177 Course Title: Thermal Engineering Course Teacher: MD Daluar Hussain Sumon Lecturer, Department of NAME, MISTDocumento12 pagineFall 2019, NAME-7 Course Code: NAME 177 Course Title: Thermal Engineering Course Teacher: MD Daluar Hussain Sumon Lecturer, Department of NAME, MISTSakib RafeeNessuna valutazione finora
- BME Syllabus - 2019 SchemeDocumento2 pagineBME Syllabus - 2019 SchemeNihal vadakkanNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 252 Applied Thermodynamics Lecture NotesDocumento412 pagineME 252 Applied Thermodynamics Lecture NotesAditya RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bput Mtech Thermal 2010Documento24 pagineBput Mtech Thermal 2010mani317Nessuna valutazione finora
- Me 2403 Syllabus - PpeDocumento2 pagineMe 2403 Syllabus - PpebsamantonyNessuna valutazione finora
- 376 - ME8595 Thermal Engineering II - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusDocumento3 pagine376 - ME8595 Thermal Engineering II - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusCAD With RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Production ElectivesDocumento20 pagineProduction ElectivesAdhi ThyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aeronautical Engineering PDFDocumento18 pagineAeronautical Engineering PDFmuruganaviator100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering Course Objectives and OutcomesDocumento2 pagineThermal Engineering Course Objectives and OutcomesVelmurugan ThiagarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Co-Requisite: Prerequisite: Data Book / Codes/Standards Course Category Course Designed by ApprovalDocumento3 pagineCo-Requisite: Prerequisite: Data Book / Codes/Standards Course Category Course Designed by Approvalrajkumar rNessuna valutazione finora
- BTD Lession PlaneDocumento6 pagineBTD Lession PlanekumarNessuna valutazione finora
- RME4C002Documento2 pagineRME4C002durgaprasad pappuNessuna valutazione finora
- ME Mechanical Engineering - I.C.E & AUTODocumento26 pagineME Mechanical Engineering - I.C.E & AUTOdjohnramboNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento11 pagineIntroductionMaherNessuna valutazione finora
- Audels Engineers and Mechanics Guide Volume 1 From WWW Jgokey ComDocumento486 pagineAudels Engineers and Mechanics Guide Volume 1 From WWW Jgokey Comjdsa123100% (2)
- FD Brochure 2017 0601 LR InekoDocumento16 pagineFD Brochure 2017 0601 LR InekomoisesNessuna valutazione finora
- 4748 Bul PDFDocumento4 pagine4748 Bul PDFMichael DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Studies in Thermal Engineering: R.A. Rouf, N. Jahan, K.C.A. Alam, A.A. Sultan, B.B. Saha, S.C. SahaDocumento7 pagineCase Studies in Thermal Engineering: R.A. Rouf, N. Jahan, K.C.A. Alam, A.A. Sultan, B.B. Saha, S.C. SahaDžana KadrićNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Documento16 pagineCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Jack KowmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Assignment MENG580 Chapter 11Documento4 pagineSolution Assignment MENG580 Chapter 11ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of High-Temperature Cycling On Conductor Systems:: 2008 Progress ReportDocumento88 pagineEffect of High-Temperature Cycling On Conductor Systems:: 2008 Progress ReportGiancarlos OliveraNessuna valutazione finora
- F ChartDocumento7 pagineF Charthemal4379Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Granulation Process For Blast FurnaceDocumento4 pagineA Review of Granulation Process For Blast FurnaceAbhay RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Loss From A Pipe Calculator - Engineers EdgeDocumento2 pagineHeat Loss From A Pipe Calculator - Engineers EdgeJA KNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment #10 Part A Parallel and Counter Flow Heat ExchangersDocumento7 pagineExperiment #10 Part A Parallel and Counter Flow Heat Exchangersibrahim sundayNessuna valutazione finora
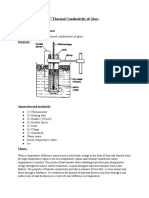
- Determine Thermal Conductivity of GlassDocumento4 pagineDetermine Thermal Conductivity of GlassDoreen Steele100% (1)
- Aga Report #10-03Documento177 pagineAga Report #10-03paolita788Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phy First Term SS 1Documento2 paginePhy First Term SS 1sulayajannyNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 - Chapter 1 PDFDocumento54 pagine07 - Chapter 1 PDFSamuel Abiodun OgunwaleNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Calorimetry LabDocumento16 pagine1 Calorimetry Labeunice_fangonNessuna valutazione finora
