Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chemistry Form 4 Definition List
Caricato da
Jelly puddinCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chemistry Form 4 Definition List
Caricato da
Jelly puddinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chemistry Form 4 Definition List
1. Element – a substance consists of one type of atom.
2. Compound – a substance consists two or more elements that are chemically bonded(molecule or ions).
3. Atom – smallest particle of an element.
4. Molecule – a group of two or more atoms.
5. Ion – a positively charged / negatively charged particle.
6. Isotopes – atoms of the same element with same proton number but different nucleon numbers.
7. Relative atomic mass of an element = the average mass of one atom of an element/((1/12) x the mass of one carbon-12
atom)
8. Relative molecular mass of an element = the average mass of one atom of an molecule/((1/12) x the mass of one carbon-12
atom)
9. Molecule formula – compound shows the actual number of atoms of each element that are present in a molecule of the
compound
10. Empirical formula – compound shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in the compound
11. Mole – amount of substance that contains as many particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 the
symbol of mole is mol.
12. One mole – Avogadro constant – 6.02 x 1023
13. Group (Periodic Table) – vertical columns of element (similar chemical properties).
14. Periods (Periodic Table) – horizontal rows of element.
15. Valence electrons – electrons that occupy the outermost shell.
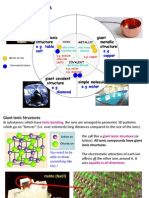
16. Ionic bond – bond formed through the transfer of electrons between atoms of metal and non-metal to achieve the stable octet
electron arrangement.
17. Ionic compound – consist of positive ions and negative ions which are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
18. Covalent bond – bond formed through the sharing of non-metal electrons to achieve the stable duplet or octet electron
arrangement.
19. Covalent compound (also simple molecular structure) – consists of neutral molecules which are held by weak intermolecular
forces (Van der Waals).
20. Alkali (base) – chemical substance which ionizes in water to produce hydroxide ions, OH-.
21. Acid – chemical substance which ionizes in water to produce hydrogen ions, H+ or hydroxonium ions, H3O+.
22. pH – degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Scale ranges from 0 to 14.
23. pH value – measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions, H+.
24. Strong alkali – ionises (dissociates) completely in water to form hydroxide ions, OH- of high concentration.
25. Weak alkali – ionises (dissociates) partially in water to form hydroxide ions, OH- of low concentration.
26. Strong acid – ionises (dissociates) completely in water to form hydrogen ions, H+ of high concentration.
27. Weak acid – ionises (dissociates) partially in water to form hydrogen ions, H+ of low concentration.
28. Polymer – long chain molecules made up by monomer (repeating unit).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocumento16 pagineIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- AFI2Documento3 pagineAFI2Austin ChingNessuna valutazione finora
- Vceasy Visual Chemistry Student Booklet v1 33Documento68 pagineVceasy Visual Chemistry Student Booklet v1 33James Wong100% (1)
- Document 1Documento16 pagineDocument 1Zsazsa TorralbaNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Definitions CHEM HLDocumento4 pagineIB Definitions CHEM HLmalakNessuna valutazione finora
- Occurrence: (B) Elements of Group 16. (Oxygen Family)Documento10 pagineOccurrence: (B) Elements of Group 16. (Oxygen Family)Harshu BhaiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nsec Solved Past Paper 2017 PDFDocumento31 pagineNsec Solved Past Paper 2017 PDFRahjjNessuna valutazione finora
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocumento8 pagineJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Science (TM) - PRDocumento46 paginePhysical Science (TM) - PRMary Vi D. Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Summary ReactionsDocumento49 pagineOrganic Chemistry Summary Reactionsjordi1710100% (1)
- Molecular GeometryDocumento3 pagineMolecular GeometryDanica Ching100% (1)
- Seeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Vanputte Test BankDocumento15 pagineSeeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Vanputte Test BankJustinDuartepaej100% (37)
- Experiment 1 IMFADocumento10 pagineExperiment 1 IMFALuis BergonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedDocumento2 pagineChapter 3 Biomolecules Test Revisitedmuhammad khursheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Unified Summative Test in Science 9 Quarter 2Documento7 pagineUnified Summative Test in Science 9 Quarter 2RaquelNessuna valutazione finora
- Lewis Structure Spring 2014Documento7 pagineLewis Structure Spring 2014Mohamed DahmaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Vsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometryDocumento16 pagineVsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometrySandra Enn BahintingNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure 2.2Documento30 pagineStructure 2.2Mohamed Ahmed FarahNessuna valutazione finora
- SSP PDFDocumento205 pagineSSP PDFAnonymous hz3n3HK1RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronegativity QuestionsDocumento3 pagineElectronegativity QuestionsThe ImmortalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 1701 2022Documento16 pagineChem 1701 2022api-585477340Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bond Type Practice: Name: Period: DateDocumento3 pagineBond Type Practice: Name: Period: DateRachel TaburdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11 ChemistryDocumento17 pagineGrade 11 ChemistryKevin George100% (1)
- Chemistry Lab Unit 1 - MurtazaDocumento3 pagineChemistry Lab Unit 1 - MurtazaMurtaza hussainNessuna valutazione finora
- IsomerismDocumento62 pagineIsomerismsubesinghNessuna valutazione finora
- WORKSHEET Chemical BondingDocumento2 pagineWORKSHEET Chemical BondingIsabel Del ValleNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomaterials and Implants: School of Biomedical Engineering Jit, Jimma UniversityDocumento81 pagineBiomaterials and Implants: School of Biomedical Engineering Jit, Jimma UniversityAmirNessuna valutazione finora
- Galingan Mo MagreviewDocumento14 pagineGalingan Mo MagreviewJuliebe Zubiri-AlfaroNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Drill QuestionsDocumento15 pagineMCQ Drill QuestionsLab Rat0% (2)
- Assessment 1 Form 5Documento12 pagineAssessment 1 Form 5Masitah Abu BakarNessuna valutazione finora