Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Risk Attached To Property
Caricato da
anshulTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Risk Attached To Property
Caricato da
anshulCopyright:
Formati disponibili
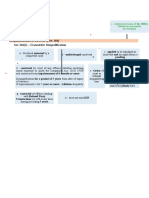
1.
Risk attached to property – whosoever is the owner the risk is with him
2. The buyer can exercise propriety rights over the goods –
can resell
creation of rights in rem
3. seller cannot sue for the price unless the goods have become the property of the buyer
4. if the buyer becomes insolvent the seller can exercise line if the goods are still in
possession with the seller – suit for price
Whether the test of reasonability can be excluded?
General property – this is ownership rights and for ownership rights there is no
In the case of Seath v Moore 1886, Lord Blackburn stated that
– it is essential that article should be specific and ascertained in a manner binding on both
parties for unless that we show the contract cannot be construe as a contract to pass the
property on that article ( the goods should either be ascertained or unascertained
How to make unascertained goods ascertained - by appropriation
– identification or agreeing upon with the consent of both the parties
identified in accordance wit the agreement after the time the contract of sale is
made and I shall assume that
* Section 19 property passes with intention of the parties by 3 things
1. Terms of contract
2. Conduct
3. Circumstances of the case
Agriculture market committee v Salmar chemical works 1997 5 Scc pg no
86
Bhagwat Narayan Tendulkar v Goa cooperative marketing and supply co
operation limited 1998 2 Mr Lg 703 Bombay
Sacks vs Tilley 1915 32 TLR 148 – when intention can be discern
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Caveat Emptor, Qui Ignorate No Debuit Quod Jus Alienum EmitDocumento8 pagineCaveat Emptor, Qui Ignorate No Debuit Quod Jus Alienum Emitshivangi paliwalNessuna valutazione finora
- 003 Chapter Three Trade 2Documento14 pagine003 Chapter Three Trade 2Annette FlemingNessuna valutazione finora
- Contract AssignmentDocumento14 pagineContract AssignmentInjila ZaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Law Worksheet10 Sale of GoodsDocumento5 pagineBusiness Law Worksheet10 Sale of GoodsTimoteo Timothy WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Actions For Breach of Contract of Sale of GoodsDocumento4 pagineActions For Breach of Contract of Sale of GoodsEdward Gamonnac BalocnitNessuna valutazione finora
- Actions For Breach of Contract of Sale of GoodsDocumento7 pagineActions For Breach of Contract of Sale of GoodsAudrey CawisNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3Documento34 pagineLesson 3sathes6Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Law On Sales: Obligations of The VendeeDocumento6 pagineThe Law On Sales: Obligations of The VendeeDarrel SapinosoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Law On Sales: Action For Breach of Contract of Sale of GoodsDocumento5 pagineThe Law On Sales: Action For Breach of Contract of Sale of GoodsDarrel SapinosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes in Midterm ExamDocumento5 pagineNotes in Midterm ExamAshley MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sale of Goods: S.4 (1), SGA 1957Documento9 pagineSale of Goods: S.4 (1), SGA 1957Harith IskandarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales Part 2Documento8 pagineSales Part 2Ralph Allen Mañalac GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide 2 (2022)Documento33 pagineStudy Guide 2 (2022)shakeetha senadheeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Soga - 1Documento17 pagineSoga - 1Ritvikh RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- compendium respondent (2)Documento12 paginecompendium respondent (2)GAMING SOUKNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales Notes 4-ADocumento6 pagineSales Notes 4-AMikee RizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales Finals Case DigestDocumento33 pagineSales Finals Case DigestJereca Ubando JubaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sale of Goods ContractsDocumento17 pagineSale of Goods ContractsBungei ZaccheausNessuna valutazione finora
- Double Sales - Article 1544Documento2 pagineDouble Sales - Article 1544moon binnieNessuna valutazione finora
- Remedies and Rights in Breach of Sale ContractDocumento3 pagineRemedies and Rights in Breach of Sale Contractandy AntsNessuna valutazione finora