- ReviewerDocumento13 pagineReviewerEncey Enerva GacasanNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE 2019 Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocumento7 pagineGATE 2019 Mechanical Engineering SyllabusAbdullah ahmed alviNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Session 9, Experiment 8: Calorimetry, Heat of ReactionDocumento3 pagineLab Session 9, Experiment 8: Calorimetry, Heat of ReactionFruitiliciousNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Ch6 (Energy Dan Termodinamika)Documento80 pagine6-Ch6 (Energy Dan Termodinamika)NiaKurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied ThermodynamicsDocumento48 pagineApplied Thermodynamicsdavesh jadonNessuna valutazione finora
- Certc Refresher Exam Esas ConvertedDocumento7 pagineCertc Refresher Exam Esas ConvertedGlendel Alivio EscuyosNessuna valutazione finora
- JSW Paper On 15Th April, 2008 Technical QuestionsDocumento2 pagineJSW Paper On 15Th April, 2008 Technical QuestionsNav ChaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Vehicle Engine Cooling System Simulation Part 1 - Model Development. SAE Technical Paper Series PDFDocumento26 pagineThe Vehicle Engine Cooling System Simulation Part 1 - Model Development. SAE Technical Paper Series PDFpeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Cooling Tower. Merkel Theory - TreybalDocumento39 pagineCooling Tower. Merkel Theory - TreybalMarx CesarNessuna valutazione finora
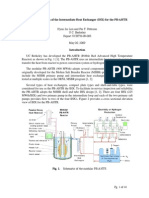
- Conceptual Design of The Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX) For The PB-AHTRDocumento41 pagineConceptual Design of The Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX) For The PB-AHTRabasakNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart TrainingDocumento426 pagineSmart TrainingVarun yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventilation Design for Electrical Equipment RoomsDocumento79 pagineVentilation Design for Electrical Equipment RoomsCarlos Herrera100% (1)
- 2 Temperature RegulationDocumento46 pagine2 Temperature RegulationAlaa ElbedriNessuna valutazione finora
- Marking SchemeDocumento6 pagineMarking SchemeIuthisam HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementDa EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849Da EverandSafety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyDa EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesDa EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsDa EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesDa EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (14)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyDa EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNessuna valutazione finora
- LNG Risk Based Safety: Modeling and Consequence AnalysisDa EverandLNG Risk Based Safety: Modeling and Consequence AnalysisNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryDa EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNessuna valutazione finora
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationDa EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNessuna valutazione finora
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachDa EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersDa EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (12)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersDa EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeDa EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (21)
- One Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthDa EverandOne Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthJoana C. PrataNessuna valutazione finora
- Benchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementDa EverandBenchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Radium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935Da EverandRadium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesDa EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Single Cure: Human Life Extension to 300+ YearsDa EverandThe Single Cure: Human Life Extension to 300+ YearsNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesDa EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EDa EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (6)
- The Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straightforward Guide to Functional Safety: IEC 61508 (2010 Edition), IEC 61511 (2015 Edition) and Related GuidanceDa EverandThe Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straightforward Guide to Functional Safety: IEC 61508 (2010 Edition), IEC 61511 (2015 Edition) and Related GuidanceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Process Safety in Bioprocess Manufacturing FacilitiesDa EverandGuidelines for Process Safety in Bioprocess Manufacturing FacilitiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Establishing an occupational health & safety management system based on ISO 45001Da EverandEstablishing an occupational health & safety management system based on ISO 45001Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)