Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Section 4 - Safety Valves
Caricato da
Sravan DasariTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Section 4 - Safety Valves
Caricato da
Sravan DasariCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SECTION 4:1 SAFETY VALVES AND RELIEF VALVES
Safety valve A valve which automatically discharges fluid to prevent a pre-determined safe pressure
being exceeded. It is generally used for compressible fluids such as steam and other gases
which demand quick over-pressure relief.
TYPES OF SAFETY VALVE
Ordinary safety A valve in which the disk lifts automatically at least D/24, where 24 = bore of valve seat.
valve The valves may be:
a. Direct spring In which the load is applied directly to the disk by a spring.
loaded
b. Lever and In which the load is applied to the disk by a weight acting through a lever and fulcrum.
weight loaded
High lift safety A safety valve in which the disk lifts automatically at least D/12,
valve where D = bore of valve seat.
Full lift safety A safety valve in which the disk lifts automatically a distance giving, when the disk is fully
valve lifted, a discharge area round the edge of the valve seat equal to the area through the seat
orifice after deducting the area of guides or other obstructions.
SECTION 4:2 RELIEF VALVES
Relief valve A valve which automatically discharges fluid to relieve pressure. It is generally related to pipeline
applications and non-compressible fluids-liquids such as water, oil, etc. Immediate full-flow discharge is not
needed since a small flow reduces the pressure.
Note:
Since the basic parts of relief valves are the same as those of ordinary safety valves, separate definitions are not
necessary. Reference should therefore be made to Section 4:1.
REGULATIONS
The regulations issued by most countries demand that safety valves be installed on all pressure vessels to
ensure that their maximum design pressure is not exceeded. These regulations vary considerably but for
example on boiler applications they all state that the safety valve or valves must be able to pass the evaporative
capacity of the boiler with a minimum rise in pressure. The permitted rise in pressure varies and is dependent
upon the regulations concerned.
DEFINITIONS
Maximum design pressure is the highest working pressure at which a vessel may be operated. Working pressure
is the pressure at which a vessel is normally operated.
Set pressure is the pressure at which the disk of a safety valve or relief valve starts to discharge flow.
Accumulated pressure is the pressure above set pressure at which the disk has reached its full lift for maximum
discharge of flow. Accumulation is the difference between set and accumulated pressures. Normally understood
as % of set pressure.
Reseating pressure is the pressure at which the disk shuts off the flow.
Blow down is the difference between set and re-seating pressures. Normally understood as % of set pressure.
RELATIONS BETWEEN DEFINITIONS
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Eave Valley Gutter Design SheetDocumento1 paginaEave Valley Gutter Design SheetIshaan AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingDa EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Lesson 21 - RP-576 - New2 (8 Q)Documento64 pagineLesson 21 - RP-576 - New2 (8 Q)VINOTHKUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogo Kunkle ValveDocumento32 pagineCatalogo Kunkle ValveKelvyn RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Relief SystemsDocumento30 paginePressure Relief SystemsBibek MerNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction PSVDocumento11 pagineIntroduction PSVNguyen Anh TungNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure PSVDocumento24 pagineProcedure PSVAbakar MahamatNessuna valutazione finora
- Writeup On Safety Valve & ErvDocumento28 pagineWriteup On Safety Valve & Ervtek_surinder100% (3)
- Fuel Oil System For BoilersDocumento41 pagineFuel Oil System For BoilersSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- 0004 Lesson API RP-576Documento65 pagine0004 Lesson API RP-576tayyab aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesDa EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Pressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831Documento32 paginePressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831JO100% (1)
- Breather ValvesDocumento3 pagineBreather Valves@@ng100% (1)
- Relief Valves PDFDocumento14 pagineRelief Valves PDFCarlos Del ToroNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety ValvesDocumento66 pagineSafety ValvesMuhammad Afiq Mohd ZaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Designand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemDocumento54 pagineDesignand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemULAGANATHAN M100% (1)
- Pressure Safety Valve FundamentalsDocumento21 paginePressure Safety Valve Fundamentalsaop10468100% (2)
- Control Valve - Surge Relief Valve Selection GuideDocumento20 pagineControl Valve - Surge Relief Valve Selection GuideSriya PetikiriarachchigeNessuna valutazione finora
- Relief Valve: Flare Header or Relief Header To A Central, Elevated Gas Flare Where It Is UsuallyDocumento3 pagineRelief Valve: Flare Header or Relief Header To A Central, Elevated Gas Flare Where It Is UsuallyKhaled RabeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Safety ValvesDocumento15 paginePressure Safety Valvesh_abdullah100% (2)
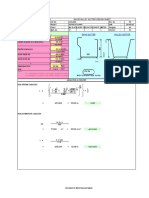
- Reinforced Concrete Rectangular Beam Design To AS3600-2009Documento4 pagineReinforced Concrete Rectangular Beam Design To AS3600-2009Rron de GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Block 9 Safety ValvesDocumento85 pagineBlock 9 Safety ValvesBabu AravindNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety ValvesDocumento8 pagineSafety ValvesvenkeekuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Relief ValvesDocumento12 paginePressure Relief ValvesyvhtejaswaroopNessuna valutazione finora
- API 576 Study NotesDocumento5 pagineAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - SVDocumento62 pagineMicrosoft Word - SVaftabulalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Function of Breather ValveDocumento29 pagineBasic Function of Breather ValveManojkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Valve IntroductionDocumento88 pagineSafety Valve Introductionbhuvi_patu12100% (3)
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsDa EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Relieve Valve Types and OperationDocumento11 pagineRelieve Valve Types and OperationBryan K. Aylas ParedesNessuna valutazione finora
- API 576 Study NotesDocumento5 pagineAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNessuna valutazione finora
- API NotesDocumento9 pagineAPI Notesking4lifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Relief Valves and Relief SystemsDocumento10 pagineRelief Valves and Relief Systemsmatteo2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- API-520 (Key Notes)Documento5 pagineAPI-520 (Key Notes)nns_12100% (1)
- PSV Safety Valves IntroductionDocumento12 paginePSV Safety Valves IntroductionKachi Ike100% (1)
- Plant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationsDocumento104 paginePlant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationskglorstadNessuna valutazione finora
- RCC Lab ReportDocumento18 pagineRCC Lab ReportShuvanjan Dahal50% (4)
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryDa EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 17 Rapid DrawdownDocumento17 pagineTutorial 17 Rapid DrawdownJustoArteagaHuacchaNessuna valutazione finora
- New Safety Valve 2Documento36 pagineNew Safety Valve 2Sravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Safety ValveDocumento11 paginePressure Safety ValveamitpallathNessuna valutazione finora
- PSV Data BookDocumento16 paginePSV Data Bookkenoly123Nessuna valutazione finora
- SpiraxSarco-B9-Safety ValvesDocumento82 pagineSpiraxSarco-B9-Safety Valvesdanenic100% (4)
- Lesson 21 RP-576 New2Documento64 pagineLesson 21 RP-576 New2gopu100% (1)
- Safety Valve SelectionDocumento56 pagineSafety Valve Selectionganesh82Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - SV - Part1Documento6 pagineMicrosoft Word - SV - Part1aftabulalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas CarriersDocumento17 pagineGuidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas Carriers123habib123fikriNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety ValvesDocumento65 pagineSafety Valvesserturkbudak_3448365Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Safety Valves Spirax SarcoDocumento70 pagineIntroduction To Safety Valves Spirax SarcoJuan LucenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety ValveDocumento10 pagineSafety ValveVignesh WarNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - SV - Part2Documento6 pagineMicrosoft Word - SV - Part2aftabulalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Calculation of The Pressure Relief ValvesDocumento53 pagineDesign and Calculation of The Pressure Relief Valvesghassan hamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Valves and Relief Valves.Documento17 pagineSafety Valves and Relief Valves.Shikhar SwaroopNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-IDocumento16 paginePressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-Isabi_shiNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualDocumento0 pagineTechnical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualgshdavidNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.3 Direct-Acting Pressure-Relief Valve: 6 Api R P 576Documento2 pagine4.3 Direct-Acting Pressure-Relief Valve: 6 Api R P 576khaled SAYEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring Loaded ValvesDocumento10 pagineSpring Loaded ValvesKarl NakouziNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Pressure Relief ValvesDocumento11 pagine5 Pressure Relief ValvesNyoman RakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pilot Operated Safety Valve: Fig. 9.2.3 Schematic Diagram of The Bellows Balanced Safety ValveDocumento6 paginePilot Operated Safety Valve: Fig. 9.2.3 Schematic Diagram of The Bellows Balanced Safety ValveaftabulalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Designand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemDocumento54 pagineDesignand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemKaiwlya BhoyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Relief ValvesDocumento16 pagineSafety Relief ValvesAhmed MokhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Writeup On Safety Valve Erv PDFDocumento28 pagineWriteup On Safety Valve Erv PDFSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Valve Terminology Ver 1Documento14 pagineControl Valve Terminology Ver 1bagastcNessuna valutazione finora
- Marvac CatalogueDocumento40 pagineMarvac CataloguedhavaleshNessuna valutazione finora
- Annexure-I For Gem Bid No:Gem/2021/B/1451378 Dated: 19-08-2021Documento15 pagineAnnexure-I For Gem Bid No:Gem/2021/B/1451378 Dated: 19-08-2021Sravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- SH RH SchemeDocumento1 paginaSH RH SchemeSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Spec 2022 03 04 09 - 36 - 25Documento65 pagine2 - Spec 2022 03 04 09 - 36 - 25Sravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping and Valvest - Week 4Documento44 paginePiping and Valvest - Week 4Sravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.tech Spec & Paint Spec-Valve PKG For Namrup-2022-09-29-05 53 44 PDFDocumento61 pagine3.tech Spec & Paint Spec-Valve PKG For Namrup-2022-09-29-05 53 44 PDFSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- HH Valves Limited: Company NameDocumento38 pagineHH Valves Limited: Company NameSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam 41 SplashDocumento1 paginaSteam 41 SplashSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Ut Pumps & Systems Pvt. LTDDocumento2 pagineUt Pumps & Systems Pvt. LTDSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Home About Us Products Process Application Quality Standards Enquiry Contact UsDocumento1 paginaHome About Us Products Process Application Quality Standards Enquiry Contact UsSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Home About Us Products Process Application Quality Standards Enquiry Contact UsDocumento1 paginaHome About Us Products Process Application Quality Standards Enquiry Contact UsSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Ekta Constant Level Oiler Page 1Documento1 pagina10 Ekta Constant Level Oiler Page 1Sravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Open Gear Compound: Product Kin. Viscosity CST at 40 Vi Min. Flash Point Coc, Min. Description / ApplicationDocumento1 paginaSpecial Open Gear Compound: Product Kin. Viscosity CST at 40 Vi Min. Flash Point Coc, Min. Description / ApplicationSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Gratings SolutionsDocumento67 pagineTechnical Gratings SolutionsSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Promblem Solving Combined March 2017 AnelleDocumento25 paginePromblem Solving Combined March 2017 AnelleSravan DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Lecturer: Ban Ahmed Khaleel: Experiment No. (1) : "Determination of Slump of Fresh Concrete"Documento4 pagineSubject Lecturer: Ban Ahmed Khaleel: Experiment No. (1) : "Determination of Slump of Fresh Concrete"AL SniperNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Control of ConcreteDocumento12 pagineQuality Control of ConcreteBaibaswata Das100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Septic Systems & Unsewered Areas: 6.1 Introduction/BackgroundDocumento36 pagineChapter 6 - Septic Systems & Unsewered Areas: 6.1 Introduction/BackgroundJoe IlaganNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Scc-HvacDocumento54 pagine3 - Scc-Hvacsarfaraz ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A999-14Documento12 pagineAstm A999-14Артем ТитовNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento38 pagineLecture 1naresh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Q Q345 345E (China / GB) E (China / GB) : Les Propriétés Des Matériels Les Propriétés Des MatérielsDocumento2 pagineQ Q345 345E (China / GB) E (China / GB) : Les Propriétés Des Matériels Les Propriétés Des MatérielsAbdelkader DraïNessuna valutazione finora
- Permeability of Compacted Landfill Soil With Different CompactionDocumento15 paginePermeability of Compacted Landfill Soil With Different CompactionFadirul AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Reservoir Detention PDFDocumento8 pagineDesign of A Reservoir Detention PDFdragos_georgescu2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sand Septic SystemDocumento5 pagineSand Septic Systemsabiha naazNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Use of Bamboo. Part 4: Element Design Equations: SynopsisDocumento4 pagineStructural Use of Bamboo. Part 4: Element Design Equations: SynopsisVictor OmotoriogunNessuna valutazione finora
- Loose Measurement Sheet-2: LamjungDocumento12 pagineLoose Measurement Sheet-2: LamjungBhim DahalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pages From (ASHRAE) - 2009 - ASHRAE - Handbook - Fundamentals - (SI)Documento2 paginePages From (ASHRAE) - 2009 - ASHRAE - Handbook - Fundamentals - (SI)Tran Canh HoanNessuna valutazione finora
- 10-11 - Shear in BeamsDocumento7 pagine10-11 - Shear in BeamsOsama TamariNessuna valutazione finora
- Taking Off Project (Contract and Estimation)Documento16 pagineTaking Off Project (Contract and Estimation)muhammad alifNessuna valutazione finora
- Inertia and Elastic Modulus CalculationDocumento14 pagineInertia and Elastic Modulus CalculationBejay BermudezNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A-A: 2 or Flatter 1 2 or FlatterDocumento2 pagineSection A-A: 2 or Flatter 1 2 or FlatterPankaj BarskarNessuna valutazione finora
- FMM QBDocumento25 pagineFMM QBrkumaravelanNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 4 in FluidsDocumento1 paginaProblem Set 4 in Fluidsnaikin_1031Nessuna valutazione finora
- HH 83-1B DDR#3Documento1 paginaHH 83-1B DDR#3Mahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNessuna valutazione finora
- Addendum Dokpil Patimban 2Documento19 pagineAddendum Dokpil Patimban 2HeriYantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Synopsis 1Documento15 pagineProject Synopsis 1Harshit Raj Gupta100% (1)
- Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and ConstructionDocumento32 pagineReinforced Soil Retaining Walls-Design and ConstructiongauravNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 6 7 8 Water TurbinesDocumento69 pagineExperiment No. 6 7 8 Water TurbinesMilon MirdhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforced - Successful Case StudyDocumento12 pagineReinforced - Successful Case Studyemadsafy20002239Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Take-Off (Rebar)Documento9 pagineStructural Take-Off (Rebar)Neil LaquianNessuna valutazione finora