- TOPIC 1 - Sale of GoodsDocumento49 pagineTOPIC 1 - Sale of GoodsnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- THE SALE OF GOOD'S ACT 1930Documento5 pagineTHE SALE OF GOOD'S ACT 1930Amol ChavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sale of Goods and Consumer Protection TutorialDocumento6 pagineSale of Goods and Consumer Protection Tutorial--bolabolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Contract of Sale Contract To SellDocumento6 pagineContract of Sale Contract To Selllifeware04Nessuna valutazione finora
- p2 Regulatory Framework and Legal Issues in Business Part 1 Domingo 2021Documento140 paginep2 Regulatory Framework and Legal Issues in Business Part 1 Domingo 2021Mae Marie De DiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of The ContractDocumento18 pagineEffects of The ContractDharma TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V: The Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Dr. Nikhila Shankar TigadiDocumento39 pagineUnit V: The Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Dr. Nikhila Shankar TigadiDanika JoplinNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Sales ReadyDocumento27 pagine5 Sales ReadyBrian DuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Purpose of Notice: To Insulate The Seller From Belated Claims of Defects andDocumento8 paginePurpose of Notice: To Insulate The Seller From Belated Claims of Defects andMarko Zero FourNessuna valutazione finora
- Contractsem 2Documento12 pagineContractsem 2Rohit Srivastava R 51Nessuna valutazione finora
- RESCISSION BY VENDOR AFTER DELIVERYDocumento11 pagineRESCISSION BY VENDOR AFTER DELIVERYYannah Hidalgo100% (1)
- National Insurance Company Ltd. V Bharatamma and Ors. AIR 2008 SC 484Documento6 pagineNational Insurance Company Ltd. V Bharatamma and Ors. AIR 2008 SC 484shivangi paliwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sale of Goods ActDocumento6 pagineSale of Goods Actshipra.sangal4717Nessuna valutazione finora
- Breach of Contract of Sale AssignmentDocumento12 pagineBreach of Contract of Sale AssignmentAnkit Kumar100% (1)
- Law of Sale of GoodsDocumento60 pagineLaw of Sale of GoodsCarlo WidjajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Auction Sales under RailwaysDocumento7 pagineAuction Sales under RailwaysAtulNessuna valutazione finora
- Part XI - Sales and Lease (Macale 2020)Documento14 paginePart XI - Sales and Lease (Macale 2020)LarajeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sale of Goods (Sales of Goods Act 1957)Documento5 pagineSale of Goods (Sales of Goods Act 1957)Yee Zhi XuanNessuna valutazione finora
- compendium applleant finalDocumento12 paginecompendium applleant finalGAMING SOUKNessuna valutazione finora
- SALES ACT EXAMDocumento13 pagineSALES ACT EXAMBhuvan PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes - Assignment No. 3 Tuazon, Blanch Ahn ADocumento16 pagineNotes - Assignment No. 3 Tuazon, Blanch Ahn ACarmel Grace KiwasNessuna valutazione finora
- Rights and Obligations of Buyers and Sellers in Contracts of SaleDocumento40 pagineRights and Obligations of Buyers and Sellers in Contracts of SaletinNessuna valutazione finora
- Sale of Goods ActDocumento30 pagineSale of Goods ActSiddhant SethiaNessuna valutazione finora
- LAW-ON-SALES-Lecture SummaryDocumento10 pagineLAW-ON-SALES-Lecture SummaryErwin LimpangogNessuna valutazione finora
- Law Chapter 3Documento6 pagineLaw Chapter 3Yap AustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Business Law Sales of Goods Week 7,8,9Documento151 pagineChapter 4 Business Law Sales of Goods Week 7,8,9Eida HidayahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales of Goods Act, 1930 ExplainedDocumento24 pagineSales of Goods Act, 1930 ExplainedNidhi JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1-3 Law On SalesDocumento5 pagineChapter 1-3 Law On SalesKathrina TonidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Extinguishment of Sale: Causes in General 1. Ordinary CausesDocumento18 pagineExtinguishment of Sale: Causes in General 1. Ordinary CausesAudrey CawisNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Sales of Goods - 1930Documento44 pagineLaw of Sales of Goods - 1930mukesharora09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Sales Chapter IV and VDocumento8 pagineNotes On Sales Chapter IV and VmarmiedyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento22 pagineUnit 2Harini SNessuna valutazione finora
