Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Protein Synthesis: Class Notes Notes
Caricato da
Dale Harding0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
134 visualizzazioni2 pagineClass notes on Protein Synthesis
Titolo originale
Protein synthesis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoClass notes on Protein Synthesis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
134 visualizzazioni2 pagineProtein Synthesis: Class Notes Notes
Caricato da
Dale HardingClass notes on Protein Synthesis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
Class Notes Name: _______________________________________
Protein Synthesis Period:_______________________________________
Date: _______________________________________
Questions/Main Idea: Notes:
The function of DNA • The DNA molecule contains all your hereditary information in the
form of genes
• A gene is a coded section of DNA; it tells our cells how to build
specific proteins
• Genes code for EVERYTHING our body needs and does (saliva,
bones, eye shape)
• Because DNA is so large, it is stuck inside the nucleus
• It needs a messenger to move the information from nucleus to
protein production locations (ribosomes!)
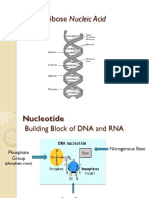
DNA needs RNA! • RNA is a nucleic acid messenger between DNA and ribosomes
• 3 differences between DNA and RNA:
– RNA has ribose sugar
– RNA is single stranded
– RNA contains a nitrogen base called uracil (U) instead of
thymine.
Compare and contrast
DNA and RNA
3 types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA):
– copies DNA in the nucleus and carries the info to the
ribosomes (in cytoplasm)
• Ribosomal RNA (rRNA):
– makes up a large part of the ribosome; reads and decodes
mRNA
• Transfer RNA (tRNA):
– carries amino acids to the ribosome where they are joined
to form proteins
Protein synthesis • Protein synthesis is the assembly of amino acids (by RNA) into
proteins
• Involves two steps:
– 1. Transcription – copying DNA code into mRNA
– 2. Translation – reading the mRNA code and assembling
amino acids into a polypeptide chain (protein)
Transcription • Performed in nucleus by mRNA
• mRNA “reads” single DNA strand and forms the complementary
copy
How transcription works 1. DNA strand splits, exposing the active strand
2. Complementary mRNA nucleotides line up opposite the active
strand, forming mRNA
3. mRNA leaves the nucleus
Translation • Translation occurs in ribosomes (in cytoplasm)
• All three types of RNA work together during translation to produce
proteins
Decoding mRNA • The sequence of bases in an mRNA molecule serves as instructions
(translation) for the order in which amino acids are joined to produce a
polypeptide
• Ribosomes decode the instructions by using codons, sets of 3 bases
that each code for 1 amino acid
• Each codon is matched to an anticodon, or complementary
sequence on the tRNA to determine the order of the amino acids
Using a codon chart • A codon chart is used to determine the sequence of the amino
acids in the polypeptide
• The sets of 3 mRNA bases (codons) are used to find the amino acid
Decoding Practice
Example 1 DNA: TAC GCA TGG AAT
mRNA:
Amino Acids:
Example 2 DNA: CGT GGA GAT ATT
mRNA:
Amino Acids:
Summary:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocumento23 pagineCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyEros James Jamero100% (1)
- Central DogmaDocumento50 pagineCentral DogmaIvilyn ManguladNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillDocumento32 pagineProtein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillIMY PAMEROYANNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)Documento2 pagineStudy Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)owls_1102Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Information: - Central Dogma - Genetic CodesDocumento34 pagineGenetic Information: - Central Dogma - Genetic Codesakhikabir100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis SummaryDocumento2 pagineProtein Synthesis SummaryTrinitee Wesner100% (1)
- Protein SynthesisDocumento1 paginaProtein SynthesismuhdmoosaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocumento34 pagineDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisJessa Mae Infante PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationDocumento37 pagineThe Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationfangirltonNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Dogma Review KEYDocumento8 pagineCentral Dogma Review KEYeula faith miracle andam0% (1)
- Lecture On Transcription and TranslationDocumento47 pagineLecture On Transcription and TranslationAnna Beatrice BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Dna DnaDocumento45 pagineStudy Dna DnaKrystel BeltranNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis DiagramDocumento1 paginaProtein Synthesis Diagramcmillica1176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atp Group 5Documento28 pagineAtp Group 5Dbez JonniNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis - Transcription and TranslationDocumento61 pagineProtein Synthesis - Transcription and Translationblackmoneygrabber100% (1)
- Cell Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocumento1 paginaCell Membrane and Transport MechanismsAldemer Laron BoretaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication NotesDocumento2 pagineDNA Replication NotesMart Tin100% (1)
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocumento36 pagineDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlex LlanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocumento30 pagineCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyAlthea Mandal100% (1)
- Gene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionDocumento17 pagineGene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionAyu Tri AgustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Mutations WorksheetDocumento3 pagineMutations Worksheetapi-293001217Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and Function of DNA and RNADocumento6 pagineStructure and Function of DNA and RNAEngr UmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento58 pagineTranscription and Translationkevin_ramos007Nessuna valutazione finora
- RNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDDocumento7 pagineRNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDcokcreNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeDocumento49 pagineBiomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeVishwajeet GhorpadeNessuna valutazione finora
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocumento20 pagineA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationArnel100% (1)
- DNA ReplicationDocumento5 pagineDNA Replicationvijayalakshmiraman100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??Documento33 pagineProtein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??jodyjodzNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps of DNA ReplicationDocumento5 pagineSteps of DNA Replicationatul mishra100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidsDocumento3 pagineNucleic AcidsBio Sciences100% (2)
- DR Okunowo Wahab's Introductory Molecular Biology Lecture Note IIDocumento39 pagineDR Okunowo Wahab's Introductory Molecular Biology Lecture Note IImodelprof100% (2)
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following:: 9. What Are The Stop Codons? (Use Your mRNA Chart) UAA UAG UGADocumento7 pagineProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following:: 9. What Are The Stop Codons? (Use Your mRNA Chart) UAA UAG UGAJamesBuensalidoDellava100% (1)
- ATP - The Energy Currency of CellsDocumento12 pagineATP - The Energy Currency of CellsJohn OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Replication Lecture NotesDocumento73 pagineDna Replication Lecture NotesAhmad ShyoukhNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocumento12 pagineDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 14 Darwin and EvolutionDocumento39 pagineCH 14 Darwin and EvolutionJane Heidi MomonganNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA ReplicationDocumento3 pagineDNA ReplicationApril Marie100% (3)
- Cell Membrane StructureDocumento17 pagineCell Membrane StructurearunNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento9 pagineTranscription and TranslationlinhNessuna valutazione finora
- NucleusDocumento10 pagineNucleusPinak ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento21 pagineChapter 6 - Cell Structure and FunctionSherry CarentonaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocumento24 pagineThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologybagyoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.biotechnology - Principle and ProcessesDocumento6 pagine4.biotechnology - Principle and ProcessesIndrajith MjNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocumento31 paginePost Transcriptional ModificationranasiddharthNessuna valutazione finora
- Prodcut of Recombinat DNA TechnologyDocumento9 pagineProdcut of Recombinat DNA TechnologySHOAIB NAVEEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Central DogmaDocumento4 pagineCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA ReplicationDocumento16 pagineDNA ReplicationStephen Moore100% (1)
- DNA ReplicationDocumento83 pagineDNA ReplicationVipin100% (8)
- Protein Synthesis Notes and DiagramDocumento34 pagineProtein Synthesis Notes and Diagramapi-267117865100% (1)
- Nervous System Summary NotesDocumento4 pagineNervous System Summary NotesIrish Buaya Gementiza100% (1)
- ANIMAL CELLS AND TISSUES Lecture Notes PDFDocumento17 pagineANIMAL CELLS AND TISSUES Lecture Notes PDFAnonymous HXLczq383% (6)
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocumento4 pagineProtein Synthesis WorksheetDen RoixNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.2 Cell Respiration NotesDocumento6 pagine8.2 Cell Respiration Notescutiecat360Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: CarbohydrateDocumento24 pagineLecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: Carbohydratesaacid bashir100% (1)
- Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocumento18 pagineRegulation of Gene Expressionchocoholic potchiNessuna valutazione finora
- 04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocumento51 pagine04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic Acidsrahul singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription in EukaryotesDocumento4 pagineTranscription in EukaryotesShaher Bano MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Expression in Prokaryotes.Documento23 pagineGene Expression in Prokaryotes.M.PRASAD NAIDU100% (1)
- Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineProtein SynthesisArlan AbraganNessuna valutazione finora
- Rna Protein SynthesisDocumento18 pagineRna Protein Synthesisapi-545652980Nessuna valutazione finora
- Replacing A Fabric InterconnectDocumento2 pagineReplacing A Fabric InterconnectDale HardingNessuna valutazione finora
- FUJITSU Server PRIMERGY RX1330 M1 Upgrade and Maintenance ManualDocumento304 pagineFUJITSU Server PRIMERGY RX1330 M1 Upgrade and Maintenance ManualDale HardingNessuna valutazione finora
- XtremIO Storage Controler Replacement ProcedureDocumento6 pagineXtremIO Storage Controler Replacement ProcedureDale HardingNessuna valutazione finora
- SeaChest Combo UserGuidesDocumento162 pagineSeaChest Combo UserGuidesDale HardingNessuna valutazione finora
- SeaChest ConfigureDocumento38 pagineSeaChest ConfigureDale HardingNessuna valutazione finora
- SeaChest EraseDocumento43 pagineSeaChest EraseDale HardingNessuna valutazione finora
- Block 1 Ebrahim Moola Mol MedDocumento88 pagineBlock 1 Ebrahim Moola Mol MedMatsiri ImmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Dogma of Biology Answer KeyDocumento5 pagineCentral Dogma of Biology Answer KeyMusah Lamusah AlaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocumento36 pagineDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlex LlanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Chapter 3Documento82 pagineAnatomy Chapter 3Jess WhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoeckle Thaler Final ReducedDocumento30 pagineStoeckle Thaler Final ReducednadutNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology IB ReviewerDocumento28 pagineMolecular Biology IB ReviewerCeline Garin ColadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gamsat Sample Test - PregenieDocumento31 pagineGamsat Sample Test - PregenieBilly Robins100% (1)
- Guyton & Hall Physiology Review 3rd Ed PDFDocumento275 pagineGuyton & Hall Physiology Review 3rd Ed PDFDhiya Muthiah Gaffari94% (36)
- Protein Synthesis2Documento56 pagineProtein Synthesis2api-248442486Nessuna valutazione finora
- Epigenetics - Rau's IASDocumento4 pagineEpigenetics - Rau's IASClinton AhongshangbamNessuna valutazione finora
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 5 Effect of Mutation On ProteinDocumento20 pagineScience: Quarter 3 - Module 5 Effect of Mutation On ProteinBxcon BloxNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocumento33 pagineLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt22 LectureDocumento66 pagineChapt22 LectureHailie JadeNessuna valutazione finora
- GeneticsDocumento20 pagineGeneticsNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- Study Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LDocumento7 pagineStudy Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LPepitinNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocumento29 pagineProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Information and Protein SynthesisDocumento22 pagineGenetic Information and Protein Synthesisjason balmasNessuna valutazione finora
- Blackline Maste - DNA - The Master Molecule of Life PDFDocumento6 pagineBlackline Maste - DNA - The Master Molecule of Life PDFghacass66Nessuna valutazione finora
- Process of Dna Replication, Transcription, TranslationDocumento8 pagineProcess of Dna Replication, Transcription, TranslationBenedictus YohanesNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Genetics PDFDocumento97 pagine6 Genetics PDFasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology AML NMAT ReviewerDocumento15 pagineBiology AML NMAT ReviewerJocelyn Mae CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology Practice Exam 1Documento5 pagineBiotechnology Practice Exam 1crazybobblaskeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxo ABioQ 08uu xs01 XxaannDocumento2 pagineOxo ABioQ 08uu xs01 XxaannajaelupNessuna valutazione finora
- BOOK Gene TherapyDocumento210 pagineBOOK Gene TherapyCarla GomesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Final ExamDocumento7 pagineBiology Final ExamJillian FajardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Biological Engineering: Tinkercell: Modular Cad Tool For Synthetic BiologyDocumento17 pagineJournal of Biological Engineering: Tinkercell: Modular Cad Tool For Synthetic Biologyr4ging8ullNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Specialization and DifferentiationDocumento2 pagineCell Specialization and DifferentiationAmachi LoweNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Review Question: Protein MetabolismDocumento13 pagineBiochemistry Review Question: Protein MetabolismrashitaNessuna valutazione finora
- hssb0800t StudygdbDocumento17 paginehssb0800t StudygdbyawahabNessuna valutazione finora
- OCR A A-Level Biology Retrieval Roulette COMPLETEDocumento115 pagineOCR A A-Level Biology Retrieval Roulette COMPLETEtikif31811Nessuna valutazione finora