Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Forests Cover About 30
Caricato da
Amu KevinTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Forests Cover About 30
Caricato da
Amu KevinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Do you know?
Forests cover about 30% of the planet, but deforestation is clearing these essential habitats on a massive
scale. What is deforestation? Find out the causes, effects, and solutions to deforestation.
Deforestation is clearing Earth's forests on a massive scale, often resulting in damage to the quality of the
land. Forests still cover about 30 percent of the world’s land area, but swaths half the size of England are lost each
year. The world’s rain forests could completely vanish in a hundred years at the current rate of deforestation.
The biggest driver of deforestation is agriculture. Farmers cut forests to provide more room for planting
crops or grazing livestock. Often, small farmers will clear a few acres by cutting down trees and burning them in a
process known as slash-and-burn agriculture.
Logging operations, which provide the world’s wood and paper products, also cut countless trees each year.
Loggers, some of them acting illegally, also build roads to access more and more remote forests—which leads to
further deforestation. Forests are also cut as a result of growing urban sprawl as land is developed for dwellings.
Not all deforestation is intentional. Some is caused by a combination of human and natural factors like wildfires and
subsequent overgrazing, which may prevent the growth of young trees.
Deforestation can have a negative impact on the environment. The most dramatic impact is a loss of habitat for
millions of species. Eighty percent of Earth’s land animals and plants live in forests, and many cannot survive the
deforestation that destroys their homes. Deforestation also drives climate change. Forest soils are moist, but
without protection from sun-blocking tree cover, they quickly dry out. Trees also help perpetuate the water cycle by
returning water vapor to the atmosphere. Without trees to fill these roles, many former forest lands can quickly
become barren deserts. Removing trees deprives the forest of portions of its canopy, which blocks the sun’s rays
during the day, and holds in heat at night.
This disruption leads to more extreme temperature swings that can be harmful to plants and animals.Trees also
play a critical role in absorbing the greenhouse gases that fuel global warming. Fewer forests means larger amounts
of greenhouse gases entering the atmosphere—and increased speed and severity of global warming.The most
feasible solution to deforestation is to carefully manage forest resources by eliminating clear-cutting to make sure
forest environments remain intact. The cutting that does occur should be balanced by planting young trees to
replace older trees felled. The number of new tree plantations is growing each year, but their total still equals a tiny
fraction of the Earth’s forested land.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Movement of The EarthDocumento21 pagineMovement of The EarthAqilah Taufik100% (1)
- Great Grammar Adjectives Compare PDFDocumento1 paginaGreat Grammar Adjectives Compare PDFAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Concentration ExercisesDocumento24 pagineConcentration Exercises5wishes100% (8)
- Line NoDocumento2 pagineLine NoAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete This Passage With Appropriate Words From The Box BelowDocumento1 paginaComplete This Passage With Appropriate Words From The Box BelowAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple TensesDocumento1 paginaSimple TensesAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Verb Part 1 BeginnerDocumento1 paginaSubject Verb Part 1 BeginnerAmu Kevin0% (1)
- What Is RedDocumento2 pagineWhat Is RedAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- General or Yes/No QuestionsDocumento3 pagineGeneral or Yes/No QuestionsAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Declarative Sentences Are Used To Convey Information or To Make StatementsDocumento1 paginaDeclarative Sentences Are Used To Convey Information or To Make StatementsAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- General or Yes/No QuestionsDocumento3 pagineGeneral or Yes/No QuestionsAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- SMK Dato Bijaya Setia Scheme of Work 2018 English Language - PeralihanDocumento9 pagineSMK Dato Bijaya Setia Scheme of Work 2018 English Language - PeralihanAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Documento5 pagine2Amu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Template - GrammarDocumento3 pagineLesson Plan Template - GrammarAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Setting Place: No Specific Time Frame Is Mentioned, But The Child Probably Just Returned From School at HomeDocumento7 pagineSetting Place: No Specific Time Frame Is Mentioned, But The Child Probably Just Returned From School at HomeAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
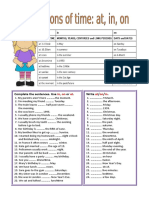
- Prepositions of Time in On at Grammar Guides 43173Documento1 paginaPrepositions of Time in On at Grammar Guides 43173Amu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions of PlaceDocumento1 paginaPrepositions of PlaceCaroline FeitalNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Tenses 1. Present SimpleDocumento1 paginaSimple Tenses 1. Present SimpleAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise: Preposition of Direction: Through OntoDocumento1 paginaExercise: Preposition of Direction: Through OntoAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- The Story Opens in The Year 1866. Everyone in Europe And: Group 1Documento8 pagineThe Story Opens in The Year 1866. Everyone in Europe And: Group 1Amu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions of Place Grammar Drills Tests 93103Documento2 paginePrepositions of Place Grammar Drills Tests 93103Amu Kevin100% (1)
- THEMESDocumento3 pagineTHEMESAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- ThemesDocumento3 pagineThemesAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing Adjectives Using AdjectivesDocumento1 paginaWriting Adjectives Using AdjectivesAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Great Grammar Adjectives Compare PDFDocumento1 paginaGreat Grammar Adjectives Compare PDFAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjective Word SearchDocumento1 paginaAdjective Word SearchAmu KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Science StandardsDocumento127 pagineScience Standardsapi-415913733Nessuna valutazione finora
- Space Physics PresentationDocumento15 pagineSpace Physics PresentationKeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Wilhelm Reich - Contact-SpaceDocumento86 pagineWilhelm Reich - Contact-SpaceJim Williams100% (2)
- Board Works KS4 Physics ContentsDocumento12 pagineBoard Works KS4 Physics ContentsKhalifa AbdulrahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 0.2. G.S. Pre Question Analysis 2011-16Documento239 pagine0.2. G.S. Pre Question Analysis 2011-16D-sumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 21Documento18 pagineModule 21Jerico CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Silver SkullsDocumento173 pagineSilver SkullsΜαρια ΔημητριουNessuna valutazione finora
- GRD 6 NS Tech T4 2018 ApprovedDocumento25 pagineGRD 6 NS Tech T4 2018 Approvedsinelungelo madonselaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit DocumentDocumento218 pagineUnit Documentapi-242278894Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Homibhabha Competition Test Series.: 1 2 Kilogram of Rice IndicatesDocumento27 pagineDr. Homibhabha Competition Test Series.: 1 2 Kilogram of Rice IndicatesSachin AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- NASA: 2166main 04budget Detail 030227Documento11 pagineNASA: 2166main 04budget Detail 030227NASAdocumentsNessuna valutazione finora
- 3as Asronomy Solar System Unit PreparationDocumento37 pagine3as Asronomy Solar System Unit Preparationسدن آرماNessuna valutazione finora
- Ielts Listening SubjectsDocumento2 pagineIelts Listening SubjectsAbder RahmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lib-Planets-Overview-2000001741-Article Quiz and AnswersDocumento4 pagineLib-Planets-Overview-2000001741-Article Quiz and Answersapi-302899266Nessuna valutazione finora
- AMORC The New Ontology Lesson 6 (August, 1908) by Royle ThurstonDocumento16 pagineAMORC The New Ontology Lesson 6 (August, 1908) by Royle ThurstonClymer777Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Rapid Electrical Formation of Stone Spherules, The Scalability of The Results, and The Similarities of The Internal and External Structures of The Spheres With Naturally Occurring ConcretionsDocumento20 pagineThe Rapid Electrical Formation of Stone Spherules, The Scalability of The Results, and The Similarities of The Internal and External Structures of The Spheres With Naturally Occurring ConcretionsGeeleegoat100% (1)
- Test Bank For Physical Geology Exploring The Earth 6th Edition James S Monroe DownloadDocumento24 pagineTest Bank For Physical Geology Exploring The Earth 6th Edition James S Monroe DownloadEricHicksmwjr100% (34)
- JAPAN and Edgar Cayce ProphesyDocumento11 pagineJAPAN and Edgar Cayce ProphesySilverbirchtruthsNessuna valutazione finora
- WORKSHEET 46.1 6.3 Grade 4 Science 2022Documento2 pagineWORKSHEET 46.1 6.3 Grade 4 Science 2022Lilly AbdelhamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Toefl Vocabulary Practice Test 1Documento8 pagineToefl Vocabulary Practice Test 1wolan hariyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3Documento15 pagineLesson 3Ace De Jesus RascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocumento8 paginePlate Tectonics TheoryWendelyn Sumpo100% (1)
- 02 Reading Assignment2Documento5 pagine02 Reading Assignment2kirana anugrahNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Warming: (Explanation Text) (Tugas Kelompok 4 Siswa/Klpk. Kelas Xii Iis//Dikumpulkan Dalam Bentuk Lembaran)Documento3 pagineGlobal Warming: (Explanation Text) (Tugas Kelompok 4 Siswa/Klpk. Kelas Xii Iis//Dikumpulkan Dalam Bentuk Lembaran)mahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Narrative Writing PDFDocumento34 pagineNarrative Writing PDFYaya Nur Hidayah100% (2)
- Solar-B Ing Low ResDocumento15 pagineSolar-B Ing Low ResicaanmpzNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP 01Documento6 pagineDLP 01MELBA ALFEREZNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth and Life ScienceDocumento2 pagineEarth and Life ScienceAmimah Balt GuroNessuna valutazione finora