- Case DigestDocumento31 pagineCase DigestYvonne MejicoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sale of Goods ActDocumento8 pagineThe Sale of Goods ActShanta NoahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales DoctrineDocumento15 pagineSales DoctrineKG FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Law Sale of Goods Act 1930 (Unit 3,4) Sugg TapDocumento4 pagineLaw Sale of Goods Act 1930 (Unit 3,4) Sugg Tapshubhamsavji13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sbaa1206 Business Law Unit 3 NotesDocumento20 pagineSbaa1206 Business Law Unit 3 NotesBharathi 3280Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cape Law: Texts and Cases - Contract Law, Tort Law, and Real PropertyDa EverandCape Law: Texts and Cases - Contract Law, Tort Law, and Real PropertyNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional EthicsDocumento49 pagineProfessional EthicsanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Arbitration Agreement Binding on Non-SignatoriesDocumento15 pagineArbitration Agreement Binding on Non-SignatoriesanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Principle of Non-Discrimination Under GatsDocumento8 paginePrinciple of Non-Discrimination Under GatsanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- PIL LAW OR NOTDocumento52 paginePIL LAW OR NOTanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- IR - LiberalismDocumento23 pagineIR - LiberalismanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Law NotesDocumento15 pagineFamily Law NotesanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- PIL LAW OR NOTDocumento52 paginePIL LAW OR NOTanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Affidavits and Its DraftingDocumento12 pagineAffidavits and Its DraftinganshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Global PoliticsDocumento42 pagineUnderstanding Global PoliticsanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- N THE Earned Istrict Ourt OF Elhi T ElhiDocumento15 pagineN THE Earned Istrict Ourt OF Elhi T ElhianshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretation of StatutesDocumento24 pagineInterpretation of StatutesanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- WTO Notes-MineDocumento24 pagineWTO Notes-MineanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- OW Conomic Risis WAS CreatedDocumento5 pagineOW Conomic Risis WAS CreatedanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Disqualification, Vacation and Independent DirectorDocumento15 pagineDisqualification, Vacation and Independent DirectoranshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Notes - Sociology (II)Documento27 pagineClass Notes - Sociology (II)anshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Balwant Rai Mehta CommitteeDocumento2 pagineBalwant Rai Mehta CommitteeanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Contracts Case Laws Sem IIDocumento16 pagineContracts Case Laws Sem IIanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral and Documentary EvidenceDocumento25 pagineOral and Documentary EvidenceArchit Bohra20% (5)
- C A O R B - A B: (Case Analysis Towards The Fulfilment of Assessment in The Subject of Code of Civil Procedure, 1908)Documento5 pagineC A O R B - A B: (Case Analysis Towards The Fulfilment of Assessment in The Subject of Code of Civil Procedure, 1908)anshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Agreement Form Between Owner and A BuilderDocumento10 pagineAgreement Form Between Owner and A Builderbittu_rajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Prison Reforms Committee Reports and ManualsDocumento13 paginePrison Reforms Committee Reports and ManualsanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral and Documentary EvidenceDocumento25 pagineOral and Documentary EvidenceArchit Bohra20% (5)
- Powers of InspectorDocumento3 paginePowers of InspectoranshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules For Calculation of Shares in A Partition by Metes and BoundsDocumento1 paginaRules For Calculation of Shares in A Partition by Metes and BoundsanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Bringing Land As A CapitalDocumento3 pagineBringing Land As A CapitalanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurisprudence - A New BeginningDocumento30 pagineJurisprudence - A New BeginninganshulNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Rights of The Victim?: VictimologyDocumento1 paginaWhat Are The Rights of The Victim?: VictimologyanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Commercial Transcations CA-2: Name - Anshul Chauhan Roll No.-1538 Section-ADocumento5 pagineCommercial Transcations CA-2: Name - Anshul Chauhan Roll No.-1538 Section-AanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Issue For Consideratio1Documento2 pagineIssue For Consideratio1anshulNessuna valutazione finora
- SSRN Id2213216Documento50 pagineSSRN Id2213216anshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 HandoutDocumento18 pagineChapter 10 HandoutChad FerninNessuna valutazione finora
- Elementary Hebrew Gram 00 GreeDocumento216 pagineElementary Hebrew Gram 00 GreeRobert CampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Narasimha EngDocumento33 pagineNarasimha EngSachin SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Prayer BuddyDocumento42 paginePrayer BuddyJoribelle AranteNessuna valutazione finora
- VDA ChinaDocumento72 pagineVDA Chinatuananh1010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Quiz: SuperlativesDocumento2 pagineAnimal Quiz: SuperlativesLuis LemusNessuna valutazione finora
- ArenavirusDocumento29 pagineArenavirusRamirez GiovarNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Djent ToneDocumento6 pagineGuide To Djent ToneCristiana MusellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled DocumentDocumento2 pagineUntitled DocumentClaudia WinNessuna valutazione finora
- Andy Landers - Freeze Zone OffenseDocumento6 pagineAndy Landers - Freeze Zone OffenseWinston Brown100% (1)
- Forms and Types of Business OrganizationDocumento2 pagineForms and Types of Business Organizationjune hetreNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling of Induction Motor PDFDocumento42 pagineModelling of Induction Motor PDFsureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 4 eDocumento22 pagineChap 4 eHira AmeenNessuna valutazione finora
- People vs. Abad SantosDocumento2 paginePeople vs. Abad SantosTrixie PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Reading Comprehension Test 03Documento5 pagineIntermediate Reading Comprehension Test 03MZNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophical Perspectives Through the AgesDocumento13 paginePhilosophical Perspectives Through the Agesshashankmay18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fusion Tech ActDocumento74 pagineFusion Tech ActrahulrsinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lung BiopsyDocumento8 pagineLung BiopsySiya PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- School For Good and EvilDocumento4 pagineSchool For Good and EvilHaizyn RizoNessuna valutazione finora
- Prophetic Prayer Declarations - September, 2021Documento5 pagineProphetic Prayer Declarations - September, 2021Jelo RichNessuna valutazione finora
- Di OutlineDocumento81 pagineDi OutlineRobert E. BrannNessuna valutazione finora
- Evelyn Nakano Glenn, "From Servitude To Service Work: Historical Continuities in The Racial Division of Paid Reproductive Labor"Documento44 pagineEvelyn Nakano Glenn, "From Servitude To Service Work: Historical Continuities in The Racial Division of Paid Reproductive Labor"s0metim3sNessuna valutazione finora
- Universitas Alumni Psikotest LolosDocumento11 pagineUniversitas Alumni Psikotest LolosPsikotes BVKNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1. Introduction To TCPIP NetworkingDocumento15 pagineChapter 1. Introduction To TCPIP NetworkingPoojitha NagarajaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Strategies For Effective Financial Management Trends in K12 SchoolsDocumento16 pagine6 Strategies For Effective Financial Management Trends in K12 SchoolsRainiel Victor M. CrisologoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Documento10 pagine1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Zuber RokhmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Urban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniDocumento1 paginaUrban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniCaramel LatteNessuna valutazione finora
- Silvianita - LK 0.1 Modul 2 English For Personal CommunicationDocumento3 pagineSilvianita - LK 0.1 Modul 2 English For Personal CommunicationSilvianita RetnaningtyasNessuna valutazione finora
- VIII MKL Duet I Etap 2018 Angielski Arkusz Dla PiszącegoDocumento5 pagineVIII MKL Duet I Etap 2018 Angielski Arkusz Dla PiszącegoKamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 2200SRM0724 (04 2005) Us en PDFDocumento98 pagine2200SRM0724 (04 2005) Us en PDFMayerson AlmaoNessuna valutazione